It is very important for modern medicine to combat brain pathologies in newborns; this task is extremely urgent, since, despite a significant reduction in child mortality in many, even developing countries, this problem still exists. Only the emergence of new methods of treatment and prevention of neurological diseases can help children feel safer.
One of the serious damage to brain structures is anoxic brain pathology, which is especially characteristic of newborn children. Anoxic brain damage is exclusively hypoxic in nature, as a result of which ventilation, blood circulation, respiration, and tissue metabolism are disrupted.
Hypoxia is oxygen starvation of the brain due to insufficient blood and nutrients. Even a short and not too long period of oxygen starvation can cause disruption of some processes in the brain. And, given the fact that all the organs of a newborn baby are still only at the stage of formation and are very fragile, the failure of nutrients to reach the brain and the slowdown in blood flow can actually contribute to the emergence of other serious pathologies.
Medicine has revealed one important but terrible fact - without oxygen and nutrients, brain cells and tissues begin to gradually die after just 4 minutes.
What is organic brain damage?
Organic brain damage is a whole complex of diseases. These include the following diseases:
- ischemic stroke - a violation of cerebral circulation with damage to brain tissue as a result of the formation of “plaques” in the vessels, which impede the flow of nutrients and oxygen to the brain;
- hemorrhagic stroke - rupture of cerebral vessels, the appearance of hematomas;
- vascular dementia - a disorder of the central nervous system (may be with or without a stroke), appears as a result of interruptions in the blood supply to the brain;
- discirculatory encephalopathy – the occurrence of small tumors as a result of lack of oxygen;
- chronic ischemic disease - develops after hypertension or other diseases of the circulatory system;
- residual organic damage to the central nervous system is a residual phenomenon after birth trauma, symptoms disappear over time, but for children in infancy this disease is very dangerous;
- early organic damage is the process of death of brain cells.
This is an incomplete list of diseases that are classified as APM. The final diagnosis is made by a neurologist. Characteristic features:
- headache;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- hypertension or hypotension;
- vision problems;
- epileptic seizures;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- convulsions;
- fainting.
Treatment methods
Treatments for anoxia and life-threatening conditions include restoring a strong flow of adequately oxygenated blood to the brain. To this end, the cause of the lack of oxygen flow is determined and appropriate measures are taken:
- Removing foreign bodies from the respiratory tract.
- Removing the patient from the danger zone of carbon dioxide or electric shock.
- Stopping strangulation (loosening and removing parts of clothing from the neck - a tie, shirt collar, or other objects that impede blood flow).
If necessary, artificial (using devices) maintenance of gas exchange and cardiac activity is carried out. Correction of mild oxygen deficiency is carried out with the help of antihypoxic drugs and antioxidants.
Antihypoxants (Amtizol, Bemitil, Mexidol) alleviate the reactions of the body, which is experiencing an episode of oxygen starvation, and accelerate the process of cell recovery after hypoxia. Treatment of oxygen starvation in infants and adult patients is aimed at eliminating the causes of the pathological condition, taking into account the primary pathology that provoked the oxygenation disorder.
Anoxic damage to brain tissue is associated with a lack of oxygen. Impaired oxygenation can be due to various reasons. Treatment is carried out taking into account etiological factors and symptoms.
Anoxic brain damage is serious damage to organ structures. Pathology develops in infants. The disorders are hypoxic in nature. With the disease, disturbances in breathing, blood circulation and tissue metabolism are observed.
Establishing diagnosis
Diagnosis of organic focal diseases of the brain is important both at the earliest stages and at later stages with already prescribed treatment. Early detection of the disease will allow you to take action and prescribe medications that can stop its progression or even reverse it. The most important diagnostic stages:
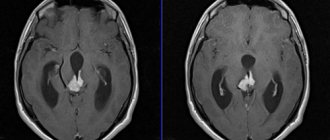
Foci of organic brain damage are shown by arrows
Anamnesis allows you to determine the duration of the disease, its course, and its connection with heredity. A neurological examination is mandatory to identify the causes. Tomography identifies atrophic lesions that cause symptoms.
Diagnosis of anoxic brain damage
The doctor asks about symptoms and medical history and performs a physical examination. You may need to see a doctor who specializes in brain problems.
Tests that allow you to find out the extent of damage and determine the part of the brain that was damaged:
- CT scan of the head is an X-ray test that uses a computer to take detailed images of the brain;
- MRI is a test that uses magnetic waves to take pictures of structures inside the head;
- An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a test that measures the electrical activity of different parts of the brain;
- SPECT scan is a type of computed tomography scan that examines blood flow and metabolism in the brain area;
- Tests used to assess visual, auditory and sensory perception.
Diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis and detect brain disease or disorders caused by traumatic brain injury, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out.
Doppler ultrasound
The technique is based on the integrated use of ultrasound analysis and Dopplerography. The diagnostic procedure is absolutely safe, informative, and allows you to determine the level of blood flow, identify areas with narrowing in the vascular lumens, atherosclerotic formations, and aneurysms.
The only disadvantage of Doppler ultrasound is its inaccessibility. Not every clinic and private office has a diagnostic device. Among the advantages is a minimal number of contraindications, which include the inability to remain in a supine position.
Rheoencephalography
The principle of operation is similar to electroencephalography. The technique allows you to assess the level of blood circulation in the vessels of the brain and examine vascular tone. No special preparation is needed for the analysis. The technique is safe and has no contraindications.
Magnetic resonance and computed tomography
Magnetic resonance imaging helps to study the small structures of the organ, assess the condition of the blood vessels and brain matter. The technique is effective for confirming microstroke and thrombosis.
Computed tomography is prescribed to identify inflammatory processes in the brain substance and membranes, increased intracranial pressure, cystic and tumor-like neoplasms, and multiple sclerosis.
Dopplerography
Dopplerography allows one to study hemodynamics, blood flow speed, functionality and filling of blood vessels. The transcranial method involves the use of digital examination, with a beam penetration depth of up to 9 cm.
Duplex scanning of vessels is prescribed to study vascular tone, lumen and structure, identify deformations, thrombus formation, and atherosclerotic changes.
Other methods
Echoencephalography or ultrasound analysis of the brain is carried out using a special device - an oscilloscope. The method is used to assess the condition of blood vessels, the activity of the organ as a whole or its individual sections.
Neurosonography is performed to detect pathological conditions in newborns and young children. The brain matter, soft tissues, and blood vessels are studied. Neurosonography can detect tumors, aneurysms, and other neoplasms.
Craniography is an x-ray diagnostic that allows you to study the structural features of the skull, identify changes after a head injury and with the development of brain pathology. In most cases, craniography is performed using a contrast agent, which is injected into the cerebral ventricle.
Electroneuromyography is a study that allows you to assess the level of transmission of nerve impulses in a certain area of the organ.
Positron emission tomography helps study the functional activity of the brain. This method makes it possible to identify small tumor-like neoplasms that do not cause severe symptoms.
Diagnosis of this brain pathology
Diagnosis of anoxic brain damage in children involves, first of all, magnetic resonance and computed tomography. Electroencephalography may also be needed. Based on the results of all these procedures, the doctor can establish the correct diagnosis and predict the further course of the disease.
Treatment usually includes two successive stages. Firstly, it is the removal of the root causes of the disease along with the restoration of the body. At this stage, it is necessary to understand what exactly caused anoxia in order to eliminate it. And directly at the second stage, taking vitamins is required along with breathing exercises and taking vascular medications in order to restore the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, among other things.
Possible outcomes
All possible consequences and outcomes are divided into three points:
- Recovery. This is possible if there are no visible defects and the depth of the lesion is small.
- Disability. The patient is alive, but to a greater or lesser extent loses the ability to work and take care of himself.
- Disability. Without outside help a person cannot survive.
- Death.
Any consequences depend on the massiveness of the lesion, the location of the pathological process, age, etiological factor and correctness of treatment.
Treatment
The method of treating brain damage depends on its type, the degree of pathological changes, and the severity of the general condition. Typically, treatment for traumatic brain injury and organ disease differs.
Traumatic brain injury
Immediately after receiving a traumatic brain injury, it is important to provide proper first aid, which will help alleviate the condition and improve the prognosis.
If there is no breathing or pulse, perform artificial respiration and cardiac massage. If these are not changed, the victim must be placed on his side, which avoids disruption of respiratory function due to vomiting.
If there is a closed injury, a cold compress is applied to the injury site to reduce pain and swelling. If there is bleeding from a wound on the skin, it is covered with a piece of gauze, and then the head is bandaged.
It is not recommended to independently remove bone fragments and other elements protruding from the wound before the ambulance arrives, because in this case the bleeding will only intensify. In addition, you can get an infection.
To correct post-traumatic disorders, the following is prescribed:
- neuropsychological treatment to restore memory, attention, and emotional state;
- taking medications to normalize blood flow in the brain;
- conducting speech therapy sessions to restore speech;
- psychotherapeutic treatment to correct the emotional background;
- a diet that includes foods that normalize brain function.
It is recommended to begin rehabilitation therapy no later than 3-4 weeks from the time of injury. Traditional treatment in such cases is not effective.
Damage of a different etiology
If brain damage is caused by an infectious agent, antibacterial drugs that are sensitive to the pathogen are prescribed. For example, for viral diseases, antiviral agents are used, for bacterial diseases, antibacterial agents are used. In combination, immunomodulators are prescribed to increase the body's protective function.
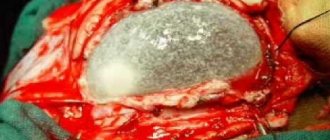
If a hemorrhagic stroke occurs, the hematoma is surgically removed. In the ischemic form of the pathology, the use of decongestants, nootropic, and anticoagulant drugs is indicated.
Mental disorders are corrected with medications (nootropics, tranquilizers, antidepressants) and non-drug (psychotherapy, etc.) methods. In most cases, they are combined.
It is worth noting that patients with acute brain tumors often have decreased memory, so they forget to take medications prescribed by the doctor. For this reason, this responsibility falls on the shoulders of relatives: they need to monitor the implementation of medical recommendations every day.
Pathology treatment options
Anoxic brain damage is treated in several ways. If the pathological process develops in an acute form, then it is urgently necessary to protect the child from the factors that caused anoxia. To do this you may need:
- sanitation of the respiratory tract;
- removal of foreign objects;
- cessation of strangulation;
- prevent exposure to electric current.
It is also necessary to carry out therapeutic techniques to support blood circulation and gas exchange at optimal levels. If necessary, the patient is connected to special devices in order to prevent the development of pathological changes in the brain.
If breathing is maintained, then the victim is sent to a hospital setting, and provided with oxygen inhalation. If breathing has stopped, the patient is incubated.
The next step of treatment is to normalize the blood circulation process and restore heart function. To restore brain function, further treatment is carried out using:
Symptomatic therapy is also carried out, the purpose of which is to eliminate pronounced manifestations of anoxia. If a patient has headaches, analgesics are recommended. In the presence of epileptic seizures, the condition is alleviated with the help of anticonvulsants.
After the blood circulation in the brain is completely restored, physiotherapeutic procedures, massages, special exercises, and psychological correction are prescribed.
Insufficient oxygen supply to the body can lead to the development of various pathological processes in the body. Anoxia is considered one of the central problems in medicine. Brain cells are the most sensitive to this process. It may be possible over time to discover methods that will reduce the depth of anoxic damage to the central nervous system. The recovery period can last for months and even years. In some cases, the damage cannot be completely repaired.
1. Etiology and pathogenesis 2. Classification 3. Clinic 4. Diagnostics 5. Methods of combating anoxia
The problems of treating a child with neurological pathology are extremely relevant in our time. This is due to a general decline in the birth rate, an increase in the number of unfavorable factors that provoke damage to the nervous system, and an increased incidence of the birth of unhealthy, physiologically immature children.
Very often, the direct causes of brain damage are hypoxic-ischemic processes as a result of insufficient oxygen supply to the nervous tissue. In ICD-10, the diagnosis is encrypted in several sections. The closest in pathophysiology are codes P21.9 (neonatal anoxia) and G 93.1 (anoxic brain damage, not classified elsewhere).
Anoxic damage to the nervous system in children is caused by a lack of adequate oxygen supply to neurons . Under such conditions, the cell quickly changes its functional properties and is not able to function fully. Subsequently, the morphology of neurons is also disrupted. Oxygen deficiency leads to cellular necrosis and/or apoptosis and forms foci of ischemia in the brain. Symptoms of cerebral anoxia can be severe and fatal.
Neurons begin to die after only 4 minutes of acute anoxia. Under conditions of hypothermia, this time is extended to 20-30 minutes, and at high temperatures it is reduced to 120 seconds.
Symptoms
Not all individuals know what an organic lesion is. Organic brain damage does not have specific symptoms due to its complex genesis; they manifest themselves individually.
General changes: decreased activity, inability to concentrate for a long time, apathy, sloppiness.
Elderly people may forget the names of relatives, the day of the week, the date, and speech is impaired. If the disorder progresses, the patient forgets words and cannot maintain a dialogue. The emotional state has 2 types: the absence of any emotions or inadequate, aggressive behavior. There are hallucinatory attacks.
Symptoms depending on severity
In children, residual organic damage is difficult to see with the naked eye, but an experienced neurologist, already at the first examination of the baby, will be able to determine the external signs of the disease.
Often this is an involuntary trembling of the chin and arms, a restless state of the baby, a syndrome of tone disorders (lack of tension in the skeletal muscles).
And, if the damage is severe, it can manifest itself as neurological symptoms:
- paralysis of any limb;
- disturbance of eye movements;
- reflex failures;
- loss of vision.
In some cases, symptoms can only be noticed after undergoing certain diagnostic procedures. This feature is called the silent course of the disease.
General symptoms of residual organic damage to the central nervous system:
- unreasonable fatigue;
- irritability;
- aggression;
- mental instability;
- changeable mood;
- decreased intellectual abilities;
- constant mental anxiety;
- inhibition of actions;
- pronounced absent-mindedness.
In addition, the patient is characterized by symptoms of mental infantilism, brain dysfunction and personality disorders. As the disease progresses, the set of symptoms can be replenished with new pathologies, which, if left untreated, can lead to disability and, in the worst case, death.
Organic damage to the central nervous system: causes, diagnosis and treatment
The entire human nervous system can be divided into central and peripheral.
The central nervous system includes the spinal cord and brain. The spinal cord is located in the spinal column and is presented in the form of a cord that starts from the foramen magnum and ends in the lumbar region. The brain is located inside the skull. Organic damage to the central nervous system means that the human brain is defective. Doctors say that the first stage of this disease can be detected in 99% of people. This stage has no symptoms and does not require treatment. However, stage 2 is a more severe type of lesion, but stage 3 is a severe disease with serious deviations.
Brain damage can be congenital or acquired. Congenital pathologies develop if during pregnancy a woman:
- drank alcohol, drugs or smoked
- had the flu, ARVI
- took certain medications that have toxic effects
- experienced severe stress.
Other reasons include hereditary predisposition and too young age of the expectant mother. In addition, organic brain damage can occur due to improper management of childbirth and birth trauma.
Acquired damage to the central nervous system occurs after:
- stroke
- traumatic brain injuries
- alcohol and drug use
- infectious diseases (meningitis, meningoencephalitis)
In addition, damage can occur against the background of autoimmune diseases and tumor processes in the brain.
Symptoms of damage to the central nervous system:
- fast fatiguability
- urinary incontinence during the daytime
- lack of coordination
- decreased vision and hearing
- sleep disturbance
- easily distractible
- reduced immunity
Children with organic damage to the central nervous system are called mentally retarded. Their normal mental development is disrupted, active perception, speech, logical thinking and voluntary memory are inhibited. Such children are characterized by either increased excitability or inertia. They have difficulty developing interests and communicating with peers.
In addition, the child’s physical development also suffers. Such children have an irregular skull shape, their gross and fine motor skills are impaired, and difficulties arise in the formation of motor automatisms.
Diseases of the central nervous system caused by organic brain damage:
Oligophrenia is a disease characterized by mental retardation. Such children have reduced intelligence, their speech, motor skills, and emotions lag behind. The disease is often congenital or develops in the first year of life. These people are able to take care of themselves independently.
The human central nervous system is made up of neurons and their processes; when these neurons begin to deteriorate, dementia occurs. Dementia is a disease in which there is a loss of skills and knowledge and the inability to acquire new ones.
The disease is acquired in nature and occurs as a symptom of many diseases:
- Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia (55–60% of cases)
- vascular
- alcoholism
- brain tumors
- traumatic brain injury
There are 3 degrees of severity of dementia. At grade 1, the patient is capable of self-care, but social activity is already impaired. At degree 2, the patient requires self-monitoring. In grade 3, the patient does not understand what is being said to him and does not say anything himself. Incapable of self-care. Needs constant monitoring.
Characteristic clinical manifestations
Symptoms of brain damage depend on which area of the organ the changes occur.
Frontal lobe
If the frontal lobe cortex is involved in the pathology, motor function is impaired, which is expressed in the development of the following symptoms:
- unsteady gait, instability of the body while walking;
- muscle rigidity, difficulties in performing passive movements of the limbs;
- paralysis of one or both limbs on one side of the body;
- paralysis of the head and motor function of the eyes;
- speech dysfunction, which is expressed in difficulty finding words during a conversation, as well as synonyms, cases, order of sounds;
- tonic or clonic spasms of the fingers;
- grand mal epileptic or tonic-clonic seizures;
- unilateral loss of smell.
A mental disorder also occurs, which is characterized by disinhibition, causeless rage, indifference, and apathy.
Parietal lobe
If the parietal lobe cortex is affected, disturbances in perception and sensitivity occur, including:
- tactile sensitivity;
- loss of ability to read, write, count;
- loss of the ability to find a specific place and occupy it.
A person loses the ability to recognize familiar objects by touching with his eyes closed.
Temporal lobe
When the temporal lobe cortex is damaged, auditory perception is disrupted, hallucinations and convulsions occur. In addition, the following symptoms may be observed:
- decreased hearing function with the occurrence of complete or partial deafness;
- manifestation of tinnitus;
- loss of ability to understand language or music;
- short-term or long-term memory loss;
- feeling of deja vu;
- dementia.
Damage to the temporal lobe is characterized by the occurrence of temporal lobe epilepsy.
Occipital lobe
Damage to the occipital region causes disruption of the visual analyzer, which manifests itself in:
- complete loss of visual function;
- loss of perception of one of the halves of the visual field;
- inability to recognize familiar faces, objects, colors.
Visual illusions may occur when a familiar object appears smaller or larger in size than it actually is.
Cerebellum and brainstem
In this case, brain pathology causes impaired coordination of movements:
- ataxia - unsteadiness of gait, awkward movements of the body;
- inability to coordinate fine motor skills in the form of tremor;
- inability to perform rapid repetitive movements of the limbs and eyes.
When the trunk is damaged, focal sensory and motor disturbances occur.
Content
Definition and general information [edit]
Delayed postanoxic encephalopathy
Synonyms: delayed posthypoxic encephalopathy syndrome
Etiology and pathogenesis[edit]
With successful CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation), it is possible to restore cardiac, sometimes simultaneously, respiratory function (primary revival) in at least half of the victims, but in the future, survival in patients is observed much less frequently (P. Safar, 1984). The reason for this is post-resuscitation disease (the name was proposed by the luminary of Russian resuscitation V. A. Negovsky in 1959).
The outcome of recovery is largely determined by the conditions of the blood supply to the brain in the early post-resuscitation period. In the first 15 minutes, blood flow can exceed the initial one by 2-3 times, after 3-4 hours it drops by 30-50% in combination with an increase in vascular resistance by 4 times. Repeated deterioration of cerebral circulation may occur 2-4 days or 2-3 weeks after CPR against the background of almost complete restoration of central nervous system function - delayed posthypoxic encephalopathy syndrome
.
Clinical manifestations[edit]
Posthypoxic encephalopathy (Lanz-Adams syndrome) is characterized by intentional and action myoclonus, sometimes in combination with dysarthria, tremor and ataxia. In severe cases, the patient is freed from myoclonus only in a position of complete relaxation while lying down; any attempts to move lead to an “explosion” of generalized myoclonus, depriving any possibility of independent movement and self-care.
Anoxic brain damage, not classified elsewhere: Diagnosis[edit]
Differential diagnosis[edit]
Anoxic brain damage, not classified elsewhere: Treatment[edit]
The drug of choice is clonazepam, and the good effect of this drug is considered one of the confirmations of the diagnosis.
Anoxic Brain Damage (Anoxic Brain Injury; Hypoxic Brain Injury)
Mechanism of damage
One of all the “inconsistencies” of the disease is the fact that a disorder of this type belongs to neuropathology, but its symptoms may relate to other branches of medicine.
Due to an external factor, the mother experiences disruptions in the formation of the phenotype of cells that are responsible for the full list of functions of the central nervous system. As a result, fetal development is delayed. It is this process that can become the last link on the path to central nervous system disorders.
Regarding the spinal cord (this is also part of the central nervous system), corresponding lesions can appear as a result of incorrect obstetric care or inaccurate turns of the head when delivering the child.
Place of pathology in the ICD
Each case of any disease, both a functional disorder and a life-threatening condition, must be submitted to medical statistics and encrypted, receiving the ICD-10 code (International Classification of Diseases).
And the central nervous system can also suffer, while the damaging factors can be firmly established, the pathogenesis of the disorder, signs are known, and there is a final separate diagnosis. Therefore, even just on the basis of the official classification of diseases, it is possible to draw a conclusion and create a definition of what this mysterious pathology is.
Encephalopathy due to gasoline poisoning
In case of severe poisoning, the peripheral nervous system is affected (lead polyneuritis, paralysis).
Gasoline intoxication is characterized by organic brain damage. Clinically, they manifest themselves in the form of convulsive seizures and increased excitability. Delayed psychomotor development, liver and kidney damage are detected. Sleep becomes restless, with nightmares. As intoxication increases, attacks of narcolepsy and episodes of muscle weakness are possible.
Similar symptoms are also observed in cases of poisoning with toluene and stain removers.
Symptoms of anoxic brain damage
Recovery from anoxic brain injury can be challenging and can take a long time. The chances of recovery depend on how long the victim was exposed to no or low oxygen supply. Severe damage can lead to coma or a vegetative state. After moderate anoxic brain damage, the following may occur:
- Headache;
- Confusion;
- Decreased concentration and attention span;
- Mood fluctuations and/or changes in mental status;
- Unstable loss of consciousness;
- Seizures;
- Parkinson's disease, in the form of a syndrome;
- Pathological muscle twitching.
Alcoholic encephalopathy
Toxic encephalopathy in alcoholism is the most common form of the disease. Although, according to the latest international classification, alcoholic encephalopathy was identified as an independent disease, many doctors, by inertia, still classify it as toxic encephalopathy.
Chronic alcoholic encephalopathy develops as a result of prolonged poisoning of the body with ethyl or methyl alcohol. On average, the appearance of the first signs of the disease begins after three years of systematic alcohol consumption (daily libations or long binges).
Ethyl and methyl alcohol destroy brain cells, and nerve connections are irreversibly lost. In addition, alcohol intoxication causes multiple small focal hemorrhages and capillary ruptures, which leads to degradation of brain structures. The course of the disease is further complicated by the fact that most patients are not ready to admit their addiction and stop the flow of poison into the body.
nightmares
In case of poisoning with alcohol surrogates, an acute course of the disease develops. There are four forms of alcoholic toxic encephalopathy.
- Gaye-Wernicke syndrome.
- Alcoholic pseudoparalysis.
- Korsakov psychosis.
- Acute mitigated form of the disease.
The distinctive symptoms of encephalopathy in alcoholism are:
- loss of coordination, tics, trembling of hands and lips;
- hallucinations;
- physical aggressiveness.
Prevention of anoxic brain damage
To reduce the risk of brain damage, you should:
- Chew food thoroughly;
- Learn to swim;
- Supervise small children near water;
- Stay away from high-voltage electrical sources (including protection from lightning strikes);
- Avoid chemical toxins and drugs;
- Check gas burning appliances and devices that produce carbon monoxide, and install carbon monoxide detectors.
Manganese encephalopathy
Manganese affects the subcortical centers of the brain (striatum). Poisoning with this metal is characterized by the following symptoms:
- lethargy, drowsiness;
- decreased muscle tone;
- dull pain in the arms and legs;
- intellectual impairment (weakened memory, loss of writing ability);
- decrease in emotional background.
In severe cases, widening of the palpebral fissures, a grimace of a smile, unnatural laughter or crying, and trembling of the tongue are noted.
Causes of anoxic brain damage
Anoxic brain damage can occur in the following cases:
- Oxygenated blood cannot reach the brain (for example, when a clot prevents blood flow to the brain, or when blood pressure is too low, such as during shock or congestive heart failure);
- The blood that reaches the brain does not contain enough oxygen (for example, with lung diseases, the blood is not sufficiently oxygenated);
- Exposure to poisons or other toxins that reduce oxygen in the blood (such as carbon monoxide poisoning).
Mercury toxic encephalopathy
sweating
Mercury poisoning is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pain in the abdomen (when poison enters through the mouth) and in the chest area;
- blue border on the gums;
- sweating;
- cardiopalmus;
- severe weakness;
- insomnia;
There is a specific trembling of the limbs, which is called “mercury tremor”. The patient’s mental state is contradictory; with emotional upsurge and excitement, difficulties arise in making the simplest decisions.
Etiology and pathogenesis
There are a number of unfavorable factors that can lead to the development of anoxic damage to the nervous system. Even minimal deviations significantly disrupt the functioning of the brain due to the fact that they affect immature nervous tissue. Subsequently, this may manifest itself as a neurological deficit, a slowdown in the rate of formation of cerebral zones and centers, and a delay in overall development. Prolonged anoxia leads to death or the formation of a vegetative state.
The root causes of anoxia may include acute thrombosis, suffocation, strangulation, drowning, electric shock, cardiac arrest, alcohol or drug intoxication, neuroinfections, as well as other factors that prevent the supply of oxygen to the brain. Separately, anoxic lesions of the nervous system of the perinatal period are distinguished. This is facilitated by:
- pathological course of pregnancy (somatic diseases of the mother, gestosis, threat of miscarriage, symptoms of qualitative and quantitative starvation, intoxication, general immaturity of the pregnant woman, etc.);
- intranatal (arising during childbirth) damaging factors. This includes symptoms of premature abruption, placenta previa, entanglement of the umbilical cord around the fetal neck, umbilical cord nodes, premature and late, rapid and protracted labor, weakness of labor;
- postnatal (postpartum) disorders. These include meconium aspiration, repeated apneas, cardiovascular defects, sepsis, and hemolytic disease of the newborn.
All of the above provocateurs cause the development of foci of ischemia. In parallel, as a compensatory reaction, the permeability of cerebral vessels increases. On the one hand, this reduces cerebral perfusion and aggravates ischemia, on the other, it serves as one of the mechanisms for the development of hypoxic-hemorrhagic lesions. Due to it, the process of diapedetic impregnation of red blood cells begins through the altered vascular wall. In addition, under conditions of oxygen starvation, glucose utilization occurs along the anaerobic pathway with the formation of lactate. During perinatal anoxia, acid compounds irritate the digestive and respiratory centers of the brain stem. During childbirth, this provokes premature passage of meconium and its aspiration into the child’s respiratory tract, which contributes to even greater hypoxia.
Morphologically, deviations are observed in the form of:
- cerebral edema (focal or multifocal);
- ischemic lesions of brain tissue, basal ganglia, thalamus, cerebellum;
- cortical and subcortical small focal necrosis;
- periventricular leukomalacia.
Classification
Depending on the predominant morphological result of the development of disorders, anoxic pathology can manifest itself in the form of cerebral ischemia, intracranial hemorrhages of hypoxic origin, and combined non-traumatic ischemic-hemorrhagic lesions of the central nervous system.
The mechanism of development of anoxia allows us to classify it into the following types:
- anoxic, formed as a result of the cessation of oxygen supply through the respiratory tract;
- anemic, occurring as a result of massive blood loss, vascular spasm, thrombosis;
- congestive, which is a consequence of cerebral circulation discirculation;
- metabolic – a manifestation of metabolic disorders.
In addition, there is acute anoxia, which develops suddenly, and a chronic form of pathology with a gradual increase in oxygen deficiency (hypoxia).
The duration of the decrease in oxygen supply determines the gradation of anoxia into mild (oxygen starvation for up to 80 seconds), moderate (up to 120 seconds) and severe (up to 240 seconds) forms. Such a division is quite arbitrary, since the severity of anoxic manifestations will depend on the ambient temperature, the age of the patient and the condition of the body itself.
Clinic
Clinical symptoms are primarily determined by the cause of anoxia and the duration of its effects. Acute anoxia is manifested by loss of consciousness, which may be accompanied by convulsive paroxysms. Subsequently, profound amnesia occurs. Severe and moderate forms of anoxia provoke persistent neurological disorders:
- Paralysis and paresis;
- Sensitivity disorders;
- Cognitive impairment;
- Vestibulocerebellar syndrome;
- Epileptic seizures.
Severe anoxic lesions can lead to decortication syndrome - functional shutdown of the cerebral cortex, and the development of a vegetative state.
Anoxic brain damage in newborns
It is very important for modern medicine to combat brain pathologies in newborns; this task is extremely urgent, since, despite a significant reduction in child mortality in many, even developing countries, this problem still exists. Only the emergence of new methods of treatment and prevention of neurological diseases can help children feel safer.
One of the serious damage to brain structures is anoxic brain pathology, which is especially characteristic of newborn children. Anoxic brain damage is exclusively hypoxic in nature, as a result of which ventilation, blood circulation, respiration, and tissue metabolism are disrupted.
Hypoxia is oxygen starvation of the brain due to insufficient blood and nutrients. Even a short and not too long period of oxygen starvation can cause disruption of some processes in the brain. And, given the fact that all the organs of a newborn baby are still only at the stage of formation and are very fragile, the failure of nutrients to reach the brain and the slowdown in blood flow can actually contribute to the emergence of other serious pathologies.
Medicine has revealed one important but terrible fact - without oxygen and nutrients, brain cells and tissues begin to gradually die after just 4 minutes.
Anatomical picture
Unfortunately, medicine has not yet identified the exact mechanism of the occurrence of anoxic damage to cells and tissues. However, anatomically, the picture of the pathology is quite simple: nerve tissues cease to receive oxygen in quantities sufficient for them, and a hypoxic-ischemic process occurs, which is detrimental to brain structures even over a short period of time.
In other words, each neuron does not receive the normal amount of oxygen during the blood supply. Neurons in a child are not yet as developed as in adults, and accordingly, the relationship between neurons and the brain is still at the stage of formation, it is very weak. If there is insufficient supply to the cell, it ceases to function normally and changes internally and morphologically. Accordingly, anoxia can be called a morphological degenerative process that has an extremely detrimental effect on healthy tissue.
The symptoms of prolonged anoxia and hypoxia are very difficult for the baby to tolerate and often result in death.
Causes
Unfortunately, doctors have not yet identified a single root cause of anoxic damage. However, there are a lot of provoking factors that can precede such a terrible phenomenon.
These factors prevent normal blood supply and the supply of sufficient oxygen to the baby’s brain:
- heart failure;
- suffocation or drowning;
- intoxication with chemicals, sometimes even dirty ecology has an impact. Children are very sensitive to the cleanliness of the environment;
- various viruses and neuroinfections;
- shock and electric shock;
- surgery on the heart or brain;
- coma or clinical death;
- prolonged arterial hypotension (low blood pressure).
One way or another, all these factors directly affect the inhibition of blood circulation, and, therefore, cause gradual tissue necrosis.
However, there are also some factors that can affect the occurrence of anoxia even at the stage of a woman’s pregnancy:
- intoxication of women with chemical narcotic substances;
- the expectant mother’s age is too young, her general immaturity;
- threats of abortion;
- entanglement of the umbilical cord around the fetal neck, causing suffocation;
- bad habits of the mother - alcohol, smoking;
- premature or delayed birth;
- intrauterine viruses and infections.
So expectant mothers need to be very careful about their health and lifestyle, because in their womb there is already a child who is so fragile that it requires constant care.
Symptoms
Anoxic damage in a newborn baby is very difficult - even short-term hypoxia can cause attacks of suffocation, convulsions, and internal necrosis. Common symptoms and signs of anoxia include:
- epileptic seizures and convulsions;
- involuntary trembling of the limbs;
- sensory disturbance;
- disruption of the organs of hearing and vision;
- photophobia and increased photosensitivity;
- paralysis and paresis of the limbs;
- attacks of suffocation, breathing problems;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- headache.
Diagnosis and treatment of anoxia
Diagnosis of anoxic lesions includes MRI or CT procedures, as well as electroencephalography. Based on their results, the doctor can make a correct diagnosis and predict the course of the disease.
Treatment includes two stages: removal of the root cause of the disease and restoration of the body. At the first stage, you need to figure out what caused the anoxia and destroy it.
The second stage includes taking vitamins, breathing exercises, and taking vascular medications to restore the functioning of blood vessels and the heart.
Video
umozg.ru
Causes and symptoms of APM in children
Depending on the cause, brain lesions can be acquired or congenital.
The following reasons for the acquired form can be identified:
- skull injuries - bruise, concussion, fracture, etc.;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system - atherosclerosis, stroke;
- impaired blood supply to the brain;
- infectious diseases: meningitis, encephalitis;
- poisoning with alcohol or psychotropic substances;
- Parkinson's or Alzheimer's disease;
- tumors;
- Vasculitis is a disease whose symptoms are immunopathological inflammation of blood vessels (arteries, capillaries and veins).
The causes of congenital APM are:
- premature placental abruption;
- infectious diseases during pregnancy;
- the pregnant mother took drugs, illegal medications, smoked or drank alcoholic beverages;
- lack of oxygen in the fetus;
- difficult childbirth;
- weak uterine muscles;
- genetic diseases.
Causes of the disease
The reasons for the development of pathology are not fully established. There are provoking factors that lead to the disease. Under the influence of these factors, circulatory disturbances and insufficient blood flow to the brain are observed.
The pathology appears in patients and develops against the background of cardiac arrest. The cause of the disease is suffocation. In newborns, the disease appears after drowning.
If a child’s body is exposed to toxic substances, this leads to poisoning. A polluted environment has a negative impact on a child's body. Anoxic brain damage occurs with neuroinfections and various viral lesions. In case of electric shock, the development of the disease is diagnosed.
If a child is diagnosed with clinical death or coma, this leads to the development of pathology. Low blood pressure over a long period of time leads to pathology.
The anoxic type of disease occurs against the background of various provoking factors that affect the brain.
How to treat?
Treatment of brain diseases has always been complex, as a combination of different methods is required to restore normal tissue structure. It is not the immediate changes that are amenable to therapy, but the symptoms of APM or the primary disease.
Such modern technologies that are currently available to humanity will still not be able to completely cure OPM. That is why the prescribed treatment will be lifelong.
Drug therapy
The main method of treatment is medication. The following medications are used:
- Cerebrolysin - improves brain activity;
- Pentoxifylline - increases vascular elasticity;
- Piracetam - corrects psychological disorders.
Additionally, medications are prescribed to relieve symptoms, such as sleeping pills (Phenobarbital), tranquilizers or antidepressants. For complex therapy, it is advisable to use the services of a psychotherapist.
Folk remedies
Treatment of APM is symptomatic, so it is possible to use traditional medicine. There are a large number of recipes, but the following are considered more effective:
- blueberry juice, 200 ml daily - significantly improves memory;
- decoction of rowan bark - 50 g of crushed bark per 200 g of boiling water, cook for several minutes, then leave for 6 hours, strain and take 50 g after meals.
Treatment of anoxic brain damage
Treatment for anoxic brain injury depends on the cause. Barbiturates may be used initially to slow brain activity. Steroids and other medications may be used to reduce swelling that occurs when brain tissue is injured. This may help limit the extent of brain damage. The doctor also prescribes pure oxygen to supply their brains. Brain cooling can be used to help limit brain damage. Additionally, hyperbaric oxygen treatment can be used in cases of hypoxia due to carbon monoxide inhalation.
Rehabilitation
During rehabilitation, the victim and his family will work with the following doctors:
- Physical therapist – helps to regain motor skills such as walking;
- Occupational Therapist – work to improve daily skills such as dressing and toileting;
- Speech therapist – work on speech problems;
- Neurologist – behavioral advice and treatment for emotional problems associated with trauma.
Recovery may take several months or even years. In many cases, full recovery is never achieved. In general, the earlier rehabilitation begins, the better the result.
Taking medications
Your doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- Antiepileptic drugs – for the treatment of ongoing seizures;
- Clonazepam (eg Klonopin) – to treat muscle cramps.
Rehabilitation is all in the hands of the mother and doctors
Rehabilitation measures for this disease, as well as for its treatment, should be prescribed by the attending physician. They are aimed at eliminating existing complications in accordance with the patient’s age.
For remaining movement disorders, physical methods are usually prescribed. First of all, it is recommended to do therapeutic exercises, the main idea of which will be aimed at “revitalizing” the affected areas. Additionally, physical therapy relieves swelling of nerve tissue and restores muscle tone.
Mental development delays are eliminated with the help of special drugs that have a nootropic effect. In addition to the pills, they also conduct classes with a speech therapist.
Anticonvulsants are used to reduce the activity of epilepsy. The dosage and the drug itself must be prescribed by the attending physician.
Increased intracranial pressure should be eliminated by constant monitoring of cerebrospinal fluid. Pharmaceutical drugs are prescribed that increase and accelerate its outflow.
It is very important to eradicate the disease at the first alarm bells. This will enable the person to lead a normal life in the future.
Degrees and symptoms of the disease
Anoxic brain damage has three stages of development, according to which the development of symptoms is observed:
Hypoxic disorders are mild. In patients at this stage of the disease, neuro-reflex excitability increases. Diagnosed with the disease is decreased muscle tone. Reflexes may increase or decrease. Trembling in the extremities is noted in the pathology.
After a week, the symptoms of the disease go away on their own. Normalization of the child's condition is observed. In case of illness, the absence of gross neurological disorders is diagnosed.
With moderate severity of the lesion, severe symptoms are observed. The child's sucking and other reflexes are suppressed. The disease is accompanied by a decrease or increase in muscle tone, blue discoloration of the skin, and an increase in intracranial pressure. In case of illness at this stage, the occurrence of autonomic disorders is diagnosed.
The pathology is accompanied by diarrhea and constipation. This pathological process is accompanied by bradycardia or tachycardia. Some patients stop breathing due to pathology. As intracranial pressure increases, an increase in anxiety in the baby is diagnosed. Poor sleep, bulging fontanel, trembling limbs are diagnosed.
In some cases, convulsions are observed. With intensive treatment, the child's condition improves. it is impossible to eliminate neurological disorders. If the condition worsens, the baby falls into a coma.
When pregnancy is complicated, severe hypoxic disorders occur. In women, swelling, increased blood pressure, and the development of kidney disease are diagnosed. A newborn girl or boy has signs of developmental delay. With a difficult labor process, the situation worsens.
After birth, the baby is unable to breathe. A decrease in tone and reflexes is diagnosed, and blood circulation is impaired. In this form of the disease, urgent cardiopulmonary resuscitation is recommended. Otherwise, the chances of survival are reduced to zero.
Complications, consequences and prognosis
According to the experience of doctors, organic damage to the central nervous system in children can cause the following consequences:
- mental development disorders;
- speech defects;
- delayed speech development;
- lack of self-control;
- hysterical attacks;
- disruption of the normal development of the brain;
- post-traumatic stress disorder;
- epilepsy attacks;
- vegetative-visceral syndrome;
- neurotic disorders;
- neurasthenia.
In children, quite often such disorders affect adaptation to environmental conditions, manifestations of hyperactivity or, on the contrary, chronic fatigue syndrome.
Today, the diagnosis of “residual organic damage to the central nervous system” is made quite often. For this reason, doctors are trying to improve their diagnostic and treatment abilities.
The exact characteristics and features of a certain type of lesion make it possible to calculate the further development of the disease and prevent it. In the best case, suspicion of the disease can be completely removed.
To determine the drug, it is necessary to pay attention to the mood and psychological state of the child (laughter, crying). Facial expression. Complexion – redness, pallor, cyanosis, rash. Facial expressions, body movements. Wrinkles on the skin. Skin turgor, sweating. Language. How a child sits and lies. What is the reaction to milk and food in general? Is there any drooling?
There are babies that look like little old men - Argentum nitricum, Calcarea carbonica, Natrium muriaticum, Opium, Secale. If a child has a frightened expression, we think of Aconite or Stramonium. A very sleepy baby may need Cannabis indica or Opium - when he sleeps clearly more than normal for his age and which is his leading characteristic. Such children never fully wake up after sleep and never seem cheerful and active. A baby's screaming and crying can provide a number of key clues. The child cries every time he is put to bed.
In Borax the child cries every time his mother puts him in bed. If the baby cries when picked up and carried, it may be Bromium or Chamomilla. But these drugs are also suitable for relieving the condition from being carried in the arms. A shrill cry in sleep is characteristic of Borax, Lycopodium, Zincum. If a shrill cry is followed by convulsions, Cuprum, Cicuta, Lycopodium may be needed.
If the trembling starts from the solar plexus and spreads throughout the body, it will be Cicuta. “Brain scream” - when the child wakes up and screams piercingly, and you think that something has happened to his head. This scream sends chills down your spine. The remedy will be Apis, especially if the cry occurs at night, is combined with convulsions and is provoked by bathing in hot water. Constant screaming of a child is a symptom of ear pain. In this case, the use of Graphites, Psorinum, Mercurius is necessary. Otitis media makes the child scream and squeal all the time, and nothing can calm him down. This is not whining or crying. It's a high-pitched, constant scream. If a child whines, whines, or is capricious, think about homeopathic remedies such as Aconitum, Belladonna, Helleborus.
The color of the ear and the smell coming from the ear can also help in the search for homeopathic remedies. Discharge from the right ear suggests Mercurius iodatus flavus, Lycopodium, Silica, Thuja or Nitricum acidum. Discharge from the left ear indicates Graphit, Psorinum, Mercurius iodatus ruber. Bloody discharge from the ear may indicate Calcarea sulfurica, Mercurius, Psorinium or Silica. But if pure blood flows from the ear, then of course you need to think about Phosphorus and Crotalus horridus.
Remember that Crotalus horridus has many retinal hemorrhages. Any foul discharge from the ear indicates Mercurius, Silica, Aurum, Lycopodium, Psorinum. If your ear discharge smells fishy, the first things to think about are Graphit., Sanicula aqua and Tellurium. Any sour-smelling discharge (such as sweat) should make you think of Sulfur. Sulfur and Calcarea carb. - good for babies who have a sour smell. But the main remedy in this case is Rheum.
If the baby has a serious condition: high fever with diarrhea and very foul-smelling stools, you should think about Baptisia, Arsenicum album, Mercurius, Sulfur.
Wrinkles on a baby's skin. If there are slightly tortuous vertical wrinkles, this indicates the presence of cerebral, meningeal problems. In this case, Helleborus, Stramonium, Chamomilla, Causticum, Lycopodium are prescribed. If wrinkles appear in the area of the ears and cheekbones, this indicates a pathology of the chest organs, deep and chronic. If the wrinkles are located downward from the chin, they indicate a problem with the intestines.
If a thin line is visible at the edge of the lower eyelid, and a second one is nearby, and because of this it seems that the eyelid is inflamed, then this indicates a predisposition to hysteria; These children often have violent emotional outbursts, and they need drugs like Natrium muriaticum, Ignatia. These are intelligent children, very excited, nervous, whose facial skin shows some kind of dryness, not even dryness, but some kind of skin tension, tension. This is the face of a man whose nerves are constantly tense. The facial expression is rather frightened. Blueness around the lips corresponds to Cina. Facial cyanosis due to respiratory pathology – Cuprum, Stramonium, Tabacum.
If there is swelling around the eyes, in the area of the upper and lower eyelids, give Apis, Calc., Arsenicum album, Kali arsenicosum. If there is swelling of the lower and upper eyelids, but stronger in the area of the lower eyelids, then this is a kidney pathology, give Apis, Kali carb., Phosphorus, Medorrhinum. If there is swelling only of the upper eyelids in the form of a hanging bag of water, then the first drug is K carb., but you will not see this in infants. In cases of inflammation of the eyelid margins, give Clematis, Graphit, Sanicula aqua. If the edges of the eyelids are uniformly inflamed, the main remedy is Euphrasia. For inflammation of the meibomian glands, swelling along the edges of the eyelids (resembling the appearance of barley), give Clematis, Staph. For conjunctivitis, redness of the eyes, give Apis, Arg.-n., Euphrasia, Rhus-t., S. If one eye is very red and looks like a piece of fresh meat from which blood is oozing, give Arg.-n. Moreover, the eye was not swollen, but very red, as if living flesh had been cut with a knife. This occurs due to bleeding of the superficial capillaries of the sclera. The pain is minor. Black eyelids - very dark - in children and adults, especially those suffering from gastrointestinal disorders, indicate Arsen. Dark circles under the eyes – Secale. Blue circles under the eyes – Phosphoricum acidum, Sulphuricum acidum, Arsenicum album
Sweating in the neck and occipital region (the pillow is wet with sweat), especially during sleep - Calcarea carbonica, Sanicula aqua, Lachesis, Phosphoricum acidum. Profuse sweating - Mercur., Na mur., Thuja, China. The baby sweats profusely, but during an attack (for example, shortness of breath) the whole body is dry. With difficulty breathing, sweating usually increases, but in this case, on the contrary, it disappears. Most of the sweat is released between attacks. The remedy for this picture, which occurs mainly in connection with bronchial asthma in children, is Sambucus nigra. This is the solution in this case for constitutional treatment.
At the age of 7-9 years, white discolored spots, such as vitiligo, may appear on the skin of children, the drug Sepia. If these spots are from birth and then they transform into one or another form of skin pathology, then Graphit, Sulfur, Psorinum are prescribed.
Red complexion is characteristic of Bell., Ferrum, Chamomilla, Apis, Puls. Hysterical children (a child has emotional outbursts when you don’t know what happened, what he wants, how you offended him and are lost, not knowing what to do), when the child is completely out of control, often need Na mur. and Ignatia.
The child cries when put to bed and stops crying when he is raised and in a semi-sitting position, especially with shortness of breath - Arsenicum album, Calcarea carb, Lach., Spongia. Better lying on stomach or any kind of pressure on abdomen - Bell., Coloc., Medor., Stram., Tub. The child lies with his hands on top of his head - Puls.
Rations for milk and other products. If you see excessive regurgitation after 10 minutes. after the start of feeding, it might be Aethusa. The child vomits milk that has already curdled. If you see a sudden aversion to milk, it is Lac defloratum that gives him the opportunity to drink milk (mother's or cow's) again.
Gesticulation - Gesticulation combined with high temperature is characteristic of Hyoscyamus. These children gesture all the time when they play or do something in a group. They often put their hands towards their genitals. Petroleum and Baptisia are characterized by different gestures - they fiddle with the bed linen.
New and popular:
- Seborrhea in a 5 year old child on the head treatment
Seborrhea of the skin in children or childhood seborrheic dermatitis, as well as in adults - a dermatological disease,… - Increased eosinophils in infants Purpose of eosinophils First of all, it should be noted that eosinophils are one of nine types of leukocytes - cells...
- 8 reasons for psychological infertility In Russia, 15% of families cannot give birth to a child. According to obstetricians themselves, more and more...
- Treatment of cough with compresses with Dimexide A compress with Dimexide for cough is a physiotherapeutic procedure that can be performed at home.…
ICD-10 code for cerebral ischemia
The use of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) helps doctors more easily navigate the wide variety of pathologies of the human body. Modern medicine is able to determine a lot of diagnoses that are impossible to remember or learn. This is especially true for vascular pathology: there are quite a lot of different variants of serious diseases associated with acute or chronic circulatory disorders of organs and systems. In particular, cerebral ischemia belongs to the “Diseases of the circulatory system” (class IX) and is located in the section “Cerebrovascular diseases”. Each condition has a code that the doctor will use to diagnose and treat it.
Classification of acute cerebral ischemia
Vascular pathology of the brain, caused by a sudden and severe disruption of arterial blood flow, is allocated to a separate group of ICD-10. All variants of cerebral infarction are divided into parts, each of which indicates the level of vascular pathology:
- difficulty in blood circulation occurred at the level of vessels located outside the brain (precerebral arteries);
- cerebral blood flow is impaired;
- a blood clot formed in the cerebral veins.
ICD-10 codes I63.0 to I63.2 indicate cerebral infarction caused by thrombosis of the precerebral arteries, I63.3 to I63.6 - occlusion of the cerebral arteries and veins. The I64.0 code encrypts a stroke in which there is no bleeding into the brain structures.
This group of ICD-10 codes does not include complications and consequences arising from acute ischemic attack.
Coding options for chronic cerebral ischemia
All chronic conditions leading to ischemic changes in brain structures are encrypted in subsection I67. Frequent causes of long-term cerebral circulatory insufficiency are the following conditions:
- dissecting aneurysm of the cerebral arteries (I67.0);
- cerebral aneurysm without signs of rupture (I67.1);
- atherosclerotic lesions of cerebral vessels (I67.2);
- encephalopathy due to vascular causes (I67.3);
- encephalopathy due to arterial hypertension (I67.4);
- a rare vascular pathology of the carotid and cerebral arteries described as Moyamoya disease (I67.5);
- inflammatory damage to the veins and arteries of the brain, leading to impaired blood flow (I67.6 - I67.7);
- when it is difficult to identify the main causative factor, codes I67.8 - I67.9 are used, which indicate all unspecified variants of diseases.
All types of consequences of acute or chronic cerebral ischemia are encrypted in subsection I69.
Additional codes to indicate the reason
Often, the doctor needs to not only identify the underlying disease with a code, but also identify additional causative factors that led to ischemic conditions in the head. For this, ciphers from other subsections are used:
- arterial hypotension (I95);
- serious heart disease (I21, I47);
- blockage of individual non-cerebral arteries (I65);
- various types of cerebral hemorrhages (I60 - I62).
If it is necessary to indicate complications, the doctor can use the coding of other sections. In particular, if severe brain disorders such as dementia occur due to vascular causes, the code F01 can be used.
Use cases for ICD-10
The main purpose of using ICD-10 in the practice of any doctor is the ability to perform statistical analysis, both within one medical institution, and across the country and the world. In addition, the international classification allows all doctors in the world to use the same diagnoses, which helps to carry out treatment effectively and correctly.
If acute thrombosis or chronic ischemia of cerebral vessels is detected, the doctor conducts a course of therapy aimed at completely curing the patient from the pathology of the precerebral or cerebral arteries. If necessary, surgery may be performed. If the treatment was successful, then upon discharge the doctor will indicate the diagnosis in the form of an ICD-10 code. The disease code will be processed by the hospital's statistical service, sending the information to the region's medical information center. If, in addition to the main diagnosis, there are complications and consequences that require additional examination and treatment, the doctor will indicate the coding of these conditions using international classification codes.
All ischemic conditions of the brain can be encrypted using ICD-10. By using the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, the physician will always use diagnoses that are used throughout the world. This will make it possible to correctly assess not only a person’s disease, but also to carry out effective treatment using modern and high-tech methods of global therapy.
Such a dangerous pathology as dyscirculatory encephalopathy according to ICD 10 has the code “I 67”. This disease belongs to the category of cerebrovascular diseases - a general group of pathological conditions of the brain that are formed as a result of pathological transformations of cerebral vessels and disorders of normal blood circulation.