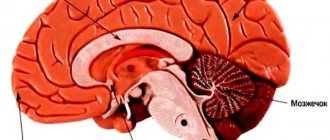
What pathology is called psychopathic-like syndrome?
In medicine, psychopathic-like syndrome is a disease that most often occurs in early and young adulthood. Teenagers and children are most susceptible to it. Experts characterize it as a disorder with exaggeration and modification of psychological pubertal properties, which leads to behavioral disturbances in the patient. Most often, the pathology occurs in males.
A psychopathic-like syndrome is characterized by the fact that patients are characterized by moral coarsening, opposition to the environment, a desire for self-affirmation, as well as infantilism, both physical and moral. Patients with this diagnosis have an attraction to alcohol, drugs and theft.
Such patients often develop a negative attitude towards established forms of human relationships and behavior. They do not perceive moral values. The patient is aggressive, arrogant and rude towards his family and friends. As a rule, he loses social connections, namely, quits work or school. Most patients begin to lead a dependent lifestyle, meet similar people and most often begin to use drugs or alcohol, and lead a promiscuous sex life. They often leave home and spend the night in public places.
Until a few years ago, there was no correct medical assessment of this condition. That is why many people who had a psychopathic-like syndrome disease spent many years in prison.
We need your bestial morality - from lantern to lantern!
Or, to use poetic language: fly wherever the wind of passion blows. Passion is almost material due to its tangible reality.
A striking illustration of the behavior and life of a heboid is the hippie movement that swept America in the recent past.
Adults, only outwardly young boys and girls, suddenly left their homes (for the most part, the homes of wealthy parents) to indulge in all kinds of hard things - giving themselves up to vagrancy, theft, drug intoxication, indulge in unrestrained sex and brutal fights.
And this was not a herd of brainless cattle - many already had a university education and a prestigious job or its prospects.
Heboid hippies did not offer anything in return for the already established way of life - they were driven solely by stubborn protest and intoxication with freedom, falsely understood as doing nothing, unbridled sex, spurred on by marijuana, and continuous self-affirmation among their own kind.
Meaningless transitions and moving from place to place are not at all the same as the search for a better life and happiness in a foreign land. No attempt is made to make money as a mattoid; everything is obtained exclusively through theft and disguised begging.
Due to the peculiarities of the psyche, which does not reach a mature level and does not allow one to see oneself with an unbiased look, and an unhealthy lifestyle, heboids become the worst enemies not only of society, which they blame for all their troubles, but also of themselves and their own kind.
Possessing a sufficiently developed mind and imagination, patients often satisfy their vanity by mentally playing out scenes of sadistic content, where parents are assigned the roles of victims. In some cases, they realize their subconscious intentions by mutilating and killing animals and mocking the defenseless and weak.
Hippies are bright representatives of mattoids:
The end of the life of such individuals is often sad: having cut off all family ties, they are not able to create full-fledged families. Those who have not taken their own lives die from diseases of the AIDS category and the consequences of alcoholism, homo- and bisexuality, become prisoners in prisons and regulars in psychiatric clinics, because every next crime requires another examination - heboids do not go for voluntary treatment due to non-recognition of the flawed state of their psyche.
Symptoms of the disease
It is important to diagnose psychopathic-like syndrome as early as possible. The symptoms of this disease will be listed in our article.
Thus, patients often exhibit mental infantilism. It most often manifests itself in those who are undergoing treatment in a special institution. If the patient's age ranges from 11 to 14 years, he has a hostile attitude towards his relatives. Patients behave aggressively and gradually get out of control. In addition, psychopathic-like syndrome is characterized by the fact that children develop pathological fantasies, which often acquire sadistic content.
Patients aged 15-17 years old show a fascination with abstract problems. They are interested in issues of philosophy, religion and history. However, they do not seek to gain new knowledge, but only contradict existing views.
It is believed that patients who have a psychopathic-like syndrome are quite cunning. When they go to a specialized clinic for treatment, they try to find a common language with doctors and avoid forced treatment.
The duration of the disease varies from person to person. For some, it may stop after puberty, while others struggle with it for many years. The condition may worsen and more serious forms of the disease may occur.
Often young people who have a psychopathic-like syndrome have a strange appearance - for example, they dye their hair an unnatural color and wear peculiar clothes. They spend their time aimlessly and have no goals in life. Quite often, patients talk with delight about emotionally negative events, such as a fire, a fight, an argument, or someone's death. They often admire what others find disgusting.
Defect of high personality traits
Heboid syndrome is characterized in situations of psychopathological conditions by an initially obvious defect in higher personal qualities:
- lack of criticism,
- lack of feeling of distance,
- gross violation of higher emotions (including moral and intellectual),
- sharp disinhibition of lower drives in the form of undisguised masturbation,
- gluttony.
Antisocial actions in such patients are usually impulsive or committed under external influence.
There may be other signs: mood swings from euphoria to irritability, exhaustion, mental inertia. Autonomic disorders can often occur: endocrine pathology (obesity, hypertrichosis), hydrocephalus with hypertension.
The difference between heboid syndrome and schizophrenia is the absence of acute behavior, special thought disorders, lower pathological fantasies or other symptoms.
Individual manifestations of the heboid, associated with the disinhibition of drives and the exacerbation of certain features of the teenage psyche, may occur in children with rapid puberty of an organic nature. These include clinical disorders, increased aggressiveness, a tendency to vagrancy and some other antisocial behavior (petty theft, alcohol consumption) in boys and emotionality combined with very high sexual desire with sexual promiscuity in girls. However, these manifestations are only a separate component of the heboid syndrome, not associated with a specific pathological picture.
Diagnosis of the disease
Unfortunately, psychopath-like syndrome is quite common in young people. Not everyone knows what this is. However, it is important to diagnose this disease as early as possible and begin its treatment.
The disease is diagnosed with mental manifestations of an adolescent crisis with desire disorders. Patients are characterized by inappropriate behavior. There is a loss of connection with reality.
The key to quick diagnosis is the presence of at least two symptoms. Otherwise, the disease may not be detected immediately.
Schizophrenia and heboid syndrome
They often walk side by side. In schizophrenia, the syndrome manifests itself in a particularly pronounced perversion of sexual desire with strong sadistic actions and emotional coldness. Autistic behavior, various thought disorders, unreasonable mood swings with attacks of fear and anxiety, alternation of anger and irritation with strange jokes, mannerisms, grimaces (similar to manifestations of heboidophrenia), autistic components of fantasies, rudimentary productive symptoms (delusions, episodic ideas of relationships) are also noted . In the case of the stage of adolescent retrograde schizophrenia, the appearance of heboid disorders is preceded by pronounced negative symptoms.
Treatment of psychopathic-like syndrome
It is important not to make a mistake when diagnosing a psychopathic-like syndrome. By the way, not every pediatrician knows how to treat such a disease. We strongly recommend that you do not neglect this diagnosis and contact a specialized clinic as soon as possible.
Most often, patients are prescribed tranquilizers: Neuleptil, Haloperidol, and Majeptil in more advanced stages. If treatment was started on time, the results of the treatment will not be long in coming, and the patient will gradually adapt to life in society.
When diagnosed with “psychopathic-like syndrome,” only an experienced specialist can determine how to treat this disease. It is worth noting that some drugs that are used for this can cause allergic reactions and changes in the body, which is just being formed. Therefore, we recommend that you treat the disease and the choice of medications responsibly. It is better to consult not one, but several specialists. In this case, the treatment will only have a positive effect.
At-risk groups
Pseudopsychopathic (psychopath-like) schizophrenia in the vast majority of cases develops in adolescents, at the time of transition from the world of children to the world of adults. Moreover, before entering adolescence, any manifestations of character accentuations, some abnormal reactions and pathologies in behavior may be completely uncharacteristic for a child.
Adolescents who have one or more relatives with mental illness are at greatest risk of developing this disease.
Also at risk are children from families in which adults lead an antisocial lifestyle, and children of drinking parents. Long-term stress and the habit of living in constant tension can provoke the development of mental illness in a child.
History of the disease
In the second half of the 19th century, experts started talking about psychopathy. Some patients experienced behavioral changes in which they were unable to balance their demands with the opportunities of the social microenvironment. That is why they came into conflict with those people with whom they communicated over a long period of time. To those around him, this behavior seemed strange. They believed that this person had an unpleasant and broken character.
At the beginning of the 20th century, conditions were described that were quite similar in appearance to psychopathy. However, upon detailed examination, it was discovered that they have different symptoms. It is believed that a psychopath is a person, and a person with a psychopath-like syndrome is something faceless. Such patients have reduced some human qualities. They often commit antisocial acts.
Pathology therapy
Treatment of heboid syndrome is symptomatic. It does not exclude the use of tranquilizers and sedatives. The prognosis of treatment depends on the dynamics of the underlying disease. In a severe, low-progressing form of schizophrenia with the end of adolescence, a noticeable decrease in the syndrome may be observed, and social and work adaptation may be restored. Heboid syndrome usually does not recur, but in those who have suffered it, one can observe a distortion of personality with obvious signs of developmental delay, the appearance of the strangest individual properties and emotional-volitional qualities.
Disease in children
Psychopathic-like syndrome in children in the early stages does not cause discomfort. This is why it is difficult to diagnose. Thus, in children who have the described disease, there is a weakening of higher moral principles. They do not distinguish between good and evil. They lack a sense of pity and compassion. From an early age, such children lose interest in productive activities, namely learning and self-development. They often skip classes or behave aggressively during them.
Heboid, or psychopathic-like, syndrome in children has been studied by many scientists. They noted that patients have a hobby disorder. They often act to spite their loved ones. Children with the disease torture animals without compassion and behave aggressively towards their peers. By doing such things they get pleasure. Children with the disease are characterized by excessive gluttony, prone to theft and running away from home.
A psychopathic-like syndrome can develop in early childhood, namely in primary school and preschool age. However, as a rule, symptoms manifest themselves most clearly during puberty. It is at this moment that it is easiest to diagnose the disease. The manifestation of symptoms is associated with accelerated puberty. Teenagers experience increased sexual activity. They talk openly about sexual topics, often masturbate and are promiscuous. They often have a perverted sexual desire.
In children who have a psychopathic-like illness, there is a lack of disgust. They refuse to carry out hygiene procedures and look untidy. Children and teenagers become rude and confrontational. They strive for everything negative and imitate bad examples. Children with the disease challenge society with their behavior and appearance.
Over time, such patients begin to communicate with negative personalities and commit crimes. As mentioned above, with the development of the syndrome, pathological fantasizing is observed, and, as a rule, it is sadistic in nature.
How does the syndrome manifest itself?
Pronounced psychopathological features of heboid syndrome:
- disinhibited state, perversion of primitive drives, especially sexual;
- disappearance or distortion of moral principles (the concept of good and evil, legal and behavioral) and a tendency in this regard to antisocial and illegal actions;
- dulling of emotions with the absence or decline of such higher emotional manifestations as feelings of pity, empathy, compassion;
- increased emotional excitability with a tendency to aggressive behavior;
- pronounced egocentrism and the desire to satisfy the lowest needs, criticism with a special desire to resist accepted social attitudes and behavioral norms;
- loss of interest in any work activity, especially learning.
Many scientists have been studying heboid syndrome, its psychopathology and its manifestations in various diseases. The dynamics of development are little described, mainly in schizophrenia in adolescents and young adults.
Psychopathic-like illness in schizophrenia
A psychopathic-like syndrome in schizophrenia is described as a peculiar form of the disease or as a certain variant of schizophrenic remission. In this case, the disease arose against the background of another disease.
A psychopathic-like syndrome during exacerbation of schizophrenia is characterized by hot temper, unreasonable aggressiveness, hypersexuality and psychasthenic manifestations. Patients often experience severe exacerbations. That is why we can conclude that in this case the syndrome is one of the forms of deterioration during the development of the underlying disease.
Experts say that the condition worsens at the age of 16-17 years. The patient gradually becomes more withdrawn. Most often, patients stop keeping in touch with old friends, and they do not make new ones. Patients have little contact with their families. Gradually they abandon their studies. Insufficient time is allocated for homework, and lessons end up being left unfinished or done poorly. Over time, the desire to achieve anything in school disappears.
In psychopathic-like schizophrenia, there is no sharp drop in potential. Most often, the patient is characterized by intense activity in the field of rather unusual hobbies and illogical actions.
Due to rare contact with family, such children tend to run away and wander meaninglessly around the city. They explore the immediate surroundings. Most often they are interested in forests and fields. Long-distance escapes are not typical for psychopathic schizophrenics. As a rule, the patient cannot explain the reason for his wandering. He can claim that he was just walking, despite the fact that he spent several days without food in the forest, field and near swamps.
Having lost all their friends, patients may come into close contact with strangers with whom they have no common interests. Trying to find a new company in most cases ends in failure.
The patient's life is gradually filled with unusual and sometimes strange hobbies. For example, they can imagine fantastic cities in every detail. There is a known case where a patient created a plan for hockey and football championships for all teams in the world for many years to come. Pathological infatuation can be defined by the following criteria:
- unusual for a given age and generation;
- aggression, which occurs if the patient is distracted from activities;
- unproductivity.
It is worth noting that in some cases the patient may retain hobbies that he was interested in even before the development of the pathology. He can still draw or write poetry, despite the fact that he has long abandoned his studies or work.
Alcoholism is uncommon in patients with psychopathic-like schizophrenia. They can use it occasionally to relieve stress, but only when alone. However, almost all patients smoke heavily. Often patients commit offenses that are associated with pathological passion. For example, a patient might steal a part to create and develop a new weapon.
Causes and manifestations of parathymia
The syndrome, carefully studied and described by the father of psychiatric nosology, Karl Kahlbaum in Germany at the end of the 19th century, was called by him hebephrenia, or heboidophrenia, or youthful insanity.
A German clinical psychiatrist with a doctorate in medical sciences has proven that frightening behavior at the age of puberty is not always due to bad upbringing; it can also have subconscious negative-nihilistic roots.
The pathogenesis of heboid syndrome is caused by the onset of puberty, while the etiological basis of the condition is a hereditary predisposition to psychopathy of the schizoid gradation.
The consequences of neuroinfections suffered are also important - an organic pathology of the brain, manifested by psychoendocrine syndrome and cerebroasthenia, causing fluctuations in the patient’s mood from deep dysphoria to unmotivated euphoria.
The development of a pathological personality undergoes a number of successive age phases, the core value of which is the obsession with the implementation of ideas of hatred and revenge against an oppressive family and society.
But due to the withdrawal into oneself, the sharp limitation of contacts with the world, the constant escape from it, the mental development of the heboid is characterized by infantilism, a narrow focus on ideas and projects unrelated to real life.
The only type of physical activity becomes the satisfaction of the body’s needs for food, sex and the need for a change of environment, and religion becomes abstract ideas of universal liberation from the shackles of society: moral, ideological, philosophical.
The duration of the existence of heboid syndrome can either be limited to the period of puberty or last for many years, and after its end, persisting in the structure of schizophrenia, psychopathic and psychopathic personality disorders.
Psychopathic-like syndrome in cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy is a disease of the central nervous system that occurs when certain areas of the brain are damaged. The disease can be either congenital or acquired. Depending on the nature of the influence of the pathogenic factor, the patient may experience mental disorders, including a psychopathic-like syndrome.
Neuropathy syndrome most often occurs in patients with cerebral palsy. The main symptoms are increased excitability and anxiety, loss of appetite. Usually this syndrome occurs in the first years of a child's life. It becomes the basis for the formation of psychopathic-like forms in the child. As a rule, such patients maintain an average level of intelligence.
What are the causes of pathology?
The causes of heboid syndrome are not fully understood. It is described in psychopathy and psychopathic states caused by brain infections and trauma. However, psychopathic individuals with heboid manifestations are often included in the group of so-called asocial or emotionally stupid. Due to age-related changes, the separation of heboid states with different classification forms is very difficult. In differentiated diagnosis, in most cases, one has to look not so much at the classification differences of the syndrome, but at the associated symptoms and the clinical picture of the disease as a whole, including the dynamics described above.
Psychopathic-like states in the presence of diabetes mellitus
Questions about mental disorders in diabetes mellitus attracted the attention of many scientists of the 19th century. They believed that such a disease could cause serious mental illness. However, after some time, the opinion was formed that this version was erroneous. Some researchers have argued that many people who suffer from diabetes are highly intelligent and intelligent.
Nowadays, scientists have conducted experiments and studied more than 600 people with diabetes. Psychopathological symptoms were present in 431 patients. They experienced increased irritability, rapid mental fatigue, apathy and sleep disturbances. Some patients had pronounced symptoms.
Psychopathic-like syndrome occurs most often in people who have diabetes and complain of vascular disorders and cerebral atherosclerosis. The most common symptom of heboid disease is significant memory loss.
Infectious asthenia
It is this symptom complex that is most common in the infection clinic. The basis of the clinical picture is the neurasthenic component (the main article is neurasthenic neurosis):
- -increased irritability;
- - hot temper;
- -subjective powerlessness of the patient;
- -sleep disorders (falling asleep, waking up);
- - nightmares;
- -decreased attention;
- -decline in creative abilities (inability to solve life problems).
Such patients become tearful, get tired very easily, and their attention quickly becomes exhausted and weakens. At the physiological level, complaints manifest themselves in the form of headaches, heaviness in the body, excessive sweating; such patients look very lethargic, physical activity is reduced to a minimum of necessary functions. Subdepressive and melancholy mood may appear.
The first signs of this condition may appear already at the initial (stage of consolidation) infection in the patient’s body.
After recovery, patients may also maintain a state of so-called post-infectious asthenia: patients are also weak, but more active. This condition can last from several days to two months.