22.09.2017
Dyscirculatory encephalopathy of the 3rd degree (DEP) is a pathology in which little oxygen enters the brain tissues of the head, as a result, hypoxia develops, and neurons die. Necrotic tissue forms and the affected brain area does not function. The third degree is the last, the most severe.
The number of patients with this disease is growing. Pathology begins to develop in young and middle-aged people. In the absence of treatment, it develops, gradually developing into the third degree. Discirculatory encephalopathy is one of the causes of the development of senile dementia.
It is important for the relatives of a patient with the third stage of DEP, as well as for himself, to know how long they live with this development of pathology.
Features of DEP grade 3
With DEP, cerebral vessels are affected. Damage that occurs in the brain is irreversible. First, the first stage of the disease appears, when the patient’s condition is satisfactory. If you treat DEP from the very beginning and lead a healthy lifestyle, you can stop the development. Otherwise, you will have to quickly face the last stage of the disease.
In DEP, cerebral vessels are affected
The change from the first to the third stage develops over months and years, it all depends on the patient’s body, his lifestyle and treatment. An unfavorable form is DEP of mixed origin. The following forms of the disease are distinguished.
- Atherosclerotic encephalopathy. The pathology occurs more often than other forms and is associated with impaired functioning of the main cerebral vessels. The cause of its appearance is atherosclerosis of the vessels of the head. The disease develops due to poor lifestyle and other factors. At first it seems harmless, but as a result it can lead to encephalopathy.
- Venous form. The cause of development is a violation of blood outflow from the skull. The resulting stagnation leads to compression of the veins, which negatively affects brain function.
- Hypertensive discirculatory encephalopathy. It can develop at a young age, which increases the risk of developing DEP. If encephalopathy is not detected on time, treatment will be delayed, the pathology will develop and the third degree will appear earlier.
- DEP of mixed origin. Combines symptoms of hypertensive and atherosclerotic forms. The functioning of the great vessels is actively weakening. The patient's condition is complicated by hypertensive crises.
According to statistics, the first two degrees of the disease develop before the age of 50. People often learn about the disease unexpectedly. After 70 years, the likelihood of developing stage three increases greatly.
If DEP has progressed to the third degree, the person’s condition becomes worse and worse. The symptoms that appear in this case cause problems more for others than for the patient himself.
Causes of dyscirculatory encephalopathy
A mass of vascular disorders can cause a diagnosis of “grade 3 dyscirculatory encephalopathy.” The prognosis is extremely disappointing. It is very important to prevent its onset.
- Arterial hypertension is an increase in blood pressure.
- Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels is a disorder of the functioning of the arteries.
- Simultaneous presence of atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension.
- Inflammatory processes – vasculitis of various origins.
Contribute to the progression of the disease: alcoholism, advanced osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, chronic stress and overexertion.
Symptoms of DEP grade 3
At the third stage, all symptoms worsen and new ones are added. If at first the deviations in the functioning of the nervous system are insignificant, then gradually they reach their apogee. The patient ceases to be aware of his condition and does not criticize actions. Grade 3 is characterized by an aggressive behavior. A person’s intellect is impaired, persistent dementia develops, i.e. dementia. The patient is able to work for some time.
Symptoms expressed:
- severe dementia;
- urinary incontinence;
- movement disorder;
- speech disorders.
The main symptom is severe dementia
How does dementia manifest? This is a dysfunction of the intellect, in which the ability to comprehend the connection between events and phenomena surrounding a person is reduced. Cognition processes become worse, emotional reactions and character traits become poorer, some of them disappear. The patient ceases to distinguish between the important and the unimportant. A person does not notice such problems; they greatly affect relatives. In severe cases of dementia, a person loses speech skills and becomes incapacitated.
Usually the patient is given a disability. The most unfavorable course is observed against the background of diabetes mellitus. With grade 3 DEP, complications arise that further aggravate the situation.
Development of the disease
The second stage of the disease is characterized by visible mental disorders, behind which there is a disruption of brain function. Patients experience frequent attacks of hypochondria and depression. From the outside it seems that the patient’s character is deteriorating. The sick person tries to adapt and shift the blame to others. Characteristic manifestations:
- Attention disturbance.
- Significant memory impairment.
- Violation of self-control.
- Pseudobulbar syndrome is difficulty swallowing food.
- Irritability, frequent mood swings.
- Depressive states.
The disease implies the presence of disability, but the patient is still able to care for himself. Based on the above symptoms, of course, a diagnosis is not made: grade 3 dyscirculatory encephalopathy. How long you can live, they won’t answer you either. Disturbances at this stage may coincide with other vascular diseases. In any case, it is necessary to identify their cause. A comprehensive examination using modern technologies is necessary.
Complications of DEP grade 3
Since the patient is unable to perform certain actions and feels a decrease in performance, he experiences unreasonable mood swings. But the direct cause is damage to the subcortex of the brain, where the areas responsible for sleep, hearing and vision are located. The frontal lobes are affected. The result of all this is depression. These are not ordinary mood problems, but a mental disorder that is characterized by the “depressive triad.” This is the name of a complex of three symptoms:
- decreased mood and loss of the ability to feel joy;
- motor retardation;
- thinking disorders.
With this disease, you may notice a decrease in mood and loss of the ability to feel joy.
Attacks of aggression occur. Damage to the occipital zone is accompanied by visual disturbances. Difficulties with breathing appear, the normal voice turns into a nasal voice. Urinary incontinence is associated with a disruption in the transmission of information to organs from nerve cells. As a result, movement disorders appear.
There are more serious complications of stage 3 encephalopathy that can affect the patient’s life expectancy.
- A stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation, as a result of which some areas of the brain stop working. Often a stroke leads to loss of coordination, mobility, and sensitivity. In severe cases, the patient dies, especially if medical assistance is not provided on time.
- Cardiovascular collapse is a type of heart failure that develops due to a severe drop in vascular tone. At the same time, the mass of circulating fluid decreases, so blood flow to the heart suffers. There is a drop in arterial-venous pressure, as a result of which the most important functions of the body suffer.
- Myocardial infarction is a complication of coronary heart disease, which occurs with the appearance of necrosis of the myocardial zone. It is explained by a relative or absolute lack of blood supply.
Each of these consequences can result in death. Life expectancy depends on the occurrence of these consequences and their results.
Treatment methods
Treatment methods at stage 3 are divided into several areas: medications, physiotherapeutic methods and psychotherapy.
Drug treatment
At stage 3 of the disease, it is necessary to improve blood circulation and supply the brain with nutrients. For this purpose, patients take medications that improve blood circulation and cleanse blood vessels, as well as enrich tissues with oxygen:
- metabolic agents and antioxidants - increase the level of oxygen in the blood and enrich brain tissue with it;
- hypocholesterolemic drugs - aimed at eliminating blockage of blood vessels and restoring blood flow;
- vascular substances - to accelerate blood circulation and reduce vascular spasms;
- angioprotectors – necessary for high blood pressure;
- nootropics – drugs that stimulate mental activity, improve memory and cognitive functions of the brain;
- sedatives and psychotropic drugs – are prescribed to eliminate excessive activity or, conversely, apathy of the patient.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy procedures are prescribed to improve blood flow and prevent muscle atrophy in the patient. Doctors recommend electrophoresis procedures for the collar area with drugs no-shpa and aminophylline.
Hyperbaric oxygenation saturates the body's tissues with oxygen, however, it is quite difficult to use the method at stage 3 of the disease, since the procedure takes place in a closed chamber. Massage procedures are also recommended for patients.
Psychotherapy
Due to the development of dementia, patients require psychiatrist supervision and specialized symptomatic treatment. The depressive state can often be replaced by abrupt behavior and physical activity.
Life expectancy with grade 3 DEP
If grade 3 dyscirculatory encephalopathy has developed, no one can give an exact answer to the question of how long you can live. But we can say for sure: the more advanced the disease, the worse the prognosis. This means that in the third stage of the disease there is no chance of improving the patient’s condition. This is due to the fact that the changes occurring in the brain matter are irreversible. Life expectancy depends on the following factors:
- the patient’s lifestyle and the conditions in which he lives;
- the depth of changes occurring with it;
- reasons for the development of the disease;
- accompanying illnesses;
- ongoing treatment;
- consequences of DEP.
It is impossible to even determine the time frame for patients, everything is individual. Some patients live for many years, while others with stage 3 disease die quickly from complications. Still, it is within the power of the patient’s relative to reduce the risks of sudden death.
What to pay attention to
So, you have noticed strange behavior of loved ones: the destruction of social skills, sloppiness, speech impairment - this can signal a very serious illness. In some cases, if you delay contacting a neurologist, you will receive a diagnosis of grade 3 dyscirculatory encephalopathy.
No doctor can say for sure how long you can live with it. The disease has the ability to progress over time.
Discirculatory encephalopathy is chronic damage to brain cells caused by various factors. The disease is divided into three stages. Each period is characterized by its own symptoms. There is also differentiation of the disease by type. Discirculatory encephalopathy of the 3rd degree is considered the most dangerous. It’s hard to say how long you can live with such a diagnosis. The disease occurs over a period of several months to five years.
Disease prevention
A healthy lifestyle is an integral part of taking care of your health. By following a diet and leading an active lifestyle, you will delay the onset of mental disorders as much as possible. If grade 3 dyscirculatory encephalopathy is detected, decompensation through surgical intervention will not improve the patient’s situation. If your blood relatives have had high blood pressure and vascular diseases, you need to undergo regular examinations by a neurologist, regardless of whether dyscirculatory encephalopathy was detected in one of your loved ones or not. It is necessary to assess your condition with the help of doctors, even if no symptoms are observed yet.
Dyscirculatory encephalopathy of the 3rd degree (DEP) is a pathology in which little oxygen enters the brain tissues of the head, as a result, hypoxia develops, and neurons die. Necrotic tissue forms and the affected brain area does not function. The third degree is the last, the most severe.
The number of patients with this disease is growing. Pathology begins to develop in young and middle-aged people. In the absence of treatment, it develops, gradually developing into the third degree. Discirculatory encephalopathy is one of the causes of the development of senile dementia.
It is important for the relatives of a patient with the third stage of DEP, as well as for himself, to know how long they live with this development of pathology.
Diagnostics
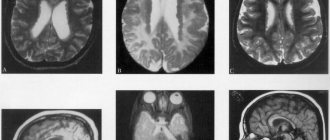
Discirculatory encephalopathy can make a person completely incapacitated. The development of the disease is extremely difficult to predict. Deterioration can occur quickly enough that loved ones will not even notice the passage of one of the stages. Also, the patient can remain in one state for a long time. The duration of the next period can be calculated using the patient’s age and stage of the disease. But identifying the first phase is quite difficult. Taking an anamnesis alone is not enough. Special studies are needed.
To make a final diagnosis, the specialist records:
- Neurological disorders, the dynamics of these disorders. The assessment is made by a neuropathologist based on collecting anamnesis, checking reflexes, and interviewing loved ones.
- An assessment of the patient's neuropsychological state is also carried out by a neurologist or psychiatrist. It is necessary to identify serious mental disorders that the disease has led to. The doctor determines the patient’s ability to concentrate, navigate time and space, and the ability to respond to criticism. Speech is tested, vision is checked.
- REG (Rheoencephalography) allows you to assess the condition of the brain vessels, their filling and the tone of the vascular walls.
- Typical changes in cerebral vessels identified on a computed tomogram. The degree of brain damage, stage and assessment of the possibility of remission are determined.
- Changes in cerebral vessels recorded by Doppler ultrasound also reflect the condition of the blood vessels. The study allows you to identify blood clots and blocked vessels.
- Changes in the patient’s blood may indicate increased coagulation, as an additional risk for blood vessels.
The final verdict is: grade 3 dyscirculatory encephalopathy. How long can you live with this disease? It's impossible to determine. Most often, this diagnosis is made to very elderly people.