10.01.2019
Myoclonic epilepsy is a disease characterized by myoclonic twitching, epileptic seizures, sometimes there are disturbances in walking movements, deterioration in the functionality of the speech apparatus, and decreased mental abilities.
To determine the form of the disease, it is necessary to conduct a diagnosis, with whose help it will be possible to draw a clinical picture based on the symptoms. The examination methods include a survey, observation of the neurological and mental state, and instrumental studies are also prescribed.
Myoclonic seizures: causes of development
Signs of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME) first appear during puberty.
The disease is diagnosed in 12% of patients suffering from epilepsy. In 23%, JME develops due to congenital anomalies (idiopathic type). Seizures in epilepsy mainly occur when a teenager wakes up, and there are often cases when seizures involve paired organs. Initially, the disease manifests itself in the form of rare muscle twitching (myoclonus) in the shoulder area or upper limbs. But as epilepsy develops, adolescents experience generalized seizures that occur with varying frequencies (from once a day).
The average incidence of febrile seizures is 3-5%. With the absence form, a sudden short-term loss of consciousness is possible.
Catamenial epilepsy is classified as a separate type. This type of disease is typical only for teenage girls. Seizures in the catamenial form are associated with the menstrual cycle. Despite the diagnosis, a girl suffering from epilepsy can have children.
Before treating a disease, it is important to identify its cause in order to prescribe adequate therapy. Myoclonus - involuntary muscle contractions, most often manifested due to a hereditary mutation transmitted according to an autosomal recessive principle. This disease is most common among adolescents and young men.
Myoclonic seizures can be caused by a number of other factors:
- head injury;
- stress, nervous shock;
- a brain tumor;
- birth injuries;
- insufficient blood supply to the brain;
- infections, including those suffered during the prenatal period.
Any factor that causes brain damage can cause myoclonic seizures. This condition can be dangerous for the patient, since during it the patient may fall to the ground and be injured. However, the attack can also pass almost unnoticed with a slight tremor.
Neurologists diagnose myoclonic seizures and concomitant diseases even with minor manifestations. Timely diagnosis and treatment of the disease allows people to avoid serious consequences.
Conventionally, the course of myoclonoepilepsy is divided into three stages:
- Epileptic-titaniform - lasts several years and is characterized by the occurrence of epileptic seizures. As the disease develops, attacks become more frequent and transform from typical to tetaniform, characterized by increased sweating, painful spasms, and a feeling of fear. During seizures the patient is conscious. There are usually no neurological changes at this stage, but in some cases patients become aggressive or withdrawn and depressed.
- The myoclonic-epileptic period can last for many years and is expressed in a reduction in the number of seizures, which are replaced by attacks of myoclonus. Initially, muscle contractions are small and do not affect vital functions; as a rule, part of the limb is affected. Over time, myoclonus spreads to other parts of the face and body, the patient cannot eat or write, and when walking he is thrown to the side. Attacks of muscle spasms in myoclonoepilepsy can be provoked by sudden movements, loud sounds, flashes of light, alcohol consumption, strong expression of emotions, stress, cold or heat. Myoclonus disappears during sleep.
- The terminal period is characterized by cachexia and serious mental changes, accompanied by speech and memory disorders and bordering on dementia.
Depending on the type of myoclonus epilepsy, the diagnostic examination may have different specifics. Most often, the diagnosis is made based on the patient’s age and the combination of attacks of myoclonus with epileptic seizures, disorders of cerebellar activity; A blood test is also performed.
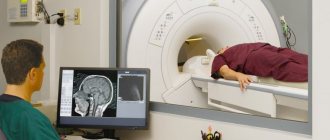
The EEG shows a disruption of the normal alpha rhythm, which intensifies during an attack and exposure to bright light. A CT or MRI scan can reveal changes in brain tissue, particularly the cerebellum and cerebral peduncles.
Patients with myoclonus epilepsy are characterized by the presence in the tissues of internal organs of the so-called. “Lafora bodies”, consisting of polysaccharide compounds. In some cases, genetic testing is necessary. It is necessary to differentiate myoclonus epilepsy from other diseases that are characterized by a combination of main symptoms (such as Kozhevnikov epilepsy or encephalopathy).
With this form of epilepsy, it is quite difficult for a non-specialist to determine that the patient is having a seizure, especially in the initial stages.
But if seizures occur, they are preceded by involuntary twitching of the upper limbs and contraction of the muscles of the face, neck and head, while the patient is conscious.
The most likely time for seizures to develop is early in the morning, immediately after waking up.
Seizures can occur once a day or once every few months, the intensity of such attacks can vary - from twitching of the eyelid to severe cramps of the upper extremities.
Diagnostic principles
Based on the patient’s complaints, life history and illness, the doctor will assume that he has one of the types of hyperkinesis. To make the doctor’s task easier, the patient should describe in detail how attacks of muscle twitching occur, what muscle groups they cover, how long they last and in what situations they occur. In order to clarify the diagnosis, the patient will be prescribed additional types of research, namely:
- electroencephalography;
- electromyography;
- radiography of the skull;
- computer or magnetic resonance imaging.
The results of these studies will help the specialist establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
Description of the pathology
The disease in ICD-10 is designated by code G40.4.
The pathology mainly manifests itself at the age of 13-18 years and is characterized by myoclonic seizures, which are expressed in involuntary twitching or activity, the attacks always affect paired organs in the upper body.
Less commonly, convulsions are observed in the lower extremities.
The main form of the disease is myoclonus epilepsy, which is a hereditary lesion of the central nervous system, due to which myoclonic seizures occur.
There is also a form of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy called Janz syndrome.
This is a generalized benign form of pathology that occurs against the background of age-related transformations in the body.
All manifestations of myoclonic epilepsy, depending on their origin, can be divided into three groups:
- symptomatic. The disease is a consequence of other pathological processes in the body;
- idiopathic. The pathology is transmitted hereditarily and manifests itself in childhood or adolescence;
- cryptogenic. It is not possible to accurately determine the etiology of such diseases. These forms of epilepsy are the most difficult to treat with medication.
Some cryptogenic forms eventually move into one of the other two groups, since with the development of the level of diagnostic medicine, it sometimes becomes possible to determine the cause of the disease.
Myoclonus is a specific idiopathic generalized epilepsy of a benign form. The manifestation of pathology occurs in the form of a seizure. Their peculiarity is that their occurrence is noted mainly after awakening. Often there may be attacks that involve paired organs, for example, the eyes or limbs.
The development of pathology begins in childhood. This is a fairly common type, since 8-10 percent of cases are precisely this form of epileptic seizures. Juvenile epilepsy can affect both females and males.
Why do my legs twitch?
The legs are more susceptible to myoclonus than other parts of the body. Many people could observe how the leg twitches involuntarily when falling asleep. The main reasons for this phenomenon have already been described. It should be emphasized that leg twitching during sleep in the case of the listed diseases is the least of the evils.
If a person constantly notices that his legs twitch when falling asleep, he should definitely contact a therapist first and tell him about this symptom. The doctor will probably refer you for examination. Do not be surprised if some serious metabolic disorder or even a disease from the above list is discovered as a result.
Many people with depression and sleep disorders describe their nighttime experiences as “restless legs” (also known as Ekbom Syndrome). All these disorders must be treated. Then the unpleasant sensations associated with falling asleep will gradually pass.
Pregnant women often notice how their legs twitch while falling asleep. This is usually associated with a deficiency of iron, potassium, and some other microelements.
What to do in such a situation? First of all, consult your doctor. You may need to adjust the menu or take an additional vitamin complex. After the birth of the baby, the described unpleasant sensations will go away on their own.
Leg twitching during sleep is common in older people. This is due to changes in the functioning of the nervous system. Myoclonus cannot be neglected in this case. It is imperative to conduct an examination to exclude the possibility of serious diseases (for example, Parkinson's disease).
Causes of occurrence in adults and children
Adolescent (juvenile) epilepsy first makes itself felt at the age of 10-12 years. The disease is divided into several types depending on the nature of its manifestations.
More often, patients are diagnosed with a form of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (Jantz syndrome). Generalized seizures are less common.
Despite the characteristics of the disease in adolescence, there is no reason to limit the behavior of a teenager. Regular taking of medications ensures a full life.
Today, they more often talk about hereditary causes of the development of myoclonic epilepsy, especially when it comes to infantile forms.
In general, the disease is always caused by genetic disorders, but they can be transmitted not only hereditarily, but also against the background of the following diseases and provoking factors:
- exposure of the fetus during pregnancy to toxic substances that enter the mother’s body through smoking, drinking alcohol and narcotic or pharmaceutical drugs;
- intrauterine infection (especially with viruses that can easily disrupt gene structure);
- effects of radiation on the fetus.
READ MORE: Manual therapy for lumbar protrusion
Pathology can develop in the embryo and with diabetes mellitus or pathologies of the lungs and heart, which occur in a chronic form in the expectant mother. In such cases, disruptions in the formation of the central nervous system of the fetus often occur.
The causes of epilepsy in adolescents are difficult to establish. In most cases, the disease is hereditary.
Also, regardless of the type of epilepsy, the causes of its occurrence in adolescents are associated with the absence form of the pathology that previously manifested itself in the child. That is, the second disorder develops against the background of the untreated first.
The reasons for the appearance of the juvenile form of the disease include the influence of the following factors:
- infectious pathologies affecting the brain;
- congenital anomalies, brain tumors;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- cerebrovascular accident.
However, a direct relationship between this disease and organic brain damage has not been established.
Epileptic seizures occur under the influence of various factors. Juvenile epilepsy mainly manifests against the background of mental or physical fatigue. Less commonly, attacks occur due to the consumption of alcoholic beverages, various diseases, and metabolic disorders.
In addition, epileptic seizures occur due to a sedentary lifestyle. Relapse of the disease also occurs due to sleep disturbances.
Features of helping the patient
Treatment of this disease is carried out only with medication. In some cases, the patient is prescribed surgical intervention. If the diagnosis was made correctly, then recovery occurs quite quickly.
Features of drug effects
A patient with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy is prescribed basic medications. The prescribed drugs are based on valproic acid derivatives.
If treatment does not bring the desired result, the doctor makes a decision regarding the prescription of polytherapy.
In this case, the patient is prescribed medications such as:
- suxilep and valproate (relevant in the presence of resistant absence seizures);
- phenobarbital and valproate;
- clonazepam, lamotrigine and valproate (relevant when myoclonic seizures are combined with photosensitivity).
In 75 percent of patients, absolute drug remission is observed. Most often, there is no need for polytherapy, and the result is achieved thanks to the effects of valproate. In 25 percent of patients, unfortunately, relapses are often diagnosed.
Cancellation of drug therapy is relevant in the 4th year of treatment. Even if the condition is relatively stabilized, drug treatment should not be stopped earlier.
Important to consider
Normalization of the daily routine is of great importance. First of all, this concerns sleep patterns. A person should train himself to go to bed and wake up at approximately the same time. Otherwise, the condition may be aggravated by insomnia.
It is equally important to constantly monitor the quality of your sleep. Considering that one of the main provoking factors is photostimulation, the patient should avoid bright light in every possible way.
So, you should not attend concerts of pop and rock performers. Until complete recovery, you do not need to visit bars and discos. You should also refrain from watching cartoons, anime and manga.
Types of attacks and accompanying symptoms
There are three types of myoclonus epilepsy attacks:
- Myoclonic. Characterized by muscle twitching that cannot be controlled. They usually occur in the morning, but can also be triggered by fatigue, strong emotions, alcohol consumption, sound or light exposure. The presence of cramps can be observed both in an individual muscle or limb, and throughout the body.
- Absence seizures. Consciousness turns off suddenly for a short period of time. It is caused by a lesion in the brain that affects its different parts. In this state, a person is in a stupor for several seconds, while his gaze also freezes, speech and movement stop. Despite their short duration, absence seizures lead to serious disturbances of consciousness.
- Tonic-clonic. The whole body is subjected to a convulsive state. In addition, loss of consciousness is observed. Involuntary urination or defecation is possible. The duration of the attack is several minutes. They are observed in more than half of patients and usually occur during awakening.
On this topic
- Natalia Sergeevna Pershina
- March 26, 2020
Myoclonic epilepsy is classified into several forms:
- Infants are benign in nature. This is a rare type of disease. Its development can last from several months to five years. However, it has not yet been possible to determine the root cause. The only thing is that in rare cases it can transform into an adolescent form, practically does not cause serious complications and quickly passes with correct and timely treatment. May be accompanied by twitching of the limbs or head, and sometimes the body. Myoclonus may also vary in intensity. During the period when a person falls asleep, they intensify, and during sleep they disappear. In this case, psychomotor development is not damaged in any way. The diagnosis is made based on the collection of anamnestic data.
- Dravet syndrome is severe and occurs in 5 percent of infants. Until the symptoms begin to manifest themselves, the child develops normally. This type of attack often provokes severe psychoneurological disorders, sometimes even fatal.
- Unferricht-Lundborg disease. It is considered the more common form. Observed during late childhood. The pathology begins to manifest itself with myoclonus, which is subsequently complicated by absence seizures and focal attacks. The disease develops slowly. Over the course of many years, the patient’s intellectual abilities remain unchanged, but afterward there is a decrease in memory and frequent depressive states. The disease has periods of remission and exacerbation, which leads to the fact that the patient is forced to spend all his time in bed. The diagnosis is based on the clinical picture. With timely treatment, there is a chance of slowing the development of pathology, which allows the patient to live to old age.
- Myoclonic epilepsy with broken fibers. This form provokes the development of abnormal DNA. In most cases it is observed in childhood and adolescence, but it also occurs in adults. In addition to the fact that this form is accompanied by tonic convulsions and myoclonus, the patient’s coordination is impaired, deafness and myopathy progress. During diagnosis, torn fibers can be seen in the skeletal muscles, and the content of lactic acid in the blood increases significantly.
Conventionally, the course of the disease can be divided into three stages:
- Epileptic-titaniform - can last for several years. As the disease progresses, attacks become more frequent, accompanied by painful spasms and increased sweating. The patient is conscious. As a rule, at this stage there are no neurological disorders, but the patient may exhibit aggression, depression or withdrawal.
- Myoclonic-epileptic – often can last for many years. The number of seizures decreases, and attacks of myoclonus occur. At the beginning, muscle contractions occur only in part of the limb, gradually spreading to the entire body. The patient loses the ability to eat and write independently. While walking, there is a bending from side to side.
- Terminal – leads to serious changes at the mental level, which is expressed by memory and speech disorders.
It should be noted that the last stage can lead to dementia of the patient.
Forecast
The prognosis of myoclonus epilepsy is unfavorable, especially if therapy is not started in a timely manner. In some cases, there is a drug-resistant form of the disease that is difficult to treat. In this case, powerful anticonvulsants are used. Without treatment, the patient becomes disabled as a result of dementia and ataxia. According to statistics, in most people the disease leads to ataxia. But modern medicine makes it possible for patients to live up to seventy years.
Myoclonic seizures of epilepsy: treatment in Moscow
Treatment of myoclonic seizures is primarily symptomatic and aims to relieve the attacks. As a rule, patients are prescribed anticonvulsants and sedatives. The Yusupov Hospital presents the most modern medicines, supplied directly from the manufacturer.
Compliance with the regime for this problem is extremely important, since seizures can occur repeatedly. The patient should stop drinking alcoholic beverages, avoid stress, follow medical recommendations, and avoid lack of sleep. A neurologist at the Yusupov Hospital develops additional recommendations for each patient, in addition to basic recommendations, taking into account lifestyle and risk factors.
People with complaints of frequent seizures need to undergo a study - electroencephalography, which will identify the patient's epilepsy and related problems. After this, the doctor may prescribe, in addition to drug therapy, other ways to eliminate the problem that are aimed at strengthening the body. These include some physical therapy, B12 injections, plasma and blood transfusions.
If you are faced with a problem such as myoclonic seizures, seek help from leading specialists in Moscow. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital see patients every day and help them get rid of their problems and return to a full life. You can make an appointment with a doctor and get advice on questions of interest, the cost of diagnosis and treatment by calling the clinic.
Medical news
07.05.2019
The incidence of meningococcal infection in the Russian Federation in 2020 (compared to 2020) increased by 10% (1). One of the common ways to prevent infectious diseases is vaccination. Modern conjugate vaccines are aimed at preventing the occurrence of meningococcal infection and meningococcal meningitis in children (even very young children), adolescents and adults.
25.04.2019
The long weekend is coming, and many Russians will go on holiday outside the city. It's a good idea to know how to protect yourself from tick bites. The temperature regime in May contributes to the activation of dangerous insects...
05.04.2019
The incidence of whooping cough in the Russian Federation in 2020 (compared to 2020) increased almost 2 times 1, including in children under the age of 14 years. The total number of reported cases of whooping cough for January-December increased from 5,415 cases in 2020 to 10,421 cases for the same period in 2020. The incidence of whooping cough has been steadily increasing since 2008...
20.02.2019
Chief children's phthisiatricians visited school No. 72 in St. Petersburg to study the reasons why 11 schoolchildren felt weak and dizzy after they were tested for tuberculosis on Monday, February 18
18.02.2019
In Russia, over the past month there has been an outbreak of measles. There is a more than threefold increase compared to the period a year ago. Most recently, a Moscow hostel turned out to be a hotbed of infection...
Bibliography
- ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases)
- Yusupov Hospital
- Bryukhanova N.O., Zhilina S.S., Ayvazyan S.O., Ananyeva T.V., Belenikin M.S., Kozhanova T.V., Meshcheryakova T.I., Zinchenko R.A., Mutovin G. R., Zavadenko N.N.. Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome in children with idiopathic epilepsy // Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics. — 2020. — No. 2. — P. 68–75.
- Victor M., Ropper A.H. Guide to neurology according to Adams and Victor: textbook. manual for the postgraduate system. prof. physician education / Maurice Victor, Allan H. Ropper; scientific ed. V. A. Parfenov; lane from English edited by N. N. Yakhno. — 7th ed. — M.: Med. information agency, 2006. - 677 p.
- Rosenbakh P. Ya.,. Epilepsy // Encyclopedic Dictionary of Brockhaus and Efron: in 86 volumes (82 volumes and 4 additional). - St. Petersburg, 1890-1907.
What is myoclonus
Myoclonus is an instantaneous contraction of muscle tissue, not accompanied by any symptoms or other disorders.
Most often, this muscle twitching is momentary in nature and rarely appears , but in case of disturbances, contractions become regular, repetitive and occur with different frequencies.
Abbreviations can be generalized , i.e. covering the entire body, or local , which affect only individual muscles.
And by inheritance and acquired
The most common cause of the disease is a hereditary mutation in an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance; cases of dominant transmission are also known.
There are other factors that can provoke myoclonus epilepsy:
- insufficient blood supply to the brain;
- infections, incl. intrauterine infection of the fetus;
- head injury;
- severe nervous shock, stress;
- brain tumors;
- damage to the fetal brain during pregnancy, as well as birth injuries.
In some cases, the cause cannot be identified.
Another name for myoclonus epilepsy is Janz syndrome. The main peak of onset of the disease occurs during puberty or late childhood, which is why the name juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME) is also common.
Children who have relatives with epilepsy have an increased chance of inheriting the juvenile form, hence another name for myoclonic epilepsy - familial.
Cases of direct transmission of myoclonus epilepsy from parents have not yet been identified, but it is often detected among brothers and sisters, as well as other blood relatives. Children suffering from absence epilepsy are also at risk.
As a rule, epilepsy attacks are primary, then myoclonus joins them, but sometimes the disease begins with mental changes.
Prevention
Measures to prevent the development of myoclonus include reducing situations associated with mental stress and maintaining a calm environment. Normal sleep for adults should last seven hours, for children - ten. To relax before going to bed, it is useful to take a warm bath.
An hour before going to bed, do not watch TV or sit at the computer. It is better to put scented candles and massage at this time.
During the day, take walks in the fresh air, eat normally, do not smoke or drink alcohol.
Cortical myoclonus (myoclonus) often manifests itself as a natural reaction to fatigue and unexpected stimuli. This form does not need to be treated. Negative is caused by various pathologies, for example, epilepsy or encephalopathy. Its treatment and prognosis depend on the underlying disease. To prevent pathology, it is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle.
The following sources were used to prepare the article: Mironov M. B., Nogovitsin V. Yu., Abramov M. O., Dombrovskaya E. A., Kvaskova N. E., Mukhin K. Yu. Fejerman syndrome (benign nonepileptic myoclonus of infancy) // Journal of Epilepsy and Paroxysmal Conditions - 2013.