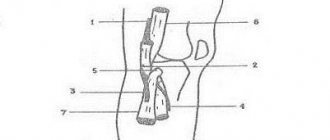
A pinched nerve in the calf is not an independent disease, but a symptom that indicates damage to the sciatic nerve. It is the largest in the human body, extends from the lumbar spine, and ends in the area of the fingers.
That is why its pinching in the back area, for example, as a result of osteochondrosis or a herniated disc, gives a variety of symptoms. The main one is pain, which can affect the back, buttocks, hips, and extend to the fingertips.
The calf muscle itself cannot cause pinching of the nerve fiber. Therefore, to eliminate the pathology, you need to contact a neurologist.
The main causes and symptoms of inflammation of the nerves in the leg
Signs of sciatica
- prolonged hypothermia;
- compression of nerve endings due to displacement of the intervertebral disc;
- mechanical injuries of the lumbar spine;
- heavy physical activity;
- viral, infectious diseases;
- pelvic organ injuries;
- piriformis syndrome;
- osteochondrosis;
- bone spurs on the vertebrae;
- narrowing of the spinal canal (stenosis);
- pregnancy;
- diabetes;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- compression of the nerve by an oncological neoplasm.
Inflammation of the sciatic nerve most often affects one limb, while the opposite side may become numb, tingling, or have a pins and needles sensation.
This is due to a violation of the innervation of muscle tissue. Bilateral inflammation of the sciatic nerve also occurs; the patient experiences severe pain when trying to stand up or make any movement. The most common cause of inflammation of the sciatic nerve is pinching of the nerve endings due to protrusion of the intervertebral hernia.
The pain syndrome can be of varying degrees of intensity, accompanied by tingling and numbness in the leg, loss of sensitivity of soft tissues.
Neuritis and neuralgia
Neuritis is usually infectious in nature. With this disease, inflammation of the femoral, sciatic, tibial or peroneal nerve is observed. The main causes of pathology include the following conditions:
When the femoral nerve becomes inflamed, pain, burning and numbness occurs in the outer thigh. Discomfort increases while walking and when making sudden movements. In addition, it is difficult for the patient to bend his leg at the knee.
Neuritis of the tibial nerve is manifested by difficulties in flexing the toes, the skin is hyperemic and hot to the touch. Symptoms of pathology are caused by mechanical injuries, viral and infectious diseases.
Neuralgia of the external femoral nerve is manifested by pain on the outer side of the thigh, the syndrome worsens at night, causes insomnia, walking and physical activity also lead to significant discomfort.
Pinched nerve in the knee joint
A condition that develops against the background of a pinched nerve can cause sharp pain in the leg or knee. The main symptoms of the pathology include the following:
- acute pain in the knee;
- decreased sensitivity, numbness;
- burning sensation, tingling sensation;
- involuntary nervous tic;
- limitation of motor activity in the knee;
- muscle atrophy of varying degrees.
Sometimes inflammation of the nerve endings in the knee is caused by pinching of the sciatic nerve in the spine or compression by intervertebral hernias. For this reason, treatment must be carried out comprehensively.
Diagnostic methods
In order to diagnose sciatica and neuralgia, the Lasegue test is performed or the “tension symptom” is checked. The essence of the technique is based on identifying spastic muscle contractions when nerve roots are pinched. When the sciatic, femoral and tibial nerves are stretched when bending a straight leg at the hip joint, the patient feels acute pain in the leg, lower back, and thigh.
Additionally, the patient may need to consult a rheumatologist, neurosurgeon, vertebrologist, oncologist, traumatologist and vascular surgeon. Specialists will help you correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Treatment of inflammatory diseases
If the symptoms of neuralgia are caused by dilation of blood vessels, ischemia, thrombophlebitis, treatment with vasodilators is prescribed. In case of injury, the limb is fixed and, if necessary, a plaster or tight bandage is applied. The patient is prescribed bed rest; he needs to sleep on a hard mattress. To relieve pain, swelling of the limb should be treated with ointments and gels containing anesthetics; diuretics are also prescribed.
If the pain is too severe, it must be stopped with novocaine or hormonal blockade.
After acute symptoms are relieved, patients are treated with physiotherapeutic procedures: massage, electrophoresis, exercise therapy, UHF, electromyostimulation, manual therapy. For carpal tunnel syndrome, medications are injected directly into the affected canal.
Inflammation of the sciatic, femoral, tibial and peroneal nerves in young people responds well to therapy, treatment has a positive prognosis. In elderly patients suffering from diabetes, the disease is progressive, and paralysis of muscle tissue and deformation of the joints of the foot may develop.
By
Prevention
For prevention purposes, experts advise adhering to the following rules:
- Exercise;
- To walk outside;
- Get enough sleep (at least 6-8 hours a day);
- Sleep on a medium-hard mattress;
- Do not wear high heels;
- Try not to overload your back;
- Avoid hypothermia.
When a nerve is pinched in the leg, a person experiences severe attacks of pain that can last for weeks or even months without treatment. It should be prescribed by a doctor after examining the patient. If you follow all the specialist’s recommendations, you can cure the pathology in the shortest possible time and without any special consequences.
Features of neuritis of the lower extremities
What is neuritis
There are three types of nerve fibers:
The symptoms of mononeuritis are the same in any part of the leg - pain and numbness. In severe forms, tendon reflexes are lost. Muscle atrophy occurs at the site of nerve damage, but paralysis is practically excluded with local neuritis. An endemic form of neuritis is common among pregnant women, caused by a lack of B vitamins.
Neuritis is inflammatory damage to a peripheral nerve. If one nerve is inflamed, then they speak of mononeuritis, or local neuritis. When several nerves are affected, we are talking about polyneuritis.
Causes and localization
Doctors distinguish the following types of neuritis according to their location on the legs.
It is noticeable that neuritis is located mainly in the upper part of the legs - on the hips and in the pelvic area. But the nerves begin to inflame from afar, that is, from the feet. It’s just that the symptoms are not obvious, and there is no severe pain yet.
Muscle performance and blood circulation in the affected area of the legs are not immediately impaired.
Characteristics of polyneuritis
Polyneuritis is divided depending on the reasons that caused it.
Causes
The sciatic nerve is the largest nerve branch in the body. Its compression is also called lumbosacral radiculitis. Only a doctor can diagnose the disease, focusing on the results of the examination, since its symptoms are characteristic of many pathological processes. The sciatic nerve is usually injured due to the following factors:
- Acute stage of osteochondrosis. When cartilage tissue and discs are deformed, there is little space left for the nerve roots of the spinal cord. Because of this reason, they are often compressed with any awkward movement, and the muscle tissue at the site of damage remains in a state of constant spasm, which further increases the pain;
- Radiculitis. This pathology is typical for people over 40 years of age and is characterized by nagging pain and numbness of the limb. The sciatic nerve is usually injured when a nerve root is compressed in the lumbosacral region;
- Physical overload. Injury due to overwork and back strain is common among people with hard work and athletes;
- Injuries. Usually, the nerve can be so pinched due to damage to the back after a fall, blow, etc. The degree of recovery in this case depends on the severity of the injuries received.
Features of neuritis of the lower extremities
What is neuritis
There are three types of nerve fibers:
The symptoms of mononeuritis are the same in any part of the leg - pain and numbness. In severe forms, tendon reflexes are lost. Muscle atrophy occurs at the site of nerve damage, but paralysis is practically excluded with local neuritis. An endemic form of neuritis is common among pregnant women, caused by a lack of B vitamins.
Neuritis is inflammatory damage to a peripheral nerve. If one nerve is inflamed, then they speak of mononeuritis, or local neuritis. When several nerves are affected, we are talking about polyneuritis.
Causes and localization
Doctors distinguish the following types of neuritis according to their location on the legs.
It is noticeable that neuritis is located mainly in the upper part of the legs - on the hips and in the pelvic area. But the nerves begin to inflame from afar, that is, from the feet. It’s just that the symptoms are not obvious, and there is no severe pain yet.
Muscle performance and blood circulation in the affected area of the legs are not immediately impaired.
Characteristics of polyneuritis
Polyneuritis is divided depending on the reasons that caused it.
Polyneuritis differs from neuritis in the severity of the patient’s general condition and the symmetrical distribution of symptoms in the legs.
Treatment of polyneuritis, neuritis and neuralgia
Therapy for these neurological diseases consists of eliminating the underlying disease that caused damage to the nerves of the legs. Treatment methods are chosen based on the stage of the disease. The success of treatment largely depends on starting it as early as possible. First of all, painkillers are used, anti-inflammatory drugs and drugs that accelerate metabolism in tissues are prescribed. Vasodilators and anticonvulsants are often used. In the acute stage, physiotherapeutic treatment is carried out: electrophoresis, UHF. There are no special medications that relieve inflammation in the nerves. Vitamin therapy, massage, and mud baths are used.
Of course, a healthy lifestyle, hardening, physical exercise, limiting contact with toxic substances is the prevention of any neurological diseases.
Angioneurosis is a disease of the vascular nerves
As angioneurosis progresses, attacks become more frequent, pain appears, and the lower extremities may turn blue and become blistered. At the critical stage of angioneurosis, the nail phalanges die. The causes of angioneurosis are the same factors as those of the previously discussed neurological diseases. These are intoxication with harmful substances and alcohol, infections, physical and mental injuries, frostbite of the extremities, hormonal disorders, finger injuries and vibration in industrial activities. This neurogenic disease is incurable and becomes chronic.
Neuritis, polyneuritis and angioneurosis often develop as a secondary disease. Therefore, it is so important to monitor your health, not to neglect the underlying disease and promptly treat neurological disorders. Take care of your nervous system!
HealFolk.ru » Treatment of diseases » Inflammation of the sciatic nerve: symptoms and treatment.
Neuralgia and neuritis bring a lot of discomfort to the patient. Stitching or cutting pain, numbness and lumbago – this is what worries a person who has sciatica.
Inflammation of the sciatic nerve, the symptoms and treatment of which until recently were common among people of mature age, has now become younger. A sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity on the body, and poor nutrition provoke the disease at an earlier age. How to identify the disease and treat it correctly is what worries patients.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
The most effective painkillers are NSAIDs. This pharmaceutical group of drugs is represented by drugs that stop the action of the COX enzyme and have an anti-inflammatory effect, these include:
Meloxicam (Movalis, Amelotex) is available in tablet and injection forms and is one of the safest drugs in the NSAID group. “Piroxicam” is available in the form of a solution (ampoules of 1-2 ml), tablets, suppositories, gel, cream; it can be used both locally and by injection - 1-2 ml once a day to relieve an acute pain attack. “Nimesulide” (“Nise”, “Nimesil”) - available in the form of powders, tablets, capsules. The usual dosage is 100 mg per day, in the first days it is possible to increase to 200 mg. "Celebrex" - capsules, the recommended daily dose is up to 200 mg, but for severe pain it can be increased to 400-600 mg at the first dose, followed by a subsequent reduction in the dose to 200 mg. “Ketonal”, “Ketanov” (“Ketoprofen”) - available both in ampoules and capsules, tablets, suppositories and as an ointment; for sciatica, it is most often used intramuscularly (up to three times a day, 2 ml), but the symptoms It also removes well when applied locally (ointments).
When pain and inflammation increase, hormonal steroids are sometimes prescribed in short courses; they relieve pain, but do not eliminate the cause of inflammation, and their use has a lot of side effects and contraindications.
See also how to choose effective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for treating joints.
Why is this nerve needed and where is it located?
The sciatic nerve is considered the largest nerve in the human body. In an adult, the diameter of the nerve can reach 1 cm. Everyone should know where the sciatic nerve is located. It begins in the pelvis and exits through an opening in the ilium. Passing between the muscles of the buttock, it goes under the lower edge of the gluteal muscles to the thigh. Then it passes along the back of the thigh and branches into smaller processes. Thus, the sciatic nerve extends from the lumbar region to the tip of the thumb.
If a lumbago occurs when lifting a heavy object or making a sudden movement, then this is a consequence of pinching the ends of the sciatic nerve, and this problem is called lumbago with sciatica.
Unblocking the sciatic nerve. Video:
Causes of inflammation
If the sciatic nerve hurts, then there are reasons for this. The pain occurs due to pinching of the nerve roots, resulting in inflammation, pain begins in the lumbar region and radiates throughout the leg. The causes of this pathology are:
- Intervertebral hernia. Rupture of the fibrous ring leads to displacement of the vertebrae, compression of the nerve endings and their inflammation are observed. Pain syndrome in this case indicates that the disease is advanced; the patient may face surgery.
- Arthrosis or chondrosis of bones. Formations that grow at the junction of the vertebrae compress the processes of the nerve in question and cause inflammation.
- Displacement of the vertebrae as a result of spinal column injury or congenital defect.
- An infectious disease, especially if untreated.
- Poisoning and intoxication. They are divided into two types: internal, occurring against the background of diabetes, and external, here toxins enter the body with food or drink.
- Sudden hypothermia of the body.
- Various tumors.
- Inflammatory process in the piriformis muscle.
- Often the pathology develops during pregnancy - a violation of the center of gravity often provokes pinching of the nerve in question.
- Constant stress, depression and nervous tension.
- Hard physical work.
- Frequent constipation.
Features of infringement
In common parlance it is called “pinched nerves in the leg.” Many may be familiar with it by its more outdated name – sciatica. A degenerative disease that develops over a fairly long period against the background of diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Only as a result of serious injuries, for example, a hip fracture, can pathology manifest itself in the form of complications. Before answering the question: how to treat a pinched nerve in the leg? – it is necessary to identify all the reasons leading to the development of this pathology.
Pinched sciatic nerve: symptoms and treatment
Signs of inflammation of the sciatic nerve differ depending on the severity of the lesion, the source of inflammation, duration and nature. In this case, the patient suffers from the following symptoms:
- Pain syndrome. Nerve roots have a huge number of receptors, so any damage to them causes severe pain. Usually the lesion covers one side; bilateral sciatica is diagnosed very rarely. Pain syndrome occurs in the buttock and radiates to the lower limb. If the affected area is large, the pain can reach the foot and even the toes.
- Limited movement. The pain intensifies with the slightest exertion, walking, bending the body, coughing, and manifests itself even when breathing.
- Numbness of the limbs. Quite often, sciatica provokes complete or partial numbness of the legs.
What to do if the sciatic nerve is pinched?
First you need to establish the correct diagnosis - this is done based on clinical manifestations and pronounced characteristic symptoms. The location of nerve damage and the severity of inflammation can be determined using hardware tests:
- Radiography. Determines disorders and damage in the structure of the spine.
- CT – computed tomography. This is a high-tech X-ray examination technique that can scan tissue components layer by layer and give a more accurate picture of the location of the source of inflammation.
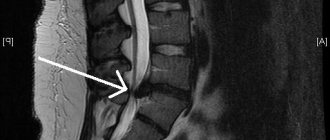
- MRI – magnetic resonance imaging. A more informative method of layer-by-layer tissue examination.
- Ultrasound – ultrasound examination. The method allows you to visualize the structure of soft tissues. It easily detects the presence of tumors that cause inflammation of the nerve.
The ultrasound method is considered the most effective in diagnosis and safety. It also has some advantages over others: it does not have radiation exposure, can be used many times during treatment, there are no contraindications, and small tissue elements are clearly visible.
Causes
The sciatic nerve is not only the largest, located in the lower extremities, but throughout the body. It is formed from large bundles of nerve endings concentrated in the lumbosacral spine.
Attention! The thickness of the sciatic nerve can be compared to the volume of the little finger of an average person.
The most common causes of pathology include degenerative changes in bone and cartilage tissue in the lumbosacral spine and hip joint. This occurs against the background of the following diseases:
Treatment with traditional methods
How to treat a pinched sciatic nerve using medication - first you need to relieve pain with painkillers, for which analgin or drugs with a pronounced direction of action are used. Such drugs include:
- Tempalgin - eliminates pain due to the content of a mild tranquilizer - tempidine.
- Sedalgin - codeine and paracetamol, which are part of the drug, have an invigorating effect on nerve endings and relieve inflammation.
- Baralgin - thanks to the action of antispasmodics, inflammation is removed and spasm of the sciatic nerve is relieved.
- Pentalgin.
Non-steroidal drugs must be used for treatment. These can be tablets, injections during periods of severe pain, ointments:
- Diclofenac tablets. Eliminates pain, swelling, inflammation. Injections of the presented remedy are more effective, but they cause adverse reactions on the liver and kidneys. That is why they are prescribed with a minimum interval of 12 hours.
- Movalis in tablet form. Quite a strong remedy that quickly eliminates pain and inflammation. Since the drug has significant side effects, drink it under medical supervision for no more than 5 days.
- Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Nise - less strong, but necessary to relieve muscle tension, eliminate inflammation and spasm.
- Corticosteroids – required if symptoms persist. These are hormonal drugs that eliminate swelling and inflammation of this nerve.
- Vitamins and vitamin-mineral complexes. Vitamins B and E are especially helpful. Drugs that improve metabolism and blood circulation are also prescribed.
It should be noted that, apart from drug treatment, the patient cannot do anything during an exacerbation. He must remain in bed, move little, get up only when necessary, apply ice and a heating pad, alternating them.
After the exacerbation passes, the patient needs to undergo full treatment. In addition, he is indicated for sanatorium treatment with mud, radon and hydrogen sulfide baths, and exhaust hoods in the pool.
Recipes" of traditional medicine
Therapy for inflammation at home involves the use of traditional medicine recipes. The most popular home treatment methods are:
- Therapeutic baths. Relieve tension from muscles, normalize the nervous system and strengthen muscles. A pine bath with the addition of grated horseradish and angelica decoction is considered a good healing bath.
- Compresses. They warm up the muscles in the inflamed area. A compress made from grated black radish and a flatbread made from rye dough are considered quite effective.
- Infusions and decoctions. Infusions are used to eliminate pain, and decoctions stop the inflammatory process. Plants such as calendula, chamomile, horse chestnut, and birch buds help cope with the disease.
- Badger or bear fat. Rubbing the affected area with these components helps relieve inflammation.
- Stone therapy. This is a procedure that replaces paraffin treatment. It is necessary to heat the stones to a certain temperature and place them around the inflamed area, placing a cloth underneath them.
You can start treatment with traditional medicine only if the exacerbation has passed.
Folk recipes are simple and accessible to use and to use. Some of the most effective recipes are as follows:
- Bay leaf tincture. Place 20 bay leaves in 200 ml of vodka and place in a dark place for 3 days. Rub the prepared infusion into the inflamed area. Improvement occurs after 3-4 sessions.
- Honey cake. Make a cake from a glass of flour and a spoon of honey and apply it to the sore spot. Cover the cake with film and wrap it with a warm scarf.
- Infusion of potato sprouts. Take a glass of sprouts, add two glasses of vodka to them and place them in a dark place for two weeks. Rub the prepared infusion into the problem area in the morning. Wrap the area in a warm shawl.
Sciatica is not difficult to cure, but it will take a lot of time, as a result of which you need to be patient. It is necessary to follow the doctor’s recommendations and not do anything that will complicate the disease.
Did you like the article – 8? Show it to your friends:
An inflammatory disease such as neuritis of the lower extremities is on the list of the most common pathologies characterized by loss of temporary ability to work. A serious complication of this disease can be paralysis of the legs. It is important to recognize the disease in the early stages and begin treatment on time.
Course of therapy
You can understand how to treat a pinched nerve in the leg by focusing on numerous therapy methods invented to relieve the manifestations of neuralgia. However, you need to entrust your treatment to an experienced specialist. He will tell you what to do if the nerve fibers are compressed.
Before going to the hospital or waiting for a diagnosis, you can take an analgesic to relieve a pain attack. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) relieve the manifestations of neuralgia well. They are taken orally or by injection and most tablets are made with ibuprofen. They relieve inflammation, as a result of which the intensity of the pain attack decreases. It is allowed to use medications from this group for no more than 1 week. Otherwise, side effects may begin to develop.
Despite the benefits of non-steroidal drugs with an anti-inflammatory effect, they have many contraindications and most of them are related to the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, people with diseases of the liver, stomach, etc. are recommended to use medications from this group only in the form of injections, for example, Diclofenac solution. The result after taking it becomes noticeable already on the 3rd day of use, which makes the injections very popular, especially among people with a tendency to sciatica.
Not only tablets and injection solutions represent a group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, because there are also various ointments and gels such as Fastum-gel and Finalgon. The intensity of pain decreases approximately 30-40 minutes after application. The use of ointments and gels from the NSAID group is allowed for no more than 1 week.
The doctor will recommend surgery only if there is no result or if the cause of the pinched nerve in the leg needs to be removed.
After eliminating the factor that prevents the nerve tissue from recovering, the compression will disappear and after 1-2 months the person will be able to live as before. However, possible complications, recovery time and severity of the operation directly depend on the cause of the pathological process.
Etiology of neuritis
The root cause of the pathology is an inflammatory process that affects one or several peripheral nerve endings. The “starting point” of infectious neuritis is an infection to which the peripheral nervous system is susceptible. The development of inflammation of the nerve endings of the lower extremities can be provoked by the activity of pathogenic microorganisms: bacteria that attack the body during bronchitis, otitis, cystitis and other diseases, and viruses that cause herpes, influenza, etc.
Provocateurs of neuritis
| Factors | Scroll |
| Exogenous (external) | Intoxication of the body (alcohol, food, chemical, carbon monoxide) |
| Injuries and damage | |
| Unintentional compression or damage to a peripheral nerve (occupational characteristics) | |
| Hypothermia | |
| Endogenous (internal) | Pregnancy and childbirth |
| Overweight and obesity | |
| Diabetes | |
| Endocrine system diseases | |
| Hereditary neuromuscular diseases | |
| Vitamin deficiency and general decrease in immunity |
Return to contents
Classification and manifestations of neuritis of the lower extremities
Diagnosis
In order to correctly diagnose the type of neuritis, it is necessary to carefully study its symptoms. If there is an existing injury, the patient should contact a traumatologist to exclude the possibility of a fracture. If neuritis is suspected, a neurologist performs functional tests to check the sensitivity of the limb, its performance, and to identify the area of nerve damage.
To clarify the diagnosis, additional studies are prescribed, such as:
- electromyography - analysis of muscle activity;
- electroneurography - checking the speed of nerve impulses;
- nerve fiber biopsy;
- CT and MRI are prescribed in controversial cases.
Return to contents
Diagnostics
The first signs of pinching can be identified using a simple self-diagnosis method. To do this, stand up straight with your feet shoulder-width apart. Gently tilt your body down, hold for a few seconds and return to the opposite position. If, while bending over, a person feels a sharp pain in the lower back, radiating to the limb, this is a clear sign that he needs to immediately seek medical help.
To make a diagnosis, doctors only need to listen to the patient’s complaints. To identify the causes of occurrence, a hardware examination is prescribed:
- X-ray.
- Magnetic resonance or computed tomography.
If the presence of infectious pathologies is suspected, the patient submits blood and urine samples for analysis. If tumors are detected, a biosample may be required.
Basic treatment for leg neuritis
Most often, treatment for neuritis is conservative; at the first stage it is aimed at eliminating the cause of inflammation. When the cause of the disease is an infection, antiviral or antibacterial therapy is indicated. In case of toxic lesions, the body is detoxified and the patient’s general condition is stabilized. When the cause is injury, immobilization of the injured limb is used.
Neuritis is often a secondary disease. Timely treatment of the underlying disease, as well as maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle, will protect peripheral nerves from inflammation.
Drug treatment of neuritis includes taking medications such as:
- vitamin B complex;
- pain-relieving ointments based on snake or bee venom;
- immunosuppressants such as Amitriptyline, Saroten;
- drugs for restoring nerve fibers, including Milgamma, Copaxone, Proserin.
In the complex treatment of neuritis, physical therapy, massage and physiotherapy play an important role. Physiotherapeutic procedures include:
For delayed rehabilitation, the following is also used:
During the period of remission the following is prescribed:
- sulfide and radon baths;
- acupuncture.
Return to contents
Exercises
After recovery, beneficial physical exercises are especially necessary, but only those in which the load is evenly distributed on both sides of the body (light jogging, race walking, swimming, leisurely skiing).
In addition, there are special exercises that are ideal for all patients in remission. Here is an example of exercises that can be easily performed at home while lying on the floor.
All exercises are performed 10 times, with a subsequent increase in load:
Bring your legs towards your body, hug them under your knees. Using your hands, press your legs towards you as much as possible, maintain this position for 30 seconds, then return to the starting position. Legs are straight, toes pointing up, arms along the body. Stretch your heels and the back of your head in different directions for 15 seconds, then relax. Turn to your side, pull your legs towards you. Pull up your socks. Then return to the starting position and turn to the other side. Roll over onto your stomach, lift your torso on your arms, and do push-ups. Do not strain your legs while doing this.
However, you need to know that if a pinched sciatic nerve is caused by a herniated intervertebral disc, you need to select a complex of physical therapy together with your doctor.
How to prevent the development of neuritis of the lower extremities?
Among the preventive measures are the following:
- Maintain proper nutrition with an emphasis on foods rich in B vitamins. And for overweight people, a special diet will be required to reduce stress on the legs.
- Regularly performing therapeutic foot exercises.
- Relaxing foot baths. Especially suitable for lovers of high heels.
- Wearing special orthopedic shoes when playing sports.
Hypothermia and dampness, as well as stressful situations, can provoke inflammation of peripheral nerve endings. And most importantly, you should not self-medicate, and at the first symptoms, be sure to see a specialist. After all, advanced neuritis of the lower extremities can lead to paralysis and even disability.
Muscle relaxants and vitamins
Muscle relaxants are prescribed to reduce reflex local muscle tension caused by pain. This:
Mydocalm; Tizalud; Baclofen;
Multivitamin complexes based on B vitamins also produce an anti-inflammatory effect:
Neurobion; Milgamma; Combilipen; Trigamma; Neurovitan.
When physical therapy and medications do not help, they resort to surgical methods - microdiscectomy, a discectomy in which part of the disc pressing on the sciatic nerve is removed.
Why do seizures occur?
There are several signs by which one can draw a conclusion about the fact of compression of the nerve fiber.
A person experiences sharp, piercing and shooting pain in the lower limb. The pain impulse travels a long way along the entire nerve, affecting the executive part of the reflex arc. When pinched, the pain is periodic: it appears quite suddenly and disappears as well. Unpleasant sensations make themselves felt again. In this case, the patient’s leg looks like this: the phalanges are in a semi-bent state, the others are relaxed, the side toe is moved to the side and tense. In the metacarpus, some muscles are atrophied.
Based on the location of pain in the leg, several types can be distinguished:
- Sciatica. The pain permeates the area from the sacral area and buttock, down to the back of the leg.
- Sciatica. Unpleasant sensations are localized in the lower back and buttock, sometimes moving to the back of the leg. In this case, you may notice redness and local swelling. In severe cases, the attack is accompanied by sweating, the inability to walk and move, and complete atrophy is also possible.
After an attack, a person continues to experience pain for a long time. It is especially aggravated by prolonged walking, standing or being in a static position. The reasons for an electric shock in the leg can be different.
What you need to know if you have a pinched nerve in your hand: methods of treating neuropathy
Causes
A pinched nerve in the leg can occur for a number of reasons, some of which are quite serious. And such a situation is a manifestation of an underlying disease that did not make itself felt before.
Nerve compression can occur due to:
- Osteochondrosis during exacerbation. This disease is accompanied by the progression of inflammation and degeneration of the vertebral body. The normal physiological state of the intervertebral discs is also disrupted. In this case, their height decreases, which leads to strong pressure on the spinal roots.
- Protrusion of intervertebral discs. This pathological condition is characterized by disc protrusions, but the integrity is not compromised. When there is protrusion at the exit point of the nerve, it becomes pinched.
- Spodylosthesis. In this condition, the vertebra is displaced from the common column, which leads to pinching of nerves and muscle fibers.
- Vertebral hernias. In this serious condition, there is a strong protrusion of parts of the intervertebral disc, exerting quite strong pressure on the spinal root.
- Tumors. Regardless of the nature of the tumor, it causes pinching of the nerve fiber, which is accompanied by pain.
- Abscesses. Localization in the lower spinal column is accompanied by pain in the legs.
- Injury. Strenuous training or incorrect body position can cause spinal column injury. Unnoticeable bruises, which are accompanied by internal swelling, damage to the vertebral horns and their dislocations cause disruption of tissue trophism and change the location of the vertebrae.
- Pregnancy. In the last trimester of pregnancy, the growing uterus can significantly compress the sacral region, which leads to disruption of the functioning of the sciatic nerve.
There are also diseases that can provoke nagging pain - these are a variety of polyneuritis, herpes zoster, neuropathies due to metabolic diseases, infectious processes, prolonged intake of heavy metals or toxins in the body, as well as excess weight.
Sciatica, like other disorders of the muscle corset and nerve fibers, can be distinguished using radiography. This type of diagnosis helps to quickly determine the cause of pain.
But if the discomfort was caused by a hernia, then additional research and more precise equipment will be needed. Magnetic resonance imaging is usually used for this.
If a tumor process is suspected, radiological studies are prescribed.
In addition, the specialist must conduct manual neurological examinations that will help assess the general condition of the nervous system.
During pregnancy, no diagnostics are carried out, since everything returns to normal after childbirth.
Therapy in cases where the nerve in the leg is pulled consists of several successive stages:
- The very first thing to do is to remove the pressure that causes pain. In this case, massage, physiotherapy and manual techniques are used. Pinching is almost always eliminated fairly quickly, unless it is caused by irreversible diseases such as a tumor or hernia.
- At the second stage, it is necessary to restore the functions of the nerve. Complex therapy includes the use of medications and mineral supplements.
- At the final stage of treatment, the root cause of the nerve compression is identified. Once it is identified, the underlying disease that caused the pain is treated.
Treatment tactics
Treatment that affects a pinched nerve must be organized comprehensively and correctly. To eliminate the occurrence of this condition, it is necessary to combine various techniques.
The complex should include the use of special medications, physiotherapeutic procedures, as well as techniques that involve direct impact on the pinched area.
Treatment is prescribed only after a complete examination, which allows us to identify the cause of the unpleasant condition.
During treatment, the patient must comply with bed rest and doctor's instructions. Patients must also follow a diet excluding pickled foods, smoked foods, spicy foods and alcohol.
Along with methods aimed at treating pinching, painkillers are prescribed. If you are sick, you can take Ibuprofen, Diclofenac and Indomethacin. Novocaine blockade has the same effect.
The same substances are available in the form of products for local use. If they are used together with the main treatment, the results will not be long in coming. Ointments and creams neutralize pain and improve the patient's condition. For the same purposes, an ointment made from turpentine, mustard and propolis is used.
DDT and UHF can be used for physiotherapeutic effects. Good results can be achieved with Darsonval.
Acupuncture therapy helps stimulate pinched nerve endings. After the course, they become toned, and the disease goes into remission.
If a nerve is pinched in your leg, you need to use some recommendations:
- firstly, in case of constant attacks, exposure to high temperatures is excluded, visiting baths and saunas is prohibited;
- It is recommended to limit physical activity and get more rest;
- massaging the area of the pinched nerve with heated oil will help relieve spasm at home;
- you need to raise your thigh so that it is above the solar plexus, placing something soft under the limb.
This seemingly harmless disease can hide a rather serious pathology. If you ignore the symptoms, your general condition may worsen.
If the pain is severe and prolonged, it must be treated.
Most often, complications such as necrosis of nerve endings, weakness of the lower extremities or paralysis, atrophic condition of the pelvic organs, and instability of spinal function occur.
To prevent this, it is necessary to take preventive measures: do light exercise in the morning and stretching. It is advisable to strengthen your back muscles.
You need to constantly monitor the position of your body in space, keeping your back straight. Avoid shoes with high heels and high insteps.
Cramps occur due to physical exertion, especially if it was sudden and too great, thermal effects (cold water), some people experience cramps even with a sudden change in weather.
Also, seizures can occur when a person undergoes any physiological changes (pregnancy, puberty, menopause). Biological changes cause changes in the levels of many substances in the blood, such as sodium, potassium, and calcium. Convulsions sometimes accompany damage to the nervous system and stress.
A change in diet can also trigger this condition; cramps are often experienced by those who abuse alcohol.
Seizures can be a manifestation of diseases such as spasmophilia, eclampsia, epilepsy, brain trauma and tumors, and inflammation.
Since seizures can be caused by serious illnesses, you should consult a doctor if this occurs.
Symptoms
If a person has developed a pinched sciatic nerve, the symptoms of this pathology will be completely different - it all depends on the degree of pinching and the localization of the process. Some people experience an asymptomatic course, when the pain is not clearly expressed, but gradually gains intensity. And in others, the pathological process manifests itself with vivid pain symptoms. As noted above, the lesion usually occurs on one side, so a person experiences pain only in one limb. The pain syndrome can be so severe that a person can hardly move his leg.
Pinched sciatic nerve
According to localization, pain can be either localized in one area (buttock, thigh), or spread throughout the entire limb - from the gluteal muscle, through the thigh and lower leg to the toes. A common symptom is numbness in a particular area of a limb or the entire leg.
Other symptoms of a pinched sciatic nerve are:
tingling or burning sensation in the lower part of the affected limb; “petrification” of muscles and decreased mobility of the limb; increased pain while sitting; the occurrence of shooting pains, especially in a standing position; the appearance of muscle weakness.
Due to pain, a person experiences a disturbance in gait, increased sweating of the feet, and impaired motor activity of the leg (flexion and extension at the knee and in the foot area).