Most adults have at one time or another encountered the problem of undiagnosed headaches. But few people know why migraine is dangerous in women and men, what are the common causes and consequences of the development of the pathology.
With timely diagnosis of the disease, the likelihood of effective drug therapy increases.
Therefore, if you notice symptoms of migraine, you should consult a doctor.
Letters from our readers
Topic: Grandma's blood pressure has returned to normal!
From: Christina ( [email protected] )
To: Administration otgipertonii.ru
Christina, Moscow
My grandmother’s hypertension is hereditary - most likely, I will have the same problems as I get older.
I accidentally found an article on the Internet that literally saved my grandmother. She was tormented by headaches and had a repeated crisis. I bought the course and monitored the correct treatment.
After 6 weeks she even started talking differently. She said that her head no longer hurts, but she still takes pills for blood pressure. I am sending a link to the article
What is migraine
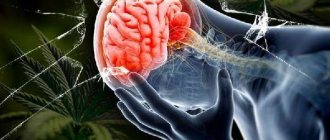
Migraine is a neurological disease that causes severe unilateral headaches.
Another name for the disease is hemicrania. Migraine sufferers often describe it as a severe, throbbing, paroxysmal headache on one side, accompanied by nausea, vomiting and increased sensitivity to light and sound.
Statistics
Migraines affect a large proportion of the population (1 in 5 women and 1 in 15 men suffer from chronic headaches). On average, 14% of Europeans suffer from the disease (Rasmussen BK et al., 1991). The incidence of migraine in Russia exceeds the world average; according to various studies, it is 15.9-20.8% (Lebedeva E.R. et al., 2015).
Main symptoms and stages of development
Migraine and other neurological disorders are diagnosed quite often in medicine.
Approximately 10% of the total population experiences migraine attacks, which can occur even in childhood. Women are most affected by the disease.
During the development of another migraine attack, patients may experience 4 stages of disease development.
The main phases of development are:
The appearance of harbingers or prodrome. This is the first stage, which occurs in half of patients with frequent migraines. The condition can be determined by changes in mood and irritability; there may be fatigue or depression. Signs appear several hours and even several days before the onset of the headache. There are patients in whom this condition is characterized by increased activity, for no apparent reason. In addition, appetite increases. Aura. The second stage of migraine appears in only 25% of migraine patients, but characteristic symptoms may not always develop. Aura is not considered a dangerous condition for a person and his health, but it does cause a lot of unpleasant sensations. The duration of the period is about half an hour, in some cases 1 hour. Characterized by visual impairment. The patient develops dark or light spots in the eyes, flickering and lines. In addition, other parts of the body or organs may be affected, resulting in tingling of the skin, difficulty with speech and motor activity. Pain syndrome. At this stage, headaches begin, of varying strength and duration. Duration from a couple of hours to several days. The attack gains maximum strength and affects one side of the head. The nature of the sensation is bursting, pulsating, and the intensity increases with movement. Additionally, the patient is accompanied by other symptoms: nausea, vomiting, fear of light, sounds, strong aromas. At the end of a migraine attack, symptoms and conditions similar to the first phase begin. When the main symptoms and headaches pass, weakness, depression, irritability sets in
Patients cannot concentrate, the stage lasts up to 24 hours.
Constant pain should be treatable, but for this you need to know the possible causes of the pathology. To reduce relapses, patients need to change their lifestyle and adhere to preventive measures.
Migraine symptoms
How does migraine manifest? Symptoms of the disease may vary slightly from patient to patient. The main symptom of the disease is a severe headache that occurs in the frontal part of the head on one side. The duration of the attack can be from 4 to 72 hours.
Additional signs of migraine include:
- nausea,
- vomiting
- increased sensitivity to sounds and light,
- increased sweating,
- inability to concentrate on specific goals and objectives,
- feeling hot or cold
- stomach ache,
- diarrhea.
In some patients, the onset of headache is preceded by a special condition or aura. Migraine with aura begins with seeing flashes of light or zigzags, narrowing of visual fields, a feeling of pointing or numbness in one arm, gradually moving to the other arm through the head and neck. Possible dizziness, difficulty speaking, and a feeling of loss of orientation. Very rarely, the onset of a headache is preceded by loss of consciousness.
Complications of migraine
Main complications of migraine:
- transition of the disease to a chronic form;
- migraine status (protracted attack of severe headaches lasting more than 3 days);
- persistent aura without a heart attack (symptoms that are precursors to a migraine attack, lasting more than a week and not associated with a stroke);
- aura with a heart attack (sometimes the symptoms of a migraine attack that last more than 1 hour can be a sign of a stroke).
Can you die from a migraine? Migraine itself is not a cause of death, but it can affect overall health. Research has found a link between headaches with aura and the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. It was found that the presence of migraine with aura indicates a twofold increase in the risk of developing acute cerebrovascular accident (stroke).
Migraine: disease prognosis
What is the prognosis if the diagnosis is migraine? It has been proven that headaches seriously reduce the quality of life and work ability of a person suffering from this common disease. According to statistics, 19% of women and 11% of men complain of characteristic symptoms. The long-term prognosis depends on the individual characteristics of the person. However, there is evidence that the prognosis worsens and the risk of developing chronic migraine increases after each migraine attack.
Modern migraine treatments help most people cope with the disease. For most women, symptoms become milder or go away after menopause. In addition, new migraine treatments are constantly being developed. The most promising direction in this area is the use of botulinum toxin preparations for the chronic form of the disease.
Therapeutic measures
Drug treatment of migraine should only be carried out under the supervision of a physician. The following drugs are used in treatment:
- painkillers;
- antidepressants;
- calcium channel blockers, beta-adrenergic receptor blockers, etc.
Treatment is also carried out using natural preparations: minerals - magnesium, calcium, iron, etc.; vitamins - riboflavin, pyridoxine, folic acid; herbal remedies - preparations of butterbur or ginger.
Traditional methods of getting rid of migraines include:
- Paracetamol or Aspirin tablet. These drugs lead to a decrease in blood viscosity, therefore, to a decrease in cranial pressure. The attack of pain goes away after 30-60 minutes.
- Papazole tablet. In a situation where a patient is diagnosed with migraine with aura, at the first symptoms of deterioration in visual or auditory perception, a Papazole tablet will help prevent another attack.
- Hot shower. Placing your head in hot water or taking a warm shower may provide short-term pain relief, but relapses may occur over the next 2-3 hours.
We recommend reading: What is the blood pressure of hypertensive patients?
Causes of migraine
Why does migraine occur? The causes of this condition remain unknown. It is believed that certain disorders in the brain can lead to headaches. There is probably also a hereditary predisposition. With migraine, there is no serious organic pathology associated with head injuries, stroke, or tumors.
Hormonal, emotional, physical, nutritional and environmental factors can trigger migraines. These are often referred to as headache triggers.
Main migraine triggers:
- stress;
- depression;
- anxiety;
- shock;
- sleep deficiency;
- change of time zones;
- low blood sugar;
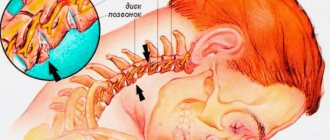
- neck and shoulder tension;
- work at night;
- dehydration;
- smoking;
- drinking alcohol;
- irregular meals;
- taking caffeine-containing products;
- loud noise;
- bright flashing lights.
Hemicrania during gestation
Scientists say that the pathology may be associated with hormonal imbalance. Attacks often occur in the fairer sex during PMS and pregnancy. Why is migraine dangerous in women during pregnancy? Severe attacks of discomfort accompanied by vomiting can provoke dehydration.
Painful attacks usually occur in the early stages. But sometimes they appear in the last months. The cause of the phenomenon may be a lack of oxygen. Why is migraine dangerous in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy? First of all, pathology exhausts the expectant mother, depriving her of the strength that is necessary before giving birth. In addition, the disease can affect the condition of the fetus.
Diagnosis of migraine
Diagnosis of migraine is based on characteristic symptoms, in the absence of signs of organic damage to the central nervous system. Russian recommendations for migraine in adults do not recommend the use of laboratory and instrumental studies if the disease has a typical course.
To exclude physical pathology, a series of tests and studies are performed using all available methods. If you have migraines, testing may be needed to help make a differential diagnosis. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can help rule out inflammatory diseases, tumors, and other organic lesions. For migraine, this study shows no change.
Experts recommend keeping a special diary describing each attack of headaches, the reasons that provoke them, the time and duration of the attack. This data can help a specialist systematize symptoms and determine the form of migraine.
Migrainous status
Manifestations of migraine over time can transform into migraine status - a series of attacks following each other or one long and severe one. The duration of this condition can be from several days to several weeks with increasing symptoms: the pain intensifies and becomes bursting. Only one in five such attacks is preceded by an aura. In case of migraine status, emergency care should be provided as quickly as possible. In children over 2 years of age and adolescents, the attack is stopped by intramuscular administration of ketoprene, diclofenac, antihistamines, and indomethacin.
During an attack in men and women, they are offered infusion treatment - the administration of drugs intravenously. Medicines include: prednisolone, antipsychotics, acetylsalicylic acid, sleeping pills and antihistamines. Frequent, prolonged attacks are the cause of impaired brain activity, ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke. Therefore, it is important not only to stop the attack, but to a greater extent to prevent it. Scientists in Cleveland have had positive experience in preventing myrgenous attacks. Surgical muscle removal or Botox injections into the muscle area near the trigeminal nerve are beneficial for both men and women. Studies on the use of drugs such as Onabotulinumtoxin and Dysport (Botox) in children have not yet been conducted.
Migraine treatment
The exact causes of migraine are unknown, so treatment is symptomatic. The simplest medicine for migraines is paracetamol. Some people find aspirin or ibuprofen more helpful. It is advisable to take painkillers immediately after the headache begins. Soluble migraine medications are more effective because they are absorbed more quickly from the intestines.
What to do if simple medications are not able to relieve migraines? How to relieve pain in other ways? Antiemetic medications help some patients. However, the mechanism of this effect is still a matter of debate.
Frequent headaches significantly impair the quality of life. The attacks can last for days. In such cases, treatment is carried out comprehensively, using analgesics, antiemetics, drugs from the group of triptans and ergotamine derivatives. It is important to avoid situations that trigger migraines. How to treat and prevent headache attacks in each specific case is not always known.
Treatment of migraine with drugs
There are several groups of medications that treat migraine. Tablets, nasal spray or injections - everyone suffering from headaches can choose the optimal form of the drug. Let's look at the main medications for migraines. These are analgesics - aspirin, paracetamol, ibuprofen and their combinations with caffeine (citramon, Excedrin). They help with migraines due to their analgesic effect. Caffeine causes cerebral vascular spasm, reducing the permeability of the vascular wall. It is believed that dilation of cerebral arteries and veins is an important factor in migraine.
The action of another group of drugs called triptans is based on this principle. They help against migraines precisely due to their pronounced vasoconstrictor effect, which blocks pain. These are drugs such as zolmitriptan (zomig), eletriptan (relpax), sumatriptan (imigran, amigrenin, imigran-spray), frovatriptan, naratriptan, rizatriptan. Triptans are considered the most effective treatments for migraines. Ergotamine (cafergot) and its derivatives also increase cerebral vascular tone, but are less effective for migraine.
All of the drugs listed have side effects. Before use, consult a doctor.
Main signs of migraine in women
Every hundredth inhabitant of the planet suffers from a hereditary neurological pathology – migraine. The majority of patients are women in the age category after 35-45 years. The consequences of the disease are varied, so timely consultation with a specialist is mandatory.
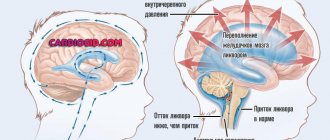
A negative predisposition to migraine, according to experts, is transmitted through the female line. The pathology is based on an imbalance in the activity of the thalamus and hypothalamus, causing fluctuations in intracranial vessels, which provokes pulsating, severe headaches characteristic of migraine.
To make an adequate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a variety of diagnostic tests recommended for a patient with repeated migraine attacks.
Negative predisposing factors
The most frequently identified negative factors predisposing to the formation of migraine are:
• hypodynamic lifestyle;
• stay in a metropolis;
• the presence of severe somatic pathologies that directly affect the intracranial vessels;
• weather dependence;
• severe stressful situations;
• excessive passion for coffee, various energy drinks;
• poor quality night rest;
• excessive physical fatigue;
• long intervals between meals - the feeling of hunger also provokes a migraine attack;
• the presence of negative individual habits, for example, abuse of tobacco and alcohol products;
• frequent exposure to flashes of light and excessively loud sounds;
• the presence of a variety of vestibular stimuli - frequent air travel, sea travel, swings.
The consequences of frequent migraine attacks in women can be quite serious, so timely seeking advice from a specialist and carrying out appropriate treatment measures is the key to good health in the future.
Symptoms
The reasons that provoke a sharp migraine attack can be quite diverse, therefore the symptoms of the disease are distinguished by their brightness and uniqueness.
But the general signs of a migraine attack in women can still be identified:
1. A classic migraine attack begins with the appearance of an aura: a gradual increase in the feeling of discomfort in the head, blurry images, hyperreactivity to external irritating factors - loud sounds, flashes of light, flashing lightning before the eyes, olfactory and auditory hallucinations.
2. After 30 minutes - 1.5 hours, the symptoms worsen significantly - the intensity of the pain increases, other signs appear: vomiting that does not bring relief, severe dizziness, widespread weakness, decreased ability to work.
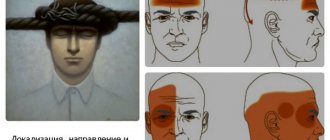
3. Debilitating pain that exhausts women, is localized in one area of the skull, for example, in the temples, crown, near the orbit of the eye. Unpleasant sensations can alternate sides of their appearance, or become bilateral. The reasons for such changes in migraine symptoms should be determined by a specialist.
4. The nature of the pain is also different: throbbing, aching, or pressing, squeezing like a hoop. The pain intensifies from the slightest movements, when trying to turn your head, lean forward or to the side.
Signs of migraine make patients strive for solitude. Often, women during a migraine attack try to hide in a darkened room, creating maximum noise insulation. The consequences of a migraine attack are a feeling of exhaustion, weakness, and complete loss of strength.
Kinds
Neurological specialists classify migraines into the following types:
1. Up to 80% of all cases of the disease occur with simple migraine, without previous aura symptoms.
2. The classic variant of the pathology - with characteristic neurological symptoms of migraine: aura.
In rare cases, pain in the skull does not form directly behind the aura - in this case, experts speak of a migraine aura without headache.
In a separate subgroup of women, another type of migraine is classified - catamenal, also known as menstrual. Acutely occurs at the time of menstrual flow. The reasons for its appearance are interconnected with a sharp decrease in estrogen parameters in the bloodstream.
Diagnostics
Pathology is a disease of exclusion - an adequate diagnosis is made by a specialist based on the characteristic complaints presented by a woman during a consultation, as well as on the basis of an analysis of information obtained from modern diagnostic examinations.
Differential diagnosis is carried out among a variety of neurological pathologies, the symptoms of which may resemble a migraine attack: from various diseases of a vascular nature to the exclusion of malignant neoplasms.
The consequences of late seeking advice from a specialist can be very serious - even death.
Treatment tactics
In the fight against migraine, a trial and error method is usually used, since the pathology is characterized by great variability of symptoms and capriciousness in the selection of effective medications that help relieve pain.
The main directions of treatment tactics for migraine:
• quick help at the time of a migraine attack;
• preventive measures to prevent new migraine attacks.
Each of the areas of treatment tactics has its own characteristics - self-medication is absolutely prohibited.
During a painful attack, medications are indicated:
• nonspecific modern analgesics, including combination drugs;
• medications from the subgroup of anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs.
The key to their effectiveness is timely administration - at the very beginning of a migraine attack. At the peak of pain, their use is not accompanied by an analgesic effect.
Specific anti-migraine medications:
• preparations based on ergot extract:
• modern serotonin agonists.
The frequency of administration of the above medications and the duration of the treatment course are the responsibility of only a neurological specialist. Self-medication, for example, on the recommendation of a friend or acquaintance, is absolutely contraindicated.
After a long course of taking the above medications, a specialist will evaluate their effectiveness and consequences, impact on ability to work, and the frequency of migraine attacks.
Each woman is unique - therefore, selecting the anti-migraine medications that are optimally suitable for this particular woman may take a specialist some time. It is absolutely prohibited to independently supplement or remove any of the medications recommended for use by a neurologist.
General recommendations
Preventive measures will be indicated for only 10-15 percent of women suffering from frequent migraine attacks: 3-5 or more times per month.
Following the recommendations below will help prevent migraine pain:
• adjust the work and rest schedule;
• refuse to drink strong coffee, tea, alcoholic beverages;
• carefully adjust the diet - remove foods that provoke migraine pain;
• give up existing negative habits, for example, smoking;
• do not visit places where there are rapid fluctuations in sounds and light pulses, for example, night discos;
• if a clear relationship with the use of hormonal contraceptives is established, they will have to be abandoned;
• is not located in stuffy, gas-filled rooms;
• ensure quality night's rest;
• try to get out of town more often, take long walks, walk in parks and forested areas.
These simple, but at the same time difficult for some women, recommendations help to significantly reduce the number and duration of migraine attacks.
Various relaxation techniques have proven effective: women suffering from frequent migraine attacks are recommended to learn yoga, auto-training techniques, self-massage, and aromatherapy. You can pamper yourself 1-2 times a year with acupuncture and relaxation in neurological sanatoriums.
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/596a6a468146c12e34f9afda/5974d7bab2d009201e3c1f76
Migraine prevention
How to get rid of migraine? Is it possible to beat migraines? Medicines only relieve symptoms, but do not prevent the development of an attack. However, migraine medications and some medications (anticonvulsants, beta blockers) can be taken regularly, daily, regardless of the presence of symptoms. In such cases, the purpose of prescribing the drug is to prevent headaches.
To get rid of migraines, you need to follow several rules.
This is keeping a diary, where you need to record the date and time of the onset of the attack, symptoms and provoking situations. Thanks to this, you will soon understand what causes your headache. There are also mobile applications developed for this purpose.
Regular physical activity and an active lifestyle, normalization of sleep also prevent headaches.
Diet and migraines: A diet rich in tyramine (tyramine is found in aged cheeses, processed meats, olives), alcohol, chocolate, coffee, and overeating can trigger headaches. Therefore, it is rational to avoid these foods. Vitamin B2 supplementation may reduce the frequency and severity of migraine attacks
Migraine in childhood
The symptoms of the disease in minors are approximately the same as in adults.
But it is difficult to identify hemicrania in young patients. Many parents confuse it with other ailments and try to treat their child on their own. In children, as in adults, attacks recur periodically. They interfere with leading a normal life: studying, communicating, attending clubs. Why is migraine dangerous in children? The consequences in this case do not differ from complications in adults. Difficulties in diagnosis and lack of treatment increase the risk of their occurrence.
Sources
- Migraine, Overview, last reviewed 10 May 2020, NHS — https://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Migraine/Pages/Symptoms.aspx
- Migraine, Overview, Mayo Clinic - https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/migraine-headache/basics/definition/CON-20026358?p=1
- Migraine and cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Authors: Schürks M1, Rist PM, Bigal ME, Buring JE, Lipton RB, Kurth T, 26 October 2009 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19861375
- Migraine, Overview, Mayo Clinic—https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/migraine-headache/basics/definition/CON-20026358?p=1
- Migraine, Causes, last reviewed: 10 May 2019https://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Migraine/Pages/Causes.aspx
- Migraine with aura, ICD-10 Version:2010 —https://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en#/G43.0
- Migraine Headache —https://fpnotebook.com/Neuro/Headache/MgrnHdch.htm
- Migraine, Overview, last reviewed 10 May 2019 https://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Migraine/Pages/Diagnosis.aspx
- https://familydoctor.org/familydoctor/en/diseases-conditions/migraines.printerview.all.html
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/migraine-headache/basics/definition/CON-20026358?p=1
- Clinical guidelines “Tension headache, tension headache in adults”, Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 2020