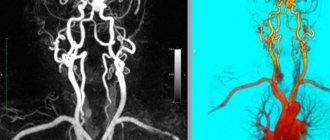
Main symptoms:
- Headache
- Speech Impairment
- Retarded physical development
- Increased agitation
- Increased intracranial pressure
- Prominence of veins on the forehead
- Irritability
- Convulsions
- Enlargement of the head
- Mental retardation
Ventriculomegaly is a pathological change in the formation of the brain in a child in the womb. The disease is characterized by changes in the size of the cerebral ventricles, which subsequently leads to various abnormalities, as the central nervous system, spinal cord and brain are affected. The process may also involve peripheral nerves, the autonomic system, and muscles.
Online consultation on the disease “Ventriculomegaly”.
Ask a question to the specialists for free: Neurologist.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications
- Prevention
Abnormal fetal development is determined during routine studies, and the degree of deviation is established. All deviations, except severe ones, are amenable to therapeutic measures. If a pathology is identified that is incompatible with the life of the child, then the pregnancy is terminated in the early stages.
The disease is very serious, can have serious consequences, and if the pathology is severe, the pregnancy is terminated. The moderately expressed form is characterized by a relatively favorable prognosis.
Symptoms
The development of symptoms occurs in accordance with the severity of intracranial pressure.
Along with general discomfort, signs such as regurgitation (they may not exist), the appearance of postural reflexes (the child throws his head back, etc.) may be observed. A possible manifestation of the disease may be an increase in head size. Very often, the pathology does not manifest itself at all, but is detected only with the help of ultrasound. Possible symptoms may also be: refusal of breastfeeding, restlessness, crying, trembling of the upper limbs, decreased muscle tone, decreased grasping and swallowing reflexes, squint. You can notice the divergence of the sagittal cranial suture, tension and swelling of the fontanelles. During a doctor's examination, the so-called rising sun syndrome may be observed - when the child's iris is slightly covered by the lower eyelid. During examination of the fundus, swelling of the optic discs is revealed.
Symptoms of enlarged ventricles
The mechanism of development of pathology has common features, regardless of the reasons. Fluid accumulates in the ventricles, they expand and compress the brain tissue. The pressure inside the cavities themselves also increases.
Patients complain of sudden headaches, nausea and vomiting, a feeling of fullness in the eyeballs, hearing and vision impairment. Performance gradually decreases, memory disorders, apathy, and drowsiness occur.
All these are signs of pathology of the liquor-conducting system.
. If the anomaly was not identified and treated in the early stages, it becomes chronic.
Causes
The ventricles of the brain are represented by several cavities deep in the brain structures, which are connected to each other, the spinal cord canal, and the subarachnoid space. The cells lining their internal space produce cerebrospinal fluid. Its main function is to nourish the nerve cells of the brain and spinal cord, as well as to protect the fibers of these brain structures.
The ventricles normally contain about 150 milliliters of cerebrospinal fluid. It is completely updated three times a day. It is the increase in its volume that leads to an increase in the size of the ventricles. This happens when there is excessive formation of cerebrospinal fluid, a violation of its outflow or absorption.
Lateroventriculoasymmetry may be congenital, or may result from other pathologies. In newborns, an increase in the volume of the ventricles (hydrocephalus) occurs more often than in adults. Approximately every 500th newborn has an increased volume of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain.
Anomalies in a child can also develop due to problems with the mother’s health during pregnancy: syphilis, toxoplasmosis, rubella, mumps. In adults, the primary pathologies that cause an increase in cerebrospinal fluid, and, as a consequence, an increase in the volume of the ventricles, can be the following reasons:
- Past neuroinfections (meningitis, meningoencephalitis). By irritating brain structures, the infection causes increased liquor production.
- Skull injuries.
- Tumors, cysts, hematomas. As they grow, they can compress the pathways of liquorodynamic outflow.
- Thrombosis of cerebral vessels.
What kind of disease is this
A pathological process affecting the fetal brain, in which the ventricles of the brain swell (change their shape), is called ventriculomegaly. Pathology has a negative impact on the developing nervous systems of the body (central and peripheral). As a result of ventriculomegaly, the fetus suffers from:
- spinal cord;
- brain;
- nerve processes and roots;
- autonomic nervous system.
Not only individual organs, but also entire body systems suffer from excess fluid.
The cerebral ventricles communicate with each other through canals. They perform a very important function for the body - they synthesize cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Normally and in the absence of abnormalities, this fluid flows into a certain space called the subarachnoid space. If an anomaly is present, then the outflow stops, fluid (CSF) accumulates in the ventricles, creating many problems for the baby.
There are three degrees of severity of ventriculomegaly:
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
With a mild degree, the lesions are isolated, quickly respond to treatment and pass without consequences for the baby. Complex drugs are not required, the ventricles quickly return to normal.
The average degree implies an increase in the ventricles (one or more) up to 15 mm inclusive. This happens because the natural outflow of fluid is disrupted. The functionality of the ventricles is also impaired.
With severe ventriculomegaly, the ventricles are greatly enlarged (up to 21 mm) due to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in them. Serious treatment and monitoring of the condition and intrauterine development of the baby is required.
Causes of ventriculomegaly in the fetus
Ventriculomegaly is a rather dangerous disease that can provoke the death of the fetus in the womb, or manifest itself in the form of anomalies (mental and physical disorders), as a prospect - disability in the future. In order, if possible, to protect the baby from the harmful consequences of ventriculomegaly, it is necessary to select the most effective treatment, identifying the real causes of this pathology. These reasons may be associated with genetic abnormalities of the parents or manifest themselves independently. Ventriculomegaly in the fetus can be caused by the following reasons:
- the age of the pregnant woman is over 35 years;
- abnormal genes and chromosomes in expectant mothers;
- the presence of pathological processes during pregnancy;
- all kinds of infections (including intrauterine ones);
- obstructive fetal hydrocephalus;
- physical injuries;
- strokes;
- periventricular leukomalacia;
- lissencephaly.
The threat can be detected as early as 17 weeks of pregnancy using ultrasound screening. From the 17th to the 34th week, the doctor pays special attention to the development of the brain, as well as the size of its ventricles. Ventriculomegaly is indicated by an increase in one or more ventricles, ranging from 12 mm to 20 mm. If ventriculomegaly is suspected, the doctor recommends undergoing additional tests and repeating the ultrasound after another 2 weeks. It is also mandatory for the expectant mother to visit a geneticist, who will determine whether the pathology is congenital or caused by injury or infection. The karyotyping procedure is also shown for a baby in the womb.
Consequences of ventriculomegaly
Ventriculomegaly in the fetus - the consequences of this disease, which began in the womb, can be very severe, starting with the death of the child in the womb (due to developmental defects), premature birth (accounts for up to 4% of all known cases), severe and disability.
If a genetic factor plays a role in the appearance of ventriculomegaly, then the following deviations and syndromes are possible:
- Down syndrome;
- hydrocephalus;
- Patau;
- Edwards;
- Turner (with gonadal dysgenesis);
- vascular malformations of the brain;
- mental retardation;
- retardation in physical development.
It has been noted that female infants are more susceptible to anomalies and defects as a result of ventriculomegaly, compared to male infants.
Despite everything, children born with a similar diagnosis have a very good chance of further normal life. So, in 80% of cases out of a hundred, babies outgrow this condition and subsequently develop fully without deviations.
Among all known cases of ventriculomegaly, 10% of infants are susceptible to serious pathologies. Deviations of moderate severity were noticed in 8% of children born with this diagnosis.
There is a treatment
Therapy is prescribed only for severe clinical signs. Only the doctor decides how to treat, based on the conclusion, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient.
A specific treatment regimen is selected, aimed directly at eliminating the cause of the pathology.
What is used:
- diuretics;
- nootropics;
- NSAIDs (anti-inflammatory);
- vasoactive substances;
- neuroprotectors;
- sedatives;
- in the presence of infectious diseases, antibacterial agents are used.
Additionally, massage, therapeutic exercises and physiotherapy are prescribed, which have a positive effect on the dynamics of recovery.
Some people prefer to see an osteopath - a specialist who treats without medication using palpation.
Dr. Komarovsky spoke in detail about the effectiveness of this technique, who devoted a series of programs to this topic.
How to detect asymmetry?
Despite all the variety of equipment, it is still impossible to make an accurate diagnosis. The examination is carried out on the following points:
- Monthly head growth is assessed. The method itself is the simplest, carried out by a local doctor or even by the baby’s mother herself. Brings correct information about the development of the diagnosis.
- Ultrasound quickly, clearly and accurately shows the true size of the ventricles.
- Examination by a neurologist. Children under three months are not examined due to the uninformative nature of this method.
- Search for edema of the vascular network, hemorrhages or spasms, examination of the fundus.
- The use of neurosonography is a method that allows you to determine the size of cavities.
If necessary, the specialist sends the patient for serious studies: MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) and CT (computed tomography). Another correct confirmation of the diagnosis is the method of taking a lumbar puncture, the study of which will provide the exact pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Related and recommended questions
MRI My son is 1.10. A diagnosis of early cerebral insufficiency, ataxic...
MR picture of moderate expansion of internal liquor spaces. Please tell me...
Asymmetry of the lateral ventricles, expansion of the main cistern I am 30 years old. Due to...
Asymmetry and dilatation of the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles We were diagnosed with asymmetry...
Enlargement of the anterior horn and body of the left lateral ventricle. We have the following problem:...
Neurosonography According to the results of neurosonography, my child had a mild…
Decipher the MRI results Give advice on deciphering the MRI. I'm worried about the conclusion...
Enlarged anterior horns of the lateral ventricles Dr. Recently, a neurologist doctor diagnosed...
Decipher the MRI The child is 1 year old, at the moment we are not crawling, not sitting, not standing. Diagnosis…
NSG of a newborn Please comment on the results of NSG of a newborn. Born...
Is it worth treating with medication? During the NSG, they concluded that there were signs of minimal...
Dilatation of the lateral ventricles Neurosonography was performed monthly: Ventricular system...
MRI of the brain, the headache is very bad. Please tell me I did an MRI of the brain...
Changes based on the results of the NSG I would like to receive advice. Daughter from 1st pregnancy,…
Neurosonography + Doppler Help me understand the situation. My daughter is 2.5 months old...
Treatment of NSG The child is a girl, now 3 months old, at birth 3960 g, 54 cm. According to Apgar...
NSG result Doctor! Help, please, we did neurosonography at 1.5 months, the conclusion...
Anterior horns of the lateral ventricles My son is 1.5 months old. They did an ultrasound of the brain - the front...
Neurosonography of a child at 3 months. Help, please. Very worried. Daughters 3…
NSG, fluid The child is a girl, at birth 3960 g, 54 cm. According to Apgar 9/9, hypoxia...
Therapeutic measures
Brain diseases are managed by a neurologist and neurosurgeon.
For ventricular asymmetry, medications are usually prescribed:
- Diuretics - Triampur, Diakarb;
- Nootropics - Nootropil, Encephabol, Piracetam;
- Sedatives - Somnol, Donormil;
- Antivirals or antibiotics if any infection is detected.
If there is a tumor, hematoma or head injury, surgery is performed. If, despite treatment, the asymmetry progresses, the patient is prescribed ETV (endoscopic ventriculostomy).
The essence of the operation is that an additional hole is created in the wall of the ventricle through which cerebrospinal fluid flows. The technology is considered highly effective and safe, guaranteeing lasting improvement in the patient’s condition.
What is asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain and how can it affect health? To understand why asymmetry occurs, it is necessary to become familiar with the structure of the brain and the functions of its individual parts.
The ventricles of the brain are hollow areas in the brain tissue that exist to store or deposit cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). In the presence of certain pathologies, the ventricles increase in volume. The lateral ventricles are the largest in size. Each has its own serial number. The third ventricle communicates with the lateral ones through the interventricular foramina. The lateral ones contain the occipital horn, the temporal horn, the frontal horn and the central part. Their location is slightly below the corpus callosum. The left ventricle is called the first, and the right - the second.
The fourth ventricle is located midway between the medulla oblongata and the cerebellum. Because of its diamond-shaped shape, there is another well-established name, the diamond-shaped fossa. The spinal canal is located there. Such cavities of the brain are created to perform their functions, namely formative and storage, and occupy an important place in the process of formation of cerebrospinal fluid. In the absence of pathological factors, the cerebrospinal fluid created with their help is transferred to the subarachnoid space. If the process does not proceed correctly, hydrocephalus appears. The asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain is that either one or both ventricles will immediately increase in size. The fact of the increase already indicates the presence of a pathological process.
Cause of pathology
Dilatation of the lateral ventricles of the brain, or ventriculomegaly, should be especially carefully studied if asymmetry is present. With symmetrically located lateral ventricles of the brain, this can be diagnosed as either hydrocephalus or a normal condition. With asymmetry, it turns out that the ventricles are different sizes and disproportionate to each other. Perhaps these are the consequences of a skull injury. In this case, a neurosurgical operation is necessary for the newborn so that there are no unexpected consequences. Also, asymmetrically located ventricles can be a normal condition, but if all this is observed in a mild form. As a rule, their difference in size should not exceed 2 mm. Although this option is not recognized as a pathological condition, dynamic monitoring is still necessary so that this number does not increase.
An increase in horns in the back of the head is considered abnormal. To recognize this in a timely manner, screening, ultrasound examination of the brain, and neurosonography are carried out. All examinations are carried out through the newborn's fontanel. Moreover, if the ventricles are not clearly visible, this does not mean that expansion of the ventricles of the brain has occurred.
For newborns, dilatation of the ventricles of the brain is recorded only when the dimensions of the diagonal sections at the level of the foramen of Monroe exceed 0.5 cm, and the smoothness of the contour of the fundus is completely eliminated.
The causes of this phenomenon can be congenital or acquired over time. List of congenital causes:
- abnormal course of pregnancy;
- difficult childbirth;
- acute hypoxia of the fetus while in the placenta;
- deviations from normative indicators of the central nervous system;
- developmental deficiency;
- early birth;
- perinatal trauma.
Specialists pay special attention to hemorrhages, both external and internal. For this reason, deviation from the symmetry of the ventricles often occurs.
Filling with blood, changing in volume, causes a change in their size. Also included in the category of acquired pathology are:
- viral infections that affected the fetus;
- septic complications;
- a long period of time spent on the birth of a child and the breaking of waters;
- maternal pathologies (for example, prophets of the heart, as well as diabetes).
The accumulation of fluid in the newborn's brain causes symptoms that affect the entire brain and can cause negative conditions.
Hydrocephalus does not contribute to the enlargement of cerebrospinal fluid cavities in a short time. It is possible that intracranial pressure may initially rise, followed by expansion of the lateral ventricles. The latter are not located relative to the center, as a result of which they experience great pressure.
What is ventriculomegaly in the fetus?
Such a pathological abnormality in the fetus as ventriculomegaly is a disease for which a characteristic feature is a significant increase in the size of the ventricles located in the brain
. In most cases, the pathology affects the lateral ventricles, which are special cavities located in the brain and filled with cerebrospinal fluid. The process of their increase and disruption of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid provokes the development of a disease such as ventriculomegaly.
In normal ventricular conditions
, their depth ranges from 1 to 4 mm. In case of pathology development, their size can increase to 20 mm. And if the disease is not treated in time, the fetus may be born with obvious mental and neurological abnormalities. Well, in the most difficult cases, ventriculomegaly can lead to impaired fetal viability.
Since the disease progresses extremely quickly, if the mother does not take action in time, she may give birth to a sick child, and in the worst case, lose him.
This is quite a serious illness.
, which, depending on the complexity of the pathological process, has three main forms.
Any person has only four ventricles, which are located directly in the brain. Moreover, their sizes can vary significantly from person to person.
and be asymmetrical, which is quite normal. However, when identifying pathology, doctors are always guided by established standards, the limits of which cannot be exceeded.
The greater the depth of each ventricle in an unborn fetus, the greater the likelihood of developing serious abnormalities in the functioning of the central nervous system.
How the problem manifests itself
If the lateral ventricles have increased slightly, then this does not affect the person’s condition in any way. We can talk about the development of a pathological process if there are pronounced changes in their volume. In addition, the patient feels all the symptoms of the primary disease, which leads to enlargement of the ventricles.
Many people have complaints of impaired sensitivity and motor activity, memory impairment and problems with concentration. With lateroventriculoasymmetry, intracranial pressure increases. This is accompanied by:
- Headache. This symptom is especially pronounced in the morning. This happens because due to prolonged exposure to a horizontal position, intracranial pressure increases significantly. The head may not hurt, but the patient has a feeling of squeezing and expansion of the head.
- Nausea and vomiting. After an attack of vomiting there is no relief. This symptom occurs even if a person eats right. Usually, with high blood pressure, you feel sick after waking up.
- Dizziness.
- State of anxiety.
The patient feels apathy, drowsiness, and fatigue. These signs indicate that the pathological process is progressing. As a result of a violation of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, compression of the brain occurs, which leads to:
- impaired consciousness, high probability of developing a coma;
- oculomotor disorders;
- blurred vision;
- development of dementia;
- problems with sleep, which manifest themselves as drowsiness during the day and insomnia at night;
- apathy, indifference to everything that happens;
- motor dysfunction. In this case, the patient cannot walk normally: the gait becomes uncertain, he places his feet incorrectly, shuffles;
- urinary incontinence;
- if the medulla oblongata is compressed, then diseases of the heart and respiratory system develop.
In children, the pathological process can manifest itself in different ways. The baby becomes capricious, refuses food, the eyes in this state will be too open, the gaze is directed downward.
Since a child’s skull bones are not yet as strong as those of adults, with such disorders the size of the head may increase, veins bulge, and the fontanel pulsates.
School-age children may also suffer from lateroventriculoasymmetry. It usually develops as a result of congenital disorders of brain development, infectious processes or genetic failures. At this age, this problem manifests itself:
- Decreased ability to move the eyeballs.
- Dehiscence of sutures between the bones of the skull.
- A specific sound when tapping on the skull.
- Slow development.
- Sudden changes in mood under the influence of minor events.
- Disturbances in mental activity.
- Decreased level of physical activity.
- Overweight.
- Reduced attachment to loved ones.
In adolescence, such disorders develop after traumatic brain injuries, infectious diseases and are accompanied by severe headaches, nausea, seizures and psychosis.
Sources
- https://BolitGolova.info/mozg/asimmetriya-bokovyh-zheludochkov-golovnogo-mozga.html
- https://sortmozg.com/structure/funktsionalnaya-asimmetriya-mozga
- https://golmozg.ru/zabolevanie/lateroventrikuloasimmetriya-golovnogo-mozga.html
- https://vseoteki.ru/golova/asimmetriya-zheludochkov-mozga.html
- https://glmozg.ru/stroenie/asimmetriya-bokovyh-zheludochkov-golovnogo-mozga.html
- https://GolovaUm.ru/zabolevaniya/lateroventrikuloasimmetriya-golovnogo-mozga.html
What is moderate ventriculomegaly?
This is an increase in the ventricular cavity from 12 to 15 mm. Moderate ventriculomegaly in infants requires regular examination by a doctor and appropriate examination. If neurological symptoms are absent or not pronounced, then no therapeutic approach is required.
Ventriculomegaly in adults can be accidentally detected during routine testing. Incidentally detected mild or moderate enlargement of the ventricular cavities does not require further examination or treatment. Since this is considered as a variant of the norm or anatomical feature. If the enlargement of cavities in the brain is a consequence of a traumatic brain injury or brain infection, then treatment should begin immediately.
Treatment
Treatment for this pathology is carried out by a neurologist together with a neurosurgeon. In order to minimize the likelihood of complications, a child with this diagnosis should be under constant medical supervision. The main methods of treating cerebral ventricle asymmetry are: taking diuretics that reduce the production of cerebrospinal fluid, taking nootropics that help improve blood supply to the brain, and taking sedatives. In addition, a course of special massage and gymnastics is required. Newborns and infants up to six months are treated on an outpatient basis. Treatment is quite long and takes up to several months. Older children are treated in accordance with the cause of the pathology. So, if the condition is caused by an infection, then the treatment program includes antibiotics or antiviral drugs. In case of a tumor or head injury, surgery may be performed.
Previous entry Micropolarization of the brain Next entry Examination of the vessels of the brain and neck
Etiology
The brain contains four ventricles, the main function of which is to produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). When disruption and stagnation of fluid occurs, ventriculomegaly develops.
A pathology is considered to be a process when the ventricles enlarge from 15 to 20 millimeters (the norm is no more than 15 millimeters). This condition may be isolated or may be accompanied by other developmental defects.
The main cause of the disease is gene and chromosomal mutations in women with pathological abnormalities during childbearing.
The causes of ventriculomegaly in the fetus are as follows:
- woman’s age – after 35 years the risk increases several times;
- intrauterine infections;
- physical damage;
- oxygen starvation;
- hemorrhage or hemorrhage;
- destructive brain damage;
- hereditary predisposition.
Ventriculomegaly in the fetus can have consequences in the form of the following diseases:
- Bonnevie-Ulrich syndrome;
The pathological size of the ventricles negatively affects the heart, the musculoskeletal system, and the structural elements of the pituitary gland are disrupted.
About the consequences
There is no direct connection between the visible difference and the functional asymmetry of the cerebral hemispheres. Sometimes the opposite pattern occurs: for example, with epilepsy, patients experience sensory seizures with loss of sensitivity in the right extremities, but in the place where the source should be - in the sensory zone of the posterior central gyrus of the cortex on the left - there are no disturbances.
The most significant disorder of asymmetry of brain structures is a violation of liquorodynamics. If hydrocephalus exists, it may again be asymptomatic. This applies to normal pressure hydrocephalus, when there is an excess of cerebrospinal fluid, but only quantitatively, its pressure is normal. But if the cerebrospinal fluid pressure increases, then a syndrome of increased intracranial hypertension occurs. It is manifested by the following disorders:
- persistent, diffuse headaches, especially in the morning;
- improvement in condition after lunch and in the evening;
- progressive decrease in vision;
- the occurrence in severe cases of vomiting, which may or may not be accompanied by nausea;
- the appearance of congestive optic discs in the fundus.
If such symptoms occur, you should urgently consult a neurologist.
In mild cases, conservative treatment leads to recovery, but sometimes surgery is required. In this case, the interhemispheric asymmetry of the brain will remain, but nothing will bother the patient, since the cerebrospinal fluid will be drained into the abdominal cavity through the ventrpiculoperitoneal shunt.
In conclusion, it should be noted that early monitoring of increased intracranial pressure in childhood always bears fruit, since atrophy of the cerebral cortex can be avoided in a timely manner. If there are no symptoms, then it is enough to observe the children with a neurologist. Direct measurement of liquor pressure is only possible by drilling a hole in the head and installing a pressure gauge (literally), but indirect signs make it possible to fairly well assess the degree of violations and take the necessary measures.
Degrees
Degrees of ventriculomegaly:
- light - 10-12 mm;
- moderate (average) - up to 15 mm;
- heavy - more than 15 mm.
Isolated
mild
ventriculomegaly has a favorable prognosis; the newborn will most likely not have developmental abnormalities. Slight enlargement of the cerebral ventricles is usually random and benign, but can occur in genetic disorders and neurocognitive deficits, and is sometimes associated with structural abnormalities due to impaired neuronal migration in the fetus during embryogenesis. Mild ventriculomegaly is more common in boys (up to 75%) than in girls.
Moderate
Ventriculomegaly also does not compromise survival, but increases the risk of neurological complications.
Heavy
Ventriculomegaly is often associated with cerebrospinal fluid obstruction and represents hydrocephalus - an increase in cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricular system, accompanied by increased intracranial pressure.
The presence of ventriculomegaly indicates that something may be wrong in the structure of the brain, but without taking into account other pathologies detected visually or using instrumental diagnostics, this is simply a discrepancy with the standard norm. It may go away on its own.
Features of asymmetry of the cerebral hemispheres
The distribution property of the function of the cerebral cortex is determined genetically. However, under the influence of the social environment, such lateralization is subject to various changes. It should be remembered that the specialization of the hemispheres is determined not only by mental functions; therefore, scientists distinguish three groups of asymmetry:
- Anatomical lateralization. This phenomenon lies in the histological and anatomical difference between the hemispheres.
- Biochemical specialization. The essence is determined by the difference in the course of cellular reactions and in the content of neurotransmitters and hormones.
- Psychophysiological asymmetry.
There is a concept of hemispheric dominance: people whose left hand is dominant have a dominant right hemisphere, and people whose right hand is dominant have a dominant left hemisphere. However, there is also an averaged concept – ambidexterity. People who have this type of interaction “control” their hemispheres evenly.
What causes asymmetry?
Scientists have precisely established that asymmetry of the ventricles of the brain quietly manifests itself with age, during which the ventricles change their size. Diagnoses, some of which entail hydrocephalus, also increase their size. The lateral ventricles may also increase in size in patients with bipolar disorder or in patients with schizophrenia.
At the slightest suspicion that your newborn baby has asymmetry of the ventricles of the brain, do not rush to panic. This condition is also caused by ordinary reasons at the physiological level. The baby may simply have a head that is smaller than the required size. This is not a common condition for them, but it happens often. There is nothing to be afraid of. A similar disorder can also occur in prematurely born children. In such children, the volume of the ventricles will be slightly larger than in those born on schedule.
This diagnosis implies its development along two paths - atrophic and hypertensive. In ninety-nine percent of cases, hypoxia is considered the basic condition for the growth of cavities. The remaining people develop extremely rare infections and other diseases. With insufficient oxygen saturation, the brain of a healthy person always produces cerebrospinal fluid, which also begins to accumulate. Under such conditions, a person develops increased pressure inside the skull - hypertension. Abnormally enlarged ventricles can be easily noticed during an ultrasound examination.
With the atrophic development of the disease, hydrocephalus appears only after severe hypoxia. Additionally, it is caused by metabolic diseases, which have now become rare diseases, after hemorrhage or when catching an infection. In this case, the brain receives irreversible damage, which is a possible cause for the appearance of cerebral palsy or the development of neurological diseases.
Basic Concepts
Functional asymmetry is a property of nervous tissue, characterized by the distribution of mental functions between the hemispheres of the telencephalon. One of the main properties is not only the specialization of the right or left hemisphere, but their careful and precise interaction. This phenomenon is considered as a fundamental law of the functioning of the higher nervous system. Lateralization is inherent not only in humans, but also in animals.
At a time when neuroscience was underdeveloped, researchers believed that the two parts of the brain were identical. However, further study of the structure showed that there are many anatomical differences.
The phenomenon of asymmetry is explained by one genetic model, which states that there is a certain gene that is a factor in the “right shift”. If this gene is in a dominant position, then most likely the person will be born right-handed, and vice versa: the recessive position of the protein determines the left-handedness of the individual.
Possible complications
Ventriculomegaly is a severe pathological process that leads to irreversible consequences, causing severe complications:
- Down syndrome - will be acquired due to defects in the structure of the brain;
- Edwards syndrome - mutational changes in chromosomes are observed, which leads to a whole group of pathological abnormalities in development;
- Turner syndrome - physical abnormalities occur in development;
- problems with the musculoskeletal system;
- hydrocephalus, when cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the head.
Moreover, if the child is in the womb, such disorders can contribute to the baby's freezing or miscarriage, and pathological processes can cause premature birth.
Ventricular system of the brain
The ventricular system consists of 4 cavities located in parts of the brain. Their main purpose is the synthesis of cerebrospinal fluid or cerebrospinal fluid, which performs a large number of tasks, but its main function is to cushion the brain matter from external influences, control intracranial pressure and stabilize metabolic processes between the blood and the brain.
The movement of cerebrospinal fluid occurs through channels connecting the common 4th ventricle and the subarachnoid space formed by the membranes of the spinal cord and brain. Moreover, its main volume is located above significant fissures and convolutions of the cortex.
The largest lateral ventricles are located equidistant from the midline below the corpus callosum. The first ventricle is considered to be the cavity located on the left side, and the second - on the right. They are C-shaped and wrap around the dorsal parts of the basal ganglia. They produce cerebrospinal fluid, which enters the third ventricle through the intergastric openings. Structurally, segments I and II of the ventricular system include the anterior (frontal) horns, body and inferior (temporal) horns.
The third ventricle is located between the visual tuberosities and has the shape of a ring. At the same time, gray matter is located in its walls, which is responsible for regulating the autonomic system. This section is connected with the midbrain aqueduct, and through the interventricular foramen, located behind the nasal commissure, with the I and II ventricles.
The most important IV ventricle is located between the cerebellum and the medulla oblongata, with the vermis and medullary velum located above it, and the medulla oblongata and pons below it. This cavity was formed from the remains of the posterior medullary vesicle and is common to the rhomboid region. At its bottom lie the nuclei of the V-XII cranial nerves. In this case, the posterior lower corner communicates with the spinal cord through the central canal, and through the upper anterior part with the aqueduct.
Sometimes, when examining a newborn, the fifth ventricle is detected, which is a feature of the structure of the brain. It is located in the anterior midline, below the corpus callosum. Usually its closure occurs by 6 months of age, but if the gap is more than 10 mm, then we are talking about a pathology of the liquorodynamic system.
If an ultrasound revealed asymmetry of the lateral ventricles in a child, the prognosis depends on the degree of pathology and the depth of damage to brain tissue, as well as the reasons that provoked the development of the disease. Thus, a significant increase interferes with normal circulation and production of cerebrospinal fluid, which entails neurological problems. But congenital asymmetry, not aggravated by outflow disorders, in most cases does not require treatment. However, such a child needs observation in order to prevent relapse of the disease and possible consequences.
Why is ventriculomegaly dangerous?
Ventriculomegaly in a child can lead to the development of serious disorders in the functioning of the central nervous system and brain. In an isolated form, when the deviation is observed on its own, the prognosis is usually favorable.
Ventriculomegaly, the causes of which are genetic disorders, is often combined with abnormalities in mental development. In particularly severe cases, the child may not be viable. It is important not to skip an ultrasound during pregnancy, when it is already possible to detect many developmental disorders, in particular, ventriculomegaly. What is dangerous about this situation is that by starting the process, you can miss precious time.
Ventriculomegaly, caused by prolonged exposure to infection on the fetus, hypoxia during gestation or childbirth can cause consequences from various kinds of psychoneurological disorders to severe forms of cerebral palsy. Such consequences of ventriculomegaly are difficult to treat. It has its effect, but requires a huge amount of time and effort from doctors and parents.
Related and recommended questions
Asthenia, deterioration of memory and concentration, anxiety, absolutely no energy 2 months ago...
MRI of the brain and blood vessels Doctor! Mom is 48 years old and smokes. I suffer from frequent headaches...
Headaches, dizziness, feeling of vacuum on the left side of the head I am being observed...
Decoding MRI of the brain I did an MRI of the brain and this is what is written in the MRI report...
Numbness in the head, it’s burning in my head. I’m worried about constant dizziness, almost...
Attacks with pressure After giving birth 7 months ago, I started having attacks every two weeks...
Unpleasant feeling in my head. Please help me figure out my problem....
Lump in throat panic attacks Tell me please. In July, a lump appeared in the throat and panic...
Darkening in the eyes, anxiety, fear On July 21, 2020, in the evening I felt...
Numbness in the left leg (a little), tingling in the fingers of the left hand Ekaterina Sergeevna Approximately...
Asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain I was admitted to a neurologist with the following symptoms...
Deviations from the norm according to neurosonogram Tell me what recommendations you would give, what...
MRI conclusion Please help me decipher the MRI conclusion.
On a series of MP tomograms...
Nervous disorder, VSD I have been tormented for a year now by a number of problems/symptoms, medical...
Asymmetry of cerebral veins In December 2020, I was hit by a car. Got a head injury...
Procedures after MRI of the brain My father is 65 years old. Over the last 2 years he has...
Pregnancy and pituitary adenoma, panic attacks I am 26 years old and planning a second pregnancy….
My eyelids are swollen. I've had a bad headache for the last week, so I have to drink...
Numbness on the left side of the head. I am 33 years old. I've been worried about numbness on my left side for two weeks now...
Constant dizziness, as if there was a drop in blood pressure. Over the course of 8 days, I developed...
Help children with ventriculomegaly disease
At the moment, there are no children with this diagnosis in the care of our foundation. However, you can help sick children with other diagnoses!
Ventriculomegaly is a pathological change in the formation of the brain in a child in the womb. The disease is characterized by changes in the size of the cerebral ventricles, which subsequently leads to various abnormalities, as the central nervous system, spinal cord and brain are affected. The process may also involve peripheral nerves, the autonomic system, and muscles.
Abnormal fetal development is determined during routine studies, and the degree of deviation is established. All deviations, except severe ones, are amenable to therapeutic measures. If a pathology is identified that is incompatible with the life of the child, then the pregnancy is terminated in the early stages.
The disease is very serious, can have serious consequences, and if the pathology is severe, the pregnancy is terminated. The moderately expressed form is characterized by a relatively favorable prognosis.
Consequences
Lateroventriculoasymmetry of the ventricles in a child can have various consequences.
With slight asymmetry, there may be a disturbance in the development of mental and motor functions, which will correct and return to normal over time.
The severe form is the most dangerous, as there is a risk of cerebral palsy, serious mental and nervous disorders, deformation of the skull bones with brain damage.
Detection of asymmetry in a newborn signals the need for comprehensive diagnostics and specialist consultation.
Up to three months, neurological disorders are difficult to identify, so the child must be constantly under the supervision of a neurologist.
If you ignore pathology in an adult, the following manifestations are possible:
- development of chronic cephalgia;
- intellectual impairment;
- the appearance of cognitive disorders;
- dementia (brain cell atrophy);
- impaired coordination of movements.
For newborns (infants)
Ventriculomegaly is dilatation of the lateral ventricles in a fetus, newborn, or infant in the first year of life.
The first signs of pathology can be detected exactly at the 17th week of pregnancy.
Most often, the pathology manifests itself in premature infants; the asymmetry of the ventricles can be seen in the photo.
Typically, such babies at birth have formed ventricles, while the skull has not yet reached the required size.
If this deviation is not caused by a specific reason, then this may mean that after some time the proportions will level out to normal.
The main causes of ventriculomegaly in newborns:
- intrauterine infections in the mother (syphilis, toxoplasmosis, rubella, mumps, etc.);
- asphyxia of the newborn;
- birth injuries;
- hydrocephalus, which is determined before birth;
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the fetus;
- heredity;
- The age of a pregnant woman over 35 years increases the risk of pathology.
Manifestations of ventriculomegaly in children depend on the age of the baby. A small child with a pathology is often capricious, inhibited, may refuse to breastfeed, and his gaze is usually directed downwards.
If a child has an isolated pathology and no other abnormalities or genetic disorders, the prognosis is usually favorable.
But this only happens if the child receives a month-long course of competent treatment immediately after birth.
In adults
Ventricular dilatation in an adult is usually a secondary symptom, which is caused by the presence of a specific pathology.
For example, dysfunction of the cerebrospinal fluid circulation occurred after a head injury, stroke or infectious disease.
Ventriculoasymmetry of the brain in an adult cannot be ignored. To cure the disease it is necessary to undergo a full medical examination.
Manifestations
Whether the fetus has ventriculomegaly and what it is, the doctor can tell by performing an ultrasound as early as the 17th week of pregnancy. Depending on the size of the ventricles, three degrees of the disease are distinguished:
- the first - the size of the ventricles is up to 12 mm;
- the second - the size of the ventricles is up to 15 mm;
- the third is the size of the ventricles up to 20 mm.
The signs of ventriculomegaly in a newborn baby depend on the degree.
Consequences may vary depending on the stage of the disease. In the first degree, the symptoms consist only of excessive excitability and activity of the child; the disease is detected by chance. A child with the second degree is lagging behind in mental and physical development, and periodically experiences convulsions. In the third degree, speech impairment and cerebral palsy are added to these symptoms.
About diagnostics
After the narrowing and closure of the fontanelles has passed (usually this occurs within a year or two), it is possible to monitor changes in the size of the cerebrospinal fluid structures of the brain using computed x-ray tomography (CT) as well as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
It shows soft tissue structures much better, including the ventricles of the baby’s brain, but there is one problem: you need to lie in the ring of tomograph magnets for about 20 minutes. And if for an adult this task is quite simple, then for a child it is often impossible. Therefore, to carry out this study, it is necessary to put the baby into medicated sleep. This is not always possible, as sometimes there are serious contraindications to this.
In this case, computed tomography comes to the rescue. It can also be used to quickly determine the size of the ventricles. True, the quality will be somewhat lower, in addition, tomography carries a certain radiation load. But it does not require anesthesia, and if the cause of the asymmetry is subdural, or, then a computed tomograph will be able to determine the accumulation of blood better than magnetic resonance imaging.
To treat or not to treat?
Often worried parents ask whether treatment is required if the ventricles are enlarged. If there are no clinical manifestations, the child grows and develops normally, then there is no need to prescribe treatment. It is required only when an increase in cerebrospinal fluid pressure is actually proven. Using tomography, this is determined indirectly; direct pressure testing is carried out only using a lumbar puncture. But doing it is a last resort. It is carried out as a necessary study for meningitis, which, by the way, despite pronounced manifestations, never causes a change in the size of the ventricles.
The fact is that this requires a long period of time, and with meningitis, within 2-3 days the clinical symptoms develop so vividly that the baby is hospitalized, and the treatment eliminates the syndrome in a matter of days (especially in the case of meningitis).
In conclusion, it should be noted that changes in the size of the ventricles of the brain in some cases can be of a family, hereditary nature. Sometimes one of the parents may have such asymptomatic ventriculomegaly, and he may not even be aware of this feature. Of course, we are not talking about a clinically significant increase in size, but about balancing at the “upper limit of normal.” In any case, parents need to calm down: the mere presence of ventriculomegaly does not always mean a disease, and in no case is it a “sentence.”
Rate this article:
- 4.39
Total votes: 167
How to treat ventriculomegaly
If significant ventriculomegaly is detected in the fetus, the question of artificial termination of pregnancy may arise. Sometimes this is necessary, because children born with such a pathology can be doomed to lifelong suffering or early death. With moderate severity of ventriculomegaly, the symptoms of which do not progress, therapy is prescribed in the prenatal period.
When ventriculomegaly is detected in a fetus, first of all they try to identify the causes. It is important to check if the mother has any infectious diseases that need treatment. Next, tendencies to hereditary ventriculomegaly are examined. It is known that with chromosomal abnormalities, other developmental defects can be added to the disease - Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, Edwards syndrome, etc.
If the conditions described above are not found, but there is only a pathology in itself, isolated ventriculomegaly, treatment includes taking diuretics, such as Diacarb, designed to remove excess fluid from the body. At the same time, additional potassium intake is prescribed to compensate for its loss. For ventriculomegaly in the fetus, antihypoxants are also indicated to help saturate tissues with oxygen. Massage sessions and therapeutic physical exercises are also necessary to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
The pediatrician and neurologist decide how to treat ventriculomegaly. In serious cases, the help of a neurosurgeon is necessary. It may be needed in cases of concomitant genetic pathologies or the presence of increased cranial pressure. The diagnosis of ventriculomegaly requires careful attention and constant medical supervision.
All of the above measures are taken to reduce the tendency towards more severe ventriculomegaly and help prevent the development of neurological disorders. Sometimes treatment for ventriculomegaly can be surgical. With significant enlargement of the ventricles, when the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is very difficult, an operation may be necessary to install a shunt through which excess fluid will be removed. Surgery for ventriculomegaly in an infant can be performed soon after birth. The very absence of excess fluid, and therefore pressure in the brain, usually immediately has a positive effect on the general well-being of children. After this treatment of ventriculomegaly, the child’s sleep improves and there are no headaches.
Danger of disease
At an early stage, the disease contributes to the development of the above symptoms, which, moreover, like some delay in movements, disappear forever with age. The appearance of such severe effects, for example, cerebral palsy, does not occur in this case. If the pressure inside the skull is already high, and the cerebrospinal fluid continues to accumulate, then the human brain will inevitably be damaged. With the tireless increase in the size of the ventricles, the very properties of the brain change, reducing nervous regulation. The child’s brain bones are elastic and not so rigidly connected to each other, so the pressure will always be slightly lower.