In this article, psychologist Evgenia Dvoretskaya answers the question “How does senile insanity manifest in women?”
The body ages, and the brain ages along with it, although old age is not at all synonymous with dementia. Many people in our country, even in old age, retain vigor, a clear mind, sanity and good memory. One of my patients, aged 78, taught at a university and was loved by her students for her sense of humor and optimistic attitude towards life. However, more often in old age people’s character deteriorates, irritability, outbursts of anger are observed, and memory deteriorates. Many relatives, noticing forgetfulness, untidiness, and loss of interest in life in a loved one, decide that this is aging, natural changes in the body, so a person with insanity consults a doctor only when disorders in his behavior make the life of his relatives unbearable.
Senile dementia that is treatable
Senile insanity is a disease that is accompanied by irreversible processes that affect the entire human body at the cellular level. It provokes the destruction of neurons responsible for intellectual and behavioral activity. It is because of this that the patient may not notice serious changes. He is unable to learn new information, remember it, or control his actions. All changes that occur are negative.
Senile dementia can be divided into primary and secondary. Secondary marasmus occurs as a result of neurological disorders. They are provoked by drug and alcohol addiction, etc. Most often, older women suffer from senile insanity. After conducting medical research, it was found that every year more and more patients suffer from this disease. Unfortunately, this disease is also observed among people of working age.
As for secondary senile insanity, it arises due to the following:
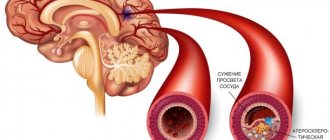
- chronic vascular insufficiency (occurs with atherosclerosis, severe and long-term hypertension);
- intoxication of the body (as a result of alcohol abuse or drug use);
- neoplasms in the brain;
- injuries;
- infectious diseases.
Dementia may also occur due to the following:
- viral diseases;
- HIV infections;
- autoimmune diseases;
- hemodialysis course;
- endocrine pathologies, severe kidney damage.
This disease can occur as a result of a combination of the above factors.
Unfortunately, many people believe that this disease cannot be cured with special medications. In their opinion, medications are not able to overcome age-related changes. Their opinion is wrong, because senile dementia is treatable. Moreover, it must be carried out without fail.
How to save a loved one from dementia? The result of treatment in many cases depends on the type of senile dementia. First you need to establish the cause of this disease. Even if it arose as a result of an incurable disease, there is still a way out. To do this, you need to purchase special medications.
Their activities are aimed at slowing down the development of negative manifestations of dementia. The patient's relatives should contact a psychiatrist. The responsibilities of this specialist include talking with the patient. After the conversation, he determines the presence of atrophic processes in the brain. In addition, the doctor may refer the patient for examinations in the form of a brain CT scan or electroencephalography.
You need to know that only a specialist can make a diagnosis! It is necessary to consult a doctor immediately after the first signs of senile dementia appear. You cannot delay this, because at the final stage it is impossible to carry out effective treatment. Only symptomatic treatment improves the patient's fate.
In order for the result to pleasantly surprise relatives, they need to create a comfortable environment at home. A person with senile dementia should be involved in household chores. This is what can stop the development of dementia. When a patient experiences hallucinations or insomnia, a specialist prescribes special psychotropic drugs. In the early stages, the patient should use nootropics, and in the later stages, tranquilizers.
Features of therapy
Senile insanity provokes organic damage to brain neurons. In this case, the pathological processes are irreversible, so it is impossible to cure the disease. However, modern treatment methods make it possible to slow down further death of nerve cells and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Drug treatment involves taking the following medications:
- Nootropics (Lucetam, Piracetam, Pramistar, Phenotropil, Pantogam, Cerebrolysin). Medicines are widely prescribed in the early stages of the disease to restore memory and improve brain activity;
Experts recommend carrying out therapeutic activities in a familiar environment for the patient in order to reduce the patient’s nervous tension. However, treatment requires constant care and supervision of an elderly person, which is not always possible to organize at home. In such cases, the optimal solution would be to place the patient in special boarding houses for elderly people with dementia.
See also:
Special attention should be paid to the nutrition of an elderly patient. You will need to exclude heavy foods from your diet (fatty, fried, spicy foods, processed foods). Nutritionists recommend adhering to the rules of a balanced diet, eating small portions every 3-4 hours.
In the initial stages of senile insanity, psychotherapy is widely used to restore or form new behavioral reactions. However, at the third stage, this treatment is not effective.
Reasons for insanity
Basically, the impetus for negative changes is already existing diseases that arose due to damage to the central nervous system, such as Alzheimer's, Pica and Lewy body syndrome. But the death of brain cells can also be provoked by:
- High blood pressure.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Benign and malignant tumors.
- Stroke.
- Addiction to tobacco and alcohol.
- Head injuries.
- AIDS.
- Meningitis.
- Viral encephalitis.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Endocrine pathologies.
- Lupus erythematosus.
At risk are people whose immediate relatives were already dementors under the age of 65, or suffered from diabetes and obesity.
Leave a request for selection of a boarding house
for an elderly person with dementia
The main cause of primary senile dementia is organic brain damage. Secondary senile dementia can develop against the background of any disease or have a polyetiological nature. At the same time, the primary form of the disease accounts for 90% of all cases, secondary senile dementia occurs in 10% of patients, respectively.
With different diseases, different organs and tissues die, so the signs of marasmus are not the same and vary depending on age and the underlying disease.
Marasmus and its causes in children are poor feeding of children; contagious, acute diseases; congenital syphilis, diarrhea, suppuration.
Marasmus and its causes in adults - prolonged fevers, diarrhea, profuse suppuration, syphilis, cancer, mercury poisoning, paralytic state. In addition, such causes of the disease in adults as atrophic changes in the brain are observed. This problem still remains unexplored.
Also, one of the causes of the disease is a hereditary predisposition, but one cannot exclude the influence of external factors, which include infectious and internal diseases.
According to the age criterion, marasmus is divided into presenile (presenile) and senile (senile).
Manifestations of marasmus are observed in Alzheimer's disease, senile dementia, atrophic systemic processes of late age (Parkinson's disease, Huntington's chorea, Pick's disease).
The cause of senile dementia is genetic programming, as well as the immunological theory of aging (dystrophic changes in nerve cells).
Recently, studies have begun to appear on disturbances in the transmission of hereditary information into the cellular elements of nervous tissue. Impaired reading of information is noted in changes in protein synthesis, cellular metabolic processes, activity of enzyme systems and cellular accumulation of toxic metabolic products.
The influence of viruses that provoke the disease cannot be ruled out. Pick's disease reveals an increased content of zinc in certain areas of the brain, which provokes a change in the activity of metal-dependent enzymes, and also disrupts energy processes in the cell and changes the functions of receptors.
Classification of the disease
As the pathological process develops, three stages of development of senile insanity are distinguished:
- first or initial - intellectual abilities deteriorate, but the person retains basic skills, there are no problems with long-term memory;
- second - intellectual abilities disappear, a depressive state increases, and there may be problems with memory. Hygienic skills are maintained;
- the third is complete insanity, the patient cannot take care of himself, and there are problems with long-term memory.
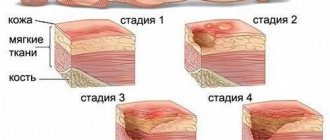
In most cases, at the third stage of development of senile marasmus, signs of cachexia, that is, exhaustion of the body, are observed. In this case, any third-party disease can lead to death, since the immune system is very weakened and metabolic processes in the body are disrupted.
Signs of cachexia
Symptoms of senile insanity. What to consider?
Dementia does not manifest itself with clearly defined signs. Most of them relate to age-related changes. It is necessary to know about the symptoms of the disease in advance, because this helps to avoid serious complications. Relatives of elderly people need to monitor their behavior and its changes. In addition, they should pay attention to the following factors:
- Memory problems. Organic brain damage leads to forgetting of events that happened recently. A person with senile dementia does not remember what happened to him yesterday, but can describe in detail events from the distant past.
- Behavior change. The patient no longer pays attention to his appearance. As a rule, he begins to take care of himself only if he is reminded about it. People with senile dementia are often apathetic. They are not interested in work or hobbies. Sometimes they can persistently prove that they are right or, conversely, become indifferent to the world around them. Shyness in such people also disappears. They can talk about erotic topics and demonstrate promiscuity.
- Disorientation in space. If patients are constantly at home, then, as a rule, they do not have any problems. Finding themselves in a place unknown to them, they may not find their way back.
- Deterioration of thinking. With dementia, people are unable to make final decisions. It is extremely difficult for them to choose the appropriate action in a given situation.
- Talkativeness. Some patients behave adequately in everyday life. Sometimes loved ones don't even notice the changes. But if you ask a person a question about his age, place of residence, date, he will be at a dead end.
Signs of dementia are becoming more pronounced every day. People who have this disease often become stingy. They may collect things in their home that they do not need at all. Symptoms of senile dementia in women at the initial stage are very original. They may experience increased appetite or great sexual desire.
Over time, the patient ceases to care for herself independently. She forgets that she has children and grandchildren. In some cases, senile dementia provokes aggression, anger, and tearfulness in people. At an advanced stage, sick people require regular care. They should not be left at home alone, because they can cause a fire, flood, etc. The interesting thing is that they themselves do not notice this.
Clinical manifestations
In order to promptly identify disorders, psychiatrists recommend that relatives of older people carefully monitor the appearance of the following symptoms of senile insanity:
- Memory loss. The development of organic brain damage provokes impairment of short-term memory. Therefore, an elderly person is unable to remember what happened yesterday, but remembers in detail the events of the distant past;
- Behavior change. People become sloppy and careless about their own appearance. Apathy develops, interest in work or hobbies disappears. Patients can often collect garbage on the street and bring it into the house. The patient's shyness disappears, so he easily communicates on erotic topics and becomes dissolute. They note the emergence of stinginess and greed, the appearance of immoderate appetite, hypersexuality;
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Senile dementia is divided into three types:
- Atrophic. It is characterized by primary degeneration in the brain.
- Vascular. It is also called secondary, as it develops against the background of existing deviations.
- Mixed. It is based on the two previous points.
- Multifocal. The entire nervous system is affected.
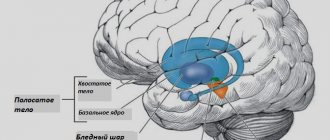
Experts also distinguish cortical and subcortical localizations.
The causes are point mutations in the DNMT3A and TET2 genes, which are responsible for vascular growth throughout the life cycle.
American and Australian scientists have proven that an unhealthy lifestyle also leads to dementia.
For prevention it is necessary:
- Do not abuse tobacco and alcohol products.
- Eat nutritiously and nutritiously. Include fish, vegetables and fruits in your diet.
- Engage in active sports.
- Strengthen neural connections by keeping the brain in good shape by reading and learning foreign languages.
- Work on a computer, master gadgets (brain “training”).
- Don't ignore depressive disorders.
- Treat yourself for hypertension and diabetes.
- Do not ignore hearing loss or deterioration and seek advice from an otolaryngologist.
Leave a request for selection of a boarding house
for an elderly person with dementia
Its representatives are by nature more emotional than men, and therefore subject to frequent mood swings
You should pay attention if you or a loved one exhibits:
- Irritability.
- Sudden aggression.
- Tearfulness or unreasonable laughter.
- Long-term severe depression.
- Excessive suspicion.
- Unreasonable stubbornness.
- Reluctance to communicate.
- Accusations against relatives, neighbors or complete strangers.
The first sign of the development of the disease is a change in character. Some qualities may become more pronounced.
Depending on the stage, dementia in the elderly is expressed in typical symptoms of varying intensity:
- memory impairment - short-term and long-term;
- slowing down the speed of thinking;
- partial and complete loss of professional and everyday skills;
- loss of the ability to be critical of one's actions;
- maladjustment in society;
- impairment of the ability to express thoughts competently;
- confusion;
- tremor of the limbs;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- partial and complete loss of self-identity;
- excitement of the nervous system for no apparent reason;
- shift in periods of sleep and wakefulness;
- loss of will;
- destruction of the emotional sphere.
Character traits with the development of pathology appear more noticeably: frugality can develop into stinginess, caution into suspicion, accuracy into meticulousness. Symptoms of senile dementia in the early stages are mistaken for age-related changes
Over time, relatives begin to notice increased grumpiness, cruelty and indifference on the part of the elderly person, which were not previously characteristic of him.
At the same time, the range of interests is narrowing. Forgetfulness manifests itself in isolated episodes. An elderly person first loses things, forgets names and other information, and then more pronounced signs of amnesia appear. Memory lapses are replaced by fictitious events. A person can “fall into childhood” and feel like a child. Behavior in this case corresponds to the age at which the patient imagines himself.
With senile insanity, the cause of which is Pick's disease, a person can become hypersexual, deliberately rude, and behave provocatively.
Subcortical instincts are released - shamelessness and sloppiness, which a person could previously control. The emotional sphere becomes impoverished, isolation and gloominess appear in the character. In some cases, sudden mood swings, increased suspicion, and violent aggression are noted.
A person loses most of his everyday skills, reducing self-care to primitive actions. Creativity is a thing of the past.
Having passed the middle stage of the disease, the patient becomes prone to vagrancy and theft.
In the severe stage, the patient cannot recognize himself in the mirror and does not recognize his relatives. He is unable to climb the stairs on his own or find the door to his own apartment.
There is a complete destruction of the psyche, hallucinations and delusions arise, speech becomes incoherent and incomprehensible to others. The ability to understand what is happening is completely lost, and personality degradation occurs.
Often patients in a severe stage refuse to eat, do not control the body’s natural urges, and resist hygiene procedures. Uncontrolled release of urine and feces occurs. A weak-minded person is not able to cope with household appliances, which poses a danger to the home and others.
In the final stage of dementia, the activity of internal organs is disrupted and neurological disorders occur. Due to physical and emotional exhaustion, the patient dies.
Experts also distinguish cortical and subcortical localizations.
There are several ways to determine the onset of senile dementia. We present one of them, which will help distinguish the natural decline of the body from dementia. It should be remembered that only a qualified physician can obtain the most reliable result. Check:
- How does a person navigate space, can he find his way home if something happens, can he distinguish between units of time.
- Short-term and long-term memory.
- Performing tasks to decompose a simple process into algorithms, for example, making coffee or washing clothes.
- Visual perception - asked to draw one or more simple shapes on paper.
- Patient's speech. It also turns out how the subject hears others.
- The client's knowledge of the world around him. The doctor asks to announce the purpose of the items.
- Intelligence. For this purpose, different research methods are used.
| Considered normal | Signs of Alzheimer's |
| Forgot to put lunch in the refrigerator | Didn't prepare food |
| Can't find a word when speaking | Speaks in an incomprehensible language where sentences are off-topic |
| I forgot the exact address of my friends | Forgot my place of residence |
| I don't remember how much 6x7 is | Forgot all the easy math operations (addition and subtraction) |
| Lost my apartment keys | Doesn't remember that he has his own place to live |
| Short-term mood swings and apathy | Constant suspicion and dissatisfaction |
In simple terms, senile dementia is a dementia in which the patient experiences impairments of intellect and memory. In the final stages, an elderly person may completely forget who he is. Unfortunately, the disease is very common, and many sufferers require constant supervision.
Senile dementia has several types, depending on which area of the brain is affected. This disease may be:
- Korkov. Cortical dementia is said to occur if the patient’s cerebral cortex is affected.
- Podcorkov. With this disease, damage to the subcortical region of the brain is observed (a striking example is Parkinson's disease).
- Cortical-subcortical. This is a mixed pathology, in which the patient is affected by both the cerebral cortex and the subcortical structures of the brain.
- Multifocal. With this disease, lesions are observed in each part of the nervous system.
Senile dementia has quite characteristic manifestations, and there can be a lot of them:
- Memory loss. Elderly people experience disorders of short-term and long-term memory functions. They cannot remember what they did recently and have trouble learning new information. At the last stage, patients forget who they are and do not recognize relatives and friends.
- Poor orientation in time and space. Senile dementia in women and men can lead to orientation problems, in which patients can get lost even in familiar areas.
- Difficulties in communication. Another manifestation of senile dementia is difficulties in communication: patients have difficulty finding words, so often those around them do not understand what idea they want to convey.
- Unacceptable behavior. Patients may behave unpredictably in society and perform actions that are unacceptable to others. As a rule, this manifests itself in the later stages of the disease.
If you notice the first signs of dementia in your relative, seek medical help immediately. Timely treatment will help delay the development of dementia and lead to a milder course of this disease.
Senile dementia is divided into primary and secondary.
Depending on the degree of brain damage, the disease occurs in the following forms:
- mild senile dementia (decrease in social activity, maintaining the ability to self-care);
- moderate senile dementia (loss of skills in using technology and instruments, inability to endure loneliness for a long time, maintaining the ability to self-care);
- severe senile dementia (complete maladjustment of the patient, loss of ability to self-care).
Prevention
As such, there is no prevention of senile marasmus, since the exact etiological factors of this disorder have not been established. You can reduce the risk of developing this disease by practicing the following:
- elimination of stress, psycho-emotional stress;
- prevention of cardiovascular pathologies;
- proper, nutritious nutrition;
- sufficient rest, moderate physical and mental stress;
- timely and correct treatment of all diseases;
- avoiding excessive alcohol consumption.
In addition, you need to systematically undergo preventive medical examinations and seek medical help if you feel unwell, and not carry out therapy at your own discretion.
What to do?
If you think you have Senile Senility
and the symptoms characteristic of this disease, then doctors can help you: a neurologist, a psychiatrist, a psychotherapist.
Stages of dementia
Symptoms of senile dementia will vary depending on whether the disease is in early or late stage. This disease has three stages:
- First stage. Symptoms and signs of dementia are not expressed. The patient remains capable of critical thinking and is aware of his condition. At this stage, the elderly person may willingly agree to treatment. Patients with senile dementia in the first stage do not need care: they can cook their own food, clean the house and take care of personal hygiene.
- Second stage. Symptoms and signs of the disease are more pronounced. A person’s critical perception is impaired, he experiences difficulties when using household appliances, and often forgets to close doors behind him, turn off the lights and gas. A person in such a state cannot be left alone, because he can cause harm to himself or others.
- Third stage. Symptoms and signs of senile dementia in the third stage are most pronounced. The disease leads to the disintegration of personality: the patient cannot eat independently, maintain hygiene, or use household appliances. An elderly person with dementia in the final stage ceases to recognize relatives and loses the ability to think logically and communicate. Often the sick person is accompanied by a state of apathy, in which he does not want to drink or eat. Over time, he develops movement disorders that cause him to lose the ability to move and chew.
The disease has become much “younger” in recent years and knows no boundaries. Dementors can become not only those who are over 70-80 years old, as was previously thought, but also fifty. The symptoms frighten those at home who are in the same area as the “monster,” who loses his memory, throws dishes and destroys the apartment, rushes to fight on loved ones, smears excrement on the walls and bed, and often runs away from home.
Often the population does not have complete information about how to deal with such patients. Doctors prescribe therapeutic treatment, but do not say how the caregiver’s existence will change in the future.
This problem can be solved, because in Russia there are a large number of institutions for the elderly. For example, the network of boarding houses for the elderly “Zabota” presents 10 cozy houses in the Moscow region. They accommodate more than 500 wards. Medically trained staff provide first-class care for the elderly.
A complete five-course meal has been developed, where the menu is compiled individually for each person, according to the recommendations of a specialist. The staff takes care of physical and mental health. Every day they try to diversify their leisure time with active games, musical evenings, thematic conversations, and picnics. Gymnastics and classes to restore mental abilities are conducted daily.
Everything we listed above is an early stage of the disease. But depending on the lesion, a person may experience:
- Severe mental disorders.
- Hallucative reasoning (when a conversation is conducted with fictional characters).
- Inability to remember past events.
- Complete collapse of personality.
- Impaired speech and ability to recognize things.
- Insanity, in which mental and physical work declines.
In addition, you can easily check for shifts by type of activity. If there is a driver in front of you, then pay attention to the following:
- how he navigates familiar terrain;
- does he drive according to the signs?
- how it reacts to force majeure circumstances;
- which turn signal turns on when changing traffic;
- what is his behavior during traffic jams, will he calmly wait for passage or will he overtake on the side of the road;
- whether control mechanisms are confused.
Senile dementia can be divided into the following stages:
- First (initial). This period is accompanied by a deterioration in mental abilities. At this stage, the patient is self-critical, but he is still able to take care of himself.
- Second. This stage is characterized by impaired intellectual abilities. The patient stops using ordinary things for their intended purpose. It is difficult for him to understand the operation of the telephone, kitchen stove, washing machine, TV, etc. The patient experiences constant depression during this period. Hygienic skills are preserved at the second stage. The patient is still able to take care of himself.
- Third. This is the final stage, which is the most dangerous and terrible for both the patient and his relatives. The person becomes insane. His close people still fail to explain that he needs to take care of himself and perform his usual actions. The patient can leave gas or water on, relieve himself anywhere, and eat without using cutlery.
The last stages are considered the most dangerous for humans. He is predominantly in a supine position. He has a metabolic disorder. Any somatic disease can cause death.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made in the presence of a complex of symptoms characteristic of dementia
, which is called “three A”):
- aphasia
(speech problems); - agnosia
(perceptual disturbances, difficulties in recognizing faces, words); - apraxia
(difficulty performing sequential actions).
Additional examinations are also indicated: computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
Diagnosis of dementia is carried out by a psychiatrist and a neurologist.
How does dementia manifest in older people?
Have you noticed strange illogical actions or an unkempt appearance in a relative, and this has alerted you? Then drop all planned activities and watch him for a few days.
Urgently go to a neurologist when you see such abnormalities:
- Decreased mental skills and memory.
- Aggression.
- Absent-mindedness.
- Loss of time and orientation.
- Forgetfulness.
- Substitution of concepts and phrases.
- Stumbling out of the blue.
- Mathematical errors when filling out invoices.
- Night wakefulness.
- Apathy at work.
- Loss of sense of humor.
- Walking aimlessly from room to room.
Select a service for your relative | |||
| Caring for bedridden people | Disability care | Elderly care | Care after a heart attack |
Relatives of a person who has been diagnosed with senile insanity need to be able to adapt to his wishes and requests. To ensure that caring for a patient does not cause hysterics and screams, it is recommended to do the following:
- Get involved in “games” even if they are annoying. For example, an elderly grandmother may tell her neighbors that she doesn’t even have crackers at home. The granddaughter, in turn, will be upset because of such words, because she buys a lot of groceries for her beloved relative. There is no reason to be upset. If grandma talks about crackers, then she should offer them. She will understand that they exist, after which she will no longer complain to strangers. There are people who demand to be in a room with closed windows. You shouldn't argue with them. It is better to do what the patient asks (within reason, of course).
- Communicate with a sick person. Even if a person has senile insanity, you need to communicate with him. Relatives of the patient should share the latest news with him. The person will constantly listen to them, as a result of which he will not switch to imaginary objects.
- Give gifts, make pleasant surprises. Many people mistakenly believe that a person with senile insanity no longer needs anything. This is not true, because even an elderly woman will not refuse a pleasant surprise. To do this, you should buy something tasty or healthy.
The nursing home is ready to gladly accept even those people who have senile dementia. The private boarding house "Valentina" offers first-class care for sick people. All requests and wishes of both the elderly person and his close relatives are taken into account here. In this boarding house, specialists monitor the health status of each client every day.
If necessary, they provide the patient with first-class medical care. This institution has everything necessary to ensure complete safety for people with this illness. The nursing home is located in a picturesque corner of the Moscow region. It is surrounded by a tennis park where people can enjoy walks and a lake, which creates a comfortable atmosphere.
Unfortunately, senile dementia is a very dangerous and unpleasant disease that brings discomfort to both the patient and his loved ones. Not all relatives have the time and energy to constantly be near an elderly person. In order not to provoke unpleasant situations, it should be registered in the private boarding house “Valentina”.
It employs highly qualified personnel who take their duties responsibly. Here, customer service is provided at the highest level, as a result of which not only he, but also his loved ones will be satisfied. Professional help will be needed if a person with dementia behaves aggressively or distractedly.
For guests with senile dementia in a private boarding house the following is offered:
- well equipped private room;
- constant surveillance;
- daily health check;
- accommodation at an affordable price policy;
- six dietary meals a day;
- moral support;
- 24-hour professional care;
- treatment control.
Unfortunately, it is now impossible to get rid of senile dementia forever. But modern medicine offers special medications that slow down the development of this disease. This treatment alleviates the plight of both the patient and his loved ones. Psychosocial rehabilitation is also an integral component of effective therapy.
The private boarding house offers guests the following:
- Creating a comfortable atmosphere. The effectiveness of treatment largely depends on the situation.
- Respectful attitude of the staff towards every elderly person. Nursing home workers are ready to feed the patient, wash him, etc.
- Safe living. The presence of anti-slip flooring, handrails, and a small amount of furniture guarantees complete safety for a person with senile dementia.
- Respectful attitude and constant support. Specialists communicate with people, listen to their requirements and wishes.
You can book a room for an elderly relative by calling 8-495-003-19-56 or using the online call back form.
Recommendations for relatives
Elderly patients with senile dementia require constant support. To do this you will need:
- Create a cozy and favorable atmosphere at home;
- Talk to the patient only in a calm tone;
- Address a person by name;
- When speaking, you should use simple phrases and words;
- Help with daily activities: dressing, eating, bathing, showering;
- When communicating, you should remember the old days;
- It is necessary to repeat the phrase if the patient does not understand its meaning.