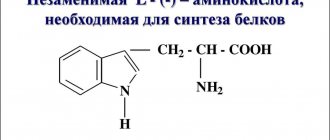
Duloxetine is a third-generation psychotropic drug that is a selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. Unlike first and second generation psychotropic drugs, Duloxetine does not affect all brain mediators. The drug selectively inhibits the uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine, dopamine and norepinephrine, since disturbances in their functioning cause depression.
The medication is a relatively new pharmacological agent that has virtually no hypnotic effect. According to the instructions, Duloxetine has a wide range of applications and is considered the safest heterocyclic psychotropic medication. Duloxetine is primarily used in psychiatry to treat depressive disorders.
General information about the drug Duloxetine
Duloxetine is used to eliminate depression and pain due to neurosis. The drug prevents the uptake of norepinephrine and serotonin by adrenergic neurons (suppresses the reuptake of these hormones). The drug has little effect on dopamine uptake. The active substance blocks severe pain in neurotic disorders.
Drug group, INN, scope of application
The clinical and pharmacological group of the drug is a third generation antidepressant. The international nonproprietary name is Duloxetine. The medication is used for specific damage to the peripheral nervous system and various mood disorders. Due to its high efficiency and relative harmlessness, this medicine has acquired a wide range of clinical use.
Release form and prices for Duloxetine Canon
Duloxetine comes in the form of blue-white or blue-green gelatin capsules. Each capsule is marked in liquid dye with a dosage (30 or 60 mg) and an identification number (9543 or 9542). The capsules are filled with smoky white or gray granules.
Cost of the drug Duloxetine Canon, produced by the Russian company:
| Dosage, mg | Number of capsules, pieces | Pharmacy name | City | Price, rubles |
| 60 | 28 | Pharma City | Moscow | 1634 |
| 30 | 14 | Samson-Pharma | Rostov-on-Don | 690 |
| 60 | 28 | Beauty and health laboratory | Moscow | 3407 |
| 30 | 14 | Eapteka.ru | Tomsk | 871 |
| 60 | 28 | Pharmacy 36.6 | Saint Petersburg | 2037 |
| 30 | 14 | Be healthy | Krasnoyarsk | 845 |
| 60 | 28 | Leaf | Novosibirsk | 1627 |
| 30 | 14 | Violet | Ufa | 709 |
Compound
The active component of the medication is the substance duloxetine hydrochloride, which suppresses the central mechanism of pain sensitivity. In addition to the active ingredient, the capsules also contain other substances:
- food coloring E171;
- mannitol;
- amylose and amylopectin polysaccharides;
- etal;
- sodium dodecyl sulfate;
- cane sugar;
- hypromellose HP55;
- hydrolyzed collagen protein;
- food additive E131.
See also:
Melipramine - instructions for use, reviews and analogues
Composition, release form and packaging
Enteric-soluble hard gelatin capsules No. 3, blue body and cap; the contents of the capsules are spherical microgranules from almost white to yellowish-white.
| 1 caps. | |
| duloxetine (as hydrochloride) | 30 mg |
Excipients: hypromellose E5 10.54 mg, hypromellose HP55 15.51 mg, starch 44.09 mg, mannitol 47.3 mg, sodium lauryl sulfate 5.22 mg, sucrose 17.46 mg, titanium dioxide 1.15 mg, cetyl alcohol 1.55 mg.
Capsule shell composition: gelatin, titanium dioxide, patented blue dye V.
7 pcs. – contour cellular packaging (aluminum/PVC) (1) – cardboard packs. 7 pcs. – contour cellular packaging (aluminum/PVC) (2) – cardboard packs. 7 pcs. – contour cellular packaging (aluminum/PVC) (4) – cardboard packs. 10 pcs. – contour cellular packaging (aluminum/PVC) (2) – cardboard packs. 10 pcs. – contour cellular packaging (aluminum/PVC) (3) – cardboard packs. 10 pcs. – contour cellular packaging (aluminum/PVC) (6) – cardboard packs. 14 pcs. – contour cellular packaging (aluminum/PVC) (1) – cardboard packs. 14 pcs. – contour cellular packaging (aluminum/PVC) (2) – cardboard packs. 14 pcs. – contour cellular packaging (aluminum/PVC) (6) – cardboard packs. 15 pcs. – contour cellular packaging (aluminum/PVC) (2) – cardboard packs. 15 pcs. – contour cellular packaging (aluminum/PVC) (4) – cardboard packs.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of Duloxetine
The antidepressant effect of the drug occurs by preventing the destruction of 5-hydroxytryptamine and norepinephrine. In addition, the active component has a weak inhibitory effect on dopamine uptake. Duloxetine does not form chemical bonds with histamine, dopamine, cholinergic and adrenergic receptors.
The main effect of the drug is to suppress the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine. The drug affects the basic mechanisms of pain, which is primarily manifested by an increase in the threshold of pain sensitivity in neuropathic pain syndrome.
Complete absorption of the substance is observed 2 hours after taking the medication. The intake of food into the body reduces the rate of absorption by 11%.
90% of duloxetine hydrochloride is bound to plasma proteins. The main chemical changes of the drug occur in the liver. As a result of biotransformation, the following substances are formed: glucuronic conjugate of 4-hydroxyduloxetine, sulfate conjugate of 5-hydroxy-6-methoxyduloxetine.
12 hours after use, the substance loses half of its pharmacological effect. The maximum concentration of the drug in the blood is observed 6 hours after taking the medication. The blood plasma purification rate is 101 l/h. For women, this figure is slightly lower.
Dysfunction of the kidneys and liver does not affect the degree of binding to proteins, but slows down the rate of biotransformation and removal of the active substance from the body.
Liver cirrhosis increases the plasma clearance rate by 15%; total concentration – 5 times; the time during which the concentration of a substance decreases by half - 3 times.
See also:
At what pressure is Diroton used and its instructions
Interaction with other drugs
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
Due to the risk of developing serotonin syndrome, duloxetine should not be used in combination with an MAOI and for at least 14 days after discontinuation of MAOI treatment. Based on the length of the half-life of duloxetine, you should wait at least 5 days after stopping duloxetine before taking an MAOI. Selective reversible MAOIs, such as moclobemide, have a lower risk of serotonin syndrome. However, the combined use of reversible MAOIs and duloxetine is not recommended.
Inhibitors of the CYP1A2 isoenzyme.
Due to the fact that the CYP1A2 isoenzyme is involved in the metabolism of duloxetine, simultaneous use of duloxetine with potential inhibitors of the CYP1A2 isoenzyme is likely to lead to increased concentrations of duloxetine. Fluvoxamine, a potent inhibitor of the CYP1A2 isoenzyme (100 mg once daily), reduced the average plasma clearance of duloxetine by approximately 77%. Caution should be exercised when prescribing duloxetine with inhibitors of the CYP1A2 isoenzyme (for example, some quinolone antibiotics) and lower doses of duloxetine should be used.
Drugs metabolized by the CYP1A2 isoenzyme.
Concomitant use of duloxetine (60 mg 2 times a day) did not have a significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of theophylline, which is metabolized by the CYP1A2 isoenzyme. Duloxetine is unlikely to have a clinically significant effect on the metabolism of CYP1A2 isoenzyme substrates.
Drugs metabolized by the CYP2D6 isoenzyme.
Duloxetine is a moderate inhibitor of the CYP2D6 isoenzyme. When taking duloxetine at a dose of 60 mg 2 times a day with a single dose of desipramine, a substrate of the CYP2D6 isoenzyme, the AUC of desipramine increases 3 times. Co-administration of duloxetine (40 mg twice daily) increased the steady-state concentration of tolterodine (2 mg twice daily) by 71%, but had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of the 5-hydroxy metabolite. Therefore, caution should be exercised when using duloxetine with drugs that are primarily metabolized by the CYP2D6 isoenzyme system and have a narrow therapeutic index.
Inhibitors of the CYP2D6 isoenzyme.
Since CYP2D6 is involved in the metabolism of duloxetine, concomitant use of duloxetine with potential CYP2D6 inhibitors may result in increased duloxetine concentrations. Paroxetine (20 mg once daily) reduced the mean clearance of duloxetine by approximately 37%. Caution should be exercised when using duloxetine with inhibitors of the CYP2D6 isoenzyme (for example, SSRIs).
Drugs affecting the central nervous system.
Caution should be exercised when using duloxetine together with other drugs and agents that affect the central nervous system, especially those that have a similar mechanism of action, including alcohol. Concomitant use with other drugs that have serotonergic effects (for example, SNRIs, SSRIs, triptans, tramadol) may lead to the development of serotonin syndrome.
Serotonin syndrome.
In rare cases, serotonin syndrome has been observed with concomitant use of SSRIs (eg, paroxetine, fluoxetine) and serotonergic drugs. Caution is advised when using duloxetine with serotonergic antidepressants such as SSRIs, tricyclic antidepressants (clomipramine or amitriptyline), St. John's wort, venlofaxine or triptans, tramadol, finidine and tryptophan.
Oral contraceptives and other steroid drugs.
The results of in vitro studies indicate that duloxetine does not induce the catalytic activity of the CYP3A isoenzyme. Specific in vivo drug interaction studies have not been conducted.
Anticoagulants and antithrombotic drugs.
Due to the potential increased risk of bleeding associated with pharmacodynamic interactions, caution should be exercised when duloxetine is coadministered with anticoagulants or antithrombotic agents. In addition, when duloxetine and warfarin were used together, the international normalized ratio (INR) increased. However, the simultaneous use of duloxetine and warfarin under stable conditions in healthy volunteers in a clinical pharmacology study did not reveal a clinically significant change in the INR from the mean or change in the pharmacokinetics of the dextro- or levorotatory isomer of warfarin.
Antacids and H2-histamine receptor antagonists.
Concomitant use of duloxetine and aluminum- and magnesium-containing antacids or duloxetine and famotidine did not have a significant effect on the extent of absorption of duloxetine when using a dose of 40 mg.
Inducers of the CYP1A2 isoenzyme.
A population pharmacokinetic analysis showed that, compared with non-smoking patients, plasma concentrations of duloxetine in smoking patients were almost 50% lower.
Drugs that are highly bound to blood proteins.
Duloxetine is highly bound to plasma proteins (>90%). Therefore, the administration of duloxetine to a patient who is taking another drug that is highly bound to plasma proteins may lead to increased concentrations of the free fractions of both drugs.
Indications and contraindications for Duloxetine
Indications for the use of this drug are:
- complications of diabetes mellitus that affect the nervous system;
- depression.
The list of contraindications is also small. The drug is not used for:
- drug hypersensitivity;
- simultaneously with antidepressants that inhibit the enzyme monoamine oxidase.
Patients with the following symptoms should take the drug with caution:
- suicidal tendencies;
- affective insanity;
- history of seizures;
- acute cornerstone glaucoma;
- kidney and liver dysfunction;
- arterial hypertension.
In addition, it is not recommended to take the medication for patients under 18 years of age, since there is no data on the effectiveness and safety of Duloxetine in patients in this group. For the same reason, the medicine is not prescribed during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
special instructions
Exacerbation of manic/hypomanic state.
As with similar drugs that affect the central nervous system, duloxetine should be used with caution in patients with a history of manic episodes.
Epileptic seizures.
As with similar drugs that act on the central nervous system, duloxetine should be used with caution in patients with a history of epileptic seizures.
Mydriaz.
Cases of mydriasis have been observed with duloxetine, so caution should be exercised when prescribing duloxetine in patients with elevated intraocular pressure or in those at risk of developing acute angle-closure glaucoma.
Increased blood pressure.
In isolated cases, an increase in blood pressure was observed during treatment with duloxetine. In patients with arterial hypertension and/or other cardiovascular diseases, it is recommended to measure blood pressure.
Suicidal behavior.
The risk of committing suicide exists in all patients with depression and some other mental disorders. This danger may persist until remission occurs. As a result, patients at greatest risk of committing suicide should be under close medical supervision during pharmacotherapy. As well as taking other drugs that have a similar mechanism of pharmacological action to duloxetine (SSRIs, SNRIs), taking duloxetine during treatment or upon its cessation in a number of cases was associated with the development of suicidal thoughts and suicidal behavior.
The use of duloxetine in patients under 18 years of age has not been studied, therefore Duloxetine Canon is not intended for use in such patients. A cause-and-effect relationship between taking duloxetine and the occurrence of suicidal events in patients of this age group has not been established. However, some analytical reviews of the results of a number of studies using antidepressants for the treatment of mental disorders indicate an increased risk of developing suicidal thoughts and/or suicidal behavior in children, adolescents and adults under 25 years of age compared with placebo. Clinicians should encourage patients to report any disturbing thoughts and feelings at any time.
Increased risk of bleeding.
SSRIs and SNRIs, including duloxetine, may increase the risk of bleeding, including gastrointestinal bleeding (see section "Side effects"). Therefore, duloxetine should be prescribed with caution to patients taking anticoagulants and/or drugs that affect platelet function (for example, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), aspirin) and to patients with a history of bleeding.
Hyponatremia.
Very rarely, cases of hyponatremia have been reported (in some cases, serum sodium levels were lower than 110 mmol/l). Most of these cases occurred in elderly patients, especially in combination with a recent history of altered fluid balance or in the presence of conditions predisposing to altered fluid balance. Hyponatremia may manifest as nonspecific symptoms (such as dizziness, weakness, nausea, vomiting, confusion, drowsiness, lethargy). Signs and symptoms in more severe cases included fainting, falls, and seizures.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
Severe reactions, sometimes fatal, have been reported in patients receiving a serotonin reuptake inhibitor in combination with a MAOI, including pyrexia, rigidity, myoclonus, peripheral disturbances with possible dramatic fluctuations in vital signs, and mental status changes including marked agitation with transition to delirium and coma. These reactions have also been observed in patients who were discontinued with a serotonin reuptake inhibitor shortly before being prescribed an MAOI. In some cases, patients experienced symptoms consistent with neuroleptic malignant syndrome. The effects of combined use of duloxetine and MAOIs have not been evaluated in humans or animals. Therefore, given the fact that duloxetine is a reuptake inhibitor of both serotonin and norepinephrine, it is not recommended to take duloxetine in combination with an MAOI or for at least 14 days after stopping treatment with an MAOI. Based on the T1/2 duration of duloxetine, a break of at least 5 days should be taken after stopping duloxetine before taking an MAOI.
Impaired liver or kidney function.
In patients with severe renal impairment (CK
Increased activity of liver enzymes.
Some patients treated with duloxetine in clinical studies experienced increased liver enzyme activity. The observed deviations were, as a rule, transient in nature and disappeared spontaneously or after discontinuation of duloxetine. Serious increases in liver enzyme activity (10 times or more above the upper limit of normal), as well as liver damage of cholestatic or mixed origin, were rare, and in some cases were associated with excessive alcohol consumption or pre-existing liver disease. It is recommended to use duloxetine with caution in patients who drink alcohol in significant quantities, as well as with existing liver diseases.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and engage in other potentially hazardous activities
During studies of duloxetine, no impairment of psychomotor reactions, cognitive functions and memory was identified. However, taking the drug may be accompanied by drowsiness. In this regard, patients taking duloxetine should exercise caution if necessary to drive vehicles or operate machinery that requires increased attention and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Instructions for use of Duloxetine
According to the instructions, therapy should begin with 60 mg of Duloxetine per day. At this dosage, the drug is taken 1 time per day. If necessary, the dosage is increased to 120 mg, but this amount of the substance must be divided into 2 doses. It is not recommended to take more than 120 mg of medication per day.
Patients with a reduced glomerular filtration rate are prescribed 30 mg of the substance per day. In case of liver dysfunction, the initial dosage of the antidepressant should also be reduced or the interval of taking the drug should be increased.
The dosage regimen for elderly patients is no different.
The product is intended for internal use. The tablets are taken regardless of meals and must be swallowed with a small amount of liquid. Damage to the capsules should be avoided.
Therapy should be discontinued gradually over 14 days. Abruptly stopping the medication may worsen the patient's condition.
Alcohol abuse is prohibited during treatment. During treatment with Duloxetine, caution should be exercised when driving and other potentially dangerous activities.
See also:
Instructions for use of Losarel® and reviews of the drug
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Due to insufficient experience with the use of duloxetine during pregnancy, the drug should be prescribed only if the potential benefit to the mother significantly outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. Patients should be warned that if pregnancy occurs or is planned during treatment with duloxetine, they should inform their doctor.
Epidemiological evidence suggests that use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) during pregnancy, particularly later in pregnancy, may increase the risk of persistent neonatal pulmonary hypertension. Although there are no studies examining the relationship between persistent neonatal pulmonary hypertension and the use of SSRIs, a potential risk cannot be excluded given the mechanism of action of duloxetine (serotonin reuptake inhibition).
As with other serotonergic drugs, withdrawal syndrome may occur in newborns if the mother takes duloxetine late in pregnancy. Withdrawal syndrome includes the following symptoms: low blood pressure, tremor, increased neuro-reflex excitability syndrome, feeding difficulties, respiratory distress syndrome, convulsions. Most symptoms were observed during labor or in the first few days after birth.
Due to the fact that duloxetine passes into breast milk (fetal concentrations based on mg/kg body weight are approximately 0.14% of maternal concentrations), breastfeeding is not recommended during duloxetine therapy.
Possible side effects of Duloxetine and overdose
Among patients taking Duloxetine, the drug was well tolerated. Side effects appear extremely rarely or occur at the beginning of treatment and go away on their own over time. But still, if the following symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor to adjust treatment:
- constipation;
- nausea;
- xerostomia;
- dizziness;
- general weakness;
- insomnia;
- hypersomnia;
- cephalgia;
- increased heart rate;
- difficult and painful digestion;
- vomit;
- decreased appetite;
- trembling of limbs;
- decreased reaction speed;
- sweating;
- feeling of heat;
- yawn;
- sexual dysfunction;
- catarrh of the stomach and intestines;
- damage to the oral mucosa;
- increased blood pressure;
- weight gain;
- muscle tension;
- taste disturbances;
- visual impairment;
- motor restlessness;
- urinary retention;
- increased levels of alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase and creatine phosphokinase.
- increased intraocular pressure;
- inflammatory liver diseases, Gospel disease;
- anaphylactic reactions;
- water-electrolyte imbalance;
- pathological elements on the skin and mucous membranes;
- Quincke's edema, rashes on the skin and mucous membranes, urticaria;
- a sharp drop in blood pressure and fainting.
Death due to exceeding the recommended dose was observed only when taking the medication together with other drugs.
Overdose is expressed by the following symptoms:
- hypersomnia;
- painful sensation in the epigastric region, vomiting;
- involuntary muscle contractions;
- increased heart rate;
- coma.
In case of overdose, it is recommended to do a gastric lavage and take Activated carbon to reduce the absorption of the substance. In severe cases, hospitalization is recommended.
See also:
Lerivon - instructions for use, reviews and analogues
Overdose
There are known cases of overdose in clinical studies with simultaneous oral administration of up to 3000 mg of duloxetine, either alone or in combination with other drugs. However, one of these cases resulted in death. However, spontaneous (post-marketing) reports contained descriptions of fatal acute overdoses, usually involving the combination of several drugs, in which the dose of duloxetine was no more than 1000 mg. An overdose of duloxetine (isolated or combined) may be accompanied by the following symptoms: drowsiness, coma, clonic convulsions, serotonin syndrome, vomiting and tachycardia. In preclinical animal studies, the main signs of intoxication associated with overdose were central nervous system and gastrointestinal disorders and included tremors, clonic seizures, ataxia, vomiting and decreased appetite.
Treatment.
A specific antidote is not known, however, in case of development of serotonin syndrome, corrective treatment with cyproheptadine and the use of methods to normalize body temperature are possible. A sufficient supply of fresh air should be provided. It is recommended to monitor cardiac activity and monitor vital signs, along with symptomatic and supportive therapy. Gastric lavage may be indicated if little time has passed since taking the drug orally, or as part of symptomatic treatment. Activated carbon may be used to limit absorption. Duloxetine is characterized by a large volume of distribution, and therefore the effectiveness of forced diuresis, hemoperfusion, and exchange perfusion seems doubtful.
Similar means
Duloxetine is a Russian medicine that has several foreign analogues. Complete analogues of the drug, having the same composition and indications for use, are:
- Cymbalta is a drug that has an antidepressant effect. Available in capsule form with dosages of 30 and 60 mg. The medication is a complete analogue of Duloxetine and has identical properties. A package of 28 capsules of 60 mg of active ingredient costs approximately 3,400 rubles.
- Duloxent is an antidepressant, a complete analogue of Duloxetine. Available in the form of capsules containing 30 or 60 mg of active substance. The drug is a weak dopamine uptake inhibitor and does not have significant affinity for histamine, dopamine, cholinergic and adrenergic receptors. 28 capsules with a dosage of 60 mg cost about 1,750 rubles.
There are also a number of medications that have the same effect as Duloxetine, but have a different composition:
- Pyrazidol is a drug that is active against depressive conditions. It is produced in the form of tablets containing 25 or 50 mg of pirlindole. It is used to relieve alcohol withdrawal syndrome and as part of therapy for senile dementia of the Alzheimer's type. Contraindications for use are: intolerance to the components, liver dysfunction, blood diseases. The cost of 50 tablets with a dosage of 50 mg is 231 rubles.
- Azafen is a psychotropic medication whose action is aimed at eliminating depression of various origins. The active component of the drug is pipofezin. One tablet contains 25 mg of this substance. Azafen is not prescribed for dysfunction of the cardiovascular system, kidneys or liver, impaired glucose absorption, pregnancy and breastfeeding, or intolerance to pipofezin. The price of the drug starts at 610 rubles.
- Venlafaxine is a drug used to combat anxiety and depressive disorders, painful headaches, and pain associated with diabetes. The main component of the drug is the substance venlafaxine. Dosage form: tablets of 37.5 and 75 mg. Contraindicated for patients suffering from kidney and liver disorders, pregnant women, breastfeeding women, and children under 18 years of age. The average cost of the drug is 453 rubles.
- Valdoxan is an antidepressant whose active ingredient is agomelatine. Dosage form: 25 mg tablets. The drug is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to agomelatine and lactose, with liver dysfunction, patients under 18 years of age, and alcohol abusers. The drug costs about 100 rubles.
You should not replace Duloxetine with analogues yourself, as this can cause significant harm to health. If there is a need to change the medication, it is important to consult a specialist.
See also:
Reviews from cardiologists about the drug Sidnopharm and instructions for its use
Side effects
In some cases, Duloxetine may lead to suicidal thoughts. Therefore, a person taking the drug needs to monitor their mental state and report any changes to their doctor. The patient's family and friends should also pay close attention to his condition. Antidepressants lead to one or another side effects in the vast majority of cases, but this largely depends on the patient’s body and his individual reaction to the drug. Some people taking antidepressants experience no side effects at all, while others experience mild side effects.
The list of mild side effects includes:
- diarrhea,
- vomit,
- weight loss,
- weakness,
- sleep disorders,
- stomach ache,
- nausea,
- loss of appetite
- increased sweating,
- headache,
- dry mouth,
- drowsiness and so on.
More serious side effects are:
- mood swings,
- loss of concentration,
- confusion,
- heat,
- fainting,
- loss of libido,
- irritability,
- anxiety,
- panic attacks,
- impulsiveness,
- aggression,
- nervous excitement,
- muscle stiffness,
- lethargy and difficulty urinating.
If any side effects occur, contact your doctor immediately. Also tell your doctor about any unusual effects that are not listed in the list of major side effects.
Additional Information
- Brand name: Cymbalta
- Dosage: 30 mg
- Generic name: Duloxetine
- Manufacturer: Sunrise Remedies, India
- Pharmaceutical form: Tablets
Reviews about the use of Duloxetine
Doctors and patients have different opinions about the effectiveness of the drug. In their comments, they highlight both positive and negative characteristics of the drug.
Doctors' opinion
Doctors consider this medicine to be an effective and cheaper domestic substitute for foreign antidepressants. Mostly they leave positive reviews about the drug:
- Savenko L.M., psychiatrist: “Patients taking this drug literally come to life before our eyes. They become more mobile and self-confident. Compared to foreign analogues, Duloxetine is inexpensive, so I often prescribe it to my patients, especially older ones.”
- Rogachevsky R. Yu., psychiatrist: “In terms of effectiveness, the medication is inferior to other antidepressants, but it also has fewer side effects. The drug perfectly helps with depression, but the inversion of affect and the transition to a hypomanic state is not achieved by taking Duloxetine.”
Thus, doctors note the effectiveness of the drug in the fight against depression. But for more serious mental disorders, it may be necessary to use a different remedy.
Contraindications for use
Uncompensated angle-closure glaucoma, simultaneous use with MAO inhibitors, increased sensitivity to duloxetine. Before using the medicine, we recommend that you consult your doctor.
A description of the active substances of the drug is presented. The scientific information provided is general and cannot be used to make a decision about the possibility of using a particular drug. There are contraindications, consult your doctor.