Glycine is prescribed for epilepsy as an adjuvant in combination with anticonvulsants. It enhances their effect and reduces the risk of adverse reactions. There is evidence that it is possible to prevent a seizure attack if you dissolve the tablet at the first symptoms.
For course use, adults are prescribed 1-2 pieces 3 times a day, newborns and children up to one year old, 0.5 tablets 2-3 times a day, and from 3 years old and adolescents, 1 piece 3-4 times a day. Glycine improves memory, sleep, mental performance, mood, and learning ability. It has low toxicity and is contraindicated only in cases of intolerance and low blood pressure.
Is it possible to take
Sometimes there are conditions that cannot be eliminated without the use of antibiotics.
For example, bronchitis that is not treated in time can result in pneumonia, and an associated bacterial infection will lead to serious consequences.
Epilepsy does not negate antibiotic therapy, but there are some drugs whose use is unacceptable.
If the doctor, knowing about the diagnosis, prescribed an antibacterial drug that raises doubts, then you cannot cancel it yourself.
You can see another doctor and get additional tests. After which, the doctor can review his prescriptions and change the list of medications.
You cannot select medications for the treatment of bacterial diseases yourself.
Surgery
Epilepsy is sometimes treated with surgery to eliminate the cause of epileptic seizures. However, when diagnosed with cryptogenic epilepsy, the patient usually does not have specific hematomas, traumatic or congenital structural disorders, neoplasms, or vascular malformations that can be corrected through surgery.
And if surgical pathologies are detected, then the diagnosis is specified. It is cryptogenic epilepsy that cannot be treated surgically.
Effect on the body of an epileptic
After the invention of such drugs, debates about the need for their use in one case or another continue.
The intestines of any person contain at least 2 kg of various beneficial bacteria, which play a vital role in maintaining immunity and normal digestion. Antibiotics are designed to destroy all bacteria, including beneficial ones.
People suffering from seizures need to take medications that have a minimum of contraindications and adverse reactions.
The most common negative effects are considered to be possible allergic manifestations, toxic damage to the kidneys and liver, and weakened immunity.
In addition, some drugs from this series have a strong effect on the nervous system and hematopoiesis, which is a direct contraindication.
Epilepsy pills: list of anticonvulsants
Epilepsy is caused by disorders of the brain. The treatment is carried out by a neurologist. Only the doctor chooses the appropriate medicine, based on the diagnostic results, symptoms, and characteristics of the attacks. Anti-epilepsy pills help control the course of the disease, reduce the number of seizures and their intensity.
Self-medication is dangerous, especially when it comes to brain disease. You need to know about the types of medications and how to take them in order to:
- Be confident about the need to take medications.
- Confirm the competence of the attending physician and the adequacy of the prescribed therapy.
Groups of drugs for epilepsy
Purpose of drug treatment:
- Minimize the number of attacks.
- Help the patient recover from a seizure.
- Bring the processes of excitation and inhibition back to normal.
The doctor strives to select for the patient one universal drug that is suitable for a specific type of disease and has minimal side effects.
Groups of drugs for epilepsy
List of drugs
Medicines for epilepsy are divided into 2 lines:
- Basic list: the tablets are safe and have shown high effectiveness in treating patients.
- Prescribed as a short course when the remedies from the first level have not helped.
| 1 line | 2nd line | ||
| Pills | Action | Pills | Action |
| Primidone, Phenobarbital | Anticonvulsant, does not depress the central nervous system, does not cause drowsiness. | Diakarb | Diuretic, inhibits pathological excitability. |
| Lamotrigine | Blocks the release of glutamic acid and prevents seizures. | Sabril | Strengthens inhibition processes in the brain |
| Benzobarbital | Reduces the permeability of nerve fibers to sodium ions, prevents the development of stroke from an epileptic focus. | Seduxen | Relieves cramps, calms, hypnotic effect |
| Convulex | Reduces the excitability of brain areas, improves mood and mental state. | Freesium | Tranquilizer. |
| Phenytolin | Bioelectric stabilizer, anticonvulsant drug for epilepsy. | ||
| Ethosuximide | Reduces the frequency of seizures | ||
| Carmabazepine | A psychotropic drug that reduces the manifestation of depression, reduces aggression and anxiety. | ||
| Keppra | Anticonvulsant |
Anticonvulsants for epilepsy
This group of tablets affects the brain in different ways. To understand chemical and metabolic processes you need to have a medical education. The general meaning is simple: prevent the onset of an attack, reduce its severity.
Drugs for the treatment of epilepsy are taken for a long time, sometimes for a lifetime. Level 1 anticonvulsants do not cause drowsiness or delayed reactions. Despite their apparent safety, it is prohibited to prescribe them independently; violation of the dosage or combination of drugs leads to complications and death.
For the treatment of epilepsy, drugs are sold by prescription, some categories of patients are given free of charge, the cost is paid by the state.
Treatment regimens
Drug treatment is carried out:
- As monotherapy.
- Combining medications.
The attending physician, based on symptoms, diagnosis and other factors, prescribes tablets and recommends a minimum dose. If the effect does not occur, the dose is increased. In case of intolerance, intense side reactions, or lack of positive dynamics, the medication is changed to another.
Combining drugs is used in cases where:
- Epilepsy is accompanied by mental illness and damage to the nervous system.
- No remedy, taken alone, helps.
Each type of tablet provides a separate dosage regimen, indicating the minimum and maximum allowable doses.
Drugs for minor seizures
If the disease manifests itself rarely, in the form of small convulsive seizures, the doctor decides to postpone the prescription of complex antiepileptic pills. In these cases it is recommended:
- Glycine. It is allowed for young children and improves brain function.
- Trimethine. Has a cumulative effect. Can be used for a long time.
- Anticonvulsant. Use with caution if the patient has had mental problems. These tablets are also used in combination therapy.
Medicines by injection
The injection is given into a muscle or intravenously. Used in rare cases:
- To relieve a severe attack.
- When a person is not aware of his actions (mental illness, etc.)
The injection is given by ambulance workers and nurses. In this case they use:
After improvement, the patient continues taking the drug in tablet form.
Treatment of epilepsy in children
The children's nervous system is not fully formed. Epilepsy at a young age occurs with frequent seizures, which must be stopped quickly and safely. Some tablets suppress breathing, so their administration to children should only be done under the supervision of a doctor. These drugs include barbiturates.
Benzodiazepines do not affect breathing, so they are used in pediatrics.
Epilepsy in children is more severe than in adults, but is more often treatable.
What drugs should not be taken for epilepsy?
Contraindications can be absolute and relative. Relative ones allow use, but in extreme cases, under the supervision of a doctor. Absolute – a complete ban.
Drugs with absolute contraindications:
- Ketamine.
- Baclofen.
- Carbamazepine.
- Triazopam.
- Nitrazepam.
- Etaperazine.
- Levomeprozine.
- Baclofen.
- Pipothiazine.
- Chlorprothixene.
- Meprotan.
- Azaleptin
- Eulithiracoc
- Schisandra tincture.
The list includes more than 20 medications. In addition, new drugs appear in pharmacies, so read the instructions before taking the medicine. Even if the pills were prescribed by a doctor, if they are contraindicated for epilepsy, seek advice again.
Interaction with antiepileptic drugs
There are many drugs whose combined use with anticonvulsants is contraindicated.
Some antiepileptics (Carbamazepine, Diphenin, Benzonal) cannot be taken together with any antidepressants and antipsychotics. This leads to depression of the nervous system and a decrease in the effectiveness of anticonvulsants.
It is important to know that drugs against seizures cannot be taken together with Levomycetin, Butadion, Suxilep, Teturam, or anesthesia.
A particularly severe reaction is caused by the combination with the anti-tuberculosis drug Isoniazid. If co-administration cannot be avoided, the dosage of anticonvulsants is significantly reduced.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
The treatment regimen for epilepsy uses general physiological procedures that have a calming effect on the central nervous system. The purpose of such procedures is to reduce the excitability of nerve cells in the brain, normalize cellular metabolism, and remove excess fluid.
Ultraviolet irradiation, soothing baths, wet wraps, medicinal electrophoresis with calcium, magnesium, and sedatives may be prescribed.
Acupuncture and therapy according to the Voight method are used (a kind of therapeutic exercises combined with massage), which allows you to restore motor functions and reduce the number of seizures. The latter method is used to treat patients from a very early age; adult patients also show good results.
Physiotherapeutic treatment helps to restore impaired functions of the central nervous system faster and better; however, it is impossible to cure epilepsy using physical methods alone.
Indications for use
Antimicrobial agents should be prescribed by a doctor based on the examination.
If the diagnosis of epilepsy is confirmed, then their use must be combined with anticonvulsants.
When using antibiotics, it is important to know when to take them.
The main indications for antibiotic therapy are:
- infections of the urinary and digestive systems;
- tuberculosis;
- pulmonary bacterial infections;
- ENT infections;
- anaerobic, intestinal infections.
Only a specialist can determine the need to use antibiotics.
In each specific case, certain medications are used that can be used for neuropsychiatric disorders.
Contraindications and side effects
There are several types of antibacterial drugs, differing not only in area of application, but also in class, group and type.
There are several most common groups:
- cephalosporins;
- quinolones;
- macrolides;
- sulfonamides;
- tetracyclines;
- nitroimidazoles:
- penicillin.
Cephalosporins are broad-spectrum drugs and are divided into five generations.
Direct contraindications include not only epilepsy, but also allergies, which cause severe allergic manifestations and gastrointestinal lesions.
Quinolones are not used for a history of epileptic seizures, allergies, or for the treatment of children.
Tetracyclines also cannot be taken for convulsive syndrome, and their side effects are standard, like cephalosporins.
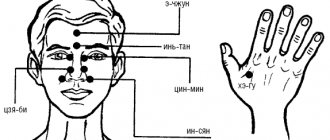
How to take Glycine for epilepsy in adults
Place one tablet under the tongue.
The standard regimen for taking Glycine for epilepsy in adults is 1-2 tablets 3 times a day for a month. Then they take a break for 2-3 weeks and repeat the course. The doctor may also recommend an individual regimen of use. It is important to take into account that the tablets dissolve, they cannot be chewed or simply washed down with water, since it is necessary for the drug to be absorbed in the oral cavity. Therefore, you should put one tablet under the tongue or behind the cheek and wait until completely dissolved.
Allowed list
When it becomes necessary to use antimicrobial tablets or injections, it is important to tell your doctor about concomitant diseases.
He must know everything about the frequency of attacks, the time and duration of the last attack.
Based on the survey, examination and test results, he can recommend a specific drug.
Allowed:
- lincosamides (Lincomycin, Clindamycin);
- macrolides (Erythromycin, Linkosamine, Azithromycin, Clarithromycin, Josamycin, etc.);
- nitroimidazoles (Metronidazole, Ornidazole).
As for others, the decision to prescribe should be made by the doctor. If you have the slightest doubt about the correctness of the recommendations, you should consult several specialists.
Is it possible to take
Sometimes there are conditions that cannot be eliminated without the use of antibiotics.
For example, bronchitis that is not treated in time can result in pneumonia, and an associated bacterial infection will lead to serious consequences.
Epilepsy does not negate antibiotic therapy, but there are some drugs whose use is unacceptable.
If the doctor, knowing about the diagnosis, prescribed an antibacterial drug that raises doubts, then you cannot cancel it yourself.
You can see another doctor and get additional tests. After which, the doctor can review his prescriptions and change the list of medications.
You cannot select medications for the treatment of bacterial diseases yourself.
Traditional treatment
There are many traditional medicine recipes for epilepsy or falling sickness. People have always tried to get rid of this serious disease and came up with different methods.
For example, to stop an epileptic seizure, it is recommended to cover the patient with a black woolen cloth (blanket, rug). The main thing is that the patient does not realize that at the time of the attack they are doing this to him. If you cover it regularly, the attacks should go away within a year.
Another way to relieve a generalized epileptic seizure: when the patient has fallen, it is recommended to step on the little finger of his left hand.
At least these methods are exactly compatible with drug therapy and do not even require prior consultation.
Traditional healers also recommend that epileptics fast for three days out of ten or switch to a raw food diet. It is not clear how fasting can be combined with proper nutrition, especially so often. But eating more raw vegetables and fruits is clearly good advice.
For epilepsy, it is recommended to apply a compress to the spine. To do this, mix equal parts olive oil and wax, melted together with the honey that was in it. A long piece of fabric is soaked in this mixture, placed along the entire length of the spinal column and attached with frequent transverse strips of adhesive tape.
Treatment with egg injections. Take a fresh fertilized chicken egg, wash and wipe the shell with alcohol. Beat the egg into a sterilized jar (250-300 ml volume). While stirring the egg, gradually pour in 150 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution, purchased at the pharmacy. Mix well until smooth, draw into a syringe and give an intramuscular injection.
A single dose of the drug is for patients 13 years of age and older - 5 ml, infants are given 0.5 ml, at one year of age - 1 ml, two to three full years - 1.5 ml, 4-5 full years - 2 ml, 6-7 full years - 3 ml , 8-9 full years - 3.5 ml, 10-12 full years - 4 ml. Injections are given once a week, on the same day and time.
This recipe is based on the technique of Dr. G.A. Kapustin. The living substance from the egg (literally taken out from under the chicken and applied immediately) is a powerful immunostimulant that helps in cases of incurable diseases. Even in advanced cases. To this we can add that in China and Japan, quail eggs are used to treat incurable diseases.
Despite all its effectiveness, it is better not to carry out embryonic therapy at home; there are clinics that provide courses of such treatment. The body's reaction to the introduction of a foreign protein is unpredictable, usually the temperature rises (for some, up to 37.5℃, and for others, up to 41℃).
Much safer is herbal treatment. For example, you can undergo the following course of treatment.
We prepare a collection from dried and crushed plant materials:
- one and a half parts each of lemon balm, peppermint, elecampane root;
- three parts each of woodruff and sweet clover;
- four parts of hop cones.
Stir and brew two tablespoons of the mixture in a thermos overnight with boiling water (500 ml). In the morning, strain and drink 2/3 cup of warm infusion half an hour before three meals. Along with the infusion, you need to take ½ teaspoon of pollen. At the same time, you need to drink another infusion of branches and leaves of black currant, bird cherry, and rose hips.
Both fresh and dry leaves are suitable. The branches are finely chopped, the leaves are crushed. The components are mixed in equal parts. Fill a three-liter kettle with this mixture, pour boiling water, close the lid and wrap for four hours. Then drink one and a half glasses of infusion six times a day (every four hours). The children's dose is half as much. The treatment is long-term, up to a year, but effective.
You can collect and dry the leaves of the parasitic mistletoe plant. They are brewed in the following proportions: a liter of water per 10 tablespoons of crushed dry leaves. Boil over low heat for 10 minutes. Strain. You need to soak an old linen sheet in the broth. Squeeze it lightly, wrap the patient, put him in a bed covered with oilcloth, cover him and let him sleep until the morning (until the sheet is dry). The procedure is repeated for a long time, until a long-term remission occurs.
[1], [2], [3], [4], [5], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10]
Effect on the body of an epileptic
After the invention of such drugs, debates about the need for their use in one case or another continue.
The intestines of any person contain at least 2 kg of various beneficial bacteria, which play a vital role in maintaining immunity and normal digestion. Antibiotics are designed to destroy all bacteria, including beneficial ones.
People suffering from seizures need to take medications that have a minimum of contraindications and adverse reactions.
The most common negative effects are considered to be possible allergic manifestations, toxic damage to the kidneys and liver, and weakened immunity.
In addition, some drugs from this series have a strong effect on the nervous system and hematopoiesis, which is a direct contraindication.
Antibiotics cause seizures in an unclear way
May 25, 2020 at 04:53 pm Medicine
Scientists from St. Petersburg studied the effects of cephalosporin antibiotics, widely used in hospitals, on brain activity.
They were able to refute assumptions about the causes of side effects in patients, such as epileptic seizures.
The study, the results of which were published in the journal Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, was supported by a grant from the Russian Science Foundation (RSF).
Among antibacterial drugs, one of the leading positions is occupied by cephalosporin antibiotics. They affect a wide range of bacteria and easily penetrate tissue, so they are often used in hospitals, but can sometimes cause epileptic seizures in patients.
Such seizures are a fairly common occurrence, accounting for about half of all possible side effects of cephalosporins. Now doctors cannot effectively predict their occurrence, and the arsenal of methods to combat them is limited.
However, even one epileptic seizure can lead to very serious long-term consequences, to the point that the patient may develop regular unprovoked spontaneous seizures - epilepsy as such.
Neurons in the brain continuously receive various input signals, which, to a first approximation, can be divided into two main types: excitatory and inhibitory.
Inhibitory inputs have the opposite effect: they make the neuron less likely to transmit its signals to others.
During an epileptic attack, as a rule, brain neurons receive many excitatory signals, but few inhibitory ones. The inhibitory signal in the brain is transmitted using gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which, when acting on a neuron, binds to its GABA receptors.
Some chemicals can bind to GABA receptors on neurons and interfere with their normal functioning. They either prevent GABA from binding to the receptor or prevent inhibitory input from occurring after the receptor binds to GABA.
Once in the nervous system, such substances can provoke epileptic seizures. Some drugs, for example, cephalosporin antibiotics, have a similar property.
It was assumed that it is for this reason that the use of cephalosporins quite often provokes seizures in patients who are prescribed these drugs.
“In our work, we investigated the ability of cephalosporin antibiotics to interfere with the normal functioning of GABA receptors in the brain and provoke epileptic seizures in vitro,” says one of the study authors Dmitry Amakhin from the Institute of Evolutionary Physiology and Biochemistry named after I.M. Sechenov RAS. — For the study, we took the two most commonly used cephalosporin antibiotics: cefepime and ceftriaxone. We prepared thin slices of rat brain and analyzed how the inhibitory signals received by neurons change under the influence of selected cephalosporins. It is known that under certain conditions, even in a thin slice of the brain, activity resembling epilepticism can be provoked. We used this feature to study the proepileptic effect of cephalosporins."
It turned out that in order to significantly affect the inhibitory input signals received by neurons of the entorhinal cortex, very high concentrations of cephalosporins are needed.
Cephalosporins had a noticeable effect on the inhibitory signal at concentrations almost 100 times higher than those that are actually achievable in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients or experimental animals.
These results indicate that, apparently, in vivo (in a living organism) there are some as yet unknown mechanisms that are triggered by cephalosporin antibiotics and lead to epileptic seizures, and blocking GABA receptors may have nothing to do with it. Scientists were also able to show that cefepime and ceftriaxone block GABA receptors in different ways. Cefepime prevents GABA from binding to the receptor, while ceftriaxone leads to a decrease in the effect of binding.
It is known that the likelihood of seizures after taking cephalosporins in patients with renal failure is significantly higher.
Very often, renal failure can be accompanied by an increased concentration of potassium ions and a decreased concentration of magnesium ions in various body fluids.
Scientists have found that with certain disturbances in the ion balance, cephalosporins are much more effective in causing epileptus-like activity in the brain slice.
In the future, scientists plan to describe the patterns of development of these epilepsy-like conditions and how the process of signal transmission between neurons changes during attacks.
“It may be possible to identify some previously unknown factor leading to the development of seizures due to the use of cephalosporins,” Amakhin sums up.
“We hope that our results will provide a better understanding of the mechanisms of abnormal synchronization of neuronal activity during an epileptic seizure.”
Did you like the material? Add Indicator.Ru to “My Sources” of Yandex.News and read us more often.
Send press releases about scientific research, information about the latest published scientific articles and conference announcements, as well as data on grants and awards won to [email protected]
Source: https://indicator.ru/medicine/antibiotiki-sudorogi-25-05-2018.htm
Indications for use
Antimicrobial agents should be prescribed by a doctor based on the examination.
If the diagnosis of epilepsy is confirmed, then their use must be combined with anticonvulsants.
When using antibiotics, it is important to know when to take them.
The main indications for antibiotic therapy are:
- infections of the urinary and digestive systems,
- tuberculosis,
- pulmonary bacterial infections,
- ENT infections,
- anaerobic, intestinal infections.
Only a specialist can determine the need to use antibiotics.
In each specific case, certain medications are used that can be used for neuropsychiatric disorders.
Find out more about epilepsy treatment:
- popular prescribed drugs, including Cortexin, Pantogam and Mexidol,
- the effectiveness of taking magnesium, folic acid and glycine,
- therapy with folk remedies, diet, gymnastics and massage at home,
- surgical methods of treating the disease.
Effective medications for epilepsy
Many people have heard about epilepsy, but not everyone understands what kind of disease it is, why it occurs and how it progresses. In most cases, we imagine an epileptic attack when a person convulses and foam comes out of his mouth.
However, such phenomena are only a small part of the possible options for the development of the disease, because there are many manifestations of such a pathological condition.
Many patients can live without seizures at all, as long as they take their epilepsy medication promptly and undergo regular testing.
This disease has been known for a long time. Epilepsy is perhaps one of the oldest forms of brain diseases, which was recognized and tried to be treated with traditional methods hundreds of years ago. For a long time, people suffering from this pathology preferred to hide their diagnosis. This often happens today.
What it is
People have been familiar with epilepsy for a long time: even the ancient Greek healers associated epileptic seizures with the world of the gods and believed that this illness was sent to them because of the unworthy way of their existence.
In 400 BC, the outstanding ancient Greek physician and philosopher Hippocrates described this phenomenon.
He believed that the cause of epileptic seizures was natural conditions that could provoke liquefaction of the brain.
In the Middle Ages, this disease was feared, believing that it was transmitted from a patient during an epileptic seizure. Meanwhile, they were in awe of her, since many saints and prophets suffered from such an illness.
Modern medicine has proven that epilepsy is a chronic brain disease, characterized by regularly recurring seizures. This is a very common disease, affecting about 50 million people worldwide, which is approximately 1% of the total population of the planet.
How does the disease appear?
Many patients wonder what caused the onset of the disease, because this is a dangerous condition and requires mandatory medical supervision. Medicine identifies three main groups of factors that can lead to the development of the disease:
- Idiopathic (genetic predisposition). Even after tens of generations, the disease can be transmitted. In this case, there are no organic defects or damage in the brain, but there is a certain reaction of neurons. With this form of pathology, an epileptic attack can begin without a reason.
- Symptomatic. The disease can appear after injury, intoxication or tumor processes in the brain. This form of epilepsy occurs spontaneously, and a seizure can occur unpredictably.
- Cryptogenic. A little-studied factor, the exact cause of which has not yet been established. A seizure can occur due to any psycho-emotional stimulus.
The disease can manifest itself at any age, however, according to statistics, epilepsy is more likely to affect young children, adolescents and adults over 60 years of age. To date, medicine has identified about 40 different types of epilepsy.
Therefore, the treating doctor must carry out an accurate diagnosis to establish the form of the disease and determine the nature of the seizures. The effectiveness of the results in certain cases depends entirely on the adequacy of the choice of antiepileptic drug and the prescription of the treatment regimen.
If treatment is untimely or inadequate, the patient may die. Therefore, a full examination of the patient and an accurate diagnosis of the disease is necessary.
A spontaneous attack can occur due to hormonal changes in the body, alcohol intoxication, or the appearance of flickering and flashing images while driving a car.
Examinations and treatment
If epilepsy is suspected, the patient is thoroughly examined. First of all, the patient is examined by a neurologist and studies the history of the disease, including family history. The patient is prescribed the following tests:
- blood;
- fundus;
- X-ray of the skull;
- Dopplerographic study of cerebral arteries.
It is mandatory to visualize the structure, functions and biochemical characteristics of the brain using X-ray, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Hours of electroencephalography (EEG) are of great importance in diagnosing the disease.
Such laboratory studies are aimed at determining the true causes of the disease and excluding pathologies that can cause seizures, but are not associated with brain diseases.
The main effect on epilepsy is medications.
The result of medical care in the treatment of pathology depends both on the correct selection of medications and on the patient’s compliance with all doctor’s recommendations.
The principle of medical intervention is an individual approach to each patient, continuity and duration of treatment. Antiepileptic therapy will be effective if:
- early onset of exposure to the manifestation of characteristic symptoms with antiepileptic drugs;
- desire for monotherapy;
- the correct choice of medication for epilepsy, depending on the type of attacks of a particular patient;
- if necessary, introduction of a rational combination of polytherapy (if there is no effect from the use of one drug);
- prescribing appropriate medications in dosages that provide complete therapy;
- taking into account the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of prescribed drugs;
- monitoring the presence of antiepileptic drugs in the patient’s body.
Epilepsy medications cannot be stopped at once. They should be taken until complete relief from pathological manifestations is obtained.
Only in cases of individual intolerance to the components of the drug, allergies, or in the event of side effects, gradual withdrawal of the drug is necessary. Doses of drugs for the treatment of epilepsy are gradually reduced.
If the doctor decides that the therapy does not bring the desired result, then new medications are also gradually introduced.
It has been proven that almost all patients newly diagnosed with epilepsy can completely control the occurrence of seizures with the help of antiepileptic drugs. After 2-5 years of full treatment, most patients can stop treatment without the risk of relapse.
Drug groups
Achieving optimal results in the treatment of epilepsy is largely determined by the correct calculation of the dose and duration of treatment. Depending on the symptomatic manifestations, the names of recommended drugs may belong to different groups of drugs:
- Anticonvulsants. Drugs belonging to this group of drugs help relax muscle tissue. They are often recommended for the treatment of various forms of epilepsy. Such drugs can be prescribed to both adults and children in the presence of tonic-clonic and myoclonic seizures.
- Tranquilizers. The purpose of drugs in this group is to relieve or suppress nervous excitability. They help in the fight against the manifestations of minor seizures. However, such drugs are used with caution, since at the beginning of use they can aggravate the severity of the disease.
- Sedatives. Not all epileptic seizures end well. Often, immediately before or after a seizure, the patient falls into severe depressive states, becomes irritable or aggressive. Sedatives in combination with a visit to a psychotherapist can calm and relieve such symptoms.
- Injections. Used for twilight states and affective disorders. Injections of nootropic drugs (Actovegin, Cerebrolysin, etc.) have proven themselves well as a means to alleviate and localize some symptoms of neurological disorders.
Effect of medications
It is known that if you regularly and promptly take anticonvulsant drugs for epilepsy, you can completely control the occurrence of epileptic seizures. Modern medications allow:
- block the excitability system of neurons of the epileptic focus;
- stimulate the activity of the inhibitory complex of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors;
- influence ion channels and stabilize neuronal membranes.
Prescribed tablets for epilepsy may have either one of these mechanisms of action or a complex of them. Modern antiepileptic drugs are conventionally divided into drugs of the 1st line (basic category) and 2nd line (drugs of the latest generations). Depending on the symptoms, the doctor recommends taking certain medications.
Basic category of antiepileptic drugs
In our country, basic therapy drugs are used as the main treatment for signs of epilepsy. The list of these drugs includes drugs that have been tested over many years of use and have good results in treatment. These include:
- Phenobarbital (Luminal);
- Primidone (Hexamidine);
- Benzobarbital (Benzene);
- Lamotrigine;
- Phenytoin (Difenin, Epanutin);
- Carbamazepine (Tegretol, Finlepsin);
- Valproic acid and its salts (Konvulex, Depakine);
- Ethosuximide (Petnidan, Suxilep, Zarontin);
- Levetiracetam (Keppra, Levetinol, etc.).
This is not the entire list of medications that are recommended for epileptics to take. The choice of a particular medication depends on the form of the disease, the nature of the attacks, the age and gender of the patient.
2nd line drugs
Drugs belonging to the second category of antiepileptic drugs do not have the same spectrum of action or have a larger list of contraindications than the basic ones. Luminal, Diacarb, Lamictal, Sabril, Frisium or Seduxen have a good therapeutic effect and are also often recommended as effective pills for epilepsy, but for a short time.
The list of drugs for the treatment of epilepsy is very long. Epilepsy must be treated by a doctor. Self-selection of medications and inadequate self-medication can lead to death.
Constant companions of epilepsy are migraine and depression. It has been proven that in patients suffering from migraines, manifestations of epilepsy occur much more often. It was found that depressive states in people with controlled seizures occur 20% less often than in people with uncontrolled seizures.
Polytherapy: combined treatment regimen
When treating this pathology, the doctor strives to achieve monotherapy. This allows you to select the appropriate drug, optimal dosage and appropriate treatment regimen, as well as achieve high clinical effectiveness. In addition, monotherapy minimizes the side effects of treatment.
However, in some situations it is more advisable to choose a combined drug regimen. This is what they do:
- In the form of the pathological process, which combines several types of attacks and there is no possibility of complete monotherapy;
- For conditions accompanied by the same type of epileptic seizures, but not treatable with any medication.
In these cases, medications with different mechanisms of action are used in treatment regimens. However, the chosen treatment tactics must be rational and combine drugs that do not interfere with each other. For example, a prohibited combination is the simultaneous use of phenobarbital with primidone and benzobarbital or phenytoin with lamotrigine.
When using a combined treatment technique, a slight decrease in the therapeutic effect is possible. Often, patients experience signs of intoxication when using one of the drugs that was previously well tolerated. Therefore, at the initial stages of polytherapy, monitoring the level of drugs used in the blood plasma is necessary.
Duration of treatment
The cessation or reduction of epileptic seizures, reducing their duration, alleviating and improving the psycho-emotional state of the patient is already considered a positive trend in treatment. The use of the latest pharmacotherapy techniques makes it possible to achieve complete relief or significant minimization of seizures.
The duration of drug therapy is determined by the type of attacks and form of the disease, age and individual characteristics of the patient. Practical recovery can occur with idiopathic forms of epilepsy.
A small percentage of relapses occur in idiopathic forms with absence seizures that occur in childhood or adolescence. Cancellation of treatment for low-recurrence epilepsy is possible after two years of remission. In other cases, the question of stopping therapy can be raised only after five years of remission.
In this case, the EEG should show a complete absence of pathological activity.
Termination of therapeutic treatment is carried out gradually, with a reduction in dosage to 1/8 daily over 6-12 months. Antiepileptic therapy should not be discontinued in patients with severe symptoms.
Epilepsy and pregnancy
With proper treatment of this pathology, a sick woman has every chance of becoming a mother. If the patient is constantly monitored by a qualified doctor, follows all his recommendations, and a long-term therapeutic remission of the disease is achieved, then, under appropriate conditions, therapy can be canceled during pregnancy.
Alternative Treatments
Among the variety of alternative treatment methods, homeopathic treatments occupy a special place. Although epilepsy cannot be completely cured, this treatment method has its advantages.
For example, the use of homeopathic recipes brings a tangible therapeutic effect, affecting the entire body. Homeopathic procedures are non-addictive and easy to use.
In addition, they have a low cost.
It is worth taking into account that such therapy is safe and gentle on the body. The obvious advantages of such methods include the fact that this is the only method that does not have a toxic effect on tissues and organs.
Source: https://vsepromozg.ru/lekarstva/lekarctva-ot-epilepsii
Contraindications and side effects
There are several types of antibacterial drugs, differing not only in area of application, but also in class, group and type.
There are several most common groups:
- cephalosporins,
- quinolones,
- macrolides,
- sulfonamides,
- tetracyclines,
- nitroimidazoles:
- penicillin.
Cephalosporins are broad-spectrum drugs and are divided into five generations.
Direct contraindications include not only epilepsy, but also allergies, which cause severe allergic manifestations and gastrointestinal lesions.
Quinolones are not used for a history of epileptic seizures, allergies, or for the treatment of children.
Tetracyclines also cannot be taken for convulsive syndrome, and their side effects are standard, like cephalosporins.
How to Treat Seizures: Methods and Principles
How to cure epilepsy?
For a successful treatment outcome, it is important to choose the right tactics, select the appropriate medications, and dosage regimen.
Each patient requires an individual approach.
Basic principles of therapy:
- Monotherapy. Treatment is carried out with only one drug. Until recently, doctors prescribed several remedies at once. However, polytherapy has many disadvantages:
- a large number of side effects;
- decreased effectiveness of drugs due to their interactions.
Today, a combination of two or more drugs is justified if an epileptic has a combination of different forms of seizures that cannot be controlled with one drug.
- Regularity of taking the drug. The drug should be taken strictly by the hour, without skipping. Abrupt withdrawal may provoke the development of status epilepticus.
- Duration of treatment. The medications are usually taken for three years.
- Individual approach to each patient.
- Compliance of the prescribed drug with the type of epileptic seizures.
- Taking the medication in a sufficient therapeutic dose. It is a mistake to prescribe too small a dosage. In this case, an erroneous opinion is created about the low effectiveness of the product.
A major seizure is accompanied by a noticeable loss of consciousness, a fall of the patient, and convulsions.
With minor seizures, the loss of consciousness can be momentary, even imperceptible to others, but the patient clearly feels a clouding of consciousness and subsequently sometimes loses some of his memories: he does not remember the names of his relatives, where he lives, etc.
For rare seizures, sodium borate is prescribed, for frequent and large ones - Phenobarbital.
In conclusion, I would like to say that the new generation of drugs (group 2, which we have already discussed) can effectively act on both short-term and severe attacks.
You just need to be prepared for them and not lose touch with doctors.
Allowed list
When it becomes necessary to use antimicrobial tablets or injections, it is important to tell your doctor about concomitant diseases.
He must know everything about the frequency of attacks, the time and duration of the last attack.
Based on the survey, examination and test results, he can recommend a specific drug.
Allowed:
- lincosamides (Lincomycin, Clindamycin),
- macrolides (Erythromycin, Linkosamine, Azithromycin, Clarithromycin, Josamycin, etc.),
- nitroimidazoles (Metronidazole, Ornidazole).
As for others, the decision to prescribe should be made by the doctor. If you have the slightest doubt about the correctness of the recommendations, you should consult several specialists.
List of prohibited
Here the list is a little longer, and prescriptions may depend not only on the severity and frequency of convulsive attacks, but also on the age of the patient and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Prohibited:
- all penicillin drugs,
- aminoglycosides (Streptomycin, Gentamicin),
- quinolones and fluoroquinolones (Oxolin, Ofloxacin, Norfloxacin),
- anti-tuberculosis (isoniazid, pyrazinamide, etc.),
- cephalosporins,
- polymyxins (Colistin).
Sulfonamides are used under constant medical supervision in a hospital.