Snoring and apnea in children occur with a frequency of 10-12% in the general population. The pathology is caused by obstruction of the upper respiratory tract. An episode of respiratory arrest (apnea) is usually associated with incomplete awakening to restore normal respiratory activity and increase the concentration of oxygen in the arterial blood. The number of apnea attacks at night can reach several dozen, which significantly worsens the quality of sleep and is accompanied by concomitant disorders (stress, depression, increased fatigue, daytime sleepiness, deterioration of cognitive abilities and, as a result, school performance).
Sleep apnea episodes: what are they?
In newborns and older children, the time interval between inhalation and exhalation may be lost during sleep. There are regular, irregular, periodic and pathological breathing, in which it is delayed from 20 seconds to 2 minutes.
Intermittent breathing during sleep in a child is a sign of sleep apnea. This feature occurs due to the lack of tone of the upper palate and uvula. After exhalation, the walls of the pharynx close, creating a barrier to oxygen entering the body.
It is important to know! An episode of sleep apnea in children of all ages is a holding of breath in which there is no movement of the chest. During the entire period of sleep, there are from 2-3 to 30 stops. At the moment, the child may wake up, spin around in the crib, shudder, scream, or even turn blue.
Prolonged apnea of up to several minutes provokes oxygen starvation of the brain, disrupting the functioning of all body systems.
Due to hypoxia, neurons die, which is why the child experiences developmental delays or psycho-emotional abnormalities. It is necessary to monitor your baby's sleep for up to a year, as there is a risk of developing sudden death syndrome. If you experience snoring, constant startling or waking up, consult your pediatrician. Apnea may develop due to a respiratory disease, which can be treated with antiviral medications and rinsing the nose.
Attention! If, in addition to regular breath-holding, the child’s skin begins to turn pale, lips and eyelids turn blue, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance. If the oxygen flow stops, coma and death will occur within six minutes.
Treatment
Sleep apnea in infants is treated taking into account the causes, which involves the use of respiratory stimulants (caffeine preparations) in the central form, caused by insufficient maturity of the central nervous system structures, or the use of such a technique as positioning the baby’s head in case of obstruction caused by improper position of the soft tissues of the pharynx.
If breathing stops for more than 20 seconds, perform artificial respiration. If breathing stops at night in children older than one year are associated with hypertrophy of the tonsils and adenoids, surgery is often performed to remove the overgrown tissue (adenotonsillectomy). An alternative method is CPAP therapy, when using a special device equipped with a compressor, air is supplied into the airways under constant pressure.
Air is supplied through a flexible breathing tube attached to a sealed mask. For overweight children, measures aimed at weight correction are recommended - diet, dosed regular physical activity. All patients are prescribed general strengthening and hardening procedures, including massage, therapeutic exercises, aquatherapy, and douches. In some cases, nootropic drugs (Hopantenic acid preparations) are prescribed as part of complex therapy.
Features of the development of night breath-holding syndrome in children
Breathing disorders at night are a symptom of many diseases of the upper respiratory tract, heart, and gastrointestinal tract. Most often, apnea occurs in premature babies due to the immaturity of the central nervous system.
The initial stages of the syndrome may not be noticed, which leads to a constantly open mouth and malocclusion. Therefore, it is necessary to closely monitor the sleep of babies up to one year old. Loud snoring, snoring, whistling or gurgling at night is not normal for a healthy child.
Direct causes and risk factors
Stopping breathing during sleep in a child occurs due to an obstruction in the nasopharynx. There are congenital pathologies and acquired diseases that cause apnea. This syndrome can even occur due to incorrect posture, an uncomfortable pillow or mattress. The main causes of night disturbances include:
- respiratory diseases;
- reflux;
- cardiac or vascular pathology;
- anemia or lack of blood sugar;
- epilepsy;
- blood poisoning;
- pneumonia;
- laryngitis, bronchitis, tonsillitis;
- allergies, especially in summer;
- enlarged adenoids or tonsils;
- metabolic disease;
- neoplasms in the nasal passages, on the palate, uvula;
- metabolic disorders, hypo- or vitamin deficiency;
- injuries, bruises, consequences of surgery.
Premature babies, newborns with Down syndrome, and cleft or cleft lip are at risk. The syndrome also develops in the presence of congenital pathologies of the skull structure and obesity. If the mother suffered an infection during pregnancy or was treated with antibiotics, the child may still have damage in utero to the areas of the brain responsible for breathing.
Mechanism of occurrence
Apnea can appear suddenly, due to an allergic reaction, poisoning with poisons, toxins, or develop gradually due to an infection or virus. Holding your breath occurs when foreign bodies appear in the nasal passage.
When examining the condition of the nasopharynx of a sick child during sleep, muscle spasms with complete closure of the septa are noted. The baby cannot breathe from 20 seconds to several minutes. The syndrome also develops when the larynx is blocked by a pathologically large tongue. Due to general muscle weakness, a lack of tone in the palate and uvula is noted. In this case, a month-old baby is not able to regulate the breathing process.
If the functioning of the central nervous system is disrupted during sleep, the brain does not receive impulses responsible for the process of oxygen consumption. In this case, apnea may occur suddenly. If a child periodically holds his breath before going to bed, it is necessary to reduce the emotional stress in the evening.
With obstructive disorders, the syndrome develops gradually. The reduction of the airways occurs due to the appearance of bronchial obstruction. The child cannot fully exhale through the nose. The started process provokes a complete stop of breathing.
Associated symptoms
Apnea occurs at night, most often in the late night or early morning. There is a delay in inhalation or exhalation or deep breathing, accompanied by constant movement of the chest. The following symptoms of the disease are typical for a newborn baby:
- blue discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes;
- frequent awakening with crying, screaming;
- open mouth during sleep and during the day;
- moodiness while awake;
- unnatural sleeping position, tilting the head back;
- intermittent, uneven breathing;
- snoring, whistling, gurgling, dry cough, shortness of breath.
In older children, breathing problems can be quickly identified by the following signs:
- grinding teeth in sleep;
- during the daytime apathy, drowsiness, headaches;
- dry mouth;
- enuresis, frequent urination;
- malocclusion, formation of an “adenoid” face.
Also, some one-year-old children, while awake, experience difficulty swallowing, often gag, and regurgitate.
It is important to know! Apnea can be determined in the initial stages by monitoring the child at night. The most indicative hours will be the morning hours, after the end of the deep sleep phase.
Types of apnea
Sleep apnea in a child has different types. Apnea is classified depending on the main causes provoking the syndrome: a disorder in the central nervous system, the appearance of obstruction in the upper respiratory tract.
- Central. This type most often develops in premature and weakened children. The nerve impulses responsible for smooth breathing are not recognized or sent to the brain. A child can forget how to breathe at any moment. In this case, there is a risk of sudden death.
- Obstructive. In the upper respiratory tract there is a barrier to the passage of air, so the baby sleeps and wakes with his mouth open. Most often, children have adenoids, enlarged tonsils, and inflammation of the lymphoid tissue. Swelling of the mucous membrane develops with a runny nose and allergies.
- Mixed. Holding your breath occurs for several reasons. This type has common symptoms of central and obstructive apnea. It occurs due to reduced immunity and an immature nervous system.
Clinical types of apnea are also distinguished: sudden death syndrome, congenital hypoventilation, ronchopathy (snoring).
Advice! The severity of the disease is determined depending on the number of episodes of nocturnal respiratory arrest. If you count more than 30 interruptions, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Why do children hold their breath in their sleep and what to do about it
Parents of a child, especially a baby, are often worried about his development and adaptation to the world around him. Some baby reactions are different from adults. It happens that sometimes a child holds his breath for several seconds while sleeping. An attentive mother will definitely notice it and may be very afraid for the child’s health. Should we be afraid? What are the reasons for this condition of the baby?
Reasons for holding your breath
Periodic breathing most often occurs in children under 6 months of age. For them, this is considered normal and does not require medical intervention. As much as 5–10% of the time a child spends sleeping may occur during such pauses.
Uneven breathing during sleep may have objective reasons:
- Oxygen deficiency. Blueness of the limbs, skin around the mouth or on the body appears. Most often it occurs in children under 1 year of age. Symptoms: the child gasps for air and cannot take a deep breath.
- Infectious diseases. Whistling, loud snoring, gurgling are added. Inflammation of the lungs is often accompanied by an increase in the rhythm, its acceleration.
- An erratic rhythm combined with shortness of breath indicates that the child has an elevated body temperature. Shortness of breath can also occur with heart problems.
- False croup and bronchitis with obstruction. Symptoms: lost rhythm, noisy exhalation, cough.
Types of breath holding in children
There are two types of periodic breathing depending on the symptoms:
- Cyanoid. Symptoms are a sudden stop in breathing, rapid spread of cyanosis to the limbs and face, the color of the skin can be from pale blue to deep purple.
- The second option often goes unnoticed by parents because it causes paleness. There is a sharp outflow of blood from the skin. The child may even lose consciousness in his sleep.
These symptoms may include seizures. Muscle tone also increases. Since periodic breathing occurs during sleep, the child cannot influence the situation.
Complications of frequent sleep apnea
This condition occurs most often in children under the age of 2–5 years. By the age of 4, in more than half of children, all signs disappear. In 17%, symptoms may occur occasionally even in adulthood.
The most dangerous condition, especially for newborns and infants, is apnea - a sudden stop in breathing during sleep.
The disease manifests itself in blue skin (especially around the mouth and nose), disruption of the heart, and oxygen starvation. Most often it affects premature babies, whose respiratory centers in the brain are not fully formed.
Heredity, birth injuries, complications during the mother’s pregnancy, and infectious diseases also matter.
Doctors define sleep apnea as episodes of sleep interruption for more than 10 seconds and with a frequency of at least 15 times per hour. OSA (obstructive sleep apnea) occurs in approximately 2% of children. Most often occurs after 2 years of age.
The causes may be diabetes mellitus, pathologies of the ENT organs, neuromuscular disorders, GERD, and arterial hypertension.
Apnea is especially dangerous for infants and newborns - the disease can lead to sudden death of the baby.
Diagnosis of breathing in babies
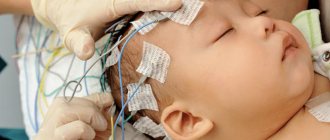
If you have frequent episodes of periodic breathing, you should definitely show your child to a pediatrician. He may be prescribed an examination - polysomnography. It is carried out in a hospital and can take several days (more precisely, nights).
Before going to bed, high-precision sensors are installed on the child’s body, which will record physiological processes in the body throughout the night. The results show the number of breathing stops and their duration.
In newborns and infants, breathing can normally be intermittent and uneven, since not all systems and organs have had time to “ripen”. Before visiting a doctor, it is recommended to measure your breathing rate at home. In infants, the measurement process can be carried out visually by observing the rise of the chest for a minute. You can simply place your hand on your baby's chest and count the breaths.
Respiration rates vary:
- newborn – 40–60 breaths per minute;
- 1–2 months – 35–47;
- up to three years – 28–35;
- 4–9 years – 24–30;
- 10–12 years – 18–20.
Write down the readings on a piece of paper and show them to your local pediatrician. Additionally, examinations by an otolaryngologist, neurologist and other “narrow” specialists may be required if the cause of periodic breathing or apnea is pathology.
Apnea Treatment Methods
The most common cause of apnea in children 2–7 years of age is chronic tonsillitis or adenoiditis, so surgery to remove the tonsils may be recommended.
If the cause is impaired nasal breathing (for example, allergic or chronic rhinitis), symptomatic treatment is indicated: rinsing the nasal passages, using vasoconstrictor drugs. An abnormal development of the nose or jaw can also lead to apnea.
In this case, surgical correction or wearing special devices while sleeping is used.
SINAP therapy is indicated for newborns and infants for moderate or severe apnea. Its essence is to put on an oxygen mask for the child before going to bed, which is connected with a hose to an air supply apparatus. In this case, respiratory arrests in children during sleep are excluded.
It is important to know what parents should do if they find a child who is not breathing. Be sure to wake him up, just very carefully. If the skin begins to turn blue, call an ambulance. If the child does not begin to breathe, it is necessary to perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation until the ambulance arrives. Any pause in breathing for more than 10–15 seconds should be a reason to urgently go to the hospital.
Our specialist comments
Holding your breath cannot be ignored. Constant disruption of the breathing rhythm leads to oxygen starvation, delayed mental and physical development, constant fatigue, drowsiness, and hyperactivity.
Apnea syndrome is even more dangerous. The baby can hold his breath even for half a minute. This condition in infancy can be fatal. The situation is complicated by the fact that everything happens in a dream and parents cannot fully control breathing. Therefore, it is worth making sure that the inconsistent rhythm is the norm and is not associated with pathology or disease.
Source: https://LechenieDetok.ru/lor/rebenok-vo-sne-zaderzhivaet-dyhanie.html
Diagnosis of breathing disorders
First of all, parents can determine the presence of apnea. Observe your baby's breathing at the beginning of sleep and from 4 to 6 am. If you hear snoring, whistling, or sobbing, you should consult your pediatrician.
If breath holding is detected, it is recommended to use a stopwatch to measure the duration of one episode of apnea. If the child stops prematurely for 10 seconds or more, the child must be examined. The pediatrician should refer you to an otolaryngologist,
cardiologist, neurologist and surgeon. Specialists study the medical history, features of the course of pregnancy and childbirth.
For an accurate diagnosis, polysomnography is prescribed. This technique allows you to determine the cause of the development of any sleep disorders. Also, after consultation with a surgeon, the child may be sent for an X-ray of the skull, which reveals congenital or acquired pathology in the structure of the nasal passages.
Treatment of pathology in children of different ages
Sleep disordered breathing is a serious pathology; sleep apnea is especially dangerous if it occurs in children under one year of age. During this period, the child’s body is actively growing, the brain is developing, skills and abilities are acquired daily. With a constant lack of oxygen, hypoxia occurs, which leads to the death of neurons.
Treatment of apnea begins after examination by an otolaryngologist and surgeon, a thorough diagnosis of the functioning of the central nervous system. Depending on the type of syndrome, conservative therapy using drops, sprays, tablets or surgery is prescribed.
Reason for urgent consultation with a doctor
A child with sleep apnea should be under parental supervision at all times. Temporary episodes can develop into complete interruption of breathing. In this case, it is necessary to urgently provide first aid and call an ambulance team. Alarming symptoms of deterioration:
- pallor, cyanosis of the skin and mucous membranes;
- epileptic seizure, convulsions;
- pulse rate less than 90 beats per minute;
- unnatural posture;
- lack of reaction to what is happening.
To prevent such a serious condition and death, consult a doctor in a timely manner. Short-term cessation of breathing should not exceed 10 seconds in duration; the episode itself does not repeat more than 2-3 times per night.
Quick help for a baby at home
When breathing stops completely, brain cells die after 6 minutes. These damages are irreversible, and in the absence of emergency assistance, death occurs. Therefore, if alarming symptoms appear, immediately call a team of doctors. Before their arrival, the following manipulations must be done:
- Try to wake up and bring the child to his senses.
- Spray your forehead, arms and legs with cold water.
- Give artificial respiration. Tilt your baby's head back, close his nose and gently inhale mouth to mouth. The procedure should last no more than 2 seconds, since a child’s lungs are much smaller than those of an adult.
If a rash or Quincke's edema appears, antihistamines should be given as quickly as possible. The most effective, based on reviews from parents and doctors, is Fenistil. Drops are given from the second month of birth.
As a last resort, before the ambulance arrives, a closed heart massage is performed. During these procedures, be sure to open the child’s mouth and hold his tongue so that the baby does not choke.
Modern methods of eliminating apnea in children
Many techniques have been developed to treat apnea. Their main task is to remove pathological symptoms and restore breathing as soon as possible. Depending on the cause of sleep disturbance, the following therapy is prescribed:
- Taking medications. If the cause of uneven breathing is respiratory diseases, antiviral drugs are prescribed. To increase the tone of the palate and uvula, and eliminate complete closure of the walls of the larynx, antispasmodics are taken. To reduce allergic swelling - antiallergenic drugs. With the help of medications, apnea is treated, caused by disruption of the central nervous system.
- Physiotherapy. For the obstructive type of apnea, inhalations and treatment with special devices that regulate the flow, pressure, and humidity of the air are prescribed. For newborns, stimulation of the respiratory center or artificial ventilation is performed.
- Surgical intervention. Prescribed for enlarged adenoids, tonsils, the presence of polyps in the nasal passages, congenital or acquired pathologies of the skull.
If apnea is a consequence of obesity or food allergies, the child is prescribed a special diet. To normalize weight, it is necessary to undergo a massage course and perform exercise therapy daily, depending on age.
What does a doctor do
Waiting for apnea to go away on its own is dangerous.
The doctor will weigh the child, determine his body weight, determine whether the child is obese, measure blood pressure and give a referral to an ENT doctor. An examination by an otolaryngologist plays an important role - it is imperative to identify the mechanical factors that cause the upper airways to collapse excessively during sleep.
Children undergo polysomnography - simultaneous recording of electrical potentials for 8 hours or more, or a polygraphic study is prescribed, during which heart rate and nasal breathing are recorded over the course of one night, and episodes of snoring are determined.
- Take the child in your arms. Run your finger along your back from bottom to top. Give it a gentle shake.
- Start massaging your ears, arms and legs, and move on to your chest.
- Spray your face with cold water.
- As a rule, the previous measures should get the child, especially an infant, to breathe. If this does not happen, artificial respiration should be performed. Open your mouth, cup it lightly with your hands, pinch your nose, then breathe a little into your baby's mouth. Exhaling forcefully can cause lung injury! 5-10 breaths should be taken artificially.
- Perform a closed cardiac massage. It is better to learn this procedure from doctors.
- Call an ambulance. It is better if the second parent calls the ambulance while the first parent revives the baby.
The doctor must conduct a thorough examination of the baby.
Therapy is based on:
- taking medications (very rarely);
- non-drug methods (oxygen therapy, establishing sleep and rest patterns, nasal rinsing, using special devices to improve nasal breathing);
- surgical intervention.
Treatment is prescribed only after the results of tests and studies.
When apnea is detected in premature babies, doctors act in the same way as with home help. If this does not help, then a resuscitation mask or bag is used. Special water or vibrating beds in incubators help stimulate the newborn’s breathing. However, episodes of respiratory arrest may recur frequently, even after all the described procedures have been completed.
We invite you to read: What do pregnant women need to know before giving birth? Behavior, exercises and breathing exercises for pregnant women before childbirth
If attacks are noticed at intervals of two or three times an hour, drastic measures are taken, such as increasing the supply of oxygen to the incubator, blood transfusions, and lowering the temperature inside the incubator. If there is no improvement, the baby is connected to a ventilator.
If a child is admitted to the hospital with suspected apnea from home, a detailed examination is carried out. When the cause of the disorder is identified, therapy is selected aimed at eliminating the provoking disease.
Also, in parallel, drugs can be prescribed to stimulate the respiratory center. In some cases, CPAP therapy is performed - this is a hardware technique, the essence of which is to maintain optimal pressure in the baby’s airways. A mask is put on the baby’s face, air is passed through it, which ensures the normalization of the condition.
The danger of nocturnal respiratory arrest in children of different age categories
If your child holds his breath during sleep, sleeps with his mouth open, and often wakes up, it is recommended to visit an otolaryngologist and neurologist. Apnea is most dangerous for children born prematurely or weighing less than 2 kilograms. Consequences of prolonged episodes of sleep apnea at night:
- increased excitability, the child often cries and is capricious;
- headache;
- attention deficit disorder;
- heart failure;
- hypoxia;
- pulse disturbance;
- epilepsy;
- physical and emotional developmental delays;
- diabetes.
Nocturnal attacks of breath holding for an infant are often fatal. At one point, a baby may forget how to breathe. Therefore, parents are recommended to pay attention to the nature of breathing: extraneous sounds, duration of inhalation and exhalation, the number of episodes of apnea per night.
Signs of apnea
As a rule, adults associate the baby’s restless sleep, frequent waking up and whims with hunger, indigestion, intestinal colic and other reasons. However, when observing a sleeping baby, in some cases a condition is noted that is described as “as if the child forgets to breathe.” A short breath hold lasting more than 10-15 seconds is the main symptom of apnea.
If the duration of stops is less than the threshold value, but they are repeated frequently, this should be reported to the pediatrician. Severe cases of prolonged apnea can cause the baby to turn blue and have difficulty breathing. In these circumstances, hospitalization is possible.
Children with signs of apnea often toss and turn at night, sleep with their mouths wide open and their necks outstretched, and breathing is complicated by snoring. At a more mature age, children may experience enuresis. Respiratory dysfunction is also accompanied by internal disorders: the heart rate slows down and the level of oxygen in the blood decreases.
Preventive recommendations for parents
To prevent your baby from developing sleep apnea, it is recommended that you maintain a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy. Stop smoking, alcohol, and avoid junk food with food additives and dyes. You cannot carry viral and infectious diseases on your feet.
The famous doctor Evgeny Komarovsky recommends adhering to the following rules:
- take a walk in the fresh air every day;
- Stick to a diet while breastfeeding;
- introduce complementary foods gradually, starting with hypoallergenic foods;
- rinse your nose before going to bed, especially if you have a runny nose;
- watch your sleeping position, do not allow your baby to sleep on his tummy;
- provide a comfortable mattress; up to 2 years you will refuse a pillow.
To promptly notice uneven breathing, place a crib in your bedroom. Control weight gain, do not feed your baby 3 hours before bedtime. Provide nutritious food rich in vitamins and microelements.
Nocturnal apnea is a pathology and requires treatment. Modern medicine has developed devices that quickly eliminate apnea syndrome: SINAP therapy, mechanical ventilation, oxygen therapy. Before prescribing a course of therapy, a thorough examination of the nasal passages and larynx is carried out, and, if necessary, an X-ray of the skull is prescribed.
Prevention: advice for parents
Closeness to the baby in the first years of life guarantees a timely response to warning symptoms.
To protect your child from such an unpleasant illness as sleep apnea, you can follow a number of recommendations to promote healthy sleep for your baby:
- Stop smoking during pregnancy. How many times has the world been told about the dangers of smoking, especially for expectant mothers. Apnea can be just one of the punishments for a child due to the mother’s bad habit.
- Until the age of two, a baby does not need a pillow. The mattress must be hard and meet all pediatric standards.
- Make sure that the child does not sleep on his stomach; when putting the baby to bed, place him on his side or back.
- Monitor the temperature of the room in which your baby sleeps. Avoid overheating or hypothermia; the optimal temperature in a child’s room is 20-22°C.
- Try to always be close to your child when he sleeps; it’s good if his crib is in the parents’ room until he is two years old. Monitor your baby's sleep and monitor his breathing. However, do not overdo it, the baby feels the nervous tension of the mother and this makes him nervous.
- If you suspect sleep apnea, do not delay visiting your doctor - it can be very dangerous for your baby's life. The older the child, the lower the risk, but timely intervention is necessary for the child’s healthy sleep and functioning.