Clinical manifestations
Neurological practice allows us to identify symptoms of short-term vasospasm (narrowing of the diameter of small arteries):
- headache - in the back of the head, temples, temporo-parietal area;
- dizziness (vestibular type of paroxysm) - with a sensation of objects rotating, imbalance, a staggering gait, “unsteady” ground underfoot;
- fainting;
- changes in vision - darkening of the eyes, sensation of “luminous points”, “veil”, loss of visual fields (optical paroxysm);
- short-term loss of orientation and consciousness;
- paroxysmal numbness, weakness, feeling of “pins and needles” in the limbs;
- temporary speech disorder;
- rushes of blood to the head, redness of the face, a feeling of pulsation in the vessels of the head and neck, tinnitus, increased blood pressure;
- sleep disorder;
- attacks of pain in the heart, a feeling of “fading”, palpitations;
- transient pallor and coldness of the hands and feet.
Insomnia during angiospastic crises is characterized by an influx of thoughts.
The first and main symptom of cerebral vasoconstriction is severe pain. It can have varying intensity and localization depending on the area in which the problem arose and how much the lumen of the artery is blocked.
The headache may be throbbing, pressing on the back of the head, temples or eyes, and feel like heaviness or buzzing. Unpleasant sensations intensify in bright light, noise, or if you suddenly stand up from a lying position (or, conversely, bend over while standing or sitting).
In addition, patients complain of:
- dizziness;
- fatigue;
- noise in ears;
- flickering of flies before the eyes;
- weakness, etc.
Symptoms of cerebral vasoconstriction can be expressed to varying degrees. In a chronic process, health problems do not bother patients much and do not always require drug treatment. But with acute spasm, urgent hospitalization is often necessary, since the manifestations are so pronounced that the patient not only loses his ability to work, but may also die.
In addition to the listed symptoms, there may be:
- loss of consciousness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- impaired facial expressions and ability to speak;
- loss of orientation and more.
Such manifestations indicate complete blockage of the vessel and the development of ischemia in this area. In this case, the patient must be immediately examined by a doctor, provide first aid and prescribe examination and treatment based on its results.
| Spicy | Chronic |
| Abrupt development against a background of complete health, symptoms progress rapidly | Violations develop gradually and slowly increase |
| Intolerable headache that does not go away with rest or medication | Headache tolerable, relieved with pills |
| A person loses orientation in space, may lose consciousness, facial expressions and speech are impaired, paresis and paralysis may develop | Concomitant symptoms lead to a gradual decrease in performance, but not to its loss |
| Without medical attention, symptoms worsen and death may occur. | Symptoms go away on their own after resting or taking pills |
Who should I contact for advice?
If heart pain or headaches are not relieved by nitroglycerin, aspirin and other drugs, and do not go away with proper rest and exclusion of provoking factors, you need to be examined by the following specialists:
- therapist;
- cardiologist;
- vascular surgeon;
- neurologist.
Laboratory and instrumental testing is mandatory:
- You need to donate blood, both a general and a detailed analysis, to understand why your heart is cramping or your head hurts.
- Get an ECG and echocardiography.
- Perform a stress electrocardiogram to understand how much stress the heart muscle can withstand and under what conditions pain occurs under the heart, in the sternum, or in other areas that indicate coronary spasm.
- Perform an ultrasound of the venous and arterial vessels to check for the formation of blood clots or plaques in the coronary arteries and other vessels. If pathologies are detected in the lower extremities, treatment should be prescribed immediately. A blood clot or plaque is a threat of blockage of the coronary arteries. Coronary spasm occurs instantly and can lead to myocardial infarction.
- If abnormalities are detected in the coronary artery during a stress ECG, coronary angiography is prescribed, which determines the location and extent of damage to the coronary vessels in which spasm is possible.
After collecting a complete history, the doctor chooses a treatment method to exclude recurrence of coronary artery spasms, angina pectoris, or more serious diseases of the heart and head. If coronary spasm is moderate and primary, drug and dietary treatment is suggested. For serious coronary attacks, surgery is indicated.
What happens in the vessels?
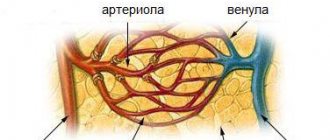
When we talk about the spastic state of blood vessels, we need to clarify that we mean small arterial branches (capillaries, arterioles). They have a smooth muscle wall that contracts according to all laws:
- the receipt of an impulse along nerve fibers or with the help of special hormonal substances in the blood;
- replacement of necessary electrolyte ions (potassium, sodium, calcium), which change the charge of the cell membrane;
- shortening of muscle fibers (contraction).
Violations occur at one or all stages. It cannot be ignored that spasm of the blood vessels in the head can be caused reflexively in response to cold (walking without a hat in winter), pain in the internal organs, and impaired blood supply at the level of the vessels of the neck (carotid, vertebral arteries).
The main cause of cerebral vascular spasm is considered to be improper regulation by the autonomic nervous system. This is most clearly manifested by the symptoms of vasospasm against the background of vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD), a disease of discirculatory disorders. With VSD, spastic contractions are replaced by a sharp dilation (paresis) of the arteries.
There are many diseases that contribute to short-term contraction of arteries:
- damage to cerebral vessels by atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots, the presence of aneurysmal expansion;
- neuroses;
- traumatic injuries of the skull;
- benign and malignant tumors of the brain, pituitary gland;
- hypertension;
- angina attacks;
- changes in the arterial wall with vasculitis, collagenosis;
- endocrine disorders in thyrotoxicosis, obesity, diabetes;
- diseases of the meninges (arachnoiditis, meningitis).
Possible reasons
Spasm of blood vessels in the head (symptoms of cerebral angyl spasm provoke a sharp decrease in performance and can cause loss of consciousness in the patient) is caused by problems in the brain itself or in the cervical spine, cardiovascular, endocrine, renal pathologies or the appearance of neoplasms, but is most often associated with severe fatigue of a person and lack of sleep, causing oxygen starvation in the body.
Severe fatigue and overwork
The human brain gets tired no less than the body itself, and with its long, continuous work and lack of sufficient rest, a deterioration in the general condition of a person occurs, accompanied by impaired cerebral circulation and manifests itself in severe headaches.
In addition to severe fatigue, vascular spasm in the brain is provoked by:
- stressful situations;
- lack of oxygen;
- insomnia;
- age-related changes in blood vessels;
- smoking.
Pathologies of internal organs and systems
The second reason that causes head spasms is hormonal imbalance caused by metabolic failure or the development of cardiovascular and nervous pathologies.
Thus, vascular spasms are characteristic of:
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- hypertension;
- heart failure;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- renal dysfunction;
- diseases of the thyroid gland;
- brain tumors.
In case of cardiovascular, endocrine and renal pathologies, a large amount of the hormones norepinephrine, cortisol, angiotensin is formed in the blood, leading to impaired blood flow.
With vegetative-vascular dystonia, vascular tone is disturbed, causing a deterioration in blood supply and provoking the appearance of oxygen starvation of brain cells.
Other
Spasm of the blood vessels in the head (symptoms of the disease are associated with sudden pain in any part of the head) can be triggered by a simple walk in severe frost without a hat or by drinking a large amount of alcohol. Accompanying cerebral vasospasms and the appearance of strong negative emotions.
The environmental situation is also of considerable importance for the development of pathology, since toxic substances emitted into the air by industrial enterprises and car exhaust negatively affect the condition of the vascular system. In large cities, toxic emissions are supplemented by a lack of oxygen, which stimulates a narrowing of the lumen of the capillaries.
Development mechanism
The basis of cerebral vascular spasm is a violation of neurohumoral regulation. Imbalance of mediators and dysfunction of calcium channels negatively affect the autonomic nervous system, which regulates vascular tone. During an attack, arteries and smaller cerebral vessels contract, and accordingly, blood flow slows down and the brain experiences oxygen starvation. As a result, characteristic symptoms appear, which can be reversible or irreversible.
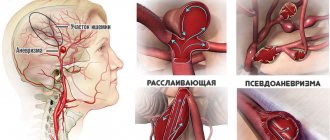
In the first case, the spasm passes without consequences, in the second it is fraught with strokes, encephalopathy, and aneurysm rupture (especially in the presence of blood clots and atherosclerotic plaques).
Prolonged vasospasm during pregnancy can lead to eclampsia, a severe form of gestosis.
Why does vasospasm occur?
Spasm of cerebral vessels can be caused by various reasons. Among them, the most common are the following conditions and pathologies:
- hypertension, atherosclerosis, heart failure;
- congenital anomalies of the vascular wall;
- systemic connective tissue diseases, brain tumors;
- TBI, acute circulatory disorders - strokes;
- neuroses, migraines;
- osteochondrosis of the spine in the neck;
- infections – encephalitis, meningitis;
- liver and kidney diseases;
- birth injuries in newborns.
Persons who abuse alcohol, smoke, or take drugs are also at risk. Due to improper nutrition (overeating, consuming large amounts of fats with quickly digestible carbohydrates), lipid metabolism is disrupted, diabetes and obesity develop.
Angiospasms often occur in mentally unstable people, as well as as a result of psycho-emotional stress. The risk of vascular spasm increases if there is a family history of cerebrovascular diseases, hypertension, and migraines.
At-risk groups
Spasm of blood vessels in the head (symptoms of the disease during overwork can be very pronounced, and are significantly blurred in the case of the development of chronic oxygen starvation caused by impaired capillary tone) several years ago was found mainly in older people, but in recent years the disease has become much younger, increasingly affecting constantly busy residents big cities.
In addition to the older generation, who are faced with the problem of circulatory disorders due to thinning of blood vessels and the appearance of plaques, cerebral angiospasm is often observed in people over the age of 30 who are engaged in mental and intellectual work.
People who are considered most sensitive to the appearance of spasms are:
- those suffering from weather dependence;
- smokers and drinkers a lot;
- those suffering from diabetes;
- having a tendency to form blood clots;
- having a family history of a hereditary predisposition to heart attacks or strokes.
What triggers attacks?
It has been established that the direct “provocateurs” of dyscirculatory disorders of the brain can be:
- poisoning with toxic substances (salts of heavy metals, carbon disulfide, nicotine during prolonged exposure to a smoky room and smoking, drugs);
- intense mental work, overwork;
- strong emotions, stressful situations in life;
- disturbed sleep, night shift work;
- atmospheric changes (magnetic storms, pressure changes, weather changes);
- abuse of tonic drinks (strong tea, coffee, tonics);
- lack of fluid in the body - dehydration with severe sweating, loss with vomiting and diarrhea.
A predisposition to impaired vascular response is inherited in families where there are hypertension, cases of stroke, acute heart attack.
Headache occurs suddenly when you feel well
Consequences
Vascular spasm can be both a cause and a consequence of acute cerebrovascular accidents - hemorrhagic stroke, rupture of an aneurysm. In case of intense pain, loss of consciousness, impaired coordination, speech, you should immediately seek medical help.
A prolonged attack can lead to ischemic stroke with death of brain tissue and disability. In children, prolonged vasospasms can cause further delays in mental development, and in pregnant women - eclampsia. This condition is considered the most severe form of gestosis, fraught with coma, pulmonary edema, and fetal death.
The resulting spasms contribute to:
- fatigue;
- decreased performance;
- deterioration of hearing and vision.
The most severe consequences include the development of stroke. This disease leads to disability or death. Often the patient experiences deterioration in speech and memory loss.
With timely treatment, in 70-80% of cases, mild vascular spasms are reduced and do not lead to the development of severe consequences. Despite the fact that the prognosis is favorable, it is important not to ignore this problem.
Types of spasm according to severity
According to the severity, vascular spastic crises are divided into 3 groups:
- angiodystonic - the mildest form, all neurological symptoms are mild, the condition is quickly restored;
- angiodystrophic - after a crisis, transient cerebral symptoms remain in the form of asthenia (weakness, dizziness), vascular changes in the arterial wall reach the stage of dystrophy;
- cerebral-necrotic - there is a short-term loss of consciousness, mild disturbances in motor activity, speech, vision, vomiting, headache, less often patients complain that “the head is filled with lead”, they feel tinnitus, swelling of the eyelids, blue lips are detected.
In severe cases, microcysts or lacunae form in the brain matter.
Depending on the extent of damage, vascular spasms are divided into:
- generalized (general) - characteristic of hypertension, increased blood viscosity, metabolic changes in the brain, typical connections with symptoms of damage to the heart (coronary-cerebral), liver and pancreas (hepatocerebral), kidneys (renal-cerebral);
- regional (local) - if diagnostics reveals a specific zone of spastic vascular contraction.
For example, spastic crises caused by stenosis of the subclavian and vertebral arteries are accompanied by impaired cerebral and local blood supply (fainting, weakness, changes in the sense of balance, pallor, paresthesia, decreased pulsation in the radial artery, cold feet and hands).
You can also read: Signs of cerebral atherosclerosis
Coronary cerebral spasms are characterized by:
- simultaneous development of hypoxia in the brain and heart;
- manifestations of secondary cardiac disorders (angina attacks, arrhythmia).
During hepatocerebral crises, patients complain of pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, vomiting, and bloating.
Renal cerebral pathology causes severe headache, mild meningeal symptoms, and urinary disorders.
Accurate diagnosis is important for the correct choice of drugs in the rational treatment of the patient's condition.
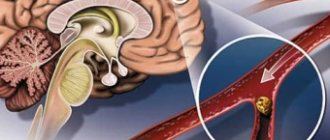
Cerebral vasospasm
Spasm of the anterior cerebral artery
The anterior cerebral artery supplies food to the medial parts of the frontal lobes of the brain, and also supplies part of the parietal lobes, the anterior parts of the hypothalamus and subcortical formations. Therefore, if a spasm occurs here, then the symptoms will be characteristic of insufficient blood supply to these areas. A decrease in blood flow in the anterior cerebral artery can combine quite a few complex symptoms, or can be completely asymptomatic.
The most common symptom of nutritional deficiency in this area is memory problems. Depending on the exact period of nutritional depletion, these amnestic disorders can be either very pronounced, up to almost complete loss of memory, or insignificant, only appearing from time to time. If the frontal lobes of the brain are affected, the patient may experience difficulties with speech, as well as impaired control of activity.
If the blood supply to the basin of this artery is disrupted as a result of cerebral vascular spasm, the patient may have poor orientation in time or place, he may experience emotional instability, decreased criticality and other symptoms characteristic of a mental disorder. The thing is that prolonged fasting of these areas of the brain, as well as the associated hypoxia, does not allow the patient to maintain full mental activity.
Middle cerebral artery spasm
If we are talking about the middle cerebral artery, then when spasm of cerebral vessels manifests itself here, the symptoms of this disease turn out to be somewhat different. The patient has a mixed form of aphasia, and in addition, he begins to experience certain difficulties in motor activity, it is difficult for him to organize movements in space, and he also has problems with vision. If memory impairments are observed, they correspond to those brain zones that fall into the basin of a given artery. It is difficult for the patient to perceive speech addressed to him; he does not understand well what exactly you are asking him to do.
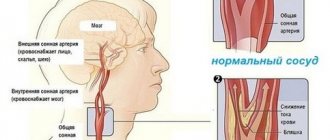
Internal carotid artery
Spasms involving the internal carotid artery, in their clinical picture, resemble spasms of cerebral vessels belonging to the middle cerebral artery basin. This is understandable, since this artery is, in fact, one of the branches of the internal carotid artery. Only the signs of this disorder have somewhat less pronounced symptoms. Apparently, this is due to the fact that disturbances in the internal pine artery system simply do not completely cover those areas of the brain that are controlled by the middle cerebral artery. As for memory impairments, they are almost identical.
As you can see, spasm of each individual cerebral artery has its own set of symptoms. This is understandable, because each part of the brain is responsible for performing its own task. Therefore, an experienced neurologist can only guess based on the totality of the patient’s complaints at what point it is necessary to look for disorders leading to vasospasm. However, all symptoms of cerebral vasospasm must be confirmed by the results of further studies.
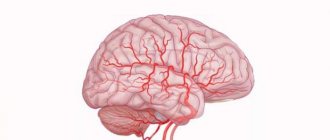
Spasm of cerebral vessels (cerebral vasospasm), that is, their narrowing, occurs when the clearance between the walls of the vessels decreases. There can be many reasons for this, and the consequences can be serious disruptions in the functioning of the body.
Diagnostic methods
There are many ways to treat cerebral vascular spasms at home. In order for the vascular walls to be stronger and retain their elasticity, and for blood circulation to normalize, it is necessary:
- include a large amount of raw vegetables, fruits, and herbs in your diet every day;
- remove fried foods, chocolate, mayonnaise, black tea, coffee, smoked meats, and fatty meats from the menu;
- drink 1.5-2 liters of water daily;
- wash your feet in cold water or use a contrast shower;
- do physical exercise.
Self-massage
It is recommended to do zonal segmental massage during spasm. With relaxed palms they stroke:
- forehead from the bridge of the nose to the temples;
- the back of the head from the neck to the shoulder blades and shoulder joints;
- face from forehead to chin.
Use your fingertips to stroke your temples in a circular motion. After this, the wrist joint is kneaded. To do this, it is wrapped around a ring of the thumb and index fingers of the opposite hand. At the same time, bend and straighten the massaged arm at the elbow. Finally, rub the knee joint with your palms. Massage should be done several times a day for 5 minutes.
Aromatherapy
Aromatherapy helps relieve vascular spasms. The most commonly used essential oils are:
- lavender - reduces headaches;
- mint - activates blood circulation, relieves pain;
- lemon balm - has an antispasmodic effect, relieves chronic headaches;
- basil - improves blood supply to the brain, dilates blood vessels;
- rosemary - normalizes blood flow, relieves dizziness;
- marjoram - has antispasmodic and analgesic effects.
To enhance the therapeutic effect, it is recommended to use a mixture of oils, with 1-2 drops of each component being sufficient:
- lavender, chamomile, lemon - 1:1:1;
- sandalwood, basil, sage - 1:1:2.
Rub the oil into the area that hurts the most, then move on to the neck, back of the head, and temples.
Folk recipes
There are many traditional medicine methods that effectively relieve vascular spasm. The most effective ways:
- Thyme infusion. Take 2 tbsp. l. herbs and pour a glass of boiling water. Leave for 2 hours, filter and add 3 drops of golden mustache plant juice. The infusion should be stored in the refrigerator. Take it 100 g twice a day. To enhance the effect, you can add 1 tsp to the infusion. garlic juice.
- Herbal decoction. To prepare it, take the following herbs in equal proportions: anise, yarrow, valerian, motherwort, brew as tea and consume 2-3 times a day, 100 g.
- Compress. Take 1 tbsp. l. St. John's wort, dandelion, plantain. Pour a glass of boiling water, cool and put in the refrigerator. A cloth bandage is moistened in a cold infusion and applied to the forehead in case of severe pain.
Treatment with folk remedies for spasms of blood vessels in the head and neck is recommended only after consulting a doctor.
In case of a mild course of the disease, the diagnosis is made based on the exclusion of other most severe brain diseases, because changes in the blood vessels cannot be detected after spontaneous relief of the spasm.
Neurologists and angiosurgeons use for examination:
- duplex scanning of the intracerebral and brachiocephalic branches of the cerebral arteries, it is possible to register the consequences of frequent vascular spasms in their moderately severe course;
- MRI of vessels;
- computed tomography of the brain.
If the above methods are not possible, contrast radiography is performed.
Dopplerography of blood vessels allows us to detect the slightest damage to the walls
Lifestyle and prevention of cerebral vasospasm
It is important to establish proper nutrition and monitor your weight. It is best to eat whole grain porridge in the morning, regularly eat seafood at lunch, and be sure to eat a lot of different vegetables. It is worth limiting the consumption of fatty dairy products and keeping the amount of sweets to a minimum.
Doctors usually recommend avoiding fatty foods, fried, smoked and canned foods. It is better to replace strong tea and coffee with herbal infusions that will help, for example, rose hips, nettle, St. John's wort. It is worth giving up carbonated drinks, especially since they harm not only blood vessels, but the entire body. But you definitely need to provide yourself with a sufficient amount of fluid (at least 2 liters per day). This will help avoid stagnation in blood vessels and the accumulation of harmful substances.
Many folk remedies help improve blood circulation and perfectly tone the walls of blood vessels, especially when used regularly.
A popular remedy for cleaning blood vessels and strengthening them is garlic. It is crushed to a pulp and poured with vegetable oil (1 head of garlic per 200 ml of oil), after 24 hours add 1 teaspoon of lemon juice. Take 1 teaspoon in the morning. The course lasts 3 months.
Physical activity always helps strengthen blood vessels and maintain their tone. This activity can be anything depending on what a person likes to do: dancing, walking or cycling, swimming, fitness, yoga. Avoiding mental overload, controlling stress levels and getting proper rest will greatly help the blood vessels cope with their functions normally.
General practitioner, candidate of medical sciences, practicing physician.
I have wild pains in my head. I used to think that I had ICP. And now they tell me that my cramps are due to problems in my neck...
After giving birth, I began to experience frequent cramps. Constant lack of sleep, stress and chronic fatigue due to the difficulties of motherhood. Sometimes I use the methods described above to reduce spasms: foot bath, massage, water with honey. I didn’t go to the doctor, but breastfeeding women shouldn’t take medications anyway. I hope the baby grows a little and it will be easier.
The narrowing of the lumen inside the vessel is a spasm that disrupts blood flow and leads to unpleasant symptoms. Vascular angiospasm occurs when the arteries contract. Causes, symptoms, treatment - everything is known to a neurologist, to whom a person turns with complaints of headaches and dizziness.
The lumen inside the vessels narrows due to frequent contraction of the artery walls.
The main reasons are:
- frequent overwork when working at the computer, causing the head to get tired, the blood supply to the brain is disrupted due to an uncomfortable tilt of the head to the monitor;
- lack of sleep, the brain needs proper rest;
- oxygen deficiency;
- smoking, in people who smoke, the likelihood of vasospasm of cerebral vessels increases due to the penetration of nicotine and harmful substances from cigarettes into the brain tissue.
Prolonged headaches, fatigue and loss of attentiveness are not at all harmless symptoms. Especially…
What should be changed
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor will require the patient to change their lifestyle and give up harmful habits:
- it is necessary to stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- be sure to arrange outdoor recreation, evening walks;
- do morning exercises, try to master yoga and self-hypnosis techniques;
- do not allow long breaks in your diet, ensure you drink plain water (up to 2 liters per day), stop abusing strong coffee and tea, replace them with herbal teas with mint and lemon balm, dried fruit compote;
- in the diet to restore the tone of the vascular wall, you need porridge (from cereals, not flakes), raw fruits and vegetables, seafood (fish, plants), lean meat, dairy products, hard cheeses. You will have to limit spicy snacks, fried and fatty meats, cakes, and carbonated drinks.
Compliance with the regime often allows young people to get rid of the manifestations of pathology and restore proper regulation of vascular tone. If clinical manifestations occur against the background of other chronic diseases, then you will have to additionally use drugs that affect cerebral circulation.
Treatment of cerebral arterial spasm
Treatment methods for vascular spasm are related to the main causes of the pathology and diseases leading to its occurrence.
- In the treatment of hypertension and atherosclerosis, antihypertensive drugs and drugs to reduce the level of low molecular weight cholesterol fraction (statins) are important.
- To relieve vasospasm, tablets from the group of calcium antagonists (Corinfar, Adalat) are used.
- To relieve pain in severe headaches, the following are used: Eufillin, Papaverine, No-shpa, Papazol. The doctor will recommend use in the form of injections or orally.
- Sedatives such as motherwort tincture, valerian or stronger drugs (Seduxen, Relanium) normalize the vascular reaction.
- To influence metabolic processes in brain tissue, a group of nootropics (Nootropil, Piracetam) is used, Trental is prescribed.
- Cavinton, Cerebrolysin, Actovegin have vasotonic properties.
- According to the patient's indications, it is possible to recommend medications to improve the adaptive response to the environment (tinctures of aralia, ginseng, eleutherococcus, lemongrass).
- You need multivitamins with microelements or separately nicotinic acid, vitamin E, group B.
Patients are recommended physiotherapeutic treatments and massage. People get a good and long-lasting effect after staying at resorts. Especially if a climatic zone, natural stimulants in baths and mud applications, and mineral waters are used.
Possible complication in the form of arterial thrombosis after spasm
The development of a disorder can be suspected based on certain symptoms. In this case, it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible.
Cerebral vasospasm manifests itself unexpectedly, and its symptoms arise abruptly; it can be distinguished from other types of cerebral spasms by the duration of the symptoms. The symptoms do not disappear for several days and become more intense.
Deviations in the blood flow of the brain appear externally in the following signs (the manifestation of one or another sign depends on the location of the hemorrhage):
- muscle weakness in the half of the body, which is opposite to the hemisphere with intracerebral hemorrhage;
- speech disorders;
- recognition problems;
- delayed reaction;
- visual field defects;
- nausea;
- numbness of the limbs.
These symptoms are not unique and may indicate the presence of other diseases. Vasospasm of the vessels of the head can be identified and diagnosed only based on the results of the examination.
Symptoms
Symptoms of spasm of blood vessels in the head develop rapidly, manifesting themselves as severe migraines caused by poor circulation and occurring in any part of the head.
In addition to headaches, the following are also observed:
- dizziness;
- increased fatigue and impaired performance;
- the appearance of “flies” before the eyes;
- tinnitus that gets worse after any physical activity;
- nausea accompanied by vomiting.
In severe cases, the following symptoms are added to the listed symptoms:
- speech disorder;
- memory losses;
- loss of orientation;
- clouding of consciousness and fainting;
- incoordination of movements.
Angiospasm, as a rule, develops sharply, indicating a severe headache, but can develop into a chronic stage, accompanied by milder symptoms, but fraught with its own possible complications. The most dangerous of them is considered to be ischemic stroke, which occurs when the blood vessels are completely blocked and provokes the death of brain cells.
In addition to adults, cerebral vasospasm can also be observed in young children, causing mental retardation, blindness, deafness and neuropathy.
How to relieve an attack at home?
To quickly relieve an attack at home, distracting reflex procedures are used:
- warm herbal tea with honey;
- washing with cold water or ice;
- cold foot baths for 10 minutes;
- massage in the temporal region, in the “collar” zone of the cervical spine.
Healthy:
- rub your forehead and temples with “Star” ointment;
- take 20 drops of Corvalol or valerian tincture;
- Chew and swallow one tablet of Aspirin, Ibuprofen, Spazgan.
In case of repeated attacks, you should consult a doctor and undergo a full examination. This is the only way to find out which treatment can really help.
To provide first aid to the patient and help quickly relieve spasm before visiting a doctor, you must:
- wash it with cold water;
- provide access to fresh air;
- make foot baths with cold water for 10 minutes;
- give warm tea;
- put the patient in a horizontal position and ensure him peace;
- Gently massage the collar area, neck, temples.
The following drugs can be given:
- painkillers - Tempalgin, Ketanov, Analgin;
- antispasmodics - Andipal, Spazmalgon, No-shpu, Papazol;
- Nitroglycerin or Validol;
- sedatives - Valerian, Corvalol.
If the headache lasts for a long time and is not relieved by medications or other methods, you should urgently seek medical help.
Folk recipes
Complete treatment of vasospasm
Treatment of vasospasms begins with examination. The doctor must identify the cause of their occurrence and select the appropriate technique, which is individual for each patient. Most often, this requires a full examination and diagnosis of the condition of the blood vessels. In many clinics, diagnosis includes duplex scanning, measurement of oxygen tension through the skin, and ultrasound diplerography.
Treatment of vascular spasms in the extremities (arms and legs) is carried out by applying a weak electric current to the affected areas. A two-week course of treatment includes daily procedures lasting no more than twelve minutes. If the disease begins to progress, necrosis may occur on the skin and small ulcers may appear. In this case, the doctor carries out additional treatment in the form of applying wound-healing and anti-inflammatory ointments to the diseased areas.
Treatment of spasms is long-term. It can last for more than one year. However, it happens that spasms cannot be controlled with medication. In this case, a surgical operation called sympathectomy is used. It is aimed at clipping the nerve fibers of the sympathetic trunk with a medical clip. In some cases they are removed. In addition to this, a number of auxiliary techniques are used, for example, plasmapheresis.
Antispasmodics (vasodilators) are used in treatment. At home, for vascular spasm, you can take a tablet of no-shpa, papaverine, dibazole or papazole.
Folk recipes
Traditional recipes are applicable in cases of vasospastic symptoms. The recommendations do not differ in the mechanism of action from medical guidelines.
The famous recipe of garlic, honey and lemons is undoubtedly recommended for everyone, as it has a positive effect on the blood vessels, immunity and mood of the patient.
For herbal tea, rose hips, nettle leaves, mint, lemon balm, currants, and lingonberries are recommended.
Diagnosis and treatment measures for spasm of cerebral arteries will help prevent serious consequences in the form of early stroke, thromboembolism and cerebral infarction. In children, this pathology causes delayed general and mental development, persistent migraine attacks, decreased vision and hearing. Timely consultation with a doctor allows you to avoid irreparable damage to your health.