Reasons for developing ALS
For a long time, the pathogenesis of the disease was unknown, but with the help of numerous studies, scientists were able to obtain the necessary information. The mechanism of development of the pathological process in ALS is a mutation in the disruption of the complex recycling system of protein compounds that are found in the nerve cells of the brain and spinal cord, as a result of which they lose regeneration and normal functioning.
There are two forms of ALS – hereditary and sporadic. In the first case, the pathology develops in people with a family history, in the presence of amniotic lateral sclerosis or frontotemporal dementia in close relatives. The overwhelming majority of patients (90-95% of cases) are diagnosed with a sporadic form of amyotrophic sclerosis, which occurs due to unknown factors. A connection has been established between mechanical injuries, military service, intense stress and exposure to harmful substances on the body, but it is not yet possible to talk about the exact causes of ALS.
Interesting: the most famous patient with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis today is physicist Stephen Hawking - the pathological process developed when he was 21 years old. At this time, he is 76 years old, and the only muscle he can control is the cheek muscle.
Breathing problems
What's happening? With ALS, the respiratory muscles are sooner or later affected. As the disease progresses—especially in the later stages—breathing problems develop. When this happens, the patient will need breathing devices and specialist consultation.
What can be done? If a person experiences shortness of breath, weakness, sleep disturbances, morning headaches, or sleepiness during the day, their healthcare provider may refer them to a pulmonologist. Methods for correcting the problem may include breathing and physical exercises, recommendations for creating a comfortable body position, effective coughing techniques, drug therapy and special equipment for ventilation.
Learn more about breathing problems in ALS
Symptoms of ALS
As a rule, the disease is diagnosed in adulthood (after 40 years), and the risk of getting sick does not depend on gender, age, ethnic group or other factors. Sometimes there are cases of a juvenile form of pathology, which is observed in young people. In the first stages of ALS, there are no symptoms, after which the patient begins to experience mild cramps, numbness, twitching and muscle weakness.
The pathology can affect any part of the body, but usually (in 75% of cases) it starts from the lower extremities - the patient feels weakness in the ankle joint, which is why he begins to stumble when walking. If symptoms begin in the upper extremities, the person loses flexibility and strength in the hands and fingers. The limb becomes thinner, the muscles begin to atrophy, and the hand becomes like a bird's paw. One of the characteristic signs of ALS is asymmetrical manifestations, that is, symptoms first develop on one side of the body, and after some time on the other .
In addition, the disease can occur in the bulbar form - affecting the speech apparatus, after which difficulties arise with swallowing function, and severe salivation appears. The muscles responsible for chewing function and facial expressions are affected later, as a result of which the patient loses facial expressions - he is unable to puff out his cheeks, move his lips, and sometimes stops holding his head up normally. Gradually, the pathological process spreads to the entire body, complete muscle paresis and immobilization occur. There is virtually no pain in people diagnosed with ALS; in some cases, it occurs at night and is associated with poor mobility and high spasticity of the joints.
Table. Main forms of pathology.
| Form of the disease | Frequency | Manifestations |
| Cervicothoracic | 50% of cases | Atrophic paralysis of the upper and lower extremities, accompanied by spasms |
| Bulbarnaya | 25% of cases | Paresis of the palatine muscles and tongue, speech disorders, weakening of the masticatory muscles, after which the pathological process affects the limbs |
| Lumbosacral | 20-25% of cases | Signs of atrophy are observed with virtually no disturbance in the tone of the leg muscles; the face and neck are affected in the last stages of the disease |
| High | 1-2% | Patients experience paresis of two or all four limbs, unnatural expression of emotions (crying, laughter) due to damage to the facial muscles |
The above signs can be called average, since all patients with ALS manifest themselves individually, so it is quite difficult to identify specific symptoms. Early symptoms may be invisible both to the person himself and to others - there is slight clumsiness, awkwardness and slurring of speech, which is usually attributed to other reasons.
Important: cognitive functions are practically not affected in ALS - moderate memory impairment and impairment of mental abilities are observed in half of the cases, but this makes the general condition of patients worsen even more. Due to the awareness of their own situation and the expectation of death, they develop severe depression.
Saliva and phlegm
What's happening? When swallowing is impaired, excess saliva accumulates in the oral cavity, which leads to drooling and the associated feeling of discomfort. The consistency of the secretion can be either watery or thick. Increased viscosity is associated with a decrease in the amount of fluid entering the body. In this case, saliva is removed with great difficulty. Dry mouth may also develop due to medications, dehydration, mouth breathing, or mucosal candidiasis.
What can be done? Options for solving this problem include dietary adjustments, drug therapy, and the use of aspiration devices for cleaning the oral cavity (suction).
Learn more about how to control salivation
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral syndrome is complicated by the fact that the disease is rare, so not all doctors can distinguish it from other pathologies.
If you suspect the development of ALS, the patient should go to an appointment with a neurologist, and then undergo a series of laboratory and instrumental tests.
- Blood tests . The main indicator of pathology is an increase in the concentration of the enzyme creatine kinase, that is, a substance that is produced in the body when muscle tissue is destroyed.
- Electroneuromyography (ENMG) . A research method that involves assessing nerve impulses in individual muscles using thin needles. The muscles of the limbs and pharynx are tested, and the results are recorded and analyzed by specialists. The electrical activity of tissues affected by pathology differs significantly from those of healthy ones, and disturbances can be noticed even if the muscle is in good shape and functions normally.
- Magnetic resonance imaging . MRI in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is used for differential diagnosis, since with this pathology no pronounced changes in the functioning of the central nervous system are observed. The study allows us to exclude Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord tumors and other similar conditions.
- Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) . An innovative diagnostic technique that allows you to assess the functions of brain neurons that are responsible for motor activity.
As additional diagnostic methods, muscle biopsy, lumbar puncture and other studies can be used, which help to obtain a complete picture of the condition of the body and make an accurate diagnosis.
For reference: today, new diagnostic methods are being developed that make it possible to detect ALS in the early stages - a connection has been discovered between the disease and an increase in the level of p75ECD protein in the urine, but so far this indicator does not allow us to judge with high accuracy the development of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Immobilizes and suffocates: what you need to know about ALS
Still from the film “The Theory of Everything”: Stephen Hawking in the early stages of ALS
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is the most common type of motor neuron disease.
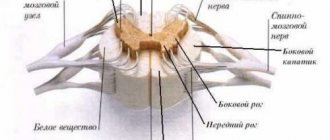
Motor neurons are cells that carry information from the central nervous system to the muscles. They can reach 1 meter in length.
Upper motor neurons are located in the cerebral cortex. Their processes (axons) descend into the spinal cord, where they contact the neurons of the spinal cord.
Neurons in the spinal cord (lower motor neurons) use processes to transmit signals to the muscles and control their contractions. Depending on their location, they are responsible for the movement of the arms, legs, torso, contraction of the diaphragm, breathing, swallowing, etc.
In ALS, motor neurons in both the brain and spinal cord are affected and killed.
The average age of patients is 45 years, but there are also much younger patients. Thus, American composer and guitarist Jason Becker was diagnosed with ALS at the age of 20.
The disease occurs in 5-7 people per 100 thousand population. Every 90 minutes, a new case of ALS is diagnosed around the world.
There are twice as many cases of men as women.
Famous people with ALS
Mao Zedong. Photo from pinterest.ru
Mao Zedong (1893-1976) - Chinese politician. At the age of 80, he was diagnosed with ALS, but died two years later from a heart attack.
Lou Gehrig (1903-1941) was an outstanding American baseball player. He was diagnosed with ALS at age 36, in 1939.
Dmitry Shostakovich (1906-1975) is a great composer. He suffered from ALS for about ten years and died of a heart attack.
Stephen Hawking (1942-2018) is a famous British physicist. Lived with ALS for over 50 years.
Vladimir Migulya (1945-1996) – composer, author of music for the songs “Grass at the House”, “Talk to Me, Mom”, “Stuntmen”, etc. The disease was discovered in 1993.
Jason Becker (born 1969) is an American composer and guitar virtuoso. He fell ill with ALS at the age of 20, in 1989.
Fernando Ricksen (born 1976) is a Dutch footballer. He was diagnosed with ALS in 2013 and lost the ability to speak in 2020.
Who's at risk
Stephen Hawking. Photo from pinterest.ru
The disease was first described in 1869 by the Frenchman Jean-Martin Charcot, but it is still poorly understood. In each case, its triggering mechanisms may be different.
There are hereditary forms of ALS, and then the main cause is a mutation in a specific gene. When making a diagnosis, a neurologist usually asks whether any other family members have suffered from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or frontotemporal dementia (the same genetic “breakage” leads to it).
But in the vast majority of patients (90-95%), none of the relatives suffered from these diseases. Moreover, in 10% of these people the mutation is still detected - it occurs for the first time in them, and is not transmitted from their parents.
There is a hypothesis that there is a connection between the non-hereditary form of ALS and certain injuries, high stress in sports, and agricultural chemicals.
But clear conclusions have not yet been made, since many data are inconsistent with each other.
The only known risk group is children of sick parents with an established mutation that caused the development of ALS. They inherit the damaged gene with a 50% probability. But a gene mutation does not necessarily lead to ALS.
Weakness in the legs
Dmitry Shostakovich. Photo from pinterest.ru
ALS is very difficult to diagnose. Firstly, because it is a rare disease that doctors are poorly aware of. Secondly, early symptoms are quite minor: clumsiness, clumsiness in the hands, slightly slurred speech. Thirdly, the disease manifests itself differently in each patient.
The first and most common symptoms of ALS are weakness in the arms or legs. Objects begin to fall out of the hands, the person stumbles when walking, and drags his foot. There is a sensation of muscle contractions under the skin (fasciculations). Painful cramps and spasms may occur. Fatigue increases.
Difficulties begin with speech, swallowing, and chewing. It becomes difficult to breathe.
Some ALS patients may cry or laugh involuntarily. The reasons for this are not psychological, but physiological: the disease affects areas responsible for emotional reactions. Sometimes there are problems with memory and concentration.
What tests are performed to make a diagnosis?
Flickr.com/ec-jpr
If the therapist suspects that a person has amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, he will send him to a neurologist, who will prescribe a series of examinations:
— a blood test (will show whether the level of creatine kinase, an enzyme that is produced during the destruction of muscle tissue, is elevated);
— magnetic resonance imaging (does not reveal specific changes in ALS, is used to exclude diseases with symptoms similar to ALS);
— electroneuromyography (registration of electrical activity of muscles);
If necessary, additional examinations such as a lumbar puncture or muscle biopsy may be performed.
What happens to the patient
Photo from the site syl.ru
The average life expectancy for ALS is two to five years from the onset of symptoms. There are cases when the disease lasts several decades. For example, Stephen Hawking lived with ALS for more than 50 years. And there are patients who leave a few months after the diagnosis is made.
As ALS progresses, a person experiences increasingly serious difficulties with moving, speaking, swallowing, and breathing. Therefore, doctors advise relatives to immediately adapt housing for the patient and buy special equipment.
If the disease begins in the legs, then at first it becomes difficult for the patient to walk and maintain balance; he may lean on pieces of furniture, so they must be stable. Then the patient begins to use a walker or wheelchair, and it is important to free up space in the house for this.
Gradually, it becomes difficult for a person to raise his arms, so it is recommended to place all necessary things no higher than 1 m from the floor. There are adapted forks, spoons and knives with thicker handles and even with straps; they allow the patient to go longer without assistance when eating.
To communicate with the outside world, such patients eventually have to resort to special devices. Stephen Hawking, for example, used a special computer system that was controlled by the cheek muscle.
And Jason Becker uses a board with letters that he points to with his eyes.
Many people benefit from the Tobii device, which connects to a regular computer and allows you to move the cursor and type on the keyboard with your eyes.
Sooner or later, a person's respiratory muscles are affected and he loses the ability to breathe on his own. Then there is a need for breathing equipment.
What helps with ALS
Photo from the site als-info.ru
ALS remains an incurable disease. Doctors can only prolong a patient’s life and improve its quality.
Riluzole is a medicine that can slightly slow down the progression of ALS (provided the person starts taking it in the early stages of the disease). This drug is not registered in Russia.
Mechanical ventilation also increases the life expectancy of people with ALS. In addition, it improves sleep, reduces shortness of breath and fatigue. There is non-invasive pulmonary ventilation (NIV), in which a special device pumps air into a face mask. Invasive ventilation uses a tracheostomy, which almost completely deprives a person of the ability to speak.
Many people with ALS find it very difficult to eat and drink. To compensate for the lack of calories and fluid, special therapeutic nutrition is used. When it becomes difficult for a person to swallow even homogeneous food, a gastrostomy is placed - a special tube through which food enters directly into the stomach.
A neurologist may prescribe medications to the patient to reduce muscle spasms, as well as medications to reduce fasciculations. Morphine-containing drugs are prescribed to reduce the feeling of suffocation. Sometimes patients with ALS are given antidepressants.
Massage, aromatherapy, and acupuncture help relieve stress and pain. (Naturally, these methods do not treat the disease itself). Physical exercise allows you to maintain muscle function, a sense of balance, and joint mobility longer. However, excessive stress can cause harm, so a set of exercises should be developed under the supervision of a physical therapist or exercise therapy doctor.
What research is being done to beat ALS?
Image from syl.ru
In motor neurons affected by ALS, pathological clots (aggregates) of protein molecules are found. Typically, proteins stick together as a result of some defect in the gene that encodes them.
In 20% of cases of hereditary and in 2% of sporadic forms of ALS, the disease is caused by a mutation of the SOD-1 gene. This mutation was first discovered in 1993.
A mutation in the TAR DNA binding protein (TDP-43) gene has been found in some families of ALS patients. In 3-5% of patients with a hereditary form of ALS and in 1% with a sporadic form of ALS, a mutation of the FUS protein gene occurs.
In 2011, scientists discovered the C9ORF72 gene mutation. It turned out that it is present in 25−40% of families where there is a patient with ALS, and in 7−10% of patients with a sporadic form of the disease.
In 2014, thanks to the IceBucketChallenge flash mob, when thousands of people around the world were doused with ice water, more than $100 million was raised to research the causes of ALS and find a cure for this disease.
Research is going in two directions. The first is the search for genes that cause the hereditary form of the disease. The second is the identification of “susceptibility genes” that increase the risk of the disease in a family where no one has previously had ALS. Understanding the mechanisms of the disease will help find a cure for it in the future.
What help does the patient and his family need?
Photo by Yuri Mozolevsky from the site sb.by
A person with ALS may need consultations with a neurologist, respiratory support specialist, physical therapist, occupational therapist, nutritionist, speech therapist, music therapist, psychologist, palliative care physician, as well as the help of a nurse and visiting nurse.
The family will have to provide him with certain equipment. This could be a wheelchair, walker, multifunctional bed, ventilator or NIV, aspirator (saliva ejector), cougher, lift (for example, for moving from a bed to a wheelchair or from a stroller to a bath). In addition, the patient needs medicine, nutritional therapy, hygiene products, etc.
Each patient with ALS needs an individual route of care, as the disease can progress in different ways.
Treatment of ALS
There are no therapeutic methods that can cure ALS - treatment is aimed at prolonging the life of patients and improving its quality. The only drug that can slow down the development of the pathological process and delay death is the drug Rilutek. It is mandatory prescribed to people with this diagnosis, but in general it has virtually no effect on the patient’s condition.
For painful muscle spasms, muscle relaxants and anticonvulsants are prescribed; for the development of intense pain, strong analgesics, including narcotics. Patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis often experience emotional instability (sudden, unreasonable laughter or crying), as well as manifestations of depression; psychotropic drugs and antidepressants are prescribed to eliminate these symptoms.
To improve muscle condition and motor activity, therapeutic exercises and orthopedic devices are used, including cervical collars, splints, and devices for grasping objects. Over time, patients lose the ability to move independently, as a result of which they have to use wheelchairs, special lifts, and ceiling systems.
As the pathology develops, patients' swallowing function is impaired, which interferes with normal food intake and leads to a deficiency of nutrients, exhaustion and dehydration. To prevent these disorders, patients are given a gastrostomy tube or a special probe is inserted through the nasal passage. As a result of weakening of the muscles of the pharynx, patients stop talking, and they are recommended to use electronic communicators to communicate with others.
In the last stages of ALS, patients' diaphragm muscles atrophy, which makes breathing difficult, not enough air gets into the blood, shortness of breath, constant fatigue, and restless sleep are observed. At these stages, a person, if there are appropriate indications, may need non-invasive ventilation using a special device with a mask connected to it.
If you want to find out in more detail the diagnosis of ALS - what it is, you can read an article about it on our portal.
Good results in eliminating the symptoms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are provided by massage, aromatherapy and acupuncture, which promote muscle relaxation, blood and lymph circulation, and reduce anxiety and depression.
An experimental method of treating ALS is the use of growth hormone and stem cells, but this area of medicine has not yet been fully studied, so it is not yet possible to talk about any positive results.
Important: the condition of people suffering from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis largely depends on the care and support of loved ones - patients require expensive equipment and round-the-clock care.
Muscle cramps and spasms
What's happening? Due to the deterioration of signal transmission from motor neurons, muscle tension or spasms develops. This leads to impaired motor activity and coordination of movements, as well as an increased risk of falls. Sudden muscle spasms can be extremely painful.
What can be done? To eliminate this symptom, as a rule, it is enough to change the position of the body while resting in a bed or chair. Exercise partially solves the problem. In addition, your doctor may prescribe medications to relax your muscles.
Find out more in the material “Pain in ALS”
Forecast
The prognosis for ALS is unfavorable - the disease leads to death, which usually occurs from paralysis of the muscles responsible for breathing. Life expectancy depends on the clinical course of the disease and the condition of the patient’s body - with the bulbar form, a person dies after 1-3 years, and sometimes death occurs even before loss of motor activity. On average, patients can live 3-5 years, 30% of patients live more than 5 years and only 10-20% live more than 10 years. At the same time, medicine knows of cases when the condition of people with this diagnosis spontaneously stabilized and their life expectancy did not differ from the life expectancy of healthy people.
There are no preventive measures to prevent amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, since the mechanism and causes of the development of the disease are practically not studied. When the first symptoms of ALS appear, you should consult a neurologist as soon as possible. Early use of symptomatic treatment methods makes it possible to increase the patient’s life expectancy by 6 to 12 years and significantly alleviate his condition.
Source: spina-expert.ru
How should a patient cope with ALS?
ALS can be devastating for the patient and family. There will obviously be a mournful period as all concerned try to come to terms with the situation. It is always important to maintain a positive attitude as this will prolong survival and improve quality of life.
Many remain intellectually active, and this is another useful facet. Making medical, financial or personal decisions early will ease the tension to a great extent.
Joining a support group is helpful as the patient and family interact with people in similar situations.
With the right approach to the disease, good treatment and support, people with ALS can live a better quality of life.
Classification and characteristic features
The classification of pathology depends on the location of the lesion. Two types of neurons are involved in motor activity: the main one, located in the cerebral hemispheres, and the peripheral one, located at different levels of the spinal column. The central one sends an impulse to the secondary one, and it, in turn, sends an impulse to the skeletal muscle cells. The type of ALS will vary depending on the center where transmission from the motor neurons is blocked.
At an early stage of the clinical course, signs appear the same regardless of the type: spasms, numbness, muscle hypotonicity, weakness of the arms and legs. General symptoms include:
- Episodic appearance of cramps (painful contractions) in the affected area.
- Gradual spread of atrophy to all parts of the body.
- Motor function disorder.
Types of the disease occur without loss of sensory reflexes.
Lumbosacral form
It is a manifestation of myelopathy (destruction of the spinal cord), caused by the death of peripheral neurons located in the sacral spine (anterior horns). ALS syndrome is accompanied by symptoms:
- Weakness of one, then both lower limbs.
- Insufficiency of tendon reflexes.
- Formation of initial muscle atrophy, visually determined by a decrease in mass (“shrinkage”).
- Wave-like fasciculations.
The process involves the upper limbs with the same manifestations.
Cervicothoracic form
The syndrome is characterized by the death of axons of secondary neurons located in the upper spine, leading to the manifestation of symptoms:
- decreased tone in one hand, after a period of time the pathological process spreads to the second;
- muscle atrophy is noted, accompanied by paresis and fasciculation;
- the phalanges are deformed, taking on the appearance of a “monkey hand”;
- foot signs appear, characterized by changes in motor function, muscle atrophy is absent.
A symptom of damage to the cervical spine is a constantly tilted head forward.
Bulbar form
This type of syndrome has a severe clinical course; motor neurons in the cerebral cortex die off. The life expectancy of patients with this form does not exceed five years. The debut is accompanied by:
- violation of articulatory function, speech apparatus;
- fixation of the tongue in a certain position, it is difficult for them to move, rhythmic twitching is noted;
- involuntary spasms of facial muscles;
- dysfunction of the swallowing act due to spasms in the esophagus.
The progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis of the bulbar type forms complete atrophy of the facial and cervical muscles. The patient cannot independently open his mouth to eat; communication abilities and the ability to clearly pronounce words are lost. The gag and jaw reflex increases. Often the disease occurs against the background of involuntary laughter or lacrimation.
High form
This type of ALS begins with damage to central neurons and, during development, covers peripheral ones. Patients with a high form of the syndrome do not survive to the stage of paralysis, because the muscles of the heart and respiratory organs quickly die, and abscesses form in the affected areas. A person cannot move independently; atrophy covers the entire skeletal muscle. Paresis leads to uncontrolled bowel movements and urination.
The condition is aggravated by the constant progression of the syndrome; in the terminal phase, breathing is impossible; ventilation of the lungs is required using a special device.
Problems with speech and communication
What's happening? As the muscles of the face and larynx weaken, and ventilation of the lungs further decreases, it becomes increasingly difficult for a person to speak. This speech difficulty is called dysarthria.
What can be done? Your doctor will help you assess the problem and select techniques to solve it. We also recommend consulting with a physiotherapist, who will recommend equipment or aids depending on what manipulations a person with ALS is capable of. Tools for speech and communication (they are also called “means of alternative and auxiliary communication”) include both simple techniques (gestures, writing, alphabet tables, etc.) and more technically complex ones (using a computer).
Learn more about alternative and assistive communication methods
Causes
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis syndrome in most cases has an unknown origin. In 10% of patients with this diagnosis, the cause of development was the autosomal dominant transmission of a mutated gene from a previous generation. The etiology of the formation of the disease can be a number of factors:
- Infectious damage to the brain and spinal cord by a persistent, little-studied neurotropic virus.
- Insufficient intake of vitamins (hypovitaminosis).
- Pregnancy can provoke ALS syndrome in women.
- Proliferation of cancer cells in the lungs.
- Gastric bypass surgery.
- Chronic form of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
People who are constantly in contact with concentrated chemicals and heavy metals (lead, mercury) are at risk.
Risk factors[edit | edit code]
ALS accounts for approximately 3% of all organic lesions of the nervous system. The disease usually develops between the ages of 30 and 50[9][10].
The total lifetime risk of developing ALS is 1:400 for women and 1:350 for men.
5-10% of patients are carriers of a hereditary form of ALS; A special, endemic form of the disease has been identified on the Pacific island of Guam. The vast majority of cases (90-95%) are not associated with heredity and cannot be positively explained by any external factors (previous diseases, injuries, environmental situation, etc.)[11].
Several scientific studies[12][13][14][15] have found statistical correlations between ALS and certain agricultural pesticides.
Diagnostic tests
The examination involves differentiating ALS syndrome from ALS disease. Independent pathology occurs without disruption of internal organs, mental abilities, and sensitive reflexes. For adequate treatment, it is necessary to exclude diseases with similar symptoms through diagnosis:
- spinal craniovertebral amyotrophy;
- residual effects of polio;
- malignant lymphoma;
- paraproteinemia;
- endocrinopathy;
- cervical cervical myelopathy with ALS syndrome.
Diagnostic measures to determine the disease include:
- chest x-ray;
- magnetic resonance imaging of the spinal cord;
- electrocardiograms;
- electroneurography;
- studies of the level of functioning of the thyroid gland;
- cerebrospinal, lumbar puncture;
- genetic analysis to identify mutations;
- spirograms;
- laboratory test in the blood of protein, ESR, creatine phosphokinase, urea.
Effective treatments
It is impossible to completely get rid of the disease; in Russia there is no patented drug that can stop its clinical development. In European countries, Riluzole is used to slow the spread of muscle atrophy. The purpose of the drug is to suppress the production of glutamate, a high concentration of which damages brain neurons. Trials have shown that patients taking the drug live slightly longer, but still die from respiratory failure.
Treatment is symptomatic; the main goal of therapy is to maintain quality of life and prolong the ability to self-care. As the syndrome develops, the muscles of the organs responsible for the respiratory act are gradually affected. Oxygen deficiency is compensated by the BIPAP, IPPV device, used at night. The equipment alleviates the patient’s condition, it is easy to use and can be used at home. After complete atrophy of the respiratory system, the patient is transferred to a stationary pulmonary ventilation device (NIV).
Conservative treatment of symptoms helps:
- Relief of seizures with Carbamazepine, Tizanil, Phenytoin, Isoptin, Baclofen, injection of quinine sulfate.
- Normalization of metabolic processes in muscle mass with anticholinesterase agents (“Berlition”, “Espa-Lipon”, “Glutoxim”, Lipoic acid, “Cortexin”, “Elcar”, “Levocarnitine”, “Prozerin”, “Kalimin”, “Pyridostigmine” “ Milgamma", "Tiogamma", Vitamins of group B A, E, C).
- Removal of fasciculation (Elenium, Sirdalud, Sibazon, Diazepam, Mydocalm, Baklosan).
- Improving swallowing function (“Proserin”, “Galantamine”).
- Eliminate pain with the analgesic Fluoxetine, followed by transferring the patient to morphine.
- Normalization of the amount of saliva secreted by Buscopan.
- Increasing muscle mass with Retabolil.
- Relieving mental disorders with antidepressants (Paxil, Sertraline, Amitriptyline, Fluoxetine).
If necessary, antibacterial therapy with antibiotics “Fluoroquinol”, “Cephalosporin”, “Carbapenem” is prescribed. The course of treatment also includes nootropic drugs: Nootropil, Piracetam, Cerebrolysin.
Patients with ALS syndrome need special devices to make life easier, including:
- automated wheelchair for movement;
- a chair equipped with a dry closet;
- computer speech synthesis program;
- bed with lifting mechanism;
- device for taking the desired item;
- orthopedic set (cervical collar, splints).
When caring for a patient, attention is paid to the diet; food should contain a sufficient amount of minerals and vitamins. The dishes have a liquid consistency, the vegetables are pureed. Feeding is carried out through a tube; in difficult cases, installation of a gastrostomy tube is indicated.
Treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
The disease is not completely cured. The basis of treatment for ALS is maintaining vital functions with the help of medications and proper care.
To relieve symptoms and maintain the nervous system, the patient is prescribed:
- drugs to block the production of glutamate and stimulate the work of Superoxide Dismutase-1;
- muscle relaxants – relieve muscle spasms;
- complex of vitamins A, B, E and C – provide nutrition to nerve cells, improve impulse conduction through them;
- anabolic steroids – restore depleted muscle mass.
Alternative methods are also used to combat the consequences of the disease:
- stem cell treatment – stops the process of neuronal death and also helps restore connections between them;
- RNA interference – with the help of nanobiotechnologies, the reproduction of a pathological protein is blocked, which prevents the subsequent death of motor neurons.
As additional therapeutic measures, the patient is given:
- feeding through a tube in case of impaired swallowing reflex;
- carrying out massages to relax muscles and prevent the formation of bedsores;
- performing physical therapy;
- consultations with a psychologist;
- ventilation of the lungs in case of damage to the nerve cells of the respiratory system.
It is extremely important to surround a patient with ALS with the warmth and care of loved ones, without leaving him alone with the disease.
Forecast
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis syndrome is a serious disease. The prognosis is complicated by the lack of specific drugs and the rapid progression of the anomaly. The patient’s condition depends on the form and possibility of symptom relief. A fatal outcome occurs in any case, but if the lumbosacral syndrome reaches the bulbar form, life expectancy is no more than two years. In the case of a genetic mutation, the development of the anomaly is not so rapid; with proper care, a person can live up to 12 years from the onset of ALS.
Source: ProSindrom.ru
Live now
Living with a rare disease is usually a huge expense. For PALS, for example, the average “estimate” looks like this: hygiene products and special food - about 100 thousand per month, breathing apparatus - 350-400 thousand rubles, consumables - at least 10 thousand per month, cougher and saliva ejector - another half a million. Plus a functional bed, an anti-decubitus mattress and other devices that will make the life of the sick person and his loved ones a little more comfortable.
Sometimes one of the above can be achieved from the state. But most of the expenses fall on the shoulders of the family. And besides this, there is the despondency and isolation that comes with the disease.
Tatyana Shestimerova has been suffering from ALS for 20 years. She learned about her diagnosis while pregnant with her second child. She and her husband Pavel learned to live with ALS even before the Live Now Foundation appeared in Russia, and their family became a source of inspiration and optimism for hundreds of families across the country who faced the same diagnosis. There are many videos on YouTube that spouses record to share their experiences of living with ALS with other families.
“The disease is an unpleasant thing,” says Tatyana. “But don’t paint yourself into a corner ahead of time.” I have a rare case: I have had ALS for 20 years, which is a very long time. And I am sure that one of the main reasons here is that my family and I built the right relationship with the disease: we accepted it as a certain circumstance of life, did not isolate ourselves in it, but continued to communicate with friends, go to the country, receive guests, receive enjoy every day."
Photo: Vladimir Eshtokin