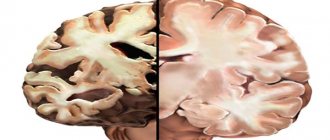
Causes of dementia after a stroke
The cause of dementia can be either hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke. If in the chronic form dementia manifests itself gradually, then after a cerebral hemorrhage it occurs suddenly. Before an attack, a completely adequate person turns into a helpless child. Typically, such consequences are observed in people from 50 to 65 years old, since a stroke damages not only parts of the brain, but the circulatory system.
Factors have been identified that influence the development of dementia after a stroke, when the patient’s body is weakened and unable to resist.
These factors are:
- diabetes;
- advanced atherosclerosis;
- hormonal imbalance;
- arterial hypertension;
- heart failure.
Not only existing diseases can become the impetus for the development of dementia. This list also includes bad habits: alcohol, smoking. Poor nutrition also has an effect, since fatty foods negatively affect the circulatory and cardiac systems. Doctors also name a reason such as a low level of intelligence; a highly developed person enters childhood more slowly.
Dementia after stroke: diagnosis, treatment, prognosis
Post-stroke dementia is acquired dementia with partial or complete loss of ability to work, occurring in approximately 30% of cases after a stroke. Dementia is accompanied by negative changes in speech, memory, and thinking, and a person’s independence suffers.
Vascular disorders, which can be caused by many diseases, cause hypoxia of brain tissue (BM), resulting in ischemic stroke. If a vessel ruptures, then such a stroke is called hemorrhagic.
This leads to the death of nerve cells and irreversible damage to the central nervous system. There is also such a thing as a transient ischemic attack (TIA) - short-term hypoxia of brain tissue, the difference of which will be the reversibility of pathological processes.
However, a TIA that occurs once is a mandatory reason to contact a specialist, since over time it can turn into an ischemic stroke. Constant ischemia of the brain or blockage of a vessel with a thrombus is a time bomb that must be eliminated before something irreparable happens.
To do this, you need to take care of your health and promptly treat existing concomitant diseases.
Diagnostics
Dementia after a stroke requires careful diagnosis by a neurologist and psychiatrist, as it can simulate a number of other diseases. The doctor collects a thorough medical history, listens to complaints, and a competent doctor should suspect dementia if less than a year has passed since the stroke.
Manifestations of dementia are sometimes so nonspecific that they can resemble normal fatigue, especially common in older people. To make a diagnosis, an MRI of the brain is necessary. Additionally, a general and biochemical blood test and a blood test for hormones are prescribed.
Post-stroke dementia requires an ECG and ECHO-CG, since in the vast majority of cases stroke is a consequence of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Treatment
Therapy for this pathological condition should be carried out under the supervision of your attending physician.
In cases of established dementia due to improper treatment of stroke, drug therapy is aimed at smoothing the clinical picture.
Drugs are prescribed to improve cerebral circulation (Curantil), psychostimulants (Mesocarb), nootropics (Piracetam), vitamin complexes with a high content of B vitamins, tranquilizers (Phenozepam), antidepressants (Elycea, Amitriptyline, Fluoxetine). The drugs are combined with each other depending on the clinical manifestations of the disease.
It is also worth paying attention to concomitant diseases to prevent a stroke in the future. To train your memory, it is recommended to read books and solve all kinds of puzzles. Knitting or playing the piano helps improve hand motor skills.
The diet should be balanced, replenishing missing microelements - mandatory consumption of fermented milk products, fish, nuts, fruits and vegetables. A psychotherapist can help you cope with the condition, and to maintain vitality you need to periodically engage in your favorite hobby, exercise, and take walks in the fresh air every evening.
RELATED MATERIALS: Let's talk about Alzheimer's type dementia
Forecast
The prognosis of dementia after a stroke depends on many reasons: age, characteristics of the body, the presence of genetic predisposition and the severity of concomitant diseases.
The clinical picture can also vary significantly depending on the number of strokes suffered and the treatment performed. As a rule, the prognosis for dementia is satisfactory.
Total personality degradation is quite rare, and regular compliance with all doctor’s recommendations can prolong life for many years.
First aid
The first signs of a stroke are a distorted face, dizziness, blurred vision, a feeling of weakness, and speech is no longer understandable to others.
If you recognize the above symptoms, you need to call an ambulance, but the person needs your help now. Before the ambulance arrives, you must:
- Provide the patient with complete rest, help him lie down so that his head is elevated;
- Open the windows in the room, if necessary, give valerian tincture to slightly reduce fear.
In the hospital, an MRI of the brain is immediately performed, which will reveal the nature of the stroke, whether it is hemorrhagic or ischemic. For the first type, Vikasol and Gordox are prescribed. In the second case - trental, heparin. In some cases, surgery is indicated, in particular, in the presence of a hematoma compressing the brain tissue.
Changes during a stroke are reversible if medical procedures were carried out within 4 hours from the onset of the attack.
Prevention
Preventive measures are primarily aimed at eliminating the causative factor that can lead to a stroke. Recommended:
- Take medications in a timely manner if you have a concomitant pathology;
- Undergo medical examination. If you know that you have a hereditary condition, see your doctor regularly;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits;
- Eat right, limit your consumption of everything salty, fatty, smoked. These products have a negative effect on the vascular bed, especially for people with hypertension;
- Regular exercise, and the load should be moderate;
- Losing weight. If you are overweight, you need to reduce it, as this will reduce the load on the heart;
- Pursuing your favorite hobby. The key to health is a good mood, if you pay yourself at least a little attention every day - this will improve your ideas about life and help you cope with accumulated problems.
Neglecting medical recommendations and refusing to treat existing diseases always leads to bad consequences, so listen to your health more carefully!
Source: https://opsihoze.ru/patologii-umstvennogo-i-psihicheskogo-razvitiya/prognoz-dementsii-posle-insulta-slaboumie-posle-insulta.html
How to recognize it?
Behavior after a stroke varies among many patients, some lose practical skills and physical mobility, others become weaker mentally. A combination of different manifestations also occurs. The affected area plays an important role in the formation of symptoms:
- Focus in the cerebral cortex . Slurred speech, loss of practical skills, disorientation in space.
- The lesion is in the subcortex . Inattention, absent-mindedness, poor facial expressions, hysteria, slow and uneven gait, depression.
Sometimes the signs are combined, and the pathology can develop due to existing diseases.
Other symptoms characteristic of dementia after a stroke:
- A person has almost no control over half of his body.
- Urinary incontinence is observed in 30% of cases.
- Loss of intelligible speech, writing and reading skills.
- Progressive sclerosis.
- Agnosia is the loss of the ability to recognize people and objects and evaluate them.
- The patient cannot move on his own.
- Frequent mood swings, depression, tendency to panic attacks.
- The appearance of delusions or hallucinations.
Identifying dementia in the early stages helps preserve identity and make life easier for the patient after a stroke.
Mechanism of development of cognitive impairment
Dementia and stroke inextricably accompany each other in varying degrees of clinical severity. There are two main pathogenetic links in acute cerebrovascular accident:
- As a result of blockage of the lumen of a blood vessel by an atherosclerotic plaque, thrombus or atherosclerotic masses, a lack of blood appears in the brain and an ischemic stroke is formed, vascular-type dementia in 30% of cases.
- When the wall weakens, a protrusion (aneurysm) appears, and arterial or intracranial pressure increases, the risk of hemorrhagic stroke with rupture of the hemovascular membrane is high.
Dementia after hemorrhagic stroke or ischemic cerebral infarction has an extremely high risk when more than 50 ml of brain volume is affected. Cognitive disorders manifest themselves acutely, noticeable in the first 3-6 months. The development of changes after six months can be attributed to another type of dementia.
After a single stroke, cognitive impairment may not change in severity, but in some cases there is a slow decline. A step-like course is typical and often has the same localization, severity and etiological factor.
When dementia occurs after a stroke, how long they live is directly related to repeated episodes of acute cerebral circulatory disorders. High mortality with recurrent stroke after 3-6 months. The risk of death is in every 2-3 patients.
Epidemiological observations show that the risk of dementia increases with recurrent stroke. Post-stroke cognitive disorders are heterogeneous. The heterogeneity of neurological, psychological characteristics and natural dynamics after an acute cerebral catastrophe is noted.
*confabulation – replacing memory lapses with fictitious actions.
Can it be cured?
Modern medicine cannot yet boast of a panacea for dementia; we are only talking about rehabilitation to alleviate symptoms and stop the development of the disease. A remedy has not yet been invented that could slow down the destruction of nerve cells, block the deposits of abnormal proteins in brain neurons and restore tissue damaged by necrosis.
The course of treatment is prescribed comprehensively, according to a specially developed scheme, with a combination of different drugs.
Medicines
It is very important to take medications during this period:
- Psychostimulants. Increases the stability of the central nervous system against possible stress.
- Nootropic substances. Activate mental activity, improve memory, reduce aggression. Provide nutrition to brain tissue. The most common: piracetam and nootropin.
- Antidepressants.
- Vitamins. Help restore lost brain functions.
- Series to improve blood supply to the brain, which prevent areas of necrosis from expanding. Tavegil and Cavinton are most often prescribed.
- Medicines to improve memory. Mamantin has proven itself well.
Physical therapy sessions are also prescribed, which help restore blood circulation and relieve muscle tightness.
Proper nutrition also helps keep the patient in an acceptable condition. Some medical experiments have proven that with the help of products, the development of dementia can even be slowed down.
It is necessary to include in the diet:
- Curcumin. A substance found in curry seasoning. It is believed that Indians are not susceptible to Alzheimer's disease because they consume these spices daily. Curcumin prevents amyloid plaques from developing in the brain.
- Natural antioxidants: vitamins E, C, coenzyme Q 10, lycopene and beta-carotene.
- Vegetables, fruits, legumes, nuts.
- Olive oil.
- Fish or seafood.
- Cottage cheese, kefir, cheese.
- Red wine in modest quantities.
It is important to know that in the early stages of dementia, appetite can be greatly reduced, and in the moderate stages it can greatly increase. Therefore, the patient needs to be fed in small portions.
Differential diagnosis
Post-stroke dementia is different from that of Alzheimer's disease. In the first case, there is a direct connection with a stroke; the disease occurs suddenly against the background of general well-being. With Alzheimer's, the clinical picture increases gradually, and the leading symptom will be considered memory impairment according to Ribot's law. Alzheimer's disease is characterized by foci of brain destruction, and if MRI for a stroke reveals these in addition to ischemia or hemorrhage, this indicates a mixed destructive-vascular form of dementia.
The difficulty is that a person who has had a stroke does not always develop dementia. It is very common for such people to fear a new attack, which can lead to the development of generalized anxiety disorder or depression. In this case, a psychiatrist and neurologist can help make the correct diagnosis. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable. If you suspect incipient dementia, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination and begin treatment as early as possible.
Prevention
To avoid relapses of stroke and manifestations of dementia, you need to give up bad habits and establish proper nutrition.
The most important recommendations:
- Select moderate physical activity that is feasible for the patient.
- Monitor blood pressure.
- Find time for mental and intellectual activities.
- Eat foods with low cholesterol levels.
Scientists have compiled a list of natural foods and herbs that help block the development of dementia. If you include them in your diet, the risk of developing dementia after a stroke is significantly reduced.
- Vitamin C. Found in green leafy vegetables and citrus fruits. Helps restore brain function.
- Folic acid . Found in oranges, strawberries, asparagus, peas, papaya.
- Almond. Includes vitamin E. To get the maximum effect, the product should be eaten on an empty stomach, after soaking in water in the evening.
- Sage. Slows down blood clotting, dilates blood vessels, improves blood flow. Relieves attacks of depression and anxiety.
- Ginseng. Helps damaged brain cells recover. You need to drink up to 600 grams of decoction per day; the herb is brewed like tea and left for 15 minutes.
- Milk thistle . The fruits contain seeds rich in silymarin, this substance prevents the loss of connections between brain cells, which manifests itself in dementia. You should take 420 milligrams of extract per day, available in the form of tinctures, tablets or capsules.
- Melissa. Improves the healing of affected brain cells, inhibits the process of memory deterioration, relieves anxiety, and normalizes sleep. Brew like tea: a teaspoon per glass of boiling water, drink 3 servings a day.
- Ginkgo biloba . Contains strong antioxidants that improve memory performance, increase blood flow to the brain, and inhibit the development of dementia. Brew 250 ml of boiling water leaves, 1 teaspoon per serving, drink twice a day.
Read also: Causes of stroke in men
Although, unlike age-related dementia, post-stroke dementia does not always lead to complete degradation, the risk of progression of the disease always remains very high. It is possible to avoid such manifestations if you recognize the symptoms in the early stages and immediately consult a doctor. With the help of medications, the patient’s condition can be regulated, keeping it at an acceptable level for existence.
Symptoms
Dementia after a stroke has the following clinical picture:
- Memory impairment;
- Absent-mindedness;
- Depending on the location of the pathological focus - impaired vision, speech, lack of pain sensitivity, etc.;
- Imperfect fine motor skills;
- Difficulty completing simple tasks;
- Decreased mental abilities;
- Urinary disorder;
- A person assimilates new knowledge worse, has difficulty reading and counting;
- In the early stages, criticism of one’s condition remains; the person realizes that he is sick. In the following, there is no criticism;
- Personality change – irritability, conflict;
- Gait disturbance, in some cases, inability to walk - paralysis.
It is worth noting the fact that the above symptoms are expressed to varying degrees in all people who have suffered a stroke. For some, behavioral disorders come to the fore, for others, neurological ones. The persistence of symptoms depends on the size of the ischemic lesion, its location and the duration of the stroke. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle and treatment with the necessary medications, the clinical picture can be smoothed out, however, unfortunately, dementia is a chronic progressive disease. Therapy is aimed at maintaining adequate vital functions and reducing the number of possible complications.
Vascular dementia
What is vascular dementia? Why does it occur? What are the symptoms, how to recognize the disease in time? Diagnostic methods. Is there an effective treatment? How long do people live with vascular dementia?
Popularly, dementia has a more crude name – “dementia”. This term refers to a complex of disorders in the cognitive sphere: deterioration of memory, thinking, and learning ability.
Dementia is not just one disease, but several different diseases. Its most common form is Alzheimer's disease. The second place is occupied by vascular dementia. According to some data, it accounts for 15–20% of all cases of dementia in older people.
Any cells in our body need a constant flow of oxygen and nutrients. The brain in this regard is perhaps the most resource-intensive organ. After cardiac arrest, the nervous system can live for 5–7 minutes, after which the neurons die irreversibly.
The severity and rate of progression of vascular dementia depend on how quickly blood flow to the brain is disrupted. Sometimes the symptoms arise suddenly, acutely, in other cases they increase gradually, and at first they are not even paid attention to.
Because the disease is so diverse, some doctors and scientists are proposing to abandon the term “vascular dementia” and replace it with “vascular cognitive impairment.”
The relationship between stroke and dementia
Traditionally, clinical manifestations after the onset of cerebral catastrophe are associated with neurological deficits. In practical terms, they are given more attention during therapy to avoid the risk of disability and to improve the patient’s quality of life. However, focal changes are almost always combined with mental and cognitive disorders. Additional domestic, social and professional adaptation is required.
- young people (up to 40-45 years old) after a single or multiple case of vascular accident, where the likelihood of Alzheimer's disease is reduced to zero;
- cognitive properties were preserved before stroke and were impaired immediately after the pathology, in addition, they continue to progress over the next 3-6 months;
- according to the results of a clinical examination, magnetic resonance or computed tomography, the lesion is located in a strategically significant area (areas of the brain under the cortex);
- a history of vasculopathy was diagnosed.
Causes of the disease
Vascular dementia develops as a result of impaired blood flow in the brain, and this is similar to stroke. It often develops after a stroke. In other cases, the disease is the result of multiple “silent” microinfarcts in the brain. Individually they do not produce symptoms, but over time they overlap each other.
The main risk factor for the disease is age. Vascular dementia is most common in older people. Other conditions that increase your chances of getting sick:
- diabetes;
- smoking;
- high blood pressure;
- unhealthy diet: lots of animal fats, few fruits and vegetables;
- excess weight;
- lack of physical activity;
- love of alcoholic drinks;
- atherosclerosis;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- temporal arteritis;
- history of strokes and heart attacks;
- atrial fibrillation.
The best prevention of vascular cognitive impairment, Alzheimer's disease, stroke, heart attack and other cardiovascular diseases is to eliminate these risk factors and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Stroke and Alzheimer's disease symptoms and signs
Post-stroke dementia is acquired dementia with partial or complete loss of ability to work, occurring in approximately 30% of cases after a stroke. Dementia is accompanied by negative changes in speech, memory, and thinking, and a person’s independence suffers.
Vascular disorders, which can be caused by many diseases, cause hypoxia of brain tissue (BM), resulting in ischemic stroke. If a vessel ruptures, then such a stroke is called hemorrhagic.
This leads to the death of nerve cells and irreversible damage to the central nervous system. There is also such a thing as a transient ischemic attack (TIA) - short-term hypoxia of brain tissue, the difference of which will be the reversibility of pathological processes.
However, a TIA that occurs once is a mandatory reason to contact a specialist, since over time it can turn into an ischemic stroke. Constant ischemia of the brain or blockage of a vessel with a thrombus is a time bomb that must be eliminated before something irreparable happens.
To do this, you need to take care of your health and promptly treat existing concomitant diseases.
Symptoms of vascular dementia
Characteristic signs of the disease:
- Memory problems . The patient cannot recognize familiar faces, does not remember what he did today, and may get lost in his own home, on the way to the store.
- Difficulty performing usual actions . For example, an avid fisherman cannot remember how to use a fishing rod. A person who has worked as a driver all his life does not understand what to do next when he finds himself behind the wheel of a car.
- Poor concentration . A person cannot concentrate on anything and is periodically in a state of confusion.
- Problems with thinking . The patient cannot make a decision for a long time, is unable to organize his thoughts and plan actions.
- Disorders in the emotional sphere . A person, for no reason, in an inappropriate situation, begins to cry or laugh.
- Speech problems . It may be difficult for the patient to find words, his speech becomes poor.
- Gait disturbance . She becomes insecure.
- Loss of bladder control . Frequent urge to urinate, urinary incontinence.
- Hallucinations and delusions.
The early stage of vascular dementia is signaled by symptoms such as impaired memory for recent events, changes in speech, and difficulty orienting oneself in a familiar area.
There are two specific forms of the disease:
- Post-stroke dementia develops after a stroke and has a clear connection with it.
- Mixed dementia is a condition in which vascular cognitive impairment is combined with other forms of dementia, most often Alzheimer's disease.
Read also: Vomiting after a stroke
Course of the disease
Most often, senile vascular dementia occurs in stages. For some time the patient's condition stabilizes, then deterioration occurs. Gradually, more and more areas of the brain are involved in the process.
Sometimes the disease occurs acutely, and the disturbances are very pronounced from the very beginning. This usually occurs after a severe stroke. If the brain stroke was mild, or it was a mini-stroke, cognitive disorders increase gradually, slowly. In general, the course of dementia is divided into three stages:
- Early stage . At this stage, relatives often do not notice that their loved one is sick. Forgetfulness occurs, a person often loses things, cannot always tell what time it is, and gets lost in familiar places. From time to time, difficulties arise with the selection of words during a conversation.
- Middle stage . A person does not remember recent events, does not recognize familiar people, experiences serious difficulties in communication, gets lost in his own home, asks the same questions every now and then, and needs outside care.
- Last (running) stage . The patient completely ceases to orient himself in time and space. He cannot recognize his relatives, cannot take care of himself and perform the simplest actions. Many patients change their behavior and become aggressive.
Consequences of stroke: vascular dementia
Vascular dementia is one of the most unfavorable variants of the course of chronic ischemic brain disease. Our consultant: Nina Minuvalievna Khasanova, angioneurologist at the First City Hospital of Arkhangelsk.
It has been noted that this disease occurs, as a rule, in old age. The cause of dementia after a stroke is associated with damage to the part of the brain that is responsible for memory or performing certain skills.
Vascular dementia (dementia) is a combination of symptoms that are manifested by deterioration of memory, thinking, and a decrease in the ability to perform skills in everyday life, which either stops or significantly complicates the patient’s independent life and his usual work.
Vascular dementia after stroke is not necessarily an emerging symptom. This condition occurs when there is severe damage to brain tissue or as a result of a repeated stroke against the background of uncontrolled arterial hypertension.
If a person, after suffering a stroke, becomes apathetic, tearful, quickly emotionally exhausted, his mental abilities deteriorate, he ceases to be interested in the life of his family and friends, this may be the first sign of advancing dementia, which requires examination by a doctor for timely treatment.
The onset of post-stroke dementia, unlike, for example, Alzheimer's disease, is acute. For example, on Wednesday a person behaved normally, but on Thursday morning he became aggressive, uncontrollable, and his memory deteriorated sharply. It is very important not to overlook the patient’s recurrent stroke: it may be hidden behind such a sharp deterioration in well-being. Therefore, each such situation is an indication for a medical examination and calling an ambulance.
Vascular dementia as a disease can occur with light intervals. This disease, as it were, erases, layer by layer, the skills that a person has acquired throughout his life.
Dementia after a stroke is necessarily combined with coronary heart disease, diabetes mellitus, and arterial hypertension. In this case, there are always changes in the vessels of the brain, neck, and fundus of the eye. Patients must be periodically examined by a cardiologist to provide assistance and select concomitant therapy.
The risk of developing post-stroke dementia depends on how carefully the relatives or the patient himself monitor his blood pressure, the level of cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins and their correct ratio, blood viscosity, and how carefully all the recommendations of the attending physician are followed.
Recommendations for relatives of a patient with vascular dementia
Unfortunately, modern medicine does not have the ability to effectively treat dementia and prevent its progression. Prescribed medications can only remove or weaken certain unpleasant manifestations of the disease and partially slow down its development. Therefore, the leading importance in providing assistance to patients with dementia belongs to daily comprehensive care for them.
The most important:
1. try to prevent the development of infectious diseases and the worsening of your loved one’s physical illness, as this negatively affects the course of dementia;
2. create a comfortable and simple environment: familiar favorite objects, their location. In a familiar environment, the patient feels most comfortable. The appearance of strangers in the house and moving sharply worsen his condition. In the room where the patient is, there must be a firmly established and familiar order for placing clothes, shoes, and other items of everyday use;
3. control the regimen of taking prescribed medications. Their irregular use or overdose can dramatically worsen the patient’s condition.
Patience is required!
When communicating with a loved one who has dementia, never forget that you are communicating with a sick person whose psyche is disturbed, many of the character traits that previously attracted you have been lost, and their behavior has changed (alas, not for the better). Remember that against the background of rare temporary improvements, the disease, as a rule, will intensify and the patient’s condition will worsen. Personality changes progress, emotional attachments to loved ones and the ability to empathize weaken, grumpiness, stubbornness and resentment increase.
Subsequently, orientation in time, space, and the surrounding environment is disrupted. Patients do not know the date, may get lost in a familiar place, do not always understand where they are, and do not recognize familiar and close people. And although such a person can take care of himself and cope with personal hygiene, he is already losing the skills of using everyday household appliances, such as a telephone, gas stove, TV remote control, etc. Then he can no longer be left alone unattended.
Vascular dementia rarely reaches the level of deep total collapse of the psyche , but over time the sick person becomes a heavy burden for others and relatives. Here are some excerpts from relatives talking about their loved ones with dementia.
“After the stroke, my mother-in-law changed a lot, she became unkind, suspicious, and capricious. The person is simply unrecognizable! Her general health is now good, she even goes out to breathe on a bench at the entrance. He tells his neighbors all sorts of tall tales: either I was going to poison her, or we don’t let her sleep at night, or we lock her in the toilet. The husband talks to her, shames her, but she either denies her stories, even shouts at him or cries that we are slandering her. I once came home from work and smelled strongly of gas. The burner tap on the stove is open. Now we turn off the gas and leave the food in thermoses.”
“I put food for mom, which we immediately eat ourselves, but she says that she’s not a pig to eat something like that, and throws the plate away. I take her hand to take her to the room or the kitchen - she starts twitching and screaming that I’m hitting her. After the stroke, my mother has been living with us for almost three years, but lately she has been wanting to return home. When we leave, we have to lock it with a key, since we left once. We literally missed it in 15 minutes, and she was already gone! They searched all evening, night, morning. We called all her relatives, her friends, hospitals, and morgues. We went around all the neighboring yards. Almost went crazy! Well, an acquaintance works in the police, and he helped us (and a missing person’s report is accepted only after three days). The next day at 12 o’clock she was found on the other side of the city.”
“Mom started talking a lot. Sometimes he talks to an imaginary woman, sometimes he calls me mom, sometimes he calls me sister. I stopped reading completely and often cries.”
In such cases, do not try to convince patients, prove that you are right, or appeal to their conscience, reason, or logic. A person's personality has already been changed by illness. This is no longer the same mother, mother-in-law, wife, father, husband whom you have known all your life. You just need to remember: everything that your loved one does and says is not due to his malice, deceit, or harmfulness. This is a manifestation of the disease. Therefore, try to be patient with his “whims” and “antics”, be attentive, friendly and sensitive when communicating with him, because he still remains your loved one!
Don’t forget that dementia is one of those diseases that must be treated before the first signs appear, so medical supervision and compliance with recommendations for the treatment of chronic diseases that affect the vascular system are the key to a high-quality and fulfilling life at any age.
Steps to prevent stroke
Concluding the story about the consequences of a stroke, I would like to remind you once again: in many cases, a vascular accident can be avoided; for this, the main attention should be paid to prevention. The most significant factors that can be corrected include arterial hypertension, coronary heart disease, diabetes mellitus, smoking, increased body weight, and elevated cholesterol levels.
- Physical activity is an effective factor in the prevention of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and arterial hypertension. During physical education, blood properties improve and the risk of blood clots decreases.
- Diet aimed at preventing atherosclerosis: limiting foods containing cholesterol and animal fats. Eat more fruits, vegetables and grains, vegetable oil, and sea fish.
- Smoking cessation: nicotine causes vasoconstriction and stimulates the progression of atherosclerosis.
- Blood pressure control: arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis are closely related diseases, so their treatment and prevention must be carried out in parallel.
- Control of blood fat levels: disturbances in blood lipid composition lead to the development of atherosclerosis, which increases the risk of stroke.
- Fighting diabetes mellitus: this disease is associated with an increased risk of vascular damage and intensive development of atherosclerosis.
Material: Irina Shaposhnikova
Photo: Vladimir Trefilov
Share link:
What diagnostic methods can a doctor prescribe?
There is no test or test that can immediately accurately diagnose vascular dementia. With the help of special tests, the doctor can detect dementia in the patient, then he will have to understand its causes. Diagnostics must be comprehensive. It is important for a neurologist to know how the patient’s cognitive impairment manifests itself, whether he has suffered a stroke, heart attack, or suffers from atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension or other cardiovascular diseases.
Neuropsychological testing
During neuropsychological testing, the patient is asked to perform some tests and tasks, based on the results of which a number of indicators are assessed:
- How well a person speaks, writes and understands what is said.
- How well can he operate with numbers, perform arithmetic calculations, and determine the date and time?
- How well does he remember new information and learn?
- How well can he plan his actions and implement his plans into reality?
- How does the doctor react to hypothetical situations?
Examination by a neurologist
Before examining a sick person, he will be examined by a neurologist, checking reflexes, movements, sensitivity, muscle strength and tone, vision, touch, sense of balance, and coordination of movements.
Head scan
In order to understand the causes of dementia, your doctor may prescribe the following diagnostic methods:
- Computed tomography can detect traces of strokes, transient ischemic attacks, vascular disorders, and intracranial tumors.
- Magnetic resonance imaging shows approximately the same thing, only, compared to CT, it provides the doctor with even more detailed information.
Lab tests
A blood test for cholesterol and sugar helps in diagnosing the causes of dementia. Sometimes you need to check your thyroid hormone levels and other substances.
Treatment
For a pathology such as dementia after a stroke, treatment is prescribed immediately with an individual selection of medications. Includes vascular, replacement and neurometabolic therapy, as well as secondary preventive measures to reduce the risk of recurrent stroke.
A prerequisite is lifestyle correction and treatment of diseases of the cardiovascular system:
- Personal selection of antihypertensive medications.
- Prescription of antiplatelet agents (Clopidogrel, Acetylsalicylic acid, Pentoxifylline).
- Anticoagulants (Warfarin).
- Correction of the lipid profile reduces the risk of atherosclerotic plaque formation: Lovastatin, Rosuvastatin.
- Vasoactive agents: Vasobral, Tanakan, Cinnarizine.
To reduce the risk of dementia, neurometabolic therapy using nootropics is indicated: Piracetam (Nootropil), Actovegin, Cerebrolysin. The drugs have low toxicity and high bioavailability to organs and tissues. Anticholinesterase drugs slow down destructive processes (Galantamine, Rivastigmine).
Treatment of vascular dementia
First of all, therapy should be aimed at the causes of the disease, which are located in the cardiovascular system. The following goals must be achieved:
- Maintaining blood pressure at an optimal level with antihypertensive medications.
- Controlling cholesterol levels in the blood. To reduce it, statin .
- Normalize blood clotting and prevent the formation of blood clots. The simplest measure that doctors prescribe to many patients is taking aspirin daily.
- If the patient suffers from type II diabetes mellitus, it is necessary to monitor blood sugar levels and take special medications.
For the treatment of vascular dementia, the same drugs are prescribed as for Alzheimer's disease. Cholinesterase inhibitors (galantamine, donepezil, rivastigmine) and memantine are used . All patients are prescribed a rehabilitation course, which involves a team of different specialists.
Treatment regimen
Therapy for vascular dementia is aimed not at the cause, but at alleviating the symptoms associated with the disease. There are no proven effective drugs approved by WHO for vascular dementia. In some cases, medications are prescribed to relieve psychiatric symptoms. So-called acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and memantine may be helpful. There is evidence that ginkgo leaf extract increases the chances of recovery in elderly patients with dementia.
The corresponding risk factors for vascular damage and major vascular diseases (high blood fat, hypertension) are also corrected with suitable means. This is an important condition for preventing further damage to blood vessels and the occurrence of a heart attack.
Non-pharmacological interventions
Vascular dementia, like other forms of dementia, is also treated with non-drug methods. Cognitive training, occupational therapy, music and dance therapy are helpful. If there are problems with gait, the patient should receive assistance with walking. In case of problems with continence, consistent teaching of the patient is recommended.
In the presence of vascular risk factors and underlying diseases, non-drug measures are important. The doctor will recommend that the patient abstain from smoking in the future and modify the diet (less animal fats and more plant fats).
What is subcortical vascular dementia?
Another name for the disease is Binswanger's disease . It is a subtype of vascular dementia in which the lesions are localized in brain structures located below the cortex. Cognitive disorders include symptoms such as:
- increased fatigue;
- decreased performance;
- headache;
- sleep disorders;
- difficulty pronouncing words and swallowing ( pseudobulbar syndrome );
- fecal and urinary incontinence;
- walking disorder ( abasia ).
Prognosis: How long do people live with vascular dementia?
Although the phrase that “nerve cells do not recover” is heard very often, recovery processes still occur in the brain. If an “accident” occurs in one of the vessels, workarounds can be enabled. However, there is a limit to everything. Vascular dementia can last for many years, but in any case it shortens life expectancy. Repeated strokes and heart attacks only worsen the situation.
The quality of life also suffers greatly, especially in the later stages of dementia: it can hardly be called satisfactory when a person does not remember himself or those around him, cannot answer what date it is, what day of the week, what time it is, is unable to take care of himself, is lost, barely leaving home.
Timely and correct treatment helps to slow down the progression of the disease, maintain work capacity and the ability to self-care longer.
Is disability given for vascular dementia?
In order for a person to be recognized as disabled, three conditions must be met:
- There must be a persistent impairment of body functions.
- This violation should lead to the fact that a person cannot care for himself, work, study, control his behavior, navigate independently, move, or communicate. In a word, the functions that are necessary for any person to live a normal life in society must be impaired.
- A person must require rehabilitation and social protection.
Read also: Duration of treatment for stroke
The picture that is observed in vascular dementia falls within these criteria. In order to receive a disability group, you need to undergo a medical and social examination (MSE). A referral is given by a psychiatrist.
Treatment
Therapy for this pathological condition should be carried out under the supervision of your attending physician.
In cases of established dementia due to improper treatment of stroke, drug therapy is aimed at smoothing the clinical picture. Drugs are prescribed to improve cerebral circulation (Curantil), psychostimulants (Mesocarb), nootropics (Piracetam), vitamin complexes with a high content of B vitamins, tranquilizers (Phenozepam), antidepressants (Elycea, Amitriptyline, Fluoxetine). The drugs are combined with each other depending on the clinical manifestations of the disease. It is also worth paying attention to concomitant diseases to prevent a stroke in the future. To train your memory, it is recommended to read books and solve all kinds of puzzles. Knitting or playing the piano helps improve hand motor skills. The diet should be balanced, replenishing missing microelements - mandatory consumption of fermented milk products, fish, nuts, fruits and vegetables. A psychotherapist can help you cope with the condition, and to maintain vitality you need to periodically engage in your favorite hobby, exercise, and take walks in the fresh air every evening.