3399 0
For the first time, the symptom of pain in the lower back and sciatic nerve during bending of the straight leg in the area of the hip joint was described by the French doctor Lasegue.
The syndrome was then named after this physician.
To understand the essence of the syndrome, you should pay attention to the largest nerve in a person - the sciatic, which is formed by the roots of the nerves of the spinal cord.
If a traumatic effect or excessive tension on this nerve causes a sharp movement in a person lying on his back when they try to lift or bend the limb, then Lasegue tension syndrome manifests itself.
What does this research method reveal?
There is a certain number of symptoms that associate pain in the back and limbs with inflammatory processes occurring in the spine.
This group of syndromes is called tension symptoms. It is in this category that Neri's symptom falls. Neri tension syndrome allows you to diagnose the following diseases:
- Myeloradiculopathy is an inflammatory process in the lumbar region, in which the L5-S1 nerve roots are pinched. As a result of this disease, a person’s sweating is impaired, and there is a decrease or complete absence of sensitivity of the skin. Laboratory testing of spinal cord fluid can detect the presence of leukocytes and red blood cells in the blood.
- Radiculitis is an inflammation affecting the spinal roots. The disease develops as a result of osteochondrosis and may be accompanied by the appearance of neoplasms and intervertebral hernias. Radiculitis also occurs as a result of previous injuries in the spinal column.
- As a result of hypothermia, spasm of the lumbar muscles occurs. This condition also affects the spinal nerves, which undergo elongation and compression. In this case, the syndrome also manifests itself.
- Osteochondrosis of 2, 3 and 4 degrees also causes the manifestation of this symptom.
Conclusion
Osteochondrosis causes complications in different organ systems. The disease leads to disruption of the functioning of the spinal nerve roots due to their mechanical compression and inflammatory processes. Depending on the area of damage, one or another symptom occurs, pain in a specific part of the body. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, the prognosis for recovery is favorable.
Treatment in our clinic:
- Free doctor consultation
- Quick relief of pain;
- Our goal: complete restoration and improvement of impaired functions;
- Visible improvements after 1-2 sessions; Safe non-surgical methods.
- The appointment is conducted by doctors
- Treatment methods
- About the clinic
- Services and prices
- Reviews
Osteochondrosis is a chronic degenerative dystrophic disease in which gradual destruction of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs occurs. They lose their elasticity and shock-absorbing ability, and stop protecting the radicular nerves extending from the spinal cord from compression. A decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs leads to instability of the position of the vertebral bodies, their constant displacement, which can cause the development of spinal canal stenosis.
Strain syndrome is excessive tension of the muscle fibers in the area of the affected area of the spinal column. In this way, the body tries to compensate for the decrease in the height of the intervertebral disc and eliminate compression from the radicular nerve. These signs are important in the differential diagnosis of osteochondrosis with other possible pathologies.
Tension syndrome in osteochondrosis helps the neurologist to clarify the degree of damage to the cartilage tissue of the disc and compression of the radicular nerve. There are several symptoms of tension: Lasegue, Neri, Matskevich, Vaserman, Sekar, Bekhterev and Dejerine. We will examine some of them in detail in the proposed material.
If you find at least one of them in yourself, then do not hesitate to contact a neurologist. Such a manifestation indicates that there is serious damage to the nerve fiber. Without timely treatment, this condition can provoke atrophy of the radicular nerve and trigger a cascade process of innervation disruption. In this case, not only the muscles of the back frame can be damaged, but also the lower limbs, vascular bed, and internal organs of the abdominal cavity and pelvis.
If you have symptoms of tension, then in Moscow you can make an appointment with a neurologist at our manual therapy clinic. The initial appointment is free for each patient. During the consultation, an experienced doctor will check whether you really have a positive symptom of tension due to osteochondrosis. Once an accurate diagnosis is made, an individual treatment plan will be developed.
Mechanism of occurrence
In a normal state, in a healthy person, the nerve root is located freely in the intervertebral foramen, without tension and without causing pain when flexing the hip (except for some discomfort at extreme degrees of flexion).
Stretching of a nerve root becomes painful to one degree or another when it is pinched in the intervertebral foramen, as well as when it is stretched due to the convexity of a herniated intervertebral disc. In these situations, any strain while slowly lifting the lower limb will be painful.
A positive Lasègue symptom occurs when pain occurs when raising the hip less than 60 degrees. The appearance of discomfort or pain at an angle of more than 60 degrees may be a false-positive Lasegue symptom. This situation can arise even when examining a healthy person who leads a sedentary lifestyle or has reduced flexibility.
Test procedure
The study should be carried out by a specialist neurologist. It is not recommended to do this on your own: incorrect technique can cause harm and correct readings will not be obtained.
For testing, the patient should lie on their back. The surface on which the patient is located is straight and hard. A person should position himself as evenly as possible so that the sides of the body are symmetrical to each other. The back is completely relaxed, the damaged nerve is not tense, so there should be no discomfort.
The doctor slowly bends the patient's lower limb at the hip joint. When this action is performed, the leg should be bent at the knee. This movement should also be painless.
At the next stage of the test, the doctor slowly and smoothly raises the straightened leg. In this case, no sudden movements should be made; The limb should be raised gradually. As soon as the patient feels pain, the test is stopped. You cannot endure pain; you must immediately inform your doctor about the appearance of unpleasant sensations.
If the patient is under the influence of anesthesia or pain medications, the test will have to be delayed. Such medications reduce sensitivity, which can distort test results. In addition, there is a risk of nerve fiber rupture, since pain will not appear with strong tension.
If the test results are positive, further testing will be required.
Carrying out diagnostics - video
As a rule, promptly and correctly diagnosing neurological diseases of the spinal region is not an easy task, since the symptoms of such disorders are often similar to other diseases, and with prolonged pain syndrome, pain may be perceived incorrectly by the brain.
Almost all diseases of the spine cause muscle spasms of varying classes and degrees, and also provoke destruction of nerve roots and numbness of the damaged limb.
In addition, quite often the symptom of tension can be an accompanying symptom of osteochondrosis and other degenerative diseases.
In neurology, there are several common tension syndromes and each of them is tested in a certain way.
How is Lasegue's symptom caused?
The symptom manifests itself when the lower leg is extended in a patient lying on his back with the hip flexed. The examination should be carried out carefully, without making sudden movements, since pain with a positive Lasègue symptom can be of high intensity. Lasègue's symptom is positive if pain occurs in the lumbar region, along the back of the thigh and lower leg of the corresponding side. Soreness is usually localized on the side of the affected nerve root. For example, Lasegue's sign on the right is caused by flexion of the right leg.
- The first phase of Lasegue's symptom: the occurrence or appearance of pain in a patient lying on his back when trying to bend or flex an extended leg at the hip joint.
- The second phase of Lasegue's symptom: if you subsequently bend the leg at the knee without straightening the hip joint, then the pain syndrome either disappears or its intensity sharply decreases.
An important point: it is not allowed to cause the Lasegue tension symptom after the use of anesthesia, since the protective pain reflex in such conditions is significantly reduced; manipulation in this case can lead to tearing of axons and cause motor disorders (up to paresis).
Neurological assessment of the syndrome
This is a test that is used in this field when a doctor suspects that a patient has diseases of the nervous system or parts of the spine.
To make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to identify areas with pathology in the spine, in which the body, trying to put up protection, forms blocks and pinches the nerve roots.
They try to find such an area by testing the patient for this symptom.
Important rules when performing an inspection are:
- smooth raising of the lower extremities;
- stopping manipulations with the leg even at a small angle of lifting the leg if pain occurs;
- the test is carried out without prior anesthesia so that the test results are not distorted.
In medicine, there are concepts of positive and negative Lasegue symptoms.
The exact presence of a tension symptom can be determined if the patient takes a supine position. The doctor carefully lifts the patient's leg until the patient feels pain in the sciatic nerve.
Lasègue syndrome can be:
- positive if, when raising the patient’s leg 30°, a sensation of pain occurs in the limb. It occurs with gradual flexion of the lower limb at the knee and hip joint. This symptom may indicate compression of the lumbar and sacral roots, which most often occurs with osteochondrosis.
- If the pain syndrome does not disappear during bending of the leg in the hip or knee region, Lasegue's symptom is called negative , and the pain can be caused by pathology of these parts of the limb. A patient with such a clinical picture during examination should be further diagnosed to identify the real cause of the pain syndrome.
- Pain in the lower extremity is often psychogenic in nature. They are often observed in hysterical women. During diagnosis, there is usually no connection between changes in leg position and the patient’s symptoms. A pseudo-positive symptom may also be diagnosed in a person with weak hamstring muscles. Typically, such signs are observed in older people.
Practice shows that the appearance of pain when raising the leg to 70° indicates the presence of pathology in the joint. A consultation with an orthopedist is required to determine the pathology of the femoral muscles.
Indications
The presence of Neri syndrome is checked if the following pathological conditions are suspected:
- Lumbar myeloradiculopathy. With this disease, the L5-S1 nerve roots are pinched, there is a loss of tendon reflexes, and a complete or partial loss of sensitivity of the epidermal integument. The patient also suffers from impaired sweating. Laboratory analysis reveals leukocytes and red blood cells in the cerebrospinal fluid.
- Radiculitis. Pathology often occurs against the background of osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernias, back injuries, tumors of nerve endings.
- Spasms of the lumbar muscles as a result of hypothermia.
- Osteochondrosis of the fourth, third, second degree. The sign of tension appears from the moment when the height of the intervertebral disc becomes less than 2/3 of its height.
Testing is recommended in the following cases:
- Backache.
- Limited mobility of the spine.
- Morning stiffness.
People's sensitivity to pain varies. Some feel the discomfort slightly, others feel it too much. Therefore, in each case, the doctor analyzes the severity of the disease individually, based on other signs and results of diagnostic procedures.
What do diseases identified using the Lasegue tension symptom lead to?
Signs of tension directly indicate the presence of a number of diseases. The most common reasons for their appearance are:
- lumbosacral region at the S1 level;
- Bekhterev's disease;
- sciatica;
- lumbosacral region.
These diseases themselves limit a person’s daily activity. Patients experience fatigue, pain in the affected areas, discomfort when moving, and aches in the joints. If the disease is not treated, symptoms will steadily progress. In advanced stages, many people become disabled. Therefore, in the treatment of such diseases, timely treatment plays an extremely important role for health.
Important! If you experience discomfort or pain during movement, you should seek medical help as soon as possible. You should not put off visiting a doctor, since the prognosis of recovery depends on this.
When does a positive Neri symptom occur?
This symptom has a characteristic feature and almost always develops gradually:
- At the first stage of development, this symptom is very mild, the pain practically does not cause any discomfort to the patient.
- The second stage is accompanied by the development of a stormy clinical picture. The pain becomes pronounced and increasing.
- The third stage is accompanied by painful manifestations of a mild nature. This happens especially in cases where the hernia between the vertebrae protrudes from the side. The Neri symptom may not be present until the size of the hernia exceeds 10 mm.
It should be noted that the syndrome occurs in everyone with different intensity. There are a number of signs that indicate the presence of a pathological process:
- Even the slightest movement causes severe pain in the lumbar region. It is caused by excessive tension of the paravertebral muscles. Pinched nerve roots are the root cause of Neri's symptom.
- Sometimes the pain symptoms are mild and the disease is sluggish. In such cases, the Neri symptom does not appear immediately, but manifests itself after 2 or 3 weeks. In this case, the pain syndrome can move to the lower extremities.
The Neri symptom appears in the following diseases:
- Myeloradiculopathy in the lumbar spine, in which there is infringement of the L5-S1 nerve roots. With pathology, loss of tendon reflexes in the lower extremities (Achilles, knee), impaired sweating, loss of skin sensitivity, and pathological changes in the affected limb occur. When performing laboratory tests of cerebrospinal fluid, red and white blood cells can be traced in it;
- Radiculitis (inflammation of the nerve roots) occurs with osteochondrosis of the spine in combination with intervertebral hernias, root tumors, and spinal injuries;
- Muscle spasm of the lumbar muscles during hypothermia is accompanied by the involvement of the spinal nerves passing through the thickness of the muscle tissue. In such a situation, Neri's symptom appears due to compression and elongation of nerve fibers;
- With osteochondrosis of the lumbar region of 2-4 degrees, the symptom of tension is formed when the height of the intervertebral disc decreases by 2/3 of the height.
Each person has their own threshold for pain sensitivity. It can be strong or weak, which does not allow the syndrome to be assessed according to general criteria. As a result, in each specific case the doctor must analyze the severity of the pathology individually.
Symptoms of tension in osteochondrosis: types and methods of modern diagnosis
Osteochondrosis is accompanied by various clinical signs, including so-called tension symptoms. This is the name for complications of the nervous tissue of the spinal cord, as a result of which the patient experiences regular pain.
When doctors use the term “tension syndrome in osteochondrosis,” they mean the appearance of pain symptoms that occur during passive movements of the arms and legs. The cause of these sensations is too much tension on the nerve roots that are located in the spinal cord. Tension also refers to spasms (sharp contractions) of muscle fibers.
The causes of such symptoms are pathogenic processes of destruction of vertebral bone tissue. As a result, they gradually shift and change location.
Therefore, the bones begin to compress the intervertebral discs, which is why they also collapse and have a mechanical effect on nerve fibers as well as muscle tissue. As a result, they become very stretched and cause significant pain to the patient.
This syndrome is a neurological manifestation of osteochondrosis, so first of all you should contact a neurologist.
Symptoms of tension intensify if, along with osteochondrosis, a person suffers from other chronic pathologies - ankylosing spondylitis, pinched sciatic nerve, hernia and protrusion of discs.
Kinds
Neurological symptoms of osteochondrosis are always accompanied by pain. Their clinical manifestations are different, therefore, in medical practice, a classification of signs accompanying osteochondrosis has been developed. Each group of symptoms is given its own name.
Symptoms of Lasègue
The emerging Lasegue symptom in osteochondrosis of the lumbar region is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased pain when raising the leg (while lying down);
- throbbing sensations in one or both legs.
With sudden movements, the sensations become unbearable. Turning and bending the legs can cause nerve fibers to become damaged or even ruptured. Therefore, the patient is advised to undergo immediate diagnosis.
First of all, the doctor determines the maximum angle at which a person can raise the lower limb without severe pain. Then set the angle of the maximum possible bend of the leg at the knee joint.
In accordance with this, the degree of development of osteochondrosis is determined.
Symptoms of tension in osteochondrosis of the lumbar region may be accompanied by lumboischialgia, when pain radiates to 1 or both lower limbs. If a person can sit without any extraneous sensations, then this pathology is absent.
Tripod symptom
This symptom of tension can be diagnosed if the following signs are observed:
- The patient can sit up in bed only if he leans on both hands, placing them behind his back. Without support, a person will not be able to sit due to pain.
- When changing position (getting out of bed), a person tries not to strain his back muscles, as this causes him severe discomfort.
- While sitting on a chair, the patient places his hands on its surface (behind the chair) and tries to tilt his back back.
Thus, the patient is looking for three points of support at once, which is why the symptom received a similar name.
Symptoms of landing
To identify this sign, the patient is asked to lie down on a bed or couch, and then gradually change position - sit down. If the legs cannot be kept in a straight position (they bend at the knee joint), a landing symptom is determined.
Wasserman-Matskevich symptom
To detect this symptom, the patient lies on his stomach, the doctor bends the leg at the knee joint until it causes pain. The discomfort is associated with tension on the femoral nerve, and the pain itself appears on the surface of the leg (femoral part, front side).
Neri's symptom
To identify Neri's symptom in osteochondrosis, a person lies on his back, with his arms and legs directed along the body.
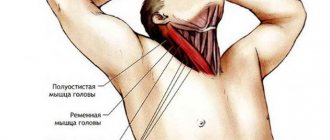
The doctor places his hand on the back of the head and tries to bend the neck with a sharp movement so that the head comes as close to the chest as possible. When discomfort occurs, this symptom of tension is diagnosed.
To understand the degree of development of the disease, the neurologist visually determines the maximum angle at which it is possible to bend the neck without extraneous sensations.
The appearance of such signs is caused by the formation of osteophytes - processes on the bones of the spine that compress nerve fibers, muscle tissue and blood vessels. The cause may also be a herniated disc, when its body pinches the nerve roots.
The symptom allows you to identify inflammation of the spinal roots (sciatica), as well as possible spasms of the lower back muscles. Associated symptoms are disturbances in sweating, complete or partial loss of sensitivity in the damaged area, surges in pulse and blood pressure.
Dejerine syndrome
Neurological manifestations of osteochondrosis of the cervical and other parts of the spine are accompanied by Dejerine syndrome. The patient himself can identify it. If, during sudden movements of the body when coughing or sneezing, noticeable pain occurs in the lumbosacral region, this indicates tension in the nerve roots.
But it should be borne in mind that such a test does not lead to unambiguous conclusions. A person should still go for diagnostics. The pain threshold for all people is not the same, so even if minor discomfort occurs, it is better to consult a neurologist.
Bonnet reaction
Occurs as a result of damage to the sciatic nerve. It can appear in 2 ways:
- A person lies down on a flat surface, bends his leg at the knee and hip joint, and moves it to the side. Determine the maximum angles at which movement is possible without pain.
- During a visual examination, the doctor draws attention to the fact that the gluteal fold is poorly expressed or practically invisible. This is explained by a decrease in muscle tone in the muscles of the buttocks, which also indicates the presence of the Bonnet reaction.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis begins with a visit to the doctor. The patient can contact his general practitioner or go straight to a neurologist. This must be done as quickly as possible, because it is extremely difficult to cure the symptoms of tension at home. To make a diagnosis, the doctor analyzes the patient’s complaints, as well as the medical history, conducts a visual examination and palpation (palpation) of the back muscles.
Additionally, instrumental examination methods are used:
- MRI;
- CT scan;
- radiography.
If necessary, a general blood and urine test is performed.
Treatment
The course of therapy is aimed at solving several problems at once:
- pain relief;
- elimination of swelling;
- cessation of inflammatory processes;
- restoration of bone tissue, nutrition of bones.
The most common disease occurs in the lower back, because it bears the main physical load. Therefore, treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis with neurological manifestations is most often used. For this purpose, medications, physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, therapeutic exercises, and in some cases surgical intervention are used.
First of all, it is necessary to relieve pain. They can be stopped with special blockades with novocaine, painkillers, and anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs:
- "Diclofenac";
- "Ibuprofen";
- "Nimesulide";
- "Aceclofenac";
- "Naproxn";
- "Ketorolac" and many others.
Among the physiotherapeutic procedures used are the following:
- ultrasound therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Additionally, the patient is prescribed massage sessions, manual therapy, and in some cases, traction traction of the spinal column is performed in air (dry) or in water (underwater). Therapy is also carried out using reflexology, as well as folk remedies. Their use is agreed with the doctor.
Treatment is always carried out comprehensively and involves mandatory correction of the patient’s lifestyle. It is unacceptable to eat food containing large amounts of salt.
There is a need to consume foods enriched with calcium and vitamin D, which promotes its absorption.
The patient is also indicated for therapeutic exercises, which are first carried out under the supervision of a doctor, and then at home.
The operation is indicated in cases where conservative treatment does not produce significant results for 2-3 months or more. Also, surgical intervention may be resorted to if the patient experiences severe pain, and the disease has been developing for a long time (advanced cases).
Interpretation of Lasegue's symptom
In the presence of a pathological process localized in the area of the nerve root, pain may appear when the hip is flexed at different angles (10, 15, 20, 30 degrees). The level at which Lasegue's symptom occurs allows us to judge the severity of the patient's condition and is of great importance for diagnosing the stage of the disease.
In order to track the dynamics of the clinical manifestations of a radicular lesion, it is advisable, when recording the examination results, to indicate the approximate angle at which the patient experiences pain (an example of such a recording: Lasegue’s symptom on the right is positive, 30 degrees). This will make it possible in the future, during repeated examinations, to compare the current result with the previous one and, based on the comparison results, make a judgment about the dynamics of the patient’s condition. In particular, an increase in the angle between the plane on which the patient lies and his thigh will indicate a gradual improvement in the patient’s condition.
Tactics for identifying a positive Lasègue phenomenon
In neurology, this phenomenon belongs to the group of so-called tension symptoms; from the name it is clear that the formation of this diagnostic sign is associated with tension and tension of the nerve trunk.
- The most common case when a positive Lasègue symptom is observed is with osteochondrosis. Inflammation in the area of the nerve root leads to its compression and tension. Other symptoms of this group (Nery, Bekhterev) will also be positive.
- Acute discogenic lumbodynia. This condition occurs when the fibrous ring is torn, leading to protrusion of the intervertebral disc in the spinal disc segment. The cause of such a violation may be awkward movement in the lumbar spine, sudden lifting of weight. Clinically, acute discogenic lumbodynia is manifested by sharp pain in the lumbar region, often causing the patient to “freeze” in the position in which the pain syndrome found him. The duration of a painful attack is from half an hour to several hours. When diagnosing, an important role is played by the symptoms of Matskevich and Lasègue, the “board” symptom (impossibility of flexion in the lumbar region).
- Subacute discogenic lumbodynia. The reason is prolonged physical activity in a position that is uncomfortable for the patient (often in a bent state). Unlike the acute condition, subacute lumbodynia is characterized by a delayed development of pain.
The symptom indicates an acute course of the disease. A patient whose examination reveals this sign is disabled (for at least 10 days).
- The first step is to relieve pain (the use of NSAIDs is optimal; in case of severe pain, drug blockades can be used).
- The patient must be provided with bed rest for the duration of the acute pain syndrome (this is especially important in case of violations of the integrity of the fibrous ring).
- An integrated approach is required: the treatment regimen includes NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, physiotherapy, and, as the exacerbation progresses, exercise therapy.
- To avoid relapses, a patient with discogenic disorders may be advised to wear a lumbosacral corset in situations involving stress on the lumbar spine.
- The most common case when a positive Lasègue symptom is observed is with osteochondrosis. Inflammation in the area of the nerve root leads to its compression and tension. Other symptoms of this group (Nery, Bekhterev) will also be positive.
- Acute discogenic lumbodynia. This condition occurs when the fibrous ring is torn, leading to protrusion of the intervertebral disc in the spinal disc segment. The cause of such a violation may be awkward movement in the lumbar spine, sudden lifting of weight. Clinically, acute discogenic lumbodynia is manifested by sharp pain in the lumbar region, often causing the patient to “freeze” in the position in which the pain syndrome found him. The duration of a painful attack is from half an hour to several hours. When diagnosing, an important role is played by the symptoms of Matskevich and Lasègue, the “board” symptom (impossibility of flexion in the lumbar region).
- Subacute discogenic lumbodynia. The reason is prolonged physical activity in a position that is uncomfortable for the patient (often in a bent state). Unlike the acute condition, subacute lumbodynia is characterized by a delayed development of pain.
Preparation and how it is carried out
A test for the presence of this symptom can be carried out by both the doctor and the patient independently. The patient needs to take a supine position, the body should be on a flat surface, and the legs should be straightened and together. The test itself involves bending the neck in a position in which the chin is pressed as close to the chest as possible.
The Neri symptom is considered positive if such manipulations result in severe pain localized in the lumbar region. This happens when spinal nerves are involved in pathological processes, which gives a similar projection. The mechanism of the symptom is formed when there are problems with the nerve roots in the interval from the 3rd lumbar to the first sacral vertebra.
The severity of the symptom is assessed depending on what angle of neck flexion became the activator of severe painful sensations. In this matter, the dependence is simple: the sharper the angle (the lower the height the patient was able to raise his head), the more advanced and pronounced the disease.
Testing does not require the use of specific tools and equipment. The test can be done independently or with the help of a doctor. The procedure does not require any special preparation.
The check is carried out as follows:
- The patient lies on the couch on his back, with his arms and legs straight.
- The doctor places his hand under the back of the head and with a sharp movement bends the neck, bringing the chin as close to the chest as possible (the upper part of the body does not rise).
The presence of severe and acute pain in the lower back will indicate Neri's symptom. The pain is explained by additional irritation of the spinal membranes. The doctor takes into account at what angle of neck flexion the pain is strongest. The sharpness of the angle indicates the neglect of the pathology and allows you to choose the most effective method of therapy.
The test is quite accurate. But you shouldn't rely on it completely. After all, each person has their own pain threshold. The syndrome only suggests a certain pathology. To create an effective treatment regimen, you need to fully examine the patient.
Evaluation of the results obtained
The occurrence of pain when raising the leg at an angle of 60 degrees cannot indicate a positive Lasègue symptom; this is due to the fact that at this angle the nerve reaches its maximum stretch.
Bending the limb at an angle of 40-60 degrees also causes maximum stretching of the nerve; painful sensations may not be associated with a symptom of tension, but indicate that the length of the nerve has reached its limit.
Only bending the leg at an angle of up to 30 degrees indicates a true Lasègue symptom.
The manifestation of Lasegue's syndrome may indicate the development of certain diseases of the lower spine, but is not a prerequisite for establishing a final diagnosis. To accurately determine the disease, methods for identifying other symptoms of tension, fluoroscopy and MRI are used.
Neri's sign was studied by an Italian neurologist in 1882 when he discovered a relationship between low back pain and head flexion in patients with.
To perform the test, bend the head of the patient, who is in a supine position, towards the chest. In this case, a person, if present, develops strong ones. Their appearance is due to additional irritation of the spinal cord membranes at the exit of the inflamed spinal nerve roots.
Neri symptom test.
Other diagnostic signs accompanying Lasegue's symptom
Symptoms of tension also include:
- Bonnet reaction. If a patient, during a preliminary neurological examination, cannot contract and spread his leg, this may mean that he has Bonnet’s symptom, which is characterized not only by an increase in the pain threshold, but also by numbness of the limbs. Painful sensations are localized only in the damaged area.
- Wasserman-Matskevich symptom. With strong muscle tension, the patient may experience Wasserman and Matskevich syndromes. They appear when there is damage to the peripheral nervous system or spinal nerves.
- Neri's symptom manifests itself when the dorsal roots of the spinal cord are irritated, developing as a result of osteochondrosis of the spine with bone osteophytes, disc herniations, tumors of the roots, which leads to unpleasant pain.
- Dejerine syndrome is a symptom of tension that is neuralgic in nature, and that is why when diagnosing the doctor pays attention to the smallest details. The pain is localized in the spinal region and appears only during physical activity. Manifests itself due to damage to the spinal cord column.
- Neri - the occurrence of pain in the lumbar region when the head is flexed.
- Matskevich's symptom is pain in the groin area and the front surface of the thigh when the patient bends the lower leg while lying on his stomach.
- Dejerine's symptom is increased pain when coughing or sneezing.
- Bekhterev's symptom (in a number of sources referred to as Lasegue's cross symptom) - when a lying patient sits down, his leg bends at the knee joint on the side of the nerve root lesion. If this leg is straightened, the healthy one will bend. In cases where a positive Lasègue symptom is recorded, ankylosing spondylitis' symptom is usually also positive.
- Lerrey's phenomenon - a pronounced increase in pain in the lumbar region in the event of a sharp transition from a lying position to a sitting position - is almost always a symptom accompanying the Lasègue sign.
- Neri - the occurrence of pain in the lumbar region when the head is flexed.
- Matskevich's symptom is pain in the groin area and the front surface of the thigh when the patient bends the lower leg while lying on his stomach.
- Dejerine's symptom is increased pain when coughing or sneezing.
- Bekhterev's symptom (in a number of sources referred to as Lasegue's cross symptom) - when a lying patient sits down, his leg bends at the knee joint on the side of the nerve root lesion. If this leg is straightened, the healthy one will bend. In cases where a positive Lasègue symptom is recorded, ankylosing spondylitis' symptom is usually also positive.
- Lerrey's phenomenon - a pronounced increase in pain in the lumbar region in the event of a sharp transition from a lying position to a sitting position - is almost always a symptom accompanying the Lasègue sign.
Diseases that provoke the appearance of the syndrome
Diseases when the sciatic nerve becomes tense include:
Treatment of diseases that are accompanied by Lasègue's symptom consists of drug therapy with the use of painkillers, physiotherapeutic procedures, acupuncture, and the use of orthopedic corrective agents.
Therapeutic blockades with anesthetics help relieve pain, and after the patient’s condition has eased, manual therapy is used only on the recommendation of a doctor.
The identified positive result is the initial step in assessing the patient’s condition in a complex manner. It allows you to pay attention to the appearance of pathological processes in the body, determine the source of the lesion and begin its treatment.
Sometimes it can be very difficult to make a correct diagnosis of a neurological disease. This is due to the fact that most patients are not able to objectively assess pain and exaggerate the extent of symptoms.
With prolonged pain, a situation may arise in which a person is unable to correctly interpret the pain, and in rare cases, it may be completely ignored. An objective picture of neurological diseases of the spine can be identified using tension symptoms.
Symptoms of tension are signs of neurological diseases of the spine, which are accompanied by muscle spasms or other reasons that provoke difficulties in movement and stretching of the nerve roots. The symptom of tension may indicate degenerative changes in the spine and osteochondrosis. Provoking passive movements causes acute pain.
In neurology, there are 7 symptoms of tension:
- Dezherina;
- tripod;
- planting;
- Wasserman-Matskevich;
- Bonner;
- Neri;
- Lasega.
The symptom was first discovered by the French neurologist Lasegue back in the mid-19th century. He conducted an experiment in which he discovered a sharp pain in a patient when raising a straight leg in a supine position; after bending the knee or hip joint, the painful sensations stopped instantly.
Pain when raising the lower limb in a straight position occurs due to stretching of the sciatic nerve, while the pain reaction can be caused by tension in only one nerve root. A painful reaction occurs due to compression of the nerve roots in the intervertebral foramen due to its excessive tension.
Normally, stretching of the nerve as part of a physiological process cannot cause its overstrain, and movement in the intervertebral foramen occurs smoothly, the root easily slides along it without excessive compression. Painful sensations may occur due to the fact that the nerve fibers of the sciatic nerve are not able to lengthen naturally, this may be due to pinching or overstretching.
The sciatic nerve is the largest nerve in the human body and positive Lasegue syndrome can indicate a number of diseases along its length. Doctors use the symptom of tension to make an accurate diagnosis of diseases of the lumbosacral spine.
Causes
The above syndrome in neurology is a fairly common phenomenon. It accompanies one or more spinal diseases. These include:
- myeloradiculopathy. Most often, the disease affects the lower back, which leads to pinched nerve roots. Symptoms of the disease include loss of tendon reflexes, failure of sweating, loss of sensitivity of the skin, and changes in the lower extremities. A biopsy reveals an excessive presence of red and white blood cells;
- an inflammatory process in the nerve roots, which is often called “sciatica.” This pathological process occurs with osteochondrosis of the spine, which is accompanied by intervertebral hernias, tumors and injuries;
- muscle spasm of the lower back muscles. This disease occurs due to hypothermia of the body, which involves muscle tissue and spinal nerves;
- osteochondrosis of the lumbar region 2-4 degrees. Occurs due to a decrease in the height of the vertebrae by more than half;
- protrusion of intervertebral discs;
- tumor neoplasms;
- vertebral displacement.