What is vagotonia
In short, this disease is a dysfunction of the vagus nerve.
It is located in the neck and transmits signals from the brain to the organs of the human body, as well as in the opposite direction. Most people have heard that humans have a central and peripheral nervous system. Along with this, the body has a vegetative system. Its function is to control the functioning of internal organs. This is where the work of the heart, digestive system, breathing and all other human systems is controlled. In fact, there is not one, but two: the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Actually, parasympathicotonia is the predominance of the vital activity of the parasympathetic section over the sympathetic one.
Vagotonia is one of the types of vegetative-vascular dystonia. In addition to this type of disorder, the opposite may also occur, which is expressed in the predominance of the vital activity of the sympathetic part of the nervous system.
Cardiopsychoneurosis
Neurocirculatory dystonia (NCD)
– a complex of disorders of the cardiovascular system of a functional nature, developing as a result of disorders of neuroendocrine regulation.
Neurocirculatory dystonia has a polyetiological genesis, is accompanied by many different, mainly cardiovascular, manifestations that arise or worsen under the influence of stress, and is characterized by a benign course and a satisfactory prognosis.
Neurocirculatory dystonia in the literature is sometimes referred to as “heart neurosis”, “neurocirculatory asthenia”, “excitable heart”.
It is customary to distinguish between two types of functional disorders of the cardiovascular system: vegetative-vascular and neurocirculatory dystonia.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia combines various manifestations of autonomic dysfunction that accompany organic lesions of the nervous, endocrine and other systems.
Neurocirculatory dystonia is an independent nosological form with its own etiology, pathogenesis, symptoms and prognosis and differs in a number of features from autonomic dysfunction.
Distinctive features of neurocirculatory dystonia are the predominance of cardiovascular symptoms among clinical manifestations, the primary functional nature of disorders of autonomic regulation and the lack of connection with organic pathology, including neurosis.
Neurologists, cardiologists, and general practitioners quite often have to deal with neurocirculatory dystonia. Among cardiological and therapeutic patients, NCD occurs in 30-50% of individuals.
Neurocirculatory dysfunction can develop at different ages, but is more common in young people, mainly women, who suffer from it 2-3 times more often than men.
The disease rarely develops in persons younger than 15 and older than 40-45 years.
Cardiopsychoneurosis
Various factors can lead to the development of neurocirculatory disorders, but they do not include organic damage to the endocrine and nervous systems.
In adolescence and youth, neurocirculatory dystonia is usually caused by imperfections in the neuroendocrine mechanism for regulating autonomic processes.
The development of NCD in the prepubertal and pubertal periods is facilitated by increased mental and physical stress and the social environment.
In people of any age, neurocirculatory dystonia can develop against the background of acute and chronic infections, lack of sleep, overwork, mental trauma, exposure to physical and chemical factors (insolation, hot climate, vibration), poor diet, physical activity (overload or physical inactivity), intoxication, including alcohol and tobacco. Periods of hormonal changes in the body (puberty, abortion, pregnancy, menopause, ovarian dysfunction) play a role in the development of neurocirculatory dystonia.
A number of patients have a hereditary constitutional predisposition to the development of neurocirculatory dystonia.
The impact of these factors causes dysfunction of the neurohumoral control of the cardiovascular system, where the leading pathogenetic link is damage to the hypothalamic-pituitary structures that coordinate these processes.
Violation of neurohumoral control is manifested by a disorder of the functions of systems that ensure homeostasis processes in the body: cholinergic, sympathetic-adrenal, kallikreinin, histamine-serotonin, etc.
This, in turn, triggers mechanisms leading to disruption and multiple changes in carbohydrate, water-electrolyte metabolism, acid-base status, mediator and hormonal systems.
In myocardial tissues, biologically active substances (histamine, serotonin, kinins, etc.) are activated, causing metabolic disorders and the development of dystrophy.
On the part of the circulatory system, fluctuations in vascular tone, spasms of peripheral vessels, and slowing of microcirculation are observed, which leads to the development of tissue hypoxia.
Once formed, the pathogenetic mechanisms become autonomous, and neurocirculatory dystonia becomes an independent disease. Any irritants (changes in weather conditions, stress, etc.) cause a pathological reaction, causing the manifestation of one or another type of neurocirculatory dystonia.
According to etiological forms, essential (constitutional-hereditary), psychogenic (neurotic), infectious-toxic, dishormonal, mixed neurocirculatory dystonia, as well as NCD of physical overexertion are distinguished.
Depending on the leading clinical syndrome according to the classification of V.P. Nikitin (1962) and N.N.
Savitsky (1964) distinguishes four types of neurocirculatory dystonia: cardiac (with a predominant disorder of cardiac activity), hypotensive (with a predominant decrease in blood pressure), hypertensive (with a predominant increase in blood pressure), mixed (combines disorders of blood pressure and cardiac activity). Based on the severity of symptoms, mild, moderate and severe degrees of neurocirculatory dystonia are distinguished; according to the variant of the course - phases of exacerbation and remission.
A common manifestation for all types of neurocirculatory dystonia is a neurosis-like state, characterized by fatigue, weakness, sleep disturbance, irritability, decreased memory, mood and volitional qualities, deterioration in concentration, which is accompanied by functional circulatory disorders of a predominant nature.
Cardiac type
The course of the cardiac type of neurocirculatory dystonia is manifested by cardialgia, palpitations, interruptions in heart function, and sometimes shortness of breath during physical activity; no significant changes in blood pressure are observed.
Objectively, tachycardia, respiratory arrhythmia, paroxysms of tachycardia, supraventricular extrasystoles, changes in cardiac output inadequate to the load can be determined, and on the ECG - a change in the voltage of the T wave (high or reduced).
Hypotensive type
Neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypotensive type is characterized by symptoms of chronic vascular insufficiency: a decrease in systolic blood pressure less than 100 mm Hg. Art.
, chilliness of the feet and hands, a tendency to orthostatic collapse and fainting. Also, for patients with the hypotensive type of NCD, complaints of fatigue, muscle weakness, and headaches are typical.
Such patients, as a rule, have an asthenic physique, pale skin, and cold and damp palms.
Hypertensive type
The hypertensive type of neurocirculatory dystonia is characterized by a transient increase in blood pressure to 130-140/85-90 mmHg. Art.
, which in half of the cases is not accompanied by a subjective change in the patients’ well-being and is detected during medical examinations. Complaints of palpitations, headaches, and fatigue are less common.
The hypertensive type of NCD in its characteristics coincides with borderline arterial hypertension.
NDC degrees
A mild degree of neurocirculatory dystonia is characterized by moderately severe symptoms that arise only in connection with psycho-emotional overload. The patients' ability to work is preserved; a slight decrease in physical endurance may be observed; drug therapy is not indicated.
With neurocirculatory dystonia of moderate severity, there is a multiplicity of symptoms and a decrease in physical performance by more than 50%.
Decreased or temporary loss of ability to work requires medication therapy.
With severe manifestations of neurocirculatory dystonia, persistent and multiple clinical symptoms are observed, a sharp decrease or loss of ability to work, requiring hospital treatment of patients.
The low specificity of the symptoms of neurocirculatory dystonia makes diagnosis difficult and requires careful verification of the diagnosis.
Confirming diagnostic criteria for neurocirculatory dystonia based on patient complaints can be symptoms that can be observed for 1-2 months: cardialgia, palpitations, feeling of lack of air, pulsation in the precordial area or in the area of the neck vessels, weakness, increased fatigue, neurotic manifestations (irritability, anxiety , sleep disturbance), dizziness, cold and wet extremities. Neurocirculatory dystonia is characterized by a multiplicity of complaints that have a clear connection with stressful situations or periods of hormonal changes, the course of the disease with periods of remissions and exacerbations, but without a tendency to progress.
Reliable physical criteria for the presence of NCD include an unstable heart rhythm with a tendency to tachycardia that appears spontaneously or inappropriately to the situation, lability of blood pressure, the presence of respiratory arrhythmias (tachypnea, dyspnea), hyperalgesia in the cardiac region. On the ECG, patients may register tachycardia, arrhythmia, migration of the pacemaker (21.3%), extrasystole (8.8%), paroxysmal tachycardia and atrial fibrillation (3%), negative T waves in two or more leads (39.4 %).
Diagnostic ECG tests with stress are informative diagnostic methods for neurocirculatory dystonia.
- A physiological test with hyperventilation involves performing forced inhalations and exhalations for 30-40 minutes, followed by recording an ECG and comparing it with the original one. A positive test indicating NCD is an increase in heart rate by 50-100% and the appearance of negative T waves on the ECG or an increase in their amplitude.
- An orthostatic test involves recording an ECG in a lying position, and then after standing for 10-15 minutes. Positive results of the test are the same changes as with the test with hyperventilation, observed with NCD in 52% of patients.
- Drug tests (with β-blockers, potassium) are aimed at distinguishing between neurocirculatory dystonia and organic heart diseases. ECG registration is carried out 40-60 minutes after taking 60-80 mg of β-blockers (obsidan, inderal, anaprilin) or 6 g of potassium chloride. In case of organic cardiopathologies (myocarditis, ischemic heart disease, myocardial hypertrophy), a positive T wave is recorded; in case of NCD, a negative T wave is recorded.
When performing bicycle ergometry, a decrease in exercise tolerance typical of neurocirculatory dystonia is determined, i.e.
a patient with neurocirculatory dystonia is able to perform less workload than a healthy person of the same age and gender.
Laboratory data indicate an increase in the activity of the sympathetic-adrenal system: in response to the load in the blood, an inadequate increase in the level of norepinephrine, adrenaline, metabolites, and lactic acid is observed.
In the treatment of neurocirculatory dystonia, an extremely important place is occupied by non-drug measures designed to increase the body's adaptive capabilities to changing conditions. For NCD, hardening procedures, sports activities (athletics, swimming), rational psychotherapy, and normalization of work and rest regimes are indicated.
Balneotherapy, physiotherapy (therapeutic showers and baths, electrosleep, reflexology, electrophoresis with bromine, magnesium, novocaine), exercise therapy, and spa treatment have a positive effect on training the system of regulation of autonomic functions. For sleep disturbances and irritability, it is possible to prescribe sedatives: motherwort, valerian, tranquilizers (oxazepam, etc.).
For the treatment of neurocirculatory dystonia of the cardiac and hypertensive type, the use of β-blockers (atenolol, propranolol, oxprenolol), which eliminate tachycardia, hypertension, cardialgia, as well as drugs that improve the metabolism of the heart muscle (inosine, potassium preparations, B vitamins), is indicated. For neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypotensive type with the presence of asthenia and orthostatic disorders, tincture of ginseng (schizandra, aralia) and caffeine are prescribed.
The course of any type of neurocirculatory dystonia does not cause the development of cardiomegaly, heart failure or life-threatening rhythm and conduction disturbances.
In adolescence, with timely treatment or self-healing, complete recovery occurs. With age, the prognosis for complete recovery of neurocirculatory dystonia decreases.
A decrease or temporary loss of ability to work can be observed during periods of exacerbation.
Patients with the hypertensive type of neurocirculatory dystonia are at risk for hypertension; with any type of NCD due to lipid metabolism disorders, the likelihood of developing atherosclerosis and ischemic heart disease cannot be excluded.
Issues of preventing neurocirculatory dystonia go beyond purely medical measures. Prevention includes proper physical, mental and hygienic education of adolescents, increasing their self-esteem and social adaptation. The role of promoting a healthy lifestyle, playing sports, avoiding smoking and drinking alcohol is great.
Medical prevention of neurocirculatory dystonia includes the fight against focal infections, stress factors, and regulation of hormonal levels in women during menopause.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_cardiology/cardiopsychoneurosis
Causes of the disease
It is believed that vagotonic disorders constitute a whole complex of causes, of which it is difficult to identify the main ones. However, there are factors that increase the likelihood of developing the disease. First of all, we are talking about age.
The disease primarily affects children and adolescents.
Moreover, girls are at higher risk compared to boys. This is due to the fact that during the growth process the body is still immature, as well as hormonal changes and rapid growth. Having fallen ill at this age, by the age of forty a person receives a clearly defined impairment of health.
It is believed that this disease is very common throughout the planet. Scientists suggest that signs of vagotonia are present in more than half of the world's population.
Hereditary predisposition to the disease also plays an important role.
Along with the above, there are also specific reasons that can lead to vagotonia.
- Severe head injuries can trigger the disease. Concussion is also worth mentioning here.
- Some birth injuries (in particular, birth hypoxia) are dangerous in this regard.
- If intracranial pressure is too high, this may become a risk factor.
- Various stressful situations. Here we are talking not only about emotional, but also about any other overload (physical overload, hypothermia, and the like).
- If the respiratory or digestive system is not functioning well.
- Lack of physical activity (hypodynamia).
- Infectious diseases are very dangerous, especially long-term foci of infection.
- Various metabolic disorders. An example is diabetes.
- Moving between different climate zones.
- Age. We talked above about the increased susceptibility of children to this disease. To this we can add the time when menopausal changes in the body occur.
Of course, these reasons do not lead to the disease with one hundred percent probability, but they significantly increase its likelihood.
How to treat vagotonia: causes and prevention of vegetative-vascular dystonia
Vagotonia is one of the manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia, more often found in children and adolescents. In modern medicine, this condition is usually considered as a symptom of a nervous system disorder, but in the absence of timely diagnosis and adequate treatment, such a sign of the disease can provoke dangerous consequences for health.
A diagnosis of vagotonia is made to a child if he often complains of neurotic problems. Such babies often suffer from increased fearfulness, apathy, and constant drowsiness.
Causes of the pathological condition
Despite the rapid development of modern diagnostic science, the emergence of complex research instruments has not yet been able to understand why vagotonia occurs in a child. There are many different theories about the occurrence of this pathology, but they all do not have a clear evidence base.
Factors that increase the risk of vegetative-vascular dystonia:
- head injuries (concussion);
- stress, strong emotional experiences;
- genetic predisposition;
- concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, colitis, Crohn's disease);
- severe mental overload.
In addition, there is a dependence of the probability of the appearance of vagotonia on a change of place of residence (moving to another climatic zone) and restructuring of the body during puberty.
Symptoms of the disease
It is quite difficult to determine such a disease in a child. The symptoms of the pathological condition are similar to other diseases and often force doctors to prescribe the wrong treatment.
Common signs of vagotonia:
- tendency to frequent fainting;
- persistent problems with bowel movements (constipation, diarrhea);
- increased sweating;
- intolerance to cold and heat;
- rapid weight gain (obesity);
- pathological change in heart rhythm (bradycardia);
- frequent allergic reactions.
It is also necessary to mention that patients with vagotonia become slow, indecisive and phlegmatic. Often the course of the disease is accompanied by severe depression.
Treatment of the disease
The choice of therapeutic actions depends entirely on the correctness of the diagnosis and the severity of the pathology.
A mild form requires lifestyle changes (increasing mobility, playing sports, walking in the fresh air), proper balanced nutrition (food must contain all the necessary vitamins and minerals) and periodic consultations with a psychologist.
In case of severe vagotonia, pharmacotherapy should be used. The drugs are prescribed by the doctor after a complete examination and identification of all the characteristics of the patient’s body. Most often, antidepressants, vitamin complexes, and medications with a sedative effect are prescribed.
Traditional medicine shows good results. Herbal teas and herbal decoctions can calm the nervous system and reduce the negative impact of pathology.
Prevention
Manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia should be taken extremely seriously. Complications of this disease include mental disorders, syncope, ischemic strokes and cholelithiasis.
Preventing vagotonia is not difficult. To do this, you need to strictly monitor the state of your baby’s nervous system. At the first signs of pathology, you should reduce mental stress, change the diet in favor of healthy natural products, and engage in the physical development of the child.
Take care of yourself, because being healthy is always great!
Similar articles
- Signs of Crohn's disease: how to treat a rare disease
- How to treat arrhythmia in a teenager
- Clinical recommendations for nonspecific...
- Pancreatitis: how to protect the pancreas
Symptoms of vagotonia
There is a set of basic symptoms that indicate a high probability of illness and should make the patient think about his health. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, but you need to know the main groups of characteristic symptoms.
- Cardiac signs. We are talking about symptoms that are associated with the activity of the cardiovascular system. This is low blood pressure, slow heart rate, and a feeling of tightness in the chest.
- Respiratory group. Shortness of breath, which resembles that in patients with asthma, respiratory arrhythmia, dry and painful cough, lack of air.
- Symptoms related to the digestive system. These include difficulty swallowing and a feeling of a lump in the throat, severe loss of appetite, nausea, heartburn and diarrhea.
- Disturbances of brain activity. In this case, the patient may feel heaviness in the head or even pain. Sometimes there may be daytime sleepiness and severe weakness for no particular reason. Apathy, depression and lethargy are possible. Poor concentration is common.
- Dizziness and fainting are also possible, which can be attributed to vestibular disorders.
The signs of the disease do not end there. These include poor tolerance to temperature changes, temperature fluctuations predominantly downward, increased weight and a tendency to various types of allergies.
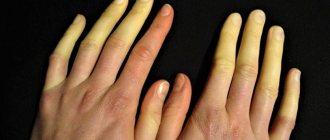
In this case, the skin may become pale, the hands and feet become cold, and there is profuse sweating.
The course of the disease itself can occur in different ways.
- These can be sudden attacks that occur from time to time.
- Or a chronic form with mild symptoms.
- Or the disease develops in a latent form.
The disease is also divided into systemic or local. In the first case, the entire body is affected, in the second, the disease affects only certain organs.
Vagotonia: treatment of the disease
It is quite difficult to treat this disease, and it must be dealt with by a specialist. But you can reduce the manifestations of the disease using fairly simple methods.
- With a mild degree of damage, you should adhere to a healthy lifestyle: do not smoke, do not drink alcohol, sleep at least 8 hours, do morning exercises and exercises, and preferably do this in the fresh air. You should not engage in serious sports, such as weightlifting or football, but a general strengthening set of exercises will benefit the patient.
- Proper nutrition is very important during treatment. To do this, you should exclude fatty, salty, and sweet foods from your diet. But fresh vegetables, fruits, and cereals (especially those with a high content of magnesium and potassium) must be consumed.
- Water procedures will help cope with vagotonia. Activities such as swimming, sauna, and medicinal baths are perfect for this. Salt, pine, radon baths, and rubbing with cold water are recommended for children.
- With this diagnosis, a specialist may prescribe a general massage.
Diagnosis of vagotonia
Since the disease affects the parasymptotic part of the autonomic nervous system, there are many different symptoms. Unfortunately, in practice the diagnosis is made in a negative way: with these symptoms, alternative diseases are gradually excluded.
Children usually exhibit the following symptoms:
- Pale or bluish skin.
- Increased sweating, possible edema.
- Having allergies.
- Increased sensitivity to weather changes.
Diagnostics
At the patient’s first visit, the doctor listens to his complaints and performs an initial examination to determine obvious disorders. After this, the doctor examines the history, not only of the patient, but also of the family. In most cases, autonomic dysfunctions are inherited.
After this, a differential diagnosis is made, which either excludes structural damage to organs and structures of the body, or confirms them.
The doctor may send a patient who is suffering from vegetative dystonia to the following types of examinations:
- Ultrasound examinations (ultrasound);
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- General blood and urine analysis;
- Electroencephalography (EEG);
- Electrocardiography (ECG study).
- 24-hour blood pressure tracking;
- Fluorography.
The choice of method for examining the body is made by the attending physician, depending on the patient’s complaints and obvious signs.
Treatment of disorders
A combination of medications and other methods is usually used. If the disease has not gone too far, the emphasis is on using a healthy lifestyle. At the same time, they monitor the presence of the required amount of physical activity, establish a healthy diet, monitor compliance with a rational daily routine, and avoid any kind of stressful circumstances.
If the symptoms are acute, then drug treatment measures are taken under the supervision of a doctor. In this case, the main efforts are aimed at combating the most severe symptoms. If there are long-term foci of infection in the body, they try to cure them.
Treatment methods
First of all, you need to normalize your daily routine, nutrition, and move as much as possible. Experts recommend taking children to gymnastics and swimming. Cold dousing and radon baths help very well - the procedures increase vascular tone.
With low blood pressure, adults are recommended to drink strong coffee, tea, and be sure to include various cereals, compote of rose hips, raisins, viburnum, and sea buckthorn in their diet. If it does not get better, antidepressants, sedatives, and antipsychotics are prescribed.
So, so that vagotonia does not bother you, analyze your lifestyle. Be healthy!
Diagnostics
Doctors themselves call VSD of the vagotonic type a diagnosis of exclusion. That is, a patient who comes to the clinic is fully examined for various diseases. However, none of the pathologies are clearly identified. In this case, doctors diagnose “VSD of the vagotonic type.” During diagnosis, the patient undergoes a number of studies depending on the primary complaints:
- Cardiac signs. The heart is examined using ECG (electrocardiography) and ultrasound (echocardiography).
- Gastrointestinal symptoms. Ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Brain disorders. CT or MRI of the brain.
- Respiratory signs. X-ray of the chest organs.
In addition, the patient undergoes a general and biochemical blood test, a general urine test and stool test for coprogram.
What is characteristic of sympathotonia?
- Dryness and pallor of the skin.
- Reduced sweating and salivation.
- Feeling hot. Poor tolerance to heat from the sun, noise, bright light, coffee.
- Tendency to increase blood pressure.
- Tendency to increase heart rate and breathing.
- Increased sensitivity to pain.
- Psychogenic dizziness, headache.
- Restlessness, anxiety, fear, irritability, absent-mindedness, short temper, inattentiveness.
- Great efficiency, as well as initiative and endurance.
- Poor sleep, insomnia
- Dilated pupils and sparkling eyes.
- Polyuria.
- Tendency to constipation.
- Increased appetite combined with thinness.
- Cold extremities.
- White dermographism
- Feel better in the evening.
- Atony of the stomach and intestines, noise of splashing in it, flatulence.
- Reduced acidity of gastric juice.
- Reduced tolerance for carbohydrates.