How does moderate stun differ from deep stun?
Moderate stunning is accompanied by a slowdown in mental activity and a decrease in the ability to actively pay attention. You can communicate with the patient, but his answers to questions are delayed, sometimes the question needs to be repeated or the victim needs to be patted. The patient quickly gets tired, his facial expressions are poor, the patient reacts to pain, and may lose orientation in the area.
With deep stupor, the patient experiences drowsiness, he rarely makes any movements and his mental activity is difficult. Verbal contact with the victim is severely difficult, answers can only be obtained after persistent requests, they are monosyllabic in nature - “yes”, “no”, while the victim is able to provide his information: full name, age. When communicating with him, you need to repeat the same word over and over again. In this case, the victim is able to follow basic commands: open his eyes, show his tongue, etc. The defensive reaction to pain is preserved, but orientation in place and time is absent.
Prevention
Prevention of panic attacks is to adjust your lifestyle and bring it as close to healthy as possible :
- At least eight hours of sleep every day.
- Sports activities.
- Proper nutrition.
- Maintaining a daily routine.
- Quitting smoking and alcoholic beverages.
- Breaks during working hours.
Unfortunately, not everyone is ready to follow a routine, exercise and eat only healthy foods.
Many experts recommend adhering to a certain list of rules:
- Take a daily hot shower for at least ten minutes a day to relax your muscles.
- Sleep should be exclusively on an orthopedic mattress and pillow so that the load on the vertebrae is distributed evenly.
- Swimming and aerobics improve blood circulation and have minimal preventive stress on all parts of the spine.
- If a person leads a sedentary lifestyle (working at a computer or with documents), then it is necessary to take breaks from work every one and a half to two hours.
In this case, it is advisable to exclude all sports associated with heavy lifting and heavy loads on the spine. Returning to heavy sports is possible only after consultation with your doctor, as well as completion of the full course of treatment.
It should be remembered that exercises associated with jumping put an additional negative load on all parts of the spine, which is why after 40 years it is advisable to abandon this type of sport.
If you follow these recommendations, you can get rid of panic attacks, lightheadedness and other symptoms of osteochondrosis.
The completed course of treatment will never give an absolute guarantee that panic attacks will not return in a more intensified manifestation in the future, so you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations and adhere to a healthy lifestyle to avoid relapses .
How is stun different from stupor?
Both disorders are characterized by severe lethargy, immobility, and difficulty in contact. However, stupor, as a rule, develops against the background of a somatic illness, trauma, infection, etc., and stupor occurs during the course of mental illness, primarily schizophrenia. When stupor occurs, the patient experiences delusions and hallucinations, while stupor is characterized by complete indifference and absence of internal experiences.
Below we will look at the most popular stages of blindness of consciousness. If you detect the slightest symptoms, you need to consult a doctor.
Mostly in patients with severe closed trauma to the skull and brain, there is a severe degree of stunned consciousness, which occurs either immediately or as a transitional stage from stupor or coma during the first day.
A deep loss of consciousness, a delayed transition to clear consciousness with changes in various degrees of stunning and the prolonged existence of its mild forms, as well as the occurrence of states of periodic excitation against this background usually indicate the severity of the injury.
How to remove confusion in your thoughts
There are several methods to try to clear your head of delirium and confused thoughts:
And do not neglect the help of a psychotherapist. Some neuroses and phobias cannot be treated at home and cannot be relieved by physical activity. But sometimes 2-3 conversations can restore a sound mind and joy in everyday life.
» alt=”What to do when the thoughts in your head are confused?”>
Neuroses are the most common diseases that have become a global problem. Obsessive-compulsive disorder is a disorder that few people attach importance to. However, the disease must be treated. Is this possible, and what measures should be taken?
Stupidity of consciousness.
The state of mild unconsciousness lasts, as a rule, 4-5 days. After this, patients regain orientation in time and space. They not only answer the questions posed, but also begin to take an interest in their condition. The facial expression ceases to be mask-like, but some hypomimicness remains. The act of swallowing is restored completely, appetite improves, sleep lasts no more than 9-10 hours a day. Such patients recover from the state of stupor already on the second day of hospital stay, consider themselves healthy and insist on discharge.
Medium stun
At the middle stage of deafening of consciousness, patients are disoriented in time and space, behave apathetically, they have a noticeable mask-like face, swallowing is impaired, and sleep lasts from 12 to 24 hours a day. At the same time, they are able to follow simple instructions and answer basic questions in monosyllables. Such patients are characterized by a weakened reaction to external stimuli (sound, light). Restoration of effective motor functions occurs gradually. In an uncomplicated course, after 4-5 days there is a noticeable improvement, and the average degree of stunning becomes mild.
Severe degree of stunning consciousness
Severe degree of stunning consciousness lasts 5-8 days, and sometimes longer. In the first 4-5 days after the injury, the clinical picture does not tend to improve and the condition of the patients generally remains stable. Such patients are poorly accessible for contact, almost do not react to external stimuli, do not answer questions asked of them, but after persistent demands, for example: “raise your hand!”, “open your mouth!” they are able to perform basic actions. The act of swallowing is preserved, but it is slow, sleep lasts at least 18-20 hours a day. Patients are predominantly inactive, apathetic, with poor facial expressions, but in many cases there is psychomotor agitation. This is manifested by the desire to constantly change position in bed, performing numerous unnecessary and meaningless movements, active resistance to attempts to put them into bed, while patients constantly mutter incomprehensible words and phrases. Comatose and stuporous state.
With stupor, consciousness is completely turned off, but the patient is able to swallow with difficulty, reacts to painful stimuli, and at the same time does not respond to words. When the angle of the lower jaw moves forward, an expression of dissatisfaction appears on the patient’s face.
Coma state
In a state of coma, the victim lies motionless, the complexion is pale or cyanotic, muscle hypotonia is observed, and there is no reaction to any irritants. Severe vegetative disorders are expressed: the pulse is weakened and slow, the pupils are dilated and do not respond to light, breathing is shallow. In some cases of coma, breathing becomes frequent (35 or more beats per minute), bubbling, and irregular. The disappearance of the swallowing reflex, even with a satisfactory pulse, is a symptom of a poor prognosis and requires the urgent use of active and consistent measures, such as spinal puncture, decompressive trepanation and others.
Patients cannot remain in a coma for more than a day: either they die, or this state turns into severe stunned consciousness, lasting 5-6 or more days. In 5% of cases, patients in a coma with severe injuries incompatible with life die.
I’ll torment you a little more with academic posts. More precisely, by fasting. This is the last of the educational ones for the outgoing year, the rest will be more fun :) We have already discussed the symptoms of impaired consciousness. Now - about syndromes. It is possible, and even most likely, that different occult schools would offer their own versions of their classification, but who are we to fly off the rails of dialectical materialism?
So, all syndromes of impaired consciousness can be divided into quantitative
(they are also non-psychotic) - these are
switching off
consciousness: it was there - it’s gone, or it’s noticeably decreased;
and qualitative
(or psychotic) ones are
obscurations
: it was clear and unclouded, and then something like that was mixed in that, mother, don’t worry!
In addition, both quantitative and qualitative syndromes can develop or suddenly and immediately reach their peak, and then they will be paroxysmal
(from the Greek παροξυσμός, which means irritation, excitement) disturbances, either gradually and consistently, and then they can be classified as
non-paroxysmal
. As a result, there will be four groups of syndromes:
non-paroxysmal blackouts
: stunning, stupor, coma;
non-paroxysmal clouding of consciousness
: delirium, oneiroid, amentia;
paroxysmal blackouts
: major and minor convulsive seizures (they are now studied by neurologists, not psychiatrists);
paroxysmal clouding of consciousness
: twilight cloudings of consciousness, special states of consciousness and aura of consciousness.
Non-paroxysmal loss of consciousness.
Stun.
It is the easiest and relatively quickly reversible, compared to stupor and coma, but it also does not bode well for the psyche, and it is better to study it in theory than in practice. Its three degrees - mild, moderate and deep - are distinguished conventionally, since, unlike computer characters, a real patient will not be so kind as to highlight a colored strip of his current condition with its decoding above his head. By yourself, all by yourself. So.
Mild degree of stunning, also known as nullification
(from the Latin
obnubilatio
- to cover with clouds, to obscure).
The patient can be confused with a person who took on the breast - not to such an extent that it was very stormy, but quite enough to make the wife upset. Disorientation is mainly about time; a person is at least oriented in space and his own personality. Moreover, if he tells you the month and year correctly, then there may be confusion with the date and approximate time. In addition, it is unlikely that the patient will be able to correctly remember what and in what order he did today and when the trouble happened to him. After talking a little, you may find that he has already forgotten what you just talked about - memory does not record current events, they simply are not retained in it. It is not possible to attract the attention of a stunned person right away; you have to make some efforts to get him to listen and respond. All movements are slow, answers follow after a pause, absent-mindedness would please any novice pickpocket. Eloquence is hardly to be expected - for it, like for any subtle action, the coordinated work of the entire psyche is needed; there is no time for aerobatics when the plane is shot down. Indifference predominates in emotions - after all, they also require a lot of effort and attention to detail. The state itself can flicker, brightening slightly from time to time, giving so-called lucid
windows (from the Latin
lux
, or light).
Medium stun. Disorientation concerns not only time, but also space. It is no longer useful to ask the patient in it where he is, what date it is and what time it is. Says last name, first name, patronymic - good. Year of birth - excellent. The address... it's unlikely. There is a complete lack of interest in the surrounding environment and people in this state - it doesn’t matter whether special forces are chasing terrorists around or naked beauties are dancing like a kan. Even a special forces pilot will not surprise you. Even in an embrace with terrorists. There is an expression of confusion and bewilderment on the face. It is extremely difficult to attract attention; to do this you need to either shout in your ear or shake something large-caliber in front of your nose. As soon as you leave such a patient alone, he lies down and seems to be dozing, indifferent to everything, often with his eyes open.
Deep degree of stunning, also known as somnolence
(from Latin
somnus
, or sleep). With her, the disorientation is complete - in time, space, one’s own personality (that is, he won’t even say what his name is). The patient is unable to understand what is happening around him. What they are trying to tell him, explain to him, shout in his ear or show him with gestures - too. You can attract a faint semblance of attention only by hurting him - physically, of course: by slapping him on the cheeks, giving him injections or pinching him well - not out of personal antipathy, but in order to understand how neglected everything is. Even in this case, the reaction will be sluggish - well, he will open his eyes, well, he will look at you thoughtlessly - and that’s all. Most of the time the patient is motionless, lies down and does not particularly remind himself of himself.
As it should be when turning off consciousness, after leaving such a state, the memory will erase part of the memories for the painful period itself ( congrade amnesia
), if the stun was light, or will not leave them at all (meaning, for the period of the stun itself) - if the stun was medium or deep.
If the condition improves, the stupor goes away (regresses), if it worsens, it deepens (progresses) and turns into stupor.
Sopor
, or
status soporosus
(from the Latin
sopor
- numbness, lethargy). Almost one step away from a coma (sometimes called precoma). Disorientation during stupor is complete, that is, asking what time, day, month, year, what kind of hole it is and trying to get acquainted with the same success can be done by approaching the monument. Only the reaction of others will be slightly different in the latter case. The patient will react even to an injection or a pinch, but sluggishly and unfocused - he will twitch, shudder, but will not look for the offender. Reflexes from the mucous membranes (sneezing in response to an attempt to tickle the nose with a feather - and don’t look so disapprovingly, this is a diagnostic procedure, not mockery!) and skin are absent. Tendon reflexes (hammer-knee-toe kick) are weakened. Protective reflexes are preserved: corneal, when the eyelids close when trying to touch the cornea with cotton wool, coughing, vomiting, swallowing. The reaction of the pupils to light is sluggish. The patient lies motionless and can only occasionally rush around the bed.
If the condition improves, then first consciousness passes through stupor to normal, while memory for the period of stupor is completely lost. If the condition deepens, coma occurs.
Coma
.
The name comes from the Greek κῶμα
, or deep sleep. The psyche in a coma completely relinquishes all powers. Most reflexes are suppressed, including protective ones. Only those unconditional ones are preserved that allow life to simmer in the body - those that support breathing, heartbeat, thermoregulation, and vascular tone. Deepening of the coma leads to death. If the situation develops favorably, a gradual exit from the coma occurs, in the reverse order: coma - stupor - three degrees of stupor - return to clear consciousness. Memory for events that occurred in a coma, as well as for the period of recovery, up to a state of mild stupor, is lost.
Impaired consciousness is expressed in quantitative and qualitative changes.
Towards quantitative syndromes
disturbances (depression) of consciousness include: stupor, stupor, coma.
Towards qualitative syndromes
disturbances (stupidity) of consciousness include: delirious syndrome, oneiric state, amentia, twilight state of consciousness.
Quantitative disturbances of consciousness (depression of consciousness) develop due to morphological or pronounced metabolic changes in the brain, and are accompanied by a decrease in the level of wakefulness, motor activity, intellectual functions, up to complete depression and switching off of consciousness.
Causes
Panic attacks manifest themselves completely differently in different people: for some it is mild, groundless anxiety, and for others it is a severe and prolonged panic attack, accompanied by hysteria.
Often this condition lasts no longer than five to seven minutes, but in severe and advanced cases it can reach an hour.
The frequency of such attacks also varies depending on the severity - from once every few months to experiencing such attacks every week.
Unfortunately, the frequency and duration of this condition directly depend not only on osteochondrosis and depression in principle, but also on the physical condition of the person.
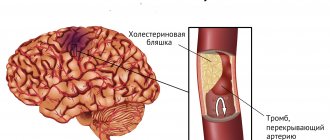
Osteochondrosis and panic attacks have a relationship that can be understood by delving into the pathology of this problem.
With osteochondrosis, destruction of the intervertebral discs occurs, as well as the appearance of bone growths that have sharp edges.
The process is pathological and leads to compression of the blood vessels and nerves that pass through the cervical spine and lead to the brain. Such pinching contributes to impaired blood circulation and leads to “starvation” of the brain : the lack of oxygen and nutrients affects it, which should be supplied in greater quantities in a normal case, different from pathology.
Often such disorders are accompanied by neurological, mental and physical disorders.
It is the combination of such deviations and symptoms that leads to the further development of pathology and the manifestation of panic attacks.
Dizziness and fear, as well as a feeling of fog in the head, do not go away without a trace and also have certain consequences for the body: calcium metabolism is disrupted, which can lead to problems with bones and joints.
Panic attacks occur not only due to osteochondrosis, but also for a number of other possible reasons, as well as their combinations:
- VSD - vegetative-vascular dystonia. Often, VSD and cervical osteochondrosis develop simultaneously and lead to more rapid development and intensification of panic attacks.
- Genetic abnormalities leading to increased production of adrenaline.
- Reduced levels of magnesium and zinc in the body, general lack of vitamins.
- Overwork: mental and physical.
- Pregnancy, breastfeeding, puberty are situations in which the body’s hormonal levels change.
- Taking medications that also lead to changes in hormonal levels.
- Hereditary or acquired mental disorders.
- Frequent use of alcohol or psychotropic substances.
If an attack of unreasonable fear and confusion are caused precisely by manifestations of osteochondrosis, then in addition to psychological discomfort there will be obvious pain in the cervical spine . This will require treatment not only of physical causes, but also identification and elimination of psychological factors that may influence the manifestation of panic attacks.
How to treat polysegmental osteochondrosis?
Find out what to do if pressure surges occur with cervical osteochondrosis.
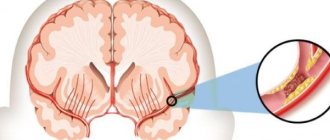
Stun
Stun
- a decrease in consciousness in which limited verbal contact with the victim is maintained against the background of an increase in the threshold for perception of external stimuli and a decrease in one’s own mental activity.
Moderate stun
accompanied by slowing down, difficulty, impoverishment of mental activity, and a decrease in the ability for active attention. Verbal contact with the victim is preserved, but answers to questions are delayed; sometimes it is necessary to repeat the question or pat the victim, who carries out the commands correctly, but slowly. The patient is lethargic, quickly exhausted, his facial expressions are impoverished, his motor reaction to pain is purposeful, orientation in his own personality is preserved, orientation in the area, and especially in time, may be impaired.
Deep Stun
accompanied by constant drowsiness with rare episodes of motor activity, a sharp difficulty in mental activity. Verbal contact with the victim is severely difficult, answers can only be obtained after persistent requests, they are monosyllabic in nature - “yes”, “no”, while the victim is able to provide his information: full name, age. It is possible to repeat the same word multiple times. The victim is able to follow basic commands: open his eyes, show his tongue, etc. The coordinated defensive reaction to pain is preserved, but orientation in place and time is absent.
Nullification
(cloudy consciousness) - a mild degree of stupor, can be observed in the first stages of stun, reminiscent of a state of mild alcoholic intoxication - the victim experiences carelessness, lability of consciousness, absent-minded attention, while the victim may give answers to questions after a while and at random.
Doubtfulness
(state of half-asleep) - is a type of stupor, characterized by minimal motor activity. The victim lies motionless with his eyes closed, makes no complaints, speech contact is minimal, only with persistent external influence. The patient gives correct answers to simple questions, but does not understand complex questions. The patient can be brought out of a state of doubt for a short time with the help of persistent external stimuli.
First aid for stunning:
- Treatment of the underlying disease.
- Normalization of electrolyte metabolism, elimination of signs of dehydration if present.
- Normalization of acid-base status.
- Detoxification therapy.
- Normalization of metabolic processes in the brain. Nootropic drugs are prescribed for this purpose.
Symptoms
Many people wonder whether there can be chills with osteochondrosis. To answer this question unambiguously, it is necessary to understand in more detail the possible symptoms that appear during osteochondrosis and panic attacks.
In addition to an unreasonable feeling of fear or a sense of danger, panic attacks can manifest themselves in other symptoms and signs that appear quite often:
- faster heartbeat;
- increased sweating;
- sleep disturbance;
- lack of air;
- confusion;
- tremor, trembling, chills;
- digestive disorders: nausea, diarrhea;
- confusion of thoughts, difficulty of formulation;
- feeling of constriction in the chest area.
There are other signs that accompany panic attacks, but they appear much less frequently:
- tingling in the limbs, numbness in the fingers;
- convulsions;
- unsteadiness of gait;
- hearing and vision impairment.
But it is still worth noting that the most important and obvious sign of a panic attack is precisely the uncontrollable feeling of fear and danger, which can reach various sizes and manifestations.
As the disease progresses, there may be a decrease in the level of fear, as if the disease is receding or disappearing altogether. The person does not experience strong fear, the frequency of manifestations is reduced.
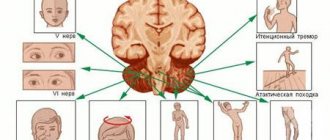
Coma
Coma is a complete shutdown of consciousness without any signs of mental life, while the victim cannot be brought out of this state with the appearance of any signs of mental activity.
- Moderate coma
(coma I) - the victim has a preserved reaction to painful stimuli (flexion and extension movements of a dystonic nature), while protective motor reactions are not coordinated, the patient does not open his eyes, pupillary and corneal reflexes are preserved, abdominal reflexes are depressed, tendon reflexes are variable. Increased pathological foot reflexes and reflexes of oral automatism. - Deep coma
(coma II) - there are no reactions to external stimuli, various changes in muscle tone are observed, spontaneous breathing and cardiovascular activity are preserved even if they are severely impaired. - Terminal coma
(coma III) - bilateral mydriasis, diffuse muscle atonia, severe disturbances in vital functions, respiratory rhythm and frequency disorders, apnea, tachycardia or bradycardia, blood pressure is not determined.
ATTENTION! Information provided on the website
is for reference only.
The site administration is not responsible for possible negative consequences if you take any medications or procedures without a doctor’s prescription! Contents of the topic “Stunning. Confusion of consciousness. Delirium. Oneiroid.”: 1. Confusion of consciousness. Delirium. Delirious syndrome. Epidemiology of delirium. Symptoms of delirium. Symptoms of delirium. 2. Stupor. Coma. Moderate coma (coma I, one). Deep coma (coma II, two). Terminal coma (coma III, three). 3. Confusion of consciousness. Delirium. Delirious syndrome. Epidemiology of delirium. Symptoms of delirium. Symptoms of delirium. 4. Clinic (signs) of delirious syndrome (delirium). The first stage (phase) of delirium. Emergency (first) aid during the first phase of delirium. 5. Clinic (signs) of the second, third stage (phase) of delirium. Second, third stage (phase) of delirium. Emergency (first) aid during the second and third phases of delirium. 6. Occupational delirium. Mumbling delirium. Alcoholic delirium (delirium tremens). 7. Clinic (signs) of alcoholic delirium. Stages of delirium. Infectious delirium. Prevention of delirium. 8. Emergency (first) aid for delirium. Drug therapy for psychomotor agitation. Calming psychotherapy. Neuroleptic (sedative) therapy for delirium. 9. Symptomatic treatment of delirium. Issues of hospitalization for delirium. When to hospitalize if a patient has delirium? 10. Oneiroid. Oneiric state. Epidemiology of oneiroid. Clinic (signs) of oneiroid. Emergency (first) aid for oneiroid.
Speech and sound changes
Pronouncing individual sounds clearly is a fairly simple task, but it is almost never necessary. They resort to it only in the process of working on new sounds. Human speech is a stream of sounds in which individual elements in one way or another influence each other, changing their “neighbors” in a certain way and changing on their own.
Both vowel sounds can undergo changes (for example, they can change or lose any of their characteristics, receive overtones) and consonant sounds (they can, for example, become similar to each other, drop out, become voiced or deafened). Some of these phenomena are the pronunciation norm, some are typical for the Russian language, and others can only be encountered when studying a foreign language. In any case, changes in sounds in the flow of speech are an inevitable phenomenon, especially clearly noticeable in the example of consonant sounds.
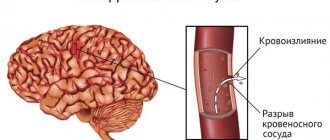
Other diseases whose symptoms are similar to stroke
You don’t always sit at home, and you can’t always notice the onset of the disease. Having found your relative in a “strange” state, you need to understand that not only a stroke can cause it.
So, if it is a seizure, it could also be an epileptic seizure. In this case, you begin to provide first aid, as described below, call an ambulance. Then you look: if consciousness is not restored or if it is restored, but the person has become inadequate, his face is distorted or his limbs do not move, this is a stroke. If everything returns to the previous level - epilepsy.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is very similar to meningitis, even temperature and pressure can be increased in both cases. Here you need to take into account the fact that meningitis does not develop out of nowhere or after stress. It is preceded by either a cold, or otitis media, or pneumonia.
A “strange” condition and headache can occur with both a stroke and a migraine. But a stroke is characterized by confusion of consciousness, but with a migraine it is preserved. With a stroke, facial asymmetry and impaired movement of the limbs appear; this is not typical for migraine.
Working on pronunciation
As mentioned above, stunning is a natural process in a number of cases. This is quite normal. However, sometimes it happens that a person unknowingly, for whatever reason, deafens a consonant where it should remain voiced. Such situations become a problem that requires a solution, including the help of a speech therapist.
If deafening is a speech therapy problem, it has several possible causes. Which ones? For example, deafening of consonants may be associated with improper functioning of the vocal cords or the immaturity of a person’s processes for recognizing pronounced sounds. One way or another, correcting pronunciation has several stages:
- work on slotted sounds;
- working on a sequence of plosive sounds.
Forecast
Risk factors leading to death:
- coma after a secondary stroke;
- creatinine level exceeding 1.5 mg/dl;
- the occurrence of convulsive muscle twitching and the preservation of an identical state for 3 days;
- absence of reactions of any kind;
- the age of the patient (after 70 years of age there is no chance);
- negative MRI readings.
Find out if you need to treat low blood pressure after a stroke by following this link.
Optimistic forecasts are directly proportional to disorders in the central nervous system and depend on certain aspects:
- causes;
- concomitant diseases;
- efficiency in stopping a blow;
- compensatory capabilities of the central nervous system.
As consciousness returns, neurological damage becomes apparent, manifesting itself in the form of speech disorder, unilateral loss of sensitivity, visual defects and other negative manifestations.
A patient with stage 3 coma is unlikely to be able to return to life. Coming out of a coma, people spend years regaining lost functions. However, there are cases where disabled people were able to return to their previous lives.
The rehabilitation stage lasts for years. Compensation of the neurological deficit occurs in the first months after a stroke, and then slows down. After 3 years, residual effects in the body are corrected.
Voicing of consonants
Voicing of consonants is a fairly common phenomenon, one of the most frequent in the flow of speech, along with deafening of sound. Most often found in several positions:
- When a sound is found at the junction of morphemes. For example, in the words “request”, “collection” and “deal”, the unvoiced consonant sound located at the junction of parts of the word is voiced, passing into its pair.
- When the sound being voiced is found at the junction of a word and the preposition that stands before it, as, for example, in the phrases “to the house” and “from the dacha.”
- At the junction of a word with the particle behind it.
The voicing of a consonant is largely due to its environment in the stream of speech and the process of incomplete assimilation. And both regressive and progressive.