Did you know that craters on the Moon were discovered before they discovered that the human brain is divided into separate sections, each with its own specialization? And at present, this unique tool for controlling our body continues to retain many of its secrets. And scientists studying its functions are still surprised as they discover more and more new properties and features of brain activity. A striking example of such unexpected discoveries is the functions of the hippocampus, a small paired formation in the temporal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres.
Hippocampal sclerosis - what is it?
To take a closer look at this disease, we need to say a little about the disease that provokes it.
Temporal lobe epilepsy is a neurological disease that is accompanied by seizures. Its focus is in the temporal lobe of the brain. Seizures can occur with or without loss of consciousness. Mesial sclerosis acts as a complication and is accompanied by loss of neurons. Due to head injuries, various infections, seizures, tumors, the tissue of the hippocampus begins to atrophy, which leads to the formation of scars. There is a possibility that the course of the disease will be aggravated by additional seizures. It can be either right- or left-handed.
Based on structural changes, hippocampal sclerosis can be divided into two types:
- There are no volumetric changes in the temporal lobe of the brain.
- There is a process of increasing volume (aneurysm, progressive tumor, hemorrhage).
Find out about the symptoms and diagnosis of sclerosis here, and how to treat the disease, read the article.
One of the oldest parts of the brain
The hippocampus arose at the dawn of the evolution of vertebrates and went through a long development path, becoming an extremely important part of the structure of the human brain. It got its slightly strange name due to its curved shape, reminiscent of a seahorse, and the literal translation of this concept is “curved horse.”
The hippocampus is a paired organ; its parts are located in different hemispheres, but are connected by special nerve fibers. Relatively small “squiggles” of the hippocampus are part of the oldest region of the brain - the limbic system, which is also called the archeocortex - “ancient cortex”. It controls elementary physiological processes and vegetative functions. We can say that the limbic system is what our brain has in common with all mammals.
The hippocampus is still ancient, but despite its small size, it is not a primitive formation at all. And he has just begun to reveal his secrets.
Main reasons
The main reasons include the following:
- Genetic factor. If parents or relatives had manifestations of temporal lobe epilepsy or sclerosis, then the likelihood of manifestation in the heirs is extremely high.
- Febrile seizures. Their influence contributes to various metabolic disorders. The cortex of the temporal lobe swells and the destruction of neurons begins, the tissue atrophies, the hippocampus decreases in volume.
- Mechanical injuries. Blows to the head, skull fractures, collisions, all this leads to irreversible damage and the development of hippocampal sclerosis.
- Bad habits. Alcoholism and nicotine addiction destroy neural connections and destroy brain cells.
- Childhood trauma. Incorrect development of the temporal lobe during the prenatal period or various birth injuries.
- Oxygen starvation of brain tissue. It can be caused by respiratory and metabolic disorders.
- Infections. Meningitis, encephalitis and other inflammations in the brain can lead to activation of mesial sclerosis.
- Poisoning. Intoxication of the body with harmful substances over a long period of time.
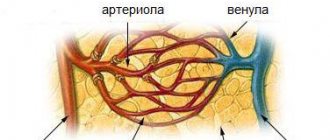
- Circulatory disorders. When blood circulation in the temporal lobe is impaired, ischemia and neuronal death begin, followed by atrophy and scarring.
You will find medications used for sclerosis here, you will find treatment with folk remedies by clicking on the link.
Artificial hippocampus[ | ]
Since 2003, at the University of California in Los Angeles (USA), a group of scientists led by Theodore Berger has been developing an artificial rat hippocampus[4][5]. Modeling suggests that the main function of the hippocampus is the storage of information for storage in other parts of the brain that play the role of long-term memory. It is also assumed that, due to the very similarity of this part of the brain in mammals, adaptation to the function of the human hippocampus will be made quite quickly. Since scientists were unfamiliar with the methods, the hippocampus was modeled as a set of neural networks operating in parallel. It has been hypothesized that this supposed structure of the real hippocampus makes it possible, in the event of injury, to bypass the damaged area entirely. Structurally, the analogue of the hippocampus is made in the form of a computer chip with two bundles of electrodes: an input one for recording the electrical activity of other parts of the brain and an output one for directing electrical signals to the brain.
In August 2006, the creation of a mathematical model of the rat hippocampus began. By December 2010, researchers at the Southern California Institute, together with colleagues at Wake Forest University, had developed and tested a circuit[6][7] that replaced the rat hippocampus. The researchers were able to make the rat remember certain actions. Moreover, the hippocampal prosthesis was able to improve the rat's brain abilities while working simultaneously with the natural hippocampus. Professor Theodor Berger anticipates the creation of an artificial human hippocampus by 2025. But first it is necessary to create and test the appropriate prosthesis on the brain of a monkey.
Symptoms
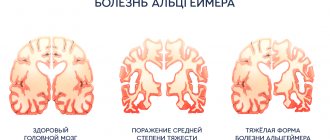
Reference! Since this disease is caused by epilepsy, its symptoms can be very similar to its manifestations, or to those of Alzheimer's disease.
The signs of hippocampal sclerosis should be examined in more detail, but only a competent specialist can make an accurate diagnosis.
Symptoms include:
A person’s habits change, he behaves differently than usual.
- Frequent dizziness.
- Headache, frequent pain of unknown pathogenesis.
- Insomnia or vice versa drowsiness.
- The appearance of panic attacks.
- Forgetfulness or complete amnesia.
- Spasms of various muscle groups.
- Various cramps.
- The person becomes anxious.
- Various cognitive disorders occur. In addition to memory problems, a person cannot concentrate on anything, and his train of thought is disrupted.
- Emotional and sexual behavior changes.
During the examination, the following changes can be diagnosed:
- Decreased white matter content in the parahippocampal gyrus.
- Depletion of the amygdala.
- Atrophy of part of the diencephalon nucleus.
- Reduction of the singular gyrus.
- Atrophy of the cerebral vault.
In the presence of left-sided mesial sclerosis, symptoms will be more severe than with right-sided mesial sclerosis and cause more serious damage to the parasympathetic system. Seizures disrupt the overall functioning of all parts of the brain and can even cause problems with the heart and other organs.
Read the article on how to deal with atherosclerosis; learn about the treatment of the disease here.
Symptoms of pathology
With hippocampal sclerosis, patients are diagnosed with partial epilepsy. This condition results in a variety of symptoms. Relatives and friends notice that a person’s behavior is changing. Mesial temporal sclerosis leads to muscle spasms. During the course of the pathology, patients are diagnosed with the occurrence of seizures.
Hippocampal sclerosis is accompanied by memory loss. When sick, patients complain of headaches and dizziness. Insomnia indicates pathology. With mesial sclerosis, an increase in anxiety and the occurrence of panic attacks are noted. The patient's cognitive abilities are impaired: memory, thinking, concentration.
When examining the patient, atrophic processes are observed in the anterior nucleus of the thalamus. Hippocampal sclerosis is characterized by atrophy of the cingulate gyrus. When the disease occurs, ipsilateral cerebral hypertrophy is diagnosed. In the brain, white matter decreases in volume.
With hippocampal sclerosis, contralateral cerebellar hemoatrophy appears. The cerebral convolutions decrease in volume. During the course of the disease, atrophic processes appear in the mastoid body and the ipsilateral fornix.
With mesial sclerosis, patients are diagnosed with seizures, which lead to disruption of brain function. Patients suddenly lose consciousness. They develop autonomic cardiac dysfunction. In left-sided hippocampal sclerosis, more severe parasympathetic dysfunction is observed.
Hippocampal sclerosis is characterized by pronounced symptoms, in the event of which the patient is advised to urgently seek help from a doctor to ensure a full diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
Development
Reference! Approximately 60-70% of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy have some degree of developed sclerosis of the hippocampus.
The clinical signs of the disease are very diverse, but the main ones are febrile convulsions. They can occur even before the onset of epilepsy, and this is associated with various neural disorders.
In this disease, the hippocampus is destroyed unevenly, the dentate gyrus and several other areas are affected. Histology indicates neuronal death and gliosis. In adults, bilateral degenerative disorders in the brain begin.
Atherosclerosis can develop for various reasons, but the consequences of the disease depend on the pathogenesis, timely diagnosis and adherence to a certain lifestyle.
Literature
- Anand, Kuljeet Singh, and Vikas Dhikav. "Hippocampus in health and disease: An overview" Annals of Indian Academy of Neurology 15.4 (2012): 239.
- Duzel, Emrah, Henriette van Praag, and Michael Sendtner. “Can physical exercise in old age improve memory and hippocampal function?” Brain (2016): awv407.
- Ming, Guo-li, and Hongjun Song. “Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: significant answers and significant questions” Neuron 70.4 (2011): 687-702.
- Piskunov, Aleksey, et al. “Chronic combined stress induces selective and long-lasting inflammatory response evoked by changes in corticosterone accumulation and signaling in the rat hippocampus” Metabolic brain disease 31.2 (2016): 445−454.
- Sapolsky, Robert M. "Depression, antidepressants, and the shrinking hippocampus" Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 98.22 (2001): 12320-12322.
Measures to be taken for treatment
To stop attacks and alleviate the manifestations of temporal sclerosis, special antiepileptic drugs are usually prescribed. These are mainly anticonvulsant medications. The dosage and regimen should be selected by a specialist. You cannot self-medicate, because you must correlate the manifestation of attacks, their type, the properties of the prescribed medication and many other things.
If the symptoms of attacks disappear, this indicates that the disease is receding. If seizures do not make themselves felt for two years, the doctor reduces the dosage of medications. Complete discontinuation of medications is prescribed only after 5 years of complete absence of symptoms.
Note! The goal of conservative therapy is complete relief of the manifestations of the disease and, if possible, a complete recovery.
When drug therapy does not bring results, surgery is prescribed. There are several types of surgical interventions for this disease, but the most commonly used is temporal lobotomy.
During this manipulation, the doctor removes the pathologically altered part of the brain, after making sure that it is not responsible for the vital functions of the body. A favorable outcome after such an intervention is observed in 55–95% of patients.
Find out how to treat atherosclerosis - by clicking on the link, drugs to block the disease, as well as folk remedies (herbs) in the fight against the disease.
General information
The hippocampus owes its name to the ancient Greeks - translated from their language it means “seahorse”.
The basis for this was the similarity of the outlines of a marine animal and an organ in the human brain. Apparently, this explains such a variety of functions assigned to it at the time of formation. However, their number has practically not decreased to this day.
The hippocampus has played an important role in mental activity since ancient times. But only modern achievements of science and medicine make it possible to identify new qualities and capabilities of this organ.