Causes of myasthenia gravis
To date, the causes of myasthenia gravis are not fully understood.
In medical practice, cases of familial myasthenia gravis are diagnosed, but the heredity of the disease has not been proven. Quite often, patients with asthenic bulbar palsy are diagnosed with hyperplasia or neoplasm of the thymus gland. Another factor contributing to the development of myasthenia gravis is the penetration of viruses and mycoplasmas into the human body. The main pathogenetic feature of this disease is dysfunction of neuromuscular transmission, which determines the characteristic clinical manifestations. The synaptic block is associated with a failure in the synthesis of acetylcholine. Antibodies to skeletal muscles and epithelial cells of the thymus gland are detected in the blood serum, which gives grounds for classifying myasthenia gravis as an autoimmune disease.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcreatorsru
The results of a study of the causes of myasthenia gravis prove that insufficient potassium levels in the body, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland and hormonal imbalance significantly increase the risks of this disease.
Unfortunately, experts cannot say exactly why myasthenia gravis develops. It is assumed that heredity plays a role. When interviewing a patient during a consultation, it often turns out that such a pathology was diagnosed in close relatives earlier.
Sometimes myasthenia gravis does not occur independently, but in combination with a thymus tumor or against the background of connective tissue diseases, oncological diseases (lung cancer, breast cancer), and accompanies ALS. If pathology develops in combination with the diseases described above, it is considered not as an independent disease, but as a syndrome.
Under the influence of certain factors (stress, the influence of infectious agents), the body begins to continuously produce antibodies to its own tissues, and more precisely to the receptors of the postsynaptic membrane. The main function of a synapse is the transmission of a nerve impulse from one neuron to another. Under the influence of antibodies, the membrane begins to sequentially collapse, impulse transmission loses strength, and then finally stops.
When examining the central nervous system, changes characteristic of myasthenia gravis are most often not observed. In 30% of cases, doctors diagnose the thymus gland as enlarged in size or with the presence of a tumor. As for muscle fibers, microscopic examination reveals signs of atrophy.
Drug treatment
Myasthenia gravis: how to treat, what pills to take? It is necessary to take potassium salts, mofertil microphenolate, anticholinesterase and cytostatic drugs, glucocorticoids, steroids, hemosorption and enterosorption. A differentiated approach has worked well.
Myasthenia gravis drugs for treatment:
- Prednisolone;
- Cellcept;
- Azathioprine;
- Cyclosporine;
- Kalimin;
- Plasmapheresis;
- Hemosorption;
- Sorbene is veiled.
If necessary, an operation is performed to remove the thymus gland - thymectomy. Anesthesia for myasthenia gravis is used with caution and constant monitoring of the patient's breathing. Anesthesia is done after therapy with anticholinesterase drugs in combination with atropine (the drugs are administered half an hour before anesthesia). Local anesthetics are not used.
Complications due to taking medications include:
- osteoporosis – calcium is washed out of the bones, increasing the risk of fractures (arms, legs, hips). Must be treated separately;
- steroid diabetes and ulcers;
- Cushing's syndrome;
- hypertension;
- stomach bleeding.
Symptoms in children
Weakness and sudden fatigue can affect any muscle in the human body. More often - the muscles of the face and neck.
Characteristic symptoms of myasthenia gravis (see photo) are:
- ptosis (drooping eyelids);
- double vision;
- nasal voice and speech disorders;
- difficulty swallowing, fatigue of the masticatory muscles;
- fatigue of the neck muscles (difficulty keeping your head straight);
- weakness in arms and legs.
Symptoms appear after exercise, even after the most minimal. The greater the load, the worse the patient's condition. For example, at first, speech impairments are minimal - a person has a slight nasal tone, but pronounces words quite clearly, then he begins to “swallow” individual sounds, and then cannot speak at all. Rest can reduce these symptoms. Symptoms are especially severe 3-4 hours after waking up.
Depending on the manifestations, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- ocular (the disease is manifested only by drooping eyelids, double vision; for such patients, therapy with anticholinesterase drugs is usually sufficient);
- bulbar (impaired speech, chewing, swallowing, breathing - the danger of this form is that breathing difficulties can increase rapidly);
- generalized (affects all muscles, this is the form of myasthenia gravis that is meant when they talk about myasthenia gravis or Erb-Goldflam disease; the disease affects all muscles, from facial and neck muscles to the muscles of the arms and legs);
- fulminant (the most dangerous form, as it leads to disability and even death, it is usually caused by a malignant tumor of the thymus gland, all muscles are affected, including skeletal muscles, while therapy simply does not have time to have its effect, it is simply impossible to prevent the dangerous consequences of myasthenia gravis).
More common is the generalized form, which usually begins with weakness of the facial muscles.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytdevru
1) Congenital myasthenia. Rapid fatigue of the muscular system can be suspected in utero during an ultrasound. With myasthenia gravis, fetal movements are less active, or may even be absent altogether. After birth, the symptoms of this myasthenia gravis are similar to neonatal myasthenia. Death occurs due to impaired spontaneous breathing.
2) Myasthenia of newborns. It occurs in those children whose mothers themselves suffer from myasthenia. It begins from the first days of life and can last about 2 months. Its main symptoms may be the following:
- the baby is more lethargic than other newborns,
- breathes shallowly
- chokes periodically
- his cry is weak, more like a squeak,
- he also sucks poorly and gets tired quickly,
- his mouth is slightly open,
- the gaze is almost motionless,
- in some cases, swallowing may also be difficult.
The child most often dies from suffocation.
- Early childhood myasthenia. According to experts, it occurs before the age of 2 years, when, against the background of complete health, vision problems begin to appear: the eyelids involuntarily droop, gaze paralysis and strabismus develop. In some cases, the baby may refuse to walk, run, have difficulty going up or down stairs, and often asks to be held. Refusal to eat can occur if the masticatory muscles are involved in the process.
- Juvenile and childhood myasthenia. Develops from 2 to 10 years or during adolescence, mainly in girls. Among the early signs, it is necessary to pay attention to the child’s complaints about sudden fatigue, blurred vision, difficulties with running, walking long distances, squats, and doing physical work around the house.
- ocular and local-pharyngeal facial;
- generalized;
- musculoskeletal.
- congenital - transmitted from mother to child. Occurs in 10% of cases. In infants, diagnosing the disease is extremely problematic. The child cries weakly and quietly and has difficulty sucking;
- preschool age;
- teenage.
- drooping eyelid. After waking up, a person opens his eyes wide and begins to blink frequently;
- difficulty chewing and swallowing food;
- voice change;
- fast fatiguability.
As the disease progresses, myasthenic crisis may develop. This condition is very dangerous. The person cannot breathe and his blood pressure rises. It is unacceptable to remain alone at home in this condition; urgent medical attention is required.
Yusupov Hospital accepts patients 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. Experienced doctors conduct examinations in a short time and take measures to improve the patient’s condition.
Treatment of myasthenia gravis (including folk remedies) - ophthalmic and other forms
Myasthenia gravis
Despite the fact that self-medication of myasthenia gravis is prohibited and experts have an extremely negative attitude towards it, traditional medicine offers its own methods of treating the disease.
In any case, before using any drug or organic component, you should consult your doctor. When using traditional methods in the treatment of myasthenia gravis, it should be remembered that it is unlikely that it will be possible to completely get rid of the disease with the help of alternative medicine alone, but it is quite possible to alleviate the patient’s condition.
When using folk remedies in the treatment of myasthenia gravis, you should pay special attention to the recipe and carefully follow the conditions for preparing the infusions.
A glass of washed oats, steamed in half a liter of water and put on low heat for 40 minutes, then leave for an hour, strain and take half a glass 4 times a day.
The best effect from such treatment can be obtained by adding a teaspoon of honey to each serving. Each serving must be taken 30 minutes before meals. The duration of one course is 3 months, after three weeks the course should be repeated.
When carrying out a course of treatment, you should pay attention to a complete and balanced diet for myasthenia gravis.
The resulting remedy should be taken 3 times a day, 30 minutes before meals, a teaspoon.
When using such recipes, do not forget about maintaining a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition for myasthenia gravis.
For two hundred grams of onion you need to take two hundred grams of sugar, pour half a liter of water over everything and mix thoroughly. You need to cook this product for an hour and a half over low heat, then cool and add 3-4 teaspoons of honey to the prepared mass. It is recommended to take the product one tablespoon three times a day.
Prevention of exacerbations is one of the most important factors in the treatment of myasthenia gravis. To do this, it is important to avoid physical activity and eat as much potassium-rich food as possible.
Normal muscle function is completely impossible if the body lacks this substance, and potassium has a positive effect on the effects of medications for myasthenia gravis.
Important components in the diet of patients with myasthenia gravis are: dried apricots, raisins, bananas, and baked potatoes. It is advisable to consume them every day in reasonable quantities.
Consult a specialist! 18
By continuing to use our site, you consent to the processing of cookies, user data (location information; OS type and version; Browser type and version; device type and screen resolution; source from where the user came to the site; from which site or on what advertising; OS and Browser language;
This disease is characterized by pathological muscle weakness and rapid fatigue, expressed below by the following symptoms of myasthenia gravis. Any muscles of the body are involved in the process, and most often the eyes, pharynx, tongue and face.
This does not happen by itself, but, for example, during heavy physical activity or after a long conversation. A person, losing strength, changes in appearance - eyelids may droop, deep wrinkles may appear on the forehead, drooling, squint, horizontally - a frozen “Pierrot smile”.
When the muscles of the tongue and pharynx are affected, swallowing is impaired, hoarseness or nasal voice is noted; if the neck muscles are affected, it is impossible to keep your head straight. If the muscles of the limbs are affected, it is difficult for a person to walk, sit, or care for himself.
By the evening, the state of weakness and powerlessness increases, and after a night's sleep in the morning the patient feels much better.
Any disease does not appear on its own. And there are reasons for pathological muscle weakness. Myasthenia gravis is considered a genetic disease, but has not been sufficiently studied at the gene level. As experience and practice show, the trigger mechanism for myasthenia gravis is most often stress, immune disorders, and viral infections.
In our body there is a substance called “acetylcholine”, which is an intermediary that transmits a nerve impulse to a muscle from a nerve. In myasthenia gravis, the immune system malfunctions and begins to produce antibodies against acetylcholine. Transmission of myasthenia gravis is also considered hereditary, but it has also not been fully proven.
Treatment of myasthenia gravis
First of all, you should undergo an examination and begin treatment. The main drugs used in the treatment of myasthenia gravis are prozerin, kalimin, galantamine, oxazil.
Their main action is to block the enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine and produce normal impulse transmission to the muscle from the nerve fiber.
With the use of these drugs (the dosage intervals and doses are strictly individual), the patient’s muscle strength returns.
In severe cases of myasthenia gravis, hormone therapy (prednisolone) and cytostatics with immunosuppressants are prescribed: cyclosporine, azathioprine, cyclophosphamide. Drugs for the treatment of myasthenia gravis are included in the federal preferential list, and therefore are dispensed free of charge with a doctor’s prescription.
Medicine is moving forward and modern treatment methods have been developed. Some of the most effective and common are cryophoresis and plasmapheresis. This is the purification of blood plasma from antibodies and harmful substances without the risk of allergic reactions and viral infection.
These methods differ in that the cryophoresis procedure is carried out under the influence of low temperatures, and all useful substances in the blood are preserved unchanged.
Another modern method of treating myasthenia gravis has proven itself well - cascade plasma filtration. The patient's blood is passed through nanofilters, returning to him already purified.
Myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis is the most common autoimmune disease characterized by damage to the neuromuscular synapses due to the production of autoantibodies to acetylcholine receptors or to specific enzymes - muscle-specific tyrosine kinase.
As a result, pathological fatigue and weakness of skeletal muscles develop, mutations in proteins of neuromuscular junctions can lead to the development of congenital myasthenic syndromes.
What it is?
Myasthenia gravis is a fairly rare autoimmune disease characterized by muscle weakness and lethargy. With myasthenia gravis, there is a disruption in the communication between nerve and muscle tissues.
The official scientific name of this disease is myasthenia gravis pseudoparalitica, which is translated into Russian as asthenic bulbar palsy. In Russian medical terminology, the concept of “myasthenia gravis” is widely used.
Causes of myasthenia gravis
To date, experts do not have clear information about what exactly provokes the symptoms of myasthenia gravis in a person.
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease, because multiple autoantibodies are found in the serum of patients.
Doctors record a certain number of familial cases of myasthenia gravis, but there is no evidence of the influence of hereditary factors on the manifestation of the disease.
More often, females suffer from myasthenia gravis. As a rule, the disease manifests itself in people aged 20–30 years. In general, the disease is diagnosed in patients aged 3 to 80 years.
In recent years, experts have shown significant interest in this disease due to the high incidence of myasthenia gravis in children and young people, which leads to subsequent disability.
This disease was first described more than a century ago.
Autoimmune processes play a role in the development of myasthenia gravis; antibodies were found in muscle tissue and the thymus gland. The muscles of the eyelids are often affected, resulting in ptosis that varies in severity throughout the day; chewing muscles are affected, swallowing is impaired, and gait changes. It is harmful for patients to be nervous, as this causes chest pain and shortness of breath.
Most often, the disease manifests itself during adolescence in girls (11-13 years old); it is less common in boys at the same age. The disease is increasingly being detected in preschool children (5-7 years old).
Classification
This disease develops differently in everyone. Most often, myasthenia gravis begins with weakness of the eye and facial muscles, then this disorder spreads to the muscles of the neck and torso. But some people have only some signs of the disease. Accordingly, there are several types of myasthenia gravis.
The ocular form is characterized by damage to the cranial nerves. The first sign of this is drooping of the upper eyelid, most often on one side first. The patient complains of double vision and difficulty moving the eyeballs.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Currently, the etiopathogenetic factors of myasthenic syndrome have not been fully determined.
Possible causes of myasthenia gravis:
- Hereditary predisposition - familial cases of the disease are known. The congenital form of myasthenia gravis is caused by a gene mutation that disrupts the normal functioning of myoneural synapses and interferes with the process of nerve-muscle interaction.
- Tumor or benign hyperplasia of the thymus - thymomegaly.
- Organic damage to the nervous system.
- Systemic diseases - vasculitis, dermatomyositis, systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Benign and malignant neoplasms of internal organs.
- Hyperthyroidism - increased function of the thyroid gland.
- Sleeping sickness.
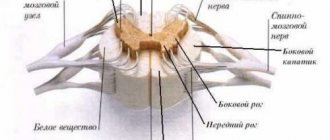
Pathogenetic links of the syndrome:
- production of autoantibodies to acetylcholine receptors;
- damage to the neuromuscular synapse;
- destruction of the postsynaptic membrane;
- disruption of the synthesis, metabolism and release of acetylcholine, a special chemical that ensures the transmission of nerve impulses from the motor nerve to the muscle;
- difficulty in neuromuscular conduction - insufficient supply of impulses to the muscle;
- difficulty performing movements;
- complete immobility of muscles.
We invite you to read: What can and cannot be done when taking antibiotics? 10 rules for their use
Currently, medical scientists have become interested in myasthenia gravis due to its high incidence among children and young people. In this category of people, the disease often ends in disability.
Myasthenia: symptoms, causes, treatment
To date, experts do not have clear information about what exactly provokes the symptoms of myasthenia gravis in a person. Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease, because multiple autoantibodies are found in the serum of patients. Doctors record a certain number of familial cases of myasthenia gravis, but there is no evidence of the influence of hereditary factors on the manifestation of the disease.
More often, females suffer from myasthenia gravis. As a rule, the disease manifests itself in people aged 20–30 years. In general, the disease is diagnosed in patients aged 3 to 80 years. In recent years, experts have shown significant interest in this disease due to the high incidence of myasthenia gravis in children and young people, which leads to subsequent disability. This disease was first described more than a century ago.
Myasthenia gravis is a congenital hereditary disease. Its signs appear in early childhood. The syndrome can develop at different speeds and degrees of severity. Due to genetic abnormalities, the connection between neurons and muscle fibers is disrupted. Due to the fact that the muscles actually turn off and do not function, their atrophy gradually develops.
Scientists have still not been able to fully identify the mechanism of the disease, but it is known for certain that the cause lies in a deficiency of the gene that is responsible for the functioning of myoneural connections. First of all, visual functions suffer, as the eye muscles atrophy. Then the process moves to the facial muscles, neck, muscles of the arms, legs, and swallowing muscles.
We suggest you read: What sweets can you eat with pancreatitis?
Often this congenital syndrome leads to serious consequences and even death of the patient, but with proper treatment, recovery or temporary remission is possible. This pathology can be inherited from one of the parents or through a generation.
Failures of biochemical processes due to pathologies of the thymus and hypothalamus. The thymus is attacked by its own immune cells, which causes less acetylcholine to be produced and broken down.
Please note that the condition of a sick child can be worsened by stressful situations, acute respiratory viral infections, and impaired immunity.
The symptoms of myasthenia gravis directly depend on its form. The main symptom is unusual weakness in the muscles. The patient gets tired quickly and is unable to cope with work or training. This is especially noticeable if you need to make a series of similar movements.
After rest, muscle function is restored. Waking up in the morning, patients feel cheerful, rested, and feel a surge of strength. After some time, characteristic symptoms begin to increase, the patient feels literally overwhelmed.
Myasthenia gravis
Treatment with folk remedies
● Myasthenia gravis is a disease characterized by pathological muscle weakness and rapid fatigue. Any muscles of the body are involved in the process, but most often the muscles of the eyes, tongue, pharynx and face.
The mechanism of the disease does not appear on its own, but in certain cases: for example, after a long conversation or heavy physical work. Hello, dear readers and guests of the medical blog “Traditional Medicine Recipes”!
● Often losing his strength, the patient changes significantly in appearance. He may develop squint, drooping eyelids (ptosis), deep wrinkles on the forehead, drooling, frozen horizontally - the so-called “Pierrot smile”.
If the muscles of the tongue and/or pharynx are involved in the pathological process, hoarseness or nasal sound is noted, swallowing is impaired; if the neck muscles are affected, the patient is unable to hold his head straight.
● If there are problems with the muscles of the upper or lower extremities, it is very difficult for a person to walk, sit, or care for himself. This state of complete powerlessness and weakness increases in the evening, and the next morning, after a full night’s rest, the patient noticeably feels better.
● Myasthenia gravis is a genetic disease, although not well studied at the gene level. As numerous clinical studies have shown, the main cause of the disease is usually a violation of the immune system, past viral infections, and stress.
In the human body there is a substance called Acetylcholine, which serves as an intermediary that transmits nerve impulses from nerve to muscle.
● With myasthenia gravis, the immune system clearly fails and produces antibodies against the above good messenger. Currently, traditional medicine is also considering hereditary transmission of the disease, but it has not been sufficiently proven either.
● In order not to let the disease take its course, you should undergo a thorough examination at a medical institution at your place of residence and begin treatment under the supervision of a local doctor.
The main drugs used to treat myasthenia gravis include: Galantamine, oxazil, prozerin, kalimin. The main purpose of these drugs is to block an enzyme that mistakenly breaks down acetylcholine, which ensures normal impulse transmission from the nerve fiber to the muscle.
● When taking these drugs, the patient gradually regains muscle strength, but it should be taken into account that the dosage intervals and doses are strictly individual.
To enhance the effect of drugs, the attending physician, as a rule, prescribes potassium salts - once a day, one teaspoon. During the treatment process, it is useful for the patient to eat foods rich in potassium: pumpkin, nuts, prunes, dried apricots, bananas, lentils, peas, beans, baked potatoes.
● In severe cases of the disease, hormones are prescribed - Prednisolone with cytostatics and immunosuppressants: Cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, azathioprine.
It should be noted that on the territory of the Russian Federation, medications intended for the treatment of myasthenia gravis are included in the federal preferential list and, according to a doctor’s prescription, are dispensed free of charge.
● Fortunately for us, modern medicine does not stand still, and new methods of treating myasthenia gravis have now been developed. The most common and effective are cryophoresis and plasmapheresis.
The methods are aimed at purifying blood plasma from toxic substances and antibodies without allergic reactions and the risk of viral infection. The above treatment methods differ in that during cryophoresis the procedure takes place under the influence of low temperatures, although all useful blood substances are preserved in their original form.
We invite you to read: Metformin for intensifying the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus
After a short course of treatment (from five to seven days), there is a clear improvement in the condition - the patient forgets about myasthenia gravis for the next six months to a year.
● There is another modern method of treating myasthenia gravis - cascade filtration of plasma, in which all the patient’s blood, passing through nanofilters, is returned back in a purified form.
● Traditional methods of treating myasthenia gravis are used in combination with conservative therapy described above. In the fight against muscle weakness, Flaxflax is recognized as the most effective.
- Brew a teaspoon of the herb in a glass of boiling water for one hour, filter and take a tablespoon before meals three or four times a day for three weeks in a row.
- pour three tablespoons of horsetail herb and half a liter of boiling water into a thermos overnight; the next morning, filter the infusion and drink ⅓ glass half an hour before meals three times a day for a course of two weeks; treatment can be continued after a ten-day break.
● To establish the normal state of striated muscles, the consumption of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is very useful. You can take it in the form of pharmaceutical preparations (1-2 tablets twice a day), as well as as part of vegetables, berries and fruits. The richest foods in this vitamin are black currants, black radishes, peppers, cabbage, rose hips, and lemons.
● A patient with myasthenia gravis is strictly prohibited from drinking alcohol and smoking (even in small doses). An active (moving) lifestyle without overwork and overload is recommended: gymnastics, Nordic walking, working in a summer cottage, going to the forest to pick berries and mushrooms.
You need to get proper sleep - it should last at least 7-8 hours, and 1-2 hours before midnight. Scientists have proven that it is at this time that the body is relieved of stress.
● Do not overheat under the sun, so as not to disrupt the functioning of your already unpredictable immune system. You cannot take hot baths or steam in a bathhouse or sauna.
Be healthy, God bless you.
When writing the article, materials from first category neurologist O. V. Antonovskaya were used
Diagnostics
- patient interview and examination;
- blood test for antibodies;
- blood test using decrement test and proserine test. The patient is administered the drug “Proserin”.
In cases where the patient's condition worsens, the diagnosis is positive;
- computed tomogram of the thymus gland;
- electroneuromyography to check the conduction of impulses along the nerves and the excitability of muscle fibers.
It is necessary to consult a neurologist. First of all, the doctor will examine the patient, ask about complaints and other identified symptoms. During the initial examination of a patient, it is quite difficult to identify myasthenia gravis, because its symptoms are similar to those of many other diseases. Therefore, a comprehensive examination is carried out.
The simplest and most valuable method for diagnosing myasthenia gravis is the proserine test. When performing this test, the patient is subcutaneously injected with a solution of proserin (0.05%, 1-2 ml), then after 20-30 minutes the neurologist re-examines the patient, determining the body’s reaction to the test. Prozerin blocks cholinesterase, the increased activity of which leads to disruption of neuromuscular junctions, so the symptoms of myasthenia gravis quickly subside, and the person feels completely healthy. It is worth noting that the effect of prozerin, although powerful, is short-lived, so it is not used for treatment, but is indispensable for diagnosis.
The following studies are also carried out for diagnosis:
- Electromyography (decrement test) – registration of bioelectric potentials in skeletal muscles. It is advisable to carry out electromyography twice: first before the proserine test, then 30-40 minutes after it, since this can reveal a violation of neuromuscular transmission.
- Electroneurography is a study of the speed of impulses passing through nerves.
- A blood test for specific antibodies, sometimes a biochemical blood test is also required.
- Genetic studies are carried out to identify congenital myasthenia gravis.
- Computed tomography of the mediastinal organs - to examine the thymus gland for its increase in volume or the presence of a tumor (thymoma).
To diagnose myasthenia gravis, special tests have been developed that allow a neurologist to identify the disease in the initial stages. Although you can perform such tests yourself at home:
- Quickly open and close your mouth within 40 seconds - normally you should have time to do 100 cycles of such movements, and with muscle weakness it is much less.
- You need to lie on your back, slightly raise your head and hold it there for 1 minute.
- Do 20 squats with the same amplitude.
- Quickly clench and unclench your hands - often due to muscle weakness in myasthenia gravis, this exercise leads to drooping eyelids.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with diseases with similar symptoms: bulbar syndrome, encephalitis, meningitis, cerebral glioma, hemangioblastoma, Guillain-Barré syndrome, etc.
Drugs containing interferon are strictly contraindicated.
Drug treatment of myasthenia gravis necessarily involves taking potassium salts, as well as cytostatic and anticholinesterase drugs, mycophenolate mofetil, steroids, and glucocorticosteroids.
- kalimin;
- cyclosporine;
- cellcept;
- prednisolone;
- azathioprine, etc.
- antibiotics (macrolides, aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones);
- antipsychotics – neuroleptics;
- anticonvulsants – carbamazepine, phenytoin;
- saluretics – furosemide, hypothiazides, etc.;
- drugs affecting the cardiovascular system - calcium channel blockers, etc.;
- neuromuscular blockers, etc.
- Excessive physical activity;
- Magnesium preparations (magnesia, panangin, asparkam);
- Diuretics (lasix, furosemide), with the exception of veroshpiron;
- Curare-like muscle relaxants, GHB, neuroleptics and tranquilizers, and sedatives (sedatives) (except for Grandaxin, Adaptol, bromine, motherwort, valerian, Corvalol, valocordin);
- Antibiotics toxic to synapses: aminoglycosides (gentamicin, streptomycin, neomycin, kanamycin, monomycin, tobramycin, sisomycin, amikacin, dideoxykanamycin-B, netilmicin), fluoroquinolones (enoxycin, norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, fleroxacin, lomefloxacin, sparf loxacin), macrolides ( doxycycline, erythromycin, tetracycline, azithromycin);
- Antimalarials - quinines, chloroquinines;
- Uroseptics - preparations of nalidixic acid (palin);
- Anticonvulsants - phenytoin, carbamazepine;
- Fluorinated corticosteroids, quinine derivatives, D-penicillamine;
- Antipsychotics - neuroleptics - phenothiazides, sulpiride, clozapine;
- Drugs acting on the cardiovascular system - B-blockers (all, including timolol, betoptik - a selective beta1-blocker - eye drops). Alpha and beta blockers - labetolol;
- Neuromuscular blockers - muscle relaxants (Relanium), non-depolarizing muscle relaxants (curare-like drugs - tubocurarine, Arduan); depolarizing muscle relaxants (succinylcholine), central muscle relaxants (long-acting benzodiazepines, baclofen);
- Local anesthetics (lidocaine);
- Botulinum toxin (Botox injections);
- Other drugs - alpha-interferon, magnesium preparations - 9-magnesium sulfate, panangin, asparkam), iodine-containing radiocontrast agents, Mercazolil (with caution), statins.
If antibiotic therapy is necessary:
- "Suprax 400", 1 tablet 1 time per day for 5-7 days, or, if necessary, IM "Ceftriaxone" 1 g. in the morning and 1 gr. in the evening (not with lidocaine, diluted in water for injection) 7–10 days;
- "Sulperazon" IM 2 g 2 times a day.
In accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated September 18, 2006. No. 665 “on approval of the list of medicines dispensed according to prescriptions of a doctor (paramedic) when providing additional free medical care. assistance to certain categories of citizens entitled to receive state social assistance”, patients with myasthenia gravis are provided with anticholinesterase drugs, steroid hormones and cytostatic immunosuppressants free of charge.
Metypred, prednisolone, azathioprine (Imuran), cyclophosphamide mycophenolate mofetil (Sellsept), cyclosporine (Sandimmune), calimine (pyridostigmine bromide), neuromidin (ipidacrine), veroshpirone (spironolactone), potassium orotate, normal human immunoglobulin 10% GAMIMUN N - all of these The funds are included in the federal preferential list of medicines.
List of medicines dispensed by prescription when providing additional free medical care. assistance to certain categories of citizens entitled to receive social assistance.
Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia) dated September 28, 2005. No. 601 Moscow on approval of the list of medicines. Registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on September 29, 2005. No. 7052.
The Neurological Center is always ready to help you. B.M. Hechta. Diseases of the nervous system and pain syndromes are not a death sentence!
Ordinatorskaya: 7 (499) 187–85–92
Making an appointment with a doctor
Call back from the hospital call center
doctor
Immunosuppressive therapy
To treat myasthenia gravis, immunosuppressants are prescribed:
- Azathioprine;
- Cyclosporine;
- Prednisolone.
However, during therapy, the risk of infectious complications and the development of malignant tumors increases.
Azathioprine is the safest drug. It affects the absorption of glucocorticoids and can significantly reduce their dose. Side effects of the drug lead to its withdrawal. The patient complains of headache, chills, and fever. A person develops symptoms of liver dysfunction.
Methotrexate is a strong immunosuppressant, it is used in a small dose, because the drug has significant toxicity. The patient experiences discomfort in the epigastric region, nausea, and vomiting. Many people experience pain in the liver area, enzyme activity changes, and signs of cirrhosis appear.
Leucovorin, prescribed after Methotrexate therapy, reduces its toxicity. For a patient suffering from myasthenia gravis, treatment with antipsychotics and tranquilizers is contraindicated.
It is not recommended to take antidepressants that worsen the patient's condition and contribute to the development of myasthenic syndrome as a complication of drug therapy.
Causes of the disease and the mechanism of its development
The prevalence of this pathology is 4 cases per 100 thousand population. It is noteworthy that at a young age the disease more often affects women and teenage girls; in old age, both men and women get sick with a gender frequency of 1:1. The reason why myasthenia gravis develops has not yet been fully studied. Today, the following factors can provoke the development of the disease:
- Pathology of the thymus or thymus gland, as well as other glands (adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid).
- Mutations in genes encoding the functioning of neuromuscular synapses.
- Exogenous causes (hypothermia, frequent stress, physical overexertion, infections, autoimmune diseases).
More than 60% of patients with diagnosed myasthenia have pathology of the thymus (thymus gland) - hyperplasia or thymoma.
The main symptoms of the disease arise due to the fact that the receptors of striated muscles cease to bind to acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter produced by nerve endings. The receptor does not receive “fuel”, which is why there is no muscle activity.
This is due to:
- production of own antibodies to acetylcholine receptors;
- insufficient production of acetylcholine;
- excessive activity of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, which destroys the neurotransmitter.
With thymic hyperplasia, excessive release of the hormone thymine into the blood occurs, which triggers a cascade of autoimmune reactions leading to the destruction of muscle receptors due to increased production of cholinesterase and antibodies.
The mechanism of development of the disease occurs at the level of the neuromuscular synapse: the impulse passing from the neuron to the myocyte is blocked - muscle contraction does not occur. More often than others, the muscles of the eyelids, trunk and limbs, and masticatory muscles are affected.
In addition to the patient’s complaints and medical history, the diagnosis of myasthenia gravis includes various tests, hardware examinations and analyses.
Electromyography helps determine muscle response to stress, and CT or MRI reveals the absence of diseases that could cause similar symptoms. After all, myasthenic syndrome is observed in encephalitis, meningitis, cancer, botulism, and thyrotoxicosis. But the differences in this case from myasthenia gravis are that the facial muscles are rarely affected, and when conducting electromyography, there is not a slowdown, but an increase in muscle potential with repeated stimulation.
We suggest you read: Is it possible to cauterize erosion with HPV?
It is also necessary to distinguish myasthenia gravis from Duchenne muscular dystrophy in time, although the symptoms are different. Muscular dystrophy occurs mainly in boys and begins in childhood.
Most often, to make a diagnosis, an immunological test is done to determine antibodies to acetylcholine and a proserine test is performed. Its meaning is that after intramuscular injection of 1 ml of the drug “Proserina”, the patient’s condition improves significantly after 30 minutes, and after 2-3 hours the symptoms return.
A very important method for diagnosing myasthenia gravis is various tests that reveal the degree of muscle weakness, as well as which of them are more affected. Since fatigue increases after repetitive movements, the following tests may be effective:
- if you ask the patient to look to the side or up for at least 30 seconds, ptosis and double vision appear;
- to provoke dysarthria and decreased voice strength, you need to ask the patient to read something out loud;
- weakness of the neck muscles can be detected if the patient lies on his back and raises his head, he will not be able to hold it up for more than a minute;
- sometimes with myasthenia gravis the M. Volker phenomenon appears - repeated clenching and unclenching of the hands causes increased ptosis.
Electromyography helps determine muscle response to stress
Why does myasthenia gravis occur?
With myasthenia gravis, the transmission of impulses between nerves and muscles is disrupted - at the so-called neuromuscular synapses.
Essentially, a synapse is a microscopic gap between a nerve ending and a muscle. At the end of the nerve a special substance is released - acetylcholine. It is a mediator, that is, a carrier of nerve impulses. On the surface of the muscle, acetylcholine interacts with special receptors, this leads to excitation and contraction. In myasthenia gravis, the immune system mistakenly attacks receptors on the surface of muscles and disrupts their function. Acetylcholine cannot fully contact the muscle, as a result it receives weak impulses and weakens.
It is believed that the formation of antibodies directed against acetylcholine receptors may be facilitated by the thymus (thymus gland), an organ of the immune system in which T-lymphocytes mature. Normally, the thymus is active in children, but in adults it gradually atrophies - in older people, only adipose tissue can be found in its place. But in patients with myasthenia gravis, the thymus is often abnormally enlarged, and sometimes benign neoplasms are found in it - thymomas.
In addition to the acetylcholine receptor, antibodies in myasthenia gravis may attack other molecules that play a role in the transmission of neuromuscular impulses.
A rare congenital form of myasthenia, the so-called congenital myasthenic syndrome, occurs. It is associated with defects in the genes that encode proteins necessary for the transmission of neuromuscular impulses. The prevalence of this form of the disease is unknown. The literature describes approximately 600 families in which sick children were born.
Some factors worsen the course of myasthenia gravis:
- Increased loads.
- Frequent illnesses and stress.
- Taking certain medications.
Myasthenia gravis is a chronic neuromuscular disease. The main manifestation is constant fatigue of the striated muscles. The causes of the disease are still completely unknown, but it is believed that hormonal disorders and autoimmune processes that are associated with the pathology of the thymus gland play a major role.
Most often, myasthenia gravis affects the muscles that move the face and eyes, as well as the muscles responsible for speech and the larynx. The first signs are oculomotor disorders (strabismus or constant double vision), weakness of skeletal muscles. The voice becomes hoarse and quiet when the laryngeal muscle is damaged.
Contraception for myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rather dangerous disease, which, if left untreated, can lead to serious conditions and have a bleak prognosis. At the same time, medicine does not stand still and every day more and more effective drugs appear on the market to combat pathology. Leading Russian doctors work at the Yusupov Hospital, who develop an individual treatment regimen for each patient. At an appointment with a specialist, you can consult about any nuances associated with myasthenia gravis.
Many girls are interested in whether it is possible to take contraceptives with this diagnosis. There is no clear answer to this question; doctors determine contraindications for each patient individually.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital explain to their patients in great detail which actions and medications are contraindicated when diagnosed with myasthenia gravis, and which can be used without health hazards. To avoid exacerbations, the patient must understand how he himself can aggravate the course of the disease and unwittingly harm himself.
Under no circumstances should you become depressed when diagnosing myasthenia gravis. Medicine is developing every day, modern drugs allow patients to lead their usual full-fledged lifestyle. The main thing is that the course of therapy is determined by an experienced doctor who has knowledge of modern advances in medicine and applies them in practice.
At the Yusupov Hospital, the staff of doctors consists of high-level professionals, which makes it possible to get back on their feet even those patients who were abandoned in other clinics.
You can make an appointment by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
Glucocorticoid therapy
Prednisolone increases the number of cholinergic receptors. After taking it, muscle strength increases. To avoid certain risks in the early stages of the disease, therapy is carried out in a hospital setting. The patient is additionally prescribed anticholinesterase drugs. Treatment with glucocorticoids is long-term. The intermittent method, where the patient takes an increased dose of medication over several hours, is very popular. Side effects may occur during treatment:
- increased blood pressure;
- stomach ulcer.
Azathioprine is used in patients with myasthenia gravis that is difficult to treat with Prednisolone. Dexamethasone is recommended by the doctor, taking into account the patient’s condition, since the drug is 10 times more active than other glucocorticoids. However, it is unsuitable for circadian therapy because it worsens the patient's condition.
Treatment with glucocorticoids involves taking alkalizing drugs: the patient is prescribed Phosphalugel or Ranitidine. To prevent the development of diabetes mellitus, the patient must follow a special diet. Limit consumption of foods containing large amounts of carbohydrates. Blood is drawn regularly to determine glucose levels.
Bibliography
- ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases)
- Yusupov Hospital
- Vinnichenko A.G., Zhivolup E.G., Shcherbakov Yu.M. and others. Instrumental methods for diagnosing neoplasms of the thymus gland: Method, recommendations of the USSR Ministry of Health. Kharkov, 1976. - P. 25.
- Gekht B.M. About clinical variants and nosological unity of myasthenia gravis. // In the book: Myasthenic disorders. - L., 1965. From 147-155.
- Zaitsev V.T., Nechitailo P.E., Zhurov Yu.E., Klimova E.M. Changes in immunoreactivity in patients with generalized myasthenia after thymectomy // Klin. hir. 1988. - No. 12. - P. 25-27.
- ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases)
- Yusupov Hospital
- Vinnichenko A.G., Zhivolup E.G., Shcherbakov Yu.M. and others. Instrumental methods for diagnosing neoplasms of the thymus gland: Method, recommendations of the USSR Ministry of Health. Kharkov, 1976. – P. 25.
- Gekht B.M. About clinical variants and nosological unity of myasthenia gravis. // In the book: Myasthenic disorders. - L., 1965. From 147-155.
- Zaitsev V.T., Nechitailo P.E., Zhurov Yu.E., Klimova E.M. Changes in immunoreactivity in patients with generalized myasthenia after thymectomy // Klin. hir. 1988. – No. 12. – P. 25-27.
Classification
Classification is carried out according to the principle of the main symptoms of myasthenia gravis and their localization, as well as according to the criterion of congenitality or age of manifestation.
The congenital form is quite rare, as a rule, it is genetically inherited; most patients with this type of disease have close relatives who also suffered from this disease.
The congenital form is almost always fatal because such infants are unable to breathe on their own.
Much more often, the first symptoms of myasthenia gravis begin to appear at the age of 13-15 years or from 30 to forty. It has been statistically proven that women are more likely to suffer from the disease than men. Congenital myasthenia gravis is almost always transmitted from mother to child.
Affects respiratory, chewing, and facial muscles. The patient cannot chew food and has difficulty breathing. Bulbar myasthenia, especially if it progresses, is life-threatening due to the occurrence of paralysis and paresis of the respiratory system. Another characteristic sign: a person cannot speak or speaks very quietly due to the inability to fully use the vocal cords.
Ocular myasthenia
Ocular myasthenia Primarily affects the visual muscles. Externally it manifests itself as ptosis: drooping of one or both eyelids. A person has difficulty concentrating and quickly gets tired of visual activity. Often, it is from the eyes that symptoms begin, subsequently affecting other muscle structures.
It begins as bulbar myasthenia or in the ocular form, but gradually all muscles fall under the influence of the pathological process. The patient experiences difficulty with any physical activity, breathing, and swallowing. This form is not always severe, especially with therapy.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=editor
Isolated as a separate subtype of the disease. Symptoms do not increase continuously, but develop over a short period of time. Bulbar paralysis is especially dangerous in the form of a crisis, since a person can suffocate due to paresis of the respiratory muscles.
Modern therapy makes it possible to completely eliminate all clinical signs. The least common is malignant myasthenia gravis, which does not respond to therapy and ends in death within a short period of time.
Myasthenic crisis
Myasthenia gravis is a chronic disease, it constantly progresses. If the patient does not receive proper treatment, his condition worsens. A severe form of the disease may be accompanied by the onset of myasthenic crisis. It is characterized by the fact that the patient experiences severe weakness of the muscles responsible for swallowing and movement of the diaphragm.
An overdose of anticholinesterase drugs may cause a cholinergic crisis. It is expressed in a slow heartbeat, salivation, convulsions, and increased intestinal motility. This condition also threatens the patient’s life, so he needs medical attention. The anticholinesterase drug must be discontinued, and its antidote, Atropine solution, must be administered intramuscularly.
Forecast
Myasthenia gravis is a complex disease, so it is quite difficult to predict its treatment. Success depends on many factors: characteristics of the course of the disease, time of onset, form, age of the patient, etc. Generalized myasthenia gravis is the most difficult to treat. With strict adherence to all the recommendations of the attending physician, good results can be achieved. The patient's condition improves significantly, and the time of remission increases.
Myasthenia gravis is a chronic disease, so patients have to take medications throughout their lives. Timely examination is of no small importance. This allows you to stop the development of the disease, prevent progression and the emergence of a crisis.
Treatment of myasthenia gravis is symptomatic and cannot be completely cured.
Women suffering from myasthenia gravis can become pregnant and give birth naturally. However, some women in labor may be offered the option of a caesarean section. This depends on the individual characteristics of the body, the course of pregnancy and myasthenia gravis.
General information. Myasthenia gravis – what is this disease?
Myasthenia gravis is a disease that affects the muscles and nerves. The main characteristic feature of this condition is muscle weakness. Myasthenia gravis is also called asthenic bulbar palsy. This disease primarily affects the muscles of the face, eyes, lips, tongue, neck, and pharynx. However, the process of damage can overtake any muscle in the body.
This disease develops due to difficulty transmitting the signal from the nerves that should cause the muscles to move. Pathology occurs due to a violation of acetylcholine metabolism in the body. If we consider the human body in general, it represents a rather complex electrochemical mechanism that moves with the help of muscle work.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Honey mask for wrinkles on the forehead
Thus, the work of human limbs is ensured by skeletal muscles, the activity of internal organs and blood vessels is ensured by smooth muscles. For skeletal muscle muscles, signals are transmitted through motor nerves. The electrical impulse at the point where the nerve is attached to the muscle is transmitted using acetylcholine, a special chemical.
Acetylcholine enters the gap between the nerve and the muscle from the nerve, resulting in an electrical discharge that causes the muscle to contract. When myasthenia gravis manifests itself in the body, changes occur in the system of synthesis and release of this chemical. As a result, the next impulse approaches the muscle more difficult each time, so it becomes more difficult for a person to make movements. Later, muscle movements stop completely. This condition is commonly called pathological muscle fatigue syndrome.
Myasthenia gravis is varied in its manifestations. According to the course of the disease, they are distinguished:
- myasthenic episodes (symptoms occur extremely rarely, myasthenia may appear only once in a lifetime and then not manifest itself at all);
- myasthenic condition (the disease has manifested itself, but does not progress);
- progressive form (the patient’s condition without therapy slowly but constantly worsens);
- malignant form (rapid development of the disease).
The progressive and malignant forms are very dangerous because serious breathing problems can develop, which is life-threatening.
Risk group
B. Protasov: — Myasthenia gravis is common among young people - from 20 to 40 years old. Women get sick much more often. Officially the ratio is 3:1, but it is very likely that the first figure is higher.
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease caused by disorders of the immune system in which it does not react correctly to its own tissues. The mechanism is triggered by “sleeping” genes. Stress and ARVI, which provoke disorders of the immune system, can lead to their activation. This, in turn, leads to the formation of antibodies against the body’s own cells.
Article on the topic
Electrical muscle stimulation - what is the essence of such treatment?
I. Mikhalev: — I think the reason for the predominance of myasthenia gravis among women is the uniqueness of their immunity. The age at which the disease begins is childbearing age. And pregnancy serves as a provoking factor for autoimmune diseases, because during it hormonal and immune changes occur in the body.
Treatment of myasthenia gravis
- “Aflubin”: 25 drops (dissolved in 1 tablespoon of water) every 3-4 hours, for 2-3 days, until the manifestations of ARVI stop;
- “Kagocel”, “Arbidol”, “Remantadine”, “Ocillococinum”, “Teraflu”, “Tamiflu”.
The main goal of treating myasthenia gravis is to increase the amount of acetylcholine. It is quite difficult to synthesize this component, so drugs are used in treatment to prevent its destruction. For this purpose, medications containing neostigmine are used in neurology.
If the disease progresses rapidly, medications are prescribed that block the immune response; this is the treatment in this case.
When choosing medications, you need to take into account that medications containing fluoride are contraindicated for myasthenic patients. People over 70 years of age have their thymus gland removed. In addition, medications are selected to block individual symptoms - eyelid twitching, stopping drooling, etc.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=https:5aGR37B5GIc
“Pulse therapy” helps improve the patient’s condition. This treatment involves the use of hormonal drugs. At first, a large dose of artificial hormones is prescribed, but gradually it is reduced and reduced to “no”. If a myasthenic crisis occurs, hospitalization may be necessary. Patients with this condition are prescribed plasmapherosis and ventilation to treat symptoms.
A relatively new method of treating myasthenia gravis is cryopherosis. Treatment involves the use of low temperatures, which help rid the blood of harmful components. Beneficial substances contained in plasma are returned to the patient’s blood. The method is safe, since there is no possibility of transmission of infection and the occurrence of an allergic reaction. Cryopherosis improves the general condition of the patient. After 5-6 procedures, a good, lasting result is established.
Often during treatment, doctors prescribe Kalimin, an anticholinesterase drug, also known as Mestinon, Pyridostigmine. As with any autoimmune disease, corticosteroids are prescribed, in particular Prednisolone, for treatment.
Complex of therapeutic measures
The main goal pursued in the treatment of myasthenia gravis is to increase acetylcholine levels at neuromuscular synapses.
Since it is very difficult to achieve this by stimulating natural synthesis, it is more rational to prevent the destruction of this substance in the tissues. The patient is prescribed medications that have a mild effect.
Pyridostigmine and Oxazil are used more often in long courses. If therapy does not bring the desired effect, the specialist may recommend the additional use of drugs that prevent the immune system from reacting to substances entering the body.
For this purpose, glucocorticoids or immunosuppressants are prescribed. Medicines containing fluoride should be avoided, because their effect on the patient’s body may be extremely undesirable.
Treatment of patients over 70 years of age is predominantly surgical - the thymus gland is completely removed.
However, methods of treating myasthenia gravis largely depend on the degree of progression of the disease.
Start…
At the initial stage, drug therapy using Kalimin or other potassium-based drugs shows good results:
- Kalimina 60N (tablets) – three times a day with time intervals between doses of 6 hours or more;
- Potassium chloride , prescribed in a volume of 1 g, three times a day;
- Potassium-normine in the amount of one tablet three times a day.
If symptoms progress
Progression of the disease, the presence of bulbar disorders and the ineffectiveness of drug treatment may cause the need to prescribe glucocorticoids. Most often this is Prednisolone at a dosage of 1 mg/1 kg of the patient’s weight.
Injections are performed once a day - in the morning. Frequency of administration: every other day.
Extreme measures
In advanced cases, or if drug therapy is ineffective, or if there are other indications, surgical treatment is performed - removal of the thymus gland.
The effect of the operation does not develop immediately, but over 1-1.5 years. Surgical intervention is also carried out at the initial stages, depending on the individual characteristics of the body and the prognosis.
Drug therapy should be carried out exclusively under the supervision of an experienced neurologist and other specialists, including an endocrinologist. Careful monitoring of the patient's blood sugar level is necessary, which may change under the influence of medications.
Description of the clinical picture (photo)
Symptoms of myasthenia gravis usually lead to severe physical limitations in affected individuals.
Gradually, the clinical picture becomes more and more pronounced. Over time, the complaints intensify even after the slightest physical exertion.
The main signs of the disease are general muscle weakness and increased fatigue. Such manifestations are observed in both children and adults (see photo below).
Children also experience the following complaints:
- excessively low mobility;
- manifestation of weakness;
- lack of appetite and even the inability to disturb the sucking of the mammary glands, as a result of which many children suffer from malnutrition;
- muscle atrophy, which is observed visually.
Young people initially experience increasing fatigue. Even simple movements, including walking and arm movements, lead to fatigue. Due to muscle pathology, serious changes in gait occur due to the need to adapt to weakening muscle activity. Soon the facial expression changes, which affects the eyes and eyelids, facial expressions.
When wondering what kind of muscle-related disease this is, there are additional diagnostic challenges in older adults. Many complaints can be explained by age-related changes, as a result of which the pathology remains undetected until a sharp deterioration in health.
In older adults, diagnosis is usually made only after severe symptoms have developed:
- weakening of the general muscle tone of the whole body;
- inability to clearly focus the eye;
- the appearance of a feeling of heaviness in the eyelids;
- weakening of the swallowing reflex;
- decreased voice pitch;
- breathing problems that become difficult and excessively frequent;
- physical exhaustion;
- development of aspiration pneumonia.
Despite the degree of manifestation of the clinical picture, there is a need for a timely and accurate diagnosis. Otherwise, myasthenia gravis leads to irreversible consequences and disability.
Folk remedies
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcopyrightru
Along with drug therapy, it is possible to treat myasthenia gravis at home with folk remedies in order to speed up recovery and alleviate the condition. However, any traditional treatment methods must be agreed with the observing specialist.
Effective means:
- Oats. The grains are thoroughly washed and filled with water in a volume of 0.5 liters. Next, the container is placed on the fire, the composition is brought to a boil, and steamed for at least half an hour. Next, to prepare the infusion, wait another 2 hours, removing the oats from the heat. The resulting decoction is taken an hour before meals, at least 4 times a day. The duration of therapy is 3 months with a break of 1 month and another course of treatment.
- Onion. The product in a volume of 200 grams (purified) is mixed with 200 grams of sugar and filled with water in a volume of 0.5 liters. The composition is placed on low heat and cooked for 1.5 hours. Next, cool the mass, add two tablespoons of honey and take two teaspoons three times a day.
- Three heads of garlic are crushed and mixed with four lemons, a liter of honey and linseed oil (200 g). All ingredients must be thoroughly mixed and taken daily, one teaspoon three times a day.
Myasthenia gravis treatment with folk remedies | Portal about traditional medicine
Myasthenia: symptoms, causes, treatment.
Myasthenia gravis
Treatment with folk remedies
The mechanism of the disease does not appear on its own, but in certain cases: for example, after a long conversation or heavy physical work. Hello, dear readers and guests of the medical blog “Traditional Medicine Recipes”!
● Myasthenia gravis is a genetic disease, although not well studied at the gene level. As numerous clinical studies have shown, the main cause of the disease is usually a violation of the immune system, past viral infections, and stress.
The human body contains a substance called acetylcholine, which serves as an intermediary that transmits nerve impulses from nerve to muscle.
● With myasthenia gravis, the immune system clearly fails and produces antibodies against the above good messenger. Currently, traditional medicine is also considering hereditary transmission of the disease, but it has not been sufficiently proven either.
To enhance the effect of drugs, the attending physician, as a rule, prescribes potassium salts - once a day, one teaspoon. During the treatment process, it is useful for the patient to eat foods rich in potassium: pumpkin, nuts, prunes, dried apricots, bananas, lentils, peas, beans, baked potatoes.
● Traditional methods of treating myasthenia gravis are used in combination with conservative therapy described above. In the fight against muscle weakness, toadflax is considered the most effective.
What signs are not typical for myasthenia gravis?
To determine the disease, you need to know that myasthenia gravis symptoms are quite symmetrical. It is not characterized by muscle damage, for example, one arm or one leg. True, drooping of one eyelid is a common manifestation of this disease.
But headaches, dizziness, problems with urination, numbness in the arms or legs, as well as pain in the muscles of the limbs have nothing to do with the signs of myasthenia gravis.
With the described pathology, by the way, the distal sections of the muscles (hands, feet) retain their strength, and it is difficult for the patient, for example, to raise and hold his arms in this position, rise from his haunches, or walk up the steps.
Rules of conduct for myasthenia gravis
If the diagnosis is made on time and the patient follows all the doctor’s instructions, his performance and lifestyle remain almost unchanged. Treatment of myasthenia gravis consists of constantly taking special medications and following certain rules.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=upload
Such patients are prohibited from sunbathing, performing heavy physical work and taking medications without a doctor’s recommendation. Patients should definitely know what contraindications for taking medications for myasthenia gravis. Many drugs can cause complications of the disease or the development of myasthenic crisis. These are the following medications:
- all magnesium and lithium preparations;
- muscle relaxants, especially curare-like ones;
- tranquilizers, antipsychotics, barbiturates and benzodiazepines;
- many antibiotics, for example, Neomycin, Gentamicin, Norfloxacin, Penicillin, Tetracycline and others;
- all diuretics, except Veroshpiron;
- Lidocaine, Quinine, oral contraceptives, antacids, some hormones.