Epilepsy in newborns - causes, symptoms and treatment
Parents of sick children wonder why this happened to their child and what are the causes of this disease.
Let's consider the factors that cause the appearance of epilepsy:
- Perhaps during the period of intrauterine development there was a failure in the formation of the brain. The reasons for this failure may be the use of alcohol and drugs during pregnancy, as well as smoking. If, while carrying a child, the expectant mother suffered from viral diseases (flu, herpes, colds), then the risk of developing epilepsy increases.
- The older a woman is, the higher the risk of having a child with pathologies.
- The prenatal process plays an important role. If a child is in the womb for a long time without amniotic fluid, entwined with an umbilical cord, and labor lasts a very long time, then the likelihood of having a child with developmental disabilities increases.
- Nervous system disorders, as well as bacterial and colds, accompanied by high fever and seizures, can cause epilepsy.
- Epileptic factors also include injuries, falls and concussions.
- Low levels of the hormone dopamine lead to inhibition of chemical processes in the brain.
- Deficiency of microelements and vitamins. In 1973, American scientists discovered that a lack of minerals in the body is associated with seizures. Parents should monitor the level of zinc and magnesium in the body. When stressful situations occur, as well as an increase in body temperature and increased physical activity, a rapid decrease in the amount of magnesium in the body occurs.
- A benign or malignant brain tumor can cause the development of pathology.
- Cryptogenic causes in which it is impossible to determine the factor causing epilepsy.
Epilepsy attacks in infants and their characteristics
The manifestation of epilepsy in infants is significantly different from seizures that occur in adults. The manifestation of epilepsy in an infant can easily be confused with normal physical activity. This factor makes diagnosis difficult.
Signs of epilepsy:
- Epilepsy is associated with seizures. During an attack, all the muscles of the body tense, and breathing stops for a short time. Then convulsions begin, varying in duration and intensity. The bladder empties spontaneously. After some time, the convulsions end, the child calms down and falls asleep.
- Epilepsy can occur without seizures. The child seems to freeze, his gaze is glassy. Twitching of the eyelids, closing of the eyes and tilting of the head back may be observed. This attack lasts about 20 seconds. After such a seizure, the baby continues his usual actions. Parents may not notice such an attack.
- Loss of consciousness and muscle relaxation are characteristic signs of an atonic attack. This attack resembles fainting. A doctor's consultation is necessary if the child frequently loses consciousness.
- A spasm occurs, accompanied by involuntary pulling of the arms to the chest, bowing of the head and straightening of the legs. Such actions can often be observed after waking up.
There are other symptoms of epilepsy. The child may have disturbing dreams. He can move around the apartment without reacting to the speech of an adult. There is also a severe headache accompanied by vomiting.
The difference between epilepsy in newborns and physiological changes
It is difficult to independently identify epilepsy in a newborn. You should pay attention to such points as:
- Twitching and contraction of all muscles;
- Sharp turn of the head or body, short freezing;
- Redness or paleness of the skin;
- Screams accompanied by shuddering;
- Simultaneous twitching of limbs;
- The look is absent.
How to diagnose epilepsy in a newborn?
By observing the symptoms and the general condition of the child, epilepsy can be recognized. The appearance of seizures for no reason may raise suspicion. You should immediately call an ambulance if your child has a seizure. A neurologist can diagnose epilepsy.
Stages of diagnosing epilepsy:
- Data is collected to compile a medical history. This collection includes information about the course of pregnancy, the condition of the child after birth, injury and illness, as well as the presence of relatives in the family with a similar pathology.
- You should talk in detail about the child’s attack.
- A medical examination is carried out, which includes an assessment of neurological, mental and cardiac status.
- To exclude other diseases, blood is given for analysis.
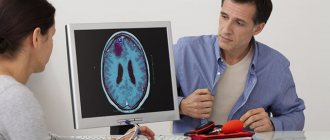
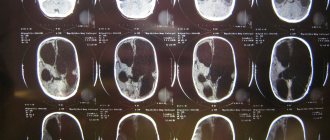
- In order to determine the nature of the attack, a CT scan of the brain is performed.
- An EEG is required.
- To assess the state of the brain and identify pathology, an MRI is performed.
After the research and analysis of the results obtained, the neurologist gives a conclusion about the presence or absence of epilepsy.
Methods for treating epilepsy
After confirming the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment, which includes taking anticonvulsants. Therapy is prescribed taking into account the diagnostic results, age and individual characteristics of the child’s body. At first, the dosage of drugs is minimal, then increases. In some cases, hormonal treatment and immunotherapy are required.
Parents' actions during an attack. First aid
If the attack was short, then there is no need for special measures. During an attack accompanied by severe seizures, parents must do everything to prevent the child from injuring himself.
First aid includes the following:
- Hold the baby's torso and head;
- Remove constrictive clothing;
- Open the window, give access to oxygen;
- If breathing stops, perform artificial ventilation.
- Do not leave the child, stay nearby.
- You can give medicine to your child only after he comes to his senses.
If such an attack occurs for the first time and lasts more than 5 minutes, then you need to call an ambulance.
After a seizure, the child falls deeply asleep. Monitoring the child after a seizure is of great importance, as seizures may recur. If the child slept peacefully for two hours, this means that the attack is over.
Impact of epilepsy on child development
The diagnosis of epilepsy frightens most parents. It should be noted that this pathology is not genetically determined. It has no effect on the psyche. The child is not at risk of mental retardation and aggression.
Some parents believe that strong medications are harmful to the child. But in fact, it is the lack of therapy that causes more harm.
Epilepsy is a well-studied disease. There are effective methods to combat this pathology. The disease is not an obstacle to normal life.
Source: https://epihelp.center/medikametoznoe-lechenie-epilepsii/epilepsiya-u-novorozhdennyh/
Diagnostics
How to diagnose epilepsy in infants? In infancy, this is quite problematic. An EEG is mandatory. With its help, it is determined where the foci of pathological activity are located in the baby’s brain. A CT scan or MRI of the brain may also be performed. Using these studies, it is possible to determine whether there are tumors, cysts or infectious diseases of the brain that lead to epilepsy.
An encephalogram is required to make a diagnosis.
Signs of epilepsy in infants and their difference from symptoms in adults
Epilepsy is a fairly common disease. According to statistics, every hundredth person suffers from this pathology, and this is a very high incidence rate. Seizures often occur in very young children and can be dangerous. Therefore, it is very important to know what signs of epilepsy occur in infants in order to respond and take action in a timely manner.
Epilepsy is a disease whose symptoms manifest themselves in the form of seizures, disturbances of consciousness and disorders of coordination movements.
The brain of a newborn with this pathology cannot cope with basic functions; its inhibition processes are not yet sufficiently developed. Therefore, various disturbances of motor activity, autonomic reactions and sensory disorders arise.
In children, this disease can occur completely atypically to such an extent that it can be missed. For this reason, such children do not receive the necessary treatment for a long time.
Mechanism of attack development
The human brain is in constant work. It emits a certain frequency and sequence of waves that determine its functional activity.
As a seizure develops, the waves become sharper and more chaotic and are interrupted; this is clearly visible in an EEG study.
Sometimes an epileptic attack in children goes completely unnoticed, especially if there are no aggravating factors in the form of a cranial injury, severe intoxication or infection.
Reasons for development
In infants, an attack can be triggered by the following factors:
- Feverish condition.
- Hypo- or vitaminosis.
- Birth trauma with hematoma, brain tumor, cystic formation.
- Fetal asphyxia.
- Severe conjugation jaundice.
- A parasitic or viral infection that damages the meninges.
- Down's disease.
- A sharp decrease in blood sugar in the presence of diabetes.
- Chronic pathologies of internal organs.
Diagnostics
How to recognize epilepsy in an infant? As soon as there is a suspicion of the development of an epileptic attack, you should immediately consult a doctor and examine the baby. But even experienced specialists cannot always determine the true cause of the development of pathology, especially at a very early age.
In this case, they talk about idiopathic epilepsy. Sometimes family history reveals patients with this disease. This means that we are talking about a hereditary predisposition to it.
Epilepsy itself is not inherited; if there are close relatives suffering from this pathology, we are only talking about the probable possibility of contracting it in the presence of provoking factors.
To clarify the diagnosis, the child must be examined using encephalography, neurosonography, CT, and MRI. Dopplerography of the brain vessels can provide an additional picture.
Signs
Symptoms of epilepsy in newborns are as follows:
- heat;
- memory loss;
- muscle tension or cramps;
- sometimes there is a lack of consciousness;
- the child seems to “freeze”;
- throws back his head;
- no reaction to the outside world;
- the duration of this state is from 2 to 20 minutes;
- look at one point.
Foaming at the mouth or biting of the cheeks and tongue are not observed in infancy. Urinary and fecal incontinence, as well as rapid falling asleep after an attack, are not typical for neonatal epilepsy.
Some diseases can present with similar symptoms, so diagnosis can be difficult at a very early age. Even a pronounced convulsive state cannot be a reliable sign of an epileptic seizure in infants.
With a convulsive syndrome that has a different origin, identifying the cause of its occurrence can be easier than with epilepsy.
Often at this age, convulsions may develop against the background of an increase in temperature, which do not require special treatment and disappear as the condition improves.
Unlike epileptic seizures, they do not occur with any regularity. This phenomenon is called epileptiform activity.
The baby's spasms resemble nodding movements and are called infantile spasms. The onset of such a syndrome can debut by 4 months, and lasts up to one or two years.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of anamnesis of the disease, identification of a possible hereditary predisposition to this disease, and the main symptoms.
Possible complications
Seizures in childhood can be dangerous due to developing complications:
- epistatus, when many seizures occur over a short period of time;
- traumatization when seizures occur;
- disturbances in mood, sleep, appetite, moodiness;
- retardation in mental and physical development;
- death due to tongue or vomit entering the respiratory tract.
Treatment and therapy
Treatment of this disease in children is carried out by a neurologist or epileptologist. The baby's regime should be as gentle as possible; he should not hear loud noise.
If possible, he should avoid stress and eating cold or hot food. You should first consult your doctor about any complementary foods.
During the transition to a normal diet, it is recommended to limit fluid and salt.
Epilepsy, if left untreated, leads to serious complications and can develop into adult epilepsy with severe mental disorders. Therefore, such a child needs timely treatment from a qualified specialist, as well as constant monitoring and observation.
Source: https://VashNevrolog.ru/epilepsiya/priznaki-epilepsii-u-grudnichkov.html
Epilepsy in infants: symptoms of seizures up to a year, diagnosis and treatment
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disease characterized by seizures. It can have different forms and different symptoms. Epilepsy in infants may be associated with a hereditary predisposition or problems with intrauterine development. This pathology is incurable, but with properly selected therapy, remission can occur.
Etiology of the disease
Epilepsy in newborns can occur for the following reasons:
- Bad heredity. According to statistics, if both parents are sick, the child will be born with pathology in 90% of cases. If only one of the parents is sick, this percentage will be lower, but the likelihood of having a sick baby will also be very high.
- Complications during pregnancy. If the fetus does not receive enough nutrients, is not positioned correctly, or the mother is sick with something, there is a high probability that it will be born with various abnormalities.
- Complicated childbirth. If the process is prolonged, oxygen starvation may occur. This can cause damage to the child's brain.
- Birth injuries. As a result, neural connections in the brain can be broken, which leads to the formation of foci of epileptic activity.
- Postpartum trauma. Do not drop the baby, as this can lead to head injuries. In this case, symptoms of epilepsy in an infant will not appear immediately, but when scar tissue forms in the cerebral cortex.
- Infectious diseases. The child's body is very delicate and sensitive, so he can easily catch an infection. To avoid the development of otitis and meningitis, the baby must wear a cap.
With epilepsy, epileptic foci form in the brain. They can affect it completely or only certain parts. From this, different forms of the disease are distinguished.
During an epileptic attack, infants may have seizures
Symptoms of manifestation
Those experiencing epilepsy for the first time can be quite shocked. Indeed, in most cases, attacks look frightening and are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- There is a blackout of consciousness. The child may play, smile or even cry, but then he suddenly becomes quiet.
- During an epileptic attack, infants may have seizures. Arms and legs may bend unnaturally, and the small body may shake violently. The muscles spasm and become hard. Cramps may involve the entire body, only one part of the body, only one limb, or be absent altogether.
- The eyes roll behind the eyelids.
- Changes in breathing are observed. The baby may begin to breathe too quickly and noisily. Or, on the contrary, his breathing slows down, it seems that the child is not breathing.
- The pupils are dilated and do not respond to changes in light.
However, not all forms of epilepsy are accompanied by such symptoms. Often the signs of epilepsy in infants are almost invisible, so sometimes parents do not pay due attention to them. But as soon as the baby’s behavior changes, you need to contact a specialist.
Symptoms of the pathology may appear in the first days of life. But most often, epilepsy first appears between the ages of 1 and 4 years.
There is also a so-called aura or precursors to epilepsy. They appear about a day before the attack. The baby becomes capricious, constantly cries, and refuses to eat.
About a day before the attack, the baby becomes capricious and constantly cries.
Minor seizures
In this case, epileptic foci spread only to part of the brain. Petite seizures include the following types of epilepsy:
- Propulsive seizure. Most often it is a consequence of birth trauma. During such a seizure, the baby bends his head and torso. The attack lasts only a few seconds. However, several repetitions per day may occur.
- Retropulsive. The baby loses consciousness. His eyes close, and his body remains in the same position it was in. It seems that the child just fell asleep.
- Impulsive attack. How to determine such epilepsy in an infant? The baby remains conscious. However, from time to time one or another part of the body trembles, as impulses are sent to it from the brain.
Minor seizures can occur even during sleep. If epilepsy is accompanied by seizures, you need to ensure that the baby sleeps only in the crib. There should be no hard objects near it that it could hit.
Generalized
Symptoms of epilepsy in infants can be very pronounced. This happens with a generalized or grand mal seizure. The whole body is attacked by convulsions, the baby bends, his legs and arms can perform sudden chaotic movements. The face turns pale, foam comes out of the mouth, and involuntary bowel movements are possible.
The danger of such an attack is that the baby may hit himself due to severe convulsions. Teething babies may bite their tongues hard. This can lead to large blood losses. To avoid this, during an attack the baby should be placed on a soft pillow, and a special device for biting should be placed in his mouth.
Features of the manifestation of night attacks
Night attacks occur with less severe symptoms, since brain activity is less intense during sleep. In addition, such seizures can only be observed during certain periods, due to which they are divided into several subtypes:
- Night early. They are observed 2 hours after the baby falls asleep.
- Early. Take place an hour before waking up.
- Morning. An hour after waking up.
- Mixed.
Another feature is that tonic convulsions are replaced by tonic-clonic ones, after which the baby falls asleep. In the tonic phase, erratic body movements appear. Due to the spasm, the chest becomes motionless, the baby breathes very slowly and silently. This phase lasts 20-30 seconds.
Then the clonic period begins, during which saliva involuntarily flows from the baby’s mouth, limbs tremble, and urination is possible. This period lasts 1-5 minutes.
As a result, the baby's sleep is disturbed, he becomes restless and cries. In older children, nocturnal epilepsy leads to nightmares.
First aid
If a minor seizure occurs, no special measures need to be taken. You just need to stay close to the baby until the attack is over.
And in case of major attacks, it is recommended to provide first aid. Usually the attack occurs suddenly. An adult with the child should do the following:
- Keep calm. You can’t panic, otherwise you can only harm the baby.
- Place something soft under the child's head and turn him on his side. If the attack happened on the street, you can fold your jacket and put it under your head.
- If the attack is accompanied by severe convulsions, the head must be held, otherwise the baby may hit it.
- It is necessary to remove the baby's clothes so that his neck is not compressed, as this may interfere with breathing.
- Open the window to allow fresh air into the room.
- handkerchief several times and place it in the child’s mouth, otherwise he may bite his tongue. It is strictly forbidden to put your fingers in his mouth - during an attack he can bite them until they bleed.
- If the baby's breathing stops and he begins to turn blue, artificial ventilation will be needed.
Until the baby comes to his senses, you need to monitor him. You can't leave him alone. It is also prohibited to give any medications until the attack is over.
Then the baby must be placed in the crib. Usually after an attack, breathing evens out and deep sleep occurs. There is a possibility that a second attack will occur. Therefore, you should not leave your child unattended for 2-3 hours.
If a seizure occurs for the first time, you must definitely call an ambulance. In addition, a medical examination is necessary if the seizure lasts more than 5 minutes or the baby received some kind of injury during it.
If the attack is accompanied by convulsions, the baby's head must be held
Treatment
Children with congenital epilepsy require long-term treatment with anticonvulsants. Monotherapy is practiced when one drug is selected. At first, its dosages are small, but gradually increase them. Preparations based on valproic acid, Carbamazepine, Topiramate and other drugs can be used.
Non-drug therapies can also be used. Psychotherapy, hormonal treatment, and the ketogenic diet are effective.
Surgical methods are rarely used. Surgery may be prescribed to treat resistant forms of epilepsy. For this purpose, temporal lobectomy, temporal resection, hemispherectomy and other methods may be prescribed.
Carbamazepine – a drug for the treatment of epilepsy
Forecast
Timely treatment can help control attacks of childhood epilepsy. Timely administration of antiepileptic drugs will help achieve stable remission. The child will be able to attend kindergarten, then school and lead a normal life.
If remission is observed for 3-4 years, the doctor may stop taking the medications. In 60% of patients, after such treatment, attacks do not recur.
Prevention measures
It is necessary to begin the prevention of epilepsy at the stage of pregnancy planning. It is necessary to follow all doctor's recommendations and take medications to ensure a successful pregnancy.
It is necessary to give birth to an experienced obstetrician, which reduces the risk of birth injuries. In the first year of life, you need to regularly visit the doctor, dress your baby well, and avoid any falls.
If manifestations of epilepsy appear in an infant under one year of age, treatment will need to be started immediately. You need to regularly visit an epileptologist and follow his recommendations.
The sooner therapy is started, the greater the chance that the disease will not develop into a more resistant form.
Source: https://NervovNet.com/epilepsiya-u-grudnichkov-01/
Prevention measures
It is necessary to begin the prevention of epilepsy at the stage of pregnancy planning. It is necessary to follow all doctor's recommendations and take medications to ensure a successful pregnancy.
It is necessary to give birth to an experienced obstetrician, which reduces the risk of birth injuries. In the first year of life, you need to regularly visit the doctor, dress your baby well, and avoid any falls. If manifestations of epilepsy appear in an infant under one year of age, treatment will need to be started immediately. You need to regularly visit an epileptologist and follow his recommendations. The sooner therapy is started, the greater the chance that the disease will not develop into a more resistant form.
How to identify epilepsy in infants
Doctors have found that out of the total number of newborns, 1.4% have seizures. At the same time, premature babies have more seizures – 20%. The period from birth to 28 days is called neonatal. This is when complications arise that cause convulsions. Most of them are focal (i.e. focal).
At the 5th month of fetal development, myelin begins to form around the nerve fibers, as well as dendrites. If these processes are disrupted, this will most likely lead to the appearance of seizures, as symptoms of epilepsy in newborns.
But most often, the activity of epileptiform is not detected by clear signs.
- 1 Reasons
- 2 Symptoms
- 3 Diagnostics
- 4 Forecast
- 5 Treatment
Causes
Seizures are caused by pathological electrical discharges in the central nervous system. Epilepsy in infants can be caused by the following:
- Hypoglycemia (drop in blood sugar).
- Hypocalcemia.
- Hypoxia.
- Hyponatremia.
- Ischemic stroke.
- Ischemia.
- Hemorrhage inside the skull.
- Meningitis.
- Tumors.
- Developmental defects.
- Sepsis.
- Encephalitis.
It is believed that intracranial processes and systemic pathologies have different clinical pictures.
Doctors have found that epilepsy in infants is most often caused by ischemia and hypoxia. These seizures are very difficult to treat, but it has been noted that they may decrease. If the newborn has one of the following pathologies:
- Polycythemia;
- Thrombophilia (associated with genetic abnormalities);
- If hypotension is severe, he will most likely develop an ischemic stroke. However, observations have shown that this pathology also occurs in children who are not at risk.
If the seizure is associated with a stroke, then it is focal and can cause temporary cessation of breathing (apnea). If the mother had diabetes mellitus, her newborn will develop hypoglycemia.
In addition, the latter occurs due to galactosemia or lactic acidosis, as well as intrauterine malnutrition.
Convulsions are focal (focal) or may be variable (variable).
If sodium chloride is infused intravenously into a baby, and an accidental overload of this saline solution occurs, hypernatremia occurs. The same thing happens if a large dose of the drug is prescribed orally.
This is often due to the fact that the solution is diluted with water in large quantities.
Epilepsy in newborns occurs due to hypocalcemia associated with prematurity, trauma during childbirth, with virtually no symptoms observed. Hypomagnesemia rarely leads to seizures, but often occurs together with hypercalcemia.
Symptoms
It is important to know: in newly born babies, seizures are focal in nature, so they are difficult to identify. However, there are manifestations by which this can be done. So, signs of epilepsy in infants include:
- Twitching is involuntary (clonic), appearing in different places (migrating).
- Stopping breathing.
- Movement of the jaw (as if the patient is chewing something).
- The eyes do not react to light or, on the contrary, are pointed at one point.
Most often, these signs of epilepsy in infants appear after a stroke associated with ischemia and (or) hypoxia. In most babies, the central nervous system was affected by infections.
We recommend reading the article: Symptoms and signs of epilepsy
Signs of epilepsy in infants - Symptoms and first aid for epilepsy, causes and treatment methods
The dream of every expectant mother is to give birth to a strong, healthy baby. But not always, even after a healthy pregnancy, following a proper diet and daily routine, a child is born without pathologies.
One of the disorders that can appear in the first days of a baby’s life is epilepsy. To ease the course of the disease, it is necessary to know the signs of epilepsy in infants and the manifestations of the pathology.
Causes of epileptic seizures in infants
In 45% of cases in infants, epilepsy occurs after severe fright, environmental influences, or illness.
But this is only part of the reasons that provoke symptoms of chronic epilepsy in a newly born baby; nervous attacks can be caused by:
- Disturbances in the formation of the brain in the prenatal period. The culprit for this is the adult - the mother, who abuses strong alcohol, smokes and takes drugs. Less often, such disorders become a consequence of late pregnancy - the older the woman giving birth, the higher the risk of the disease. Even less often, the fetal brain is formed incorrectly due to preeclampsia or acute respiratory infections suffered by the expectant mother.
- The peculiarity of the course of labor is a long anhydrous period, the use of obstetric forceps to remove the fetus from the womb, asphyxia or hypoxia, prolonged passage through the birth canal, blunt head injuries in the first minutes of life.
- Idiopathic grounds - the child may have low levels of dopamine, which is responsible for inhibiting processes in the brain. In this case, the disease is inherited.
- Deficiency of micro- and macroelements in the mother's womb. It is important for a pregnant woman to maintain normal levels of zinc and magnesium in the body.
Useful to know: What is cerebral edema?
Also, epilepsy in newborns can become the basis of malignant formations in the head area or a previous infectious disease - encephalitis, meningitis, encephalomyelitis.
Doctors are not omnipotent, so there is another reason for the occurrence of convulsive attacks - cryptogenic, that is, without explanation.
How to distinguish epilepsy in a newborn from physiological changes
A baby in the first 12 months of life is very different from a child 2-3 years old: he often screams, flinches, and makes unconscious movements.
Therefore, it can be difficult for parents to recognize the signs of nervous epilepsy in newborns, but it is possible to recognize the following manifestations:
- Sudden freezing, the baby concentrates on one point. Chaotic facial expressions and a grimace appear on the face.
- Lack of response of the child to external stimuli - voice, light, movements around.
- The gaze freezes, the eyes become like glass. A frightening visual sign is that the eyes roll behind the upper eyelids.
Along with these signs, others appear: increased body temperature, involuntary acts of urination and defecation, difficulty breathing or its complete stop, convulsions (from 2 to 20 minutes). The newborn may also lose consciousness. After the seizure ends, the baby continues to behave as usual.
Differences in symptoms for different forms of the disease
The course of epilepsy attacks in children under 12 months varies - the duration and symptoms depend on the form of the disease. There are the following types of pathology: absence, idiopathic, rolandic and cryptogenic. Cryptogenic, absence and idiopathic varieties occur in newborns.
In the absence form, the attack is accompanied by body immobility, gaze stopping, severe muscle tension, the head and limbs are turned in one direction.
At the end of the seizure, the child does not remember the symptoms that appear; pain in the abdomen and head, nausea, and increased body temperature may remind of a recent incident.
The idiopathic form is more frightening: infants may foam at the mouth, sometimes red due to a bitten tongue. Stopping breathing and loss of consciousness can also accompany an attack. The cryptogenic variety combines the two above-mentioned forms.
Doctors identify another mild form of pathology - infantile spasm, which in 90% of cases disappears before 4-5 years.
Signs of a spasm: the arms are involuntarily pressed to the chest, the head or the entire torso leans forward strongly, the legs straighten sharply. The baby may also twitch its head.
Manifestations are often noticeable in the morning, after a night's sleep. It is important to distinguish pathological manifestations from normal physiological processes in time: the reaction of a tiny organism to colic, teething, the desire to eat or drink, a dirty diaper.
Negative effects of epilepsy on child development
In cases where epilepsy in children under one year of age was not recognized in time, complications are possible. Parents can help a specialist correctly diagnose the pathology if they remember the smallest details of the baby’s condition.
The first is the period of occurrence of the first attack, its duration and nature. By character we mean muscle tone (weak, strong), head position, direction of gaze and pupil size.
An attack in a newborn may also be preceded by poor sleep, addiction to computer games or television, and frequent stress.
Regular repetition of convulsive conditions leads to mood disorders, poor appetite, and sleep disorders. In the future, a “special” child may lag behind in physical and mental development.
What to do during an attack?
If a child has a tendency to epilepsy, then parents should learn in advance methods to alleviate his condition:
- If before the onset of the attack there were other negative manifestations, then the baby must be urgently placed on a flat surface with his back down. His throat should not be constricted by buttons or collar.
- It is best if there are no objects nearby that could harm the baby. Additionally, it is also recommended to remove it away from water.
- The relative should not panic. It is important to take complete control of the situation. The body must be securely fixed until the end of the attack.
- You need to tilt your head to the side. This will prevent tongue retraction and saliva aspiration. The same position should be when vomiting.
- Foreign objects should not be placed in the mouth.
- Anticonvulsants will help ease your general well-being. Only a doctor can choose them correctly.
- After the attack ends, the child should rest or sleep.
- Parents should monitor the baby's body temperature.
- The drugs are administered rectally. This method is considered the safest.