Essay on shaking palsy
Scientists and doctors around the world note that the percentage of older people suffering from neurodegenerative pathologies is increasing year by year. Most of them do not have effective therapeutic or surgical methods to cure or at least slow down the pathological process. Parkinson's disease, first described by the English physician James Parkinson in 1817, is just such a disease.
Parkinson's disease is a chronically progressive disease that primarily affects older people. It is characterized by trembling of the limbs and head, muscle stiffness and slow movements. Patients' balance is impaired and their gait changes, but in most cases their intelligence and thinking ability are preserved. All these symptoms were noticed and described in his “Essay on Shaking Palsy” by Parkinson, after whom this disease was later named.
The author of the Essay, Parkinson, had the opportunity to observe sick people who were not his patients. He met them on the streets of London when he walked, and was amazed at the changes in their posture, gait and movements. Perhaps that is why an ordinary London doctor was able to describe in detail and vividly the “portrait” of a patient with parkinsonism.
It is worth noting that the phrase “shaking palsy” was not coined by Parkinson, but by the English writer D. Aubrey. He used this term to describe the then incurable disease that the hero of his autobiographical story, the famous philosopher Thomas Hobbes, suffered from. Hobbes suffered from shaking palsy at the age of 90.
People have tried to treat Parkinson's disease at all times; references to medicinal drugs and recommendations are found in the texts of the New and Old Testaments. Ancient healers advised not only to play outdoor games and walk in the fresh air, but also to use beaver testes for treatment.
The first medicine to relieve symptoms and slow the progression of the disease was the so-called “velvet bean”, or “mucuna pruriens”. It was used by the people of India and Pakistan, which is reflected in the sacred Vedic scriptures. This legume contains the substance L-dopa, a precursor to the neurotransmitter dopamine, which is so lacking in Parkinson's disease.
Scientific experiments have shown that velvet beans are as effective as levodopa or carbidopa, used in modern medicine, but are safer for health. However, no data were available on long-term efficacy and tolerability.
Medications
Although there are no medications to directly treat Parkinson's disease, there are several classes of medications available to successfully treat motor symptoms throughout the disease. Be sure to consult with a neurologist or movement disorder specialist about your troubling symptoms and your recommendations for medical treatment for them. Conditions for purchasing some drugs for the treatment of Parkinson's disease are more accessible through special programs.
Secrets of neurons
Despite many years of active research, the causes of Parkinson's disease have not yet been established. There is no doubt that the development of pathology is influenced by many factors, one of which is natural aging. In old age, even healthy people often have symptoms resembling parkinsonism. This suggests that age-related decline in brain neurons may be one reason. But thanks to the compensatory capabilities of the brain, clinical symptoms develop only after the destruction of 80% of all neurons.
This is why early diagnosis in Parkinson's disease is so important. By starting treatment as early as possible, there is a chance to slow down the pathological process and, consequently, increase life expectancy. In this regard, an experiment conducted by German scientists is very indicative.
Since the olfactory bulbs are among the first to be affected, the experiment participants were asked to sniff various substances with a familiar and pungent aroma. 187 volunteers smelled cinnamon, vanilla, lemon and lavender, but 46 of them were unable to identify the corresponding aroma. As a result of the examination, Parkinson's disease was identified in three. This is explained by the fact that in the early stages, when there are no symptoms yet, the olfactory bulbs are affected - paired formations consisting of bipolar neurons.
Tremor of the hands and other parts of the body is almost always the main symptom that cannot be controlled without medication.
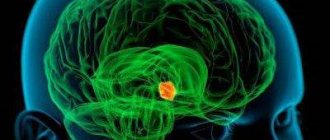
In Parkinson's disease, the number of neurons in the substantia nigra (substantia nigra), where the neurotransmitter dopamine, which is necessary to inhibit the functioning of the central nervous system, is synthesized gradually decreases. This leads to an imbalance of excitatory and inhibitory impulses in different parts of the brain and the appearance of characteristic signs - tremor and muscle rigidity.
However, the body is well adapted to dopamine deficiency, and therefore clinical symptoms occur only if its level decreases by 75% or more. Without treatment, the pathological process progresses rapidly, which affects life expectancy and its quality.
The quality of life
Violations in the patient’s quality of life affect several areas at once:
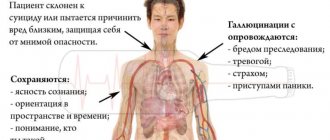
- Physiological. It becomes difficult for a person to care for himself, his coordination and sense of balance are impaired. The patient is unable to eat normally due to tremors. It becomes difficult for him to get dressed and go to the toilet. In the final stages, profuse salivation appears.
- Emotional. Often the patient does not want anything. Emotional lethargy appears. Apathetic states are replaced by attacks of depression.
- Sexy. There is a sharp decrease in libido. In some cases, patients experience impotence.
To increase the patient's life span, it is necessary to carry out complex therapy.
Forecast for life
Parkinson's disease has a conditionally unfavorable prognosis because it progresses steadily. How long they live with her depends on several factors:
- age;
- level of medical care;
- environmental situation;
- presence of systemic diseases;
- quality of patient care.
Predicting life expectancy depends to the greatest extent on the age at which the disease started. If it manifests at the age of 25-39, you can live on average up to 75 years, if the first signs appeared between the ages of 40 and 65 - up to 73 years. With a later onset, after 65 years, patients can live about 5 years.
It is worth noting that Parkinson's disease itself is not fatal; deaths are usually caused by its complications. Most often, death occurs as a result of pneumonia, obstruction syndrome (bronchial obstruction), and urological infections leading to blood poisoning. The mortality rate from such cases accounts for almost half of the total number of deaths. In almost 25% of patients, the cause of death is exacerbation of cardiovascular pathologies.
Infectious diseases can cause complications in the form of meningitis and encephalitis, which in some cases leads to the development of cerebral ischemia. It is quite possible to prevent such a complication by maintaining normal immune function and starting antibacterial treatment in a timely manner. Cerebral ischemia in Parkinson's disease occurs in approximately 4% of all cases.
Malignant tumors can also affect life expectancy, but a direct relationship between Parkinson's disease and the development of the cancer process has not been found. Long-term therapy with levodopa may be complicated by neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
According to statistics, almost half of patients develop a depressive state. This can happen either after the diagnosis is announced or as a result of chemical changes in the brain. Mental disorders are one of the many symptoms of Parkinson's disease and not so rarely lead to suicidal thoughts.
Suicide is another cause of death, especially in the absence of medical supervision or self-medication. In this regard, a sick person also needs psychological help, which can be provided by close relatives.
End-of-life care
In Parkinson's disease, degeneration of nigrostriatal neurons and neurons of the locus coeruleus occurs, and intracellular inclusions (Lewy bodies) appear in nerve cells, which are products of protein degeneration.
An insufficient amount of dopamine is produced, the excitatory amino acid glutamate and the neurotransmitter acetylcholine are produced in excess (in the neostriatum). There is also insufficient synthesis of norepinephrine, serotonin, and acetylcholine in the cerebral cortex. Due to degeneration of neurons in the nucleus nigra and disruption of the functioning of neuronal circuits, patients suffering from Parkinson's disease develop motor disorders. Initially, the limbs on one side of the body are involved in the pathological process.
Neurologists identify the following symptoms:
- hypokinesia;
- rest tremor;
- rigidity;
- postural instability.
Hypokinesia is manifested by a decrease in motor activity. This is expressed by a violation of the initiative to perform movements, slowness and a decrease in the amplitude of all actions. If there is severe hypokinesia, it is difficult for the patient to get up from a chair or turn over in bed; he begins to stoop when walking and takes a “petitioner” pose with his arms pressed to his body and bent at the elbow joints.
A resting tremor appears: the patient makes movements with his fingers that resemble counting coins or rolling pills. Later, tremor of the legs and lower jaw occurs. When holding a pose, postural tremors are noted, usually less pronounced than tremor in the resting limb. Tremor is not necessarily present in Parkinson's disease.
A manifestation of rigidity is a plastic increase in muscle tone, which increases during the study. In advanced stages of Parkinson's disease, postural instability occurs. It is characterized by staggering when walking, frequent falls, and propulsion (tendency to fall forward). Patients need to use support devices (sticks, tripods).
30-70% of patients develop depressive states, 20-40% of patients suffer from cognitive disorders, and 20% from psychotic disorders, but it should be noted that psychoses in Parkinson's disease are most often provoked by anti-Parkinsonian drugs. Autonomic dysfunction is manifested by orthostatic hypotension, constipation, urination disorders, seborrhea, drooling and other disorders.
Quite often, phenomena such as chronic fatigue and pain of various localizations occur. Depending on which motor symptom predominates in the clinical picture of Parkinson’s disease, tremulous, akinetic-rigid, rigid-tremor and tremulous-rigid forms are distinguished; the last two forms are conveniently combined into mixed forms of the disease.
At the last stage of Parkinson's disease, patients experience motor fluctuations, drug-induced dyskinesias, walking is impaired, they fall or freeze in place. Akinetic and non-motor (vegetative, cognitive, neuropsychic) crises are characteristic.
Motor fluctuations are manifested by the phenomenon of “depletion of the effect of a single and daily dose,” freezing, and the “on-off” phenomenon. In later stages, patients experience long periods of decompensation, lasting from several days to several weeks, as well as akinetic crises. They are accompanied by dysphagia, oliguria, hyperthermia, autonomic disorders, and confusion.
The last stage of Parkinson's disease is characterized by the progression of all symptoms:
- motor disorders;
- tremors and stiffness of movements;
- swallowing disorders;
- inability to control urination and bowel movements.
At the last stage of Parkinson's disease, the patient is in a wheelchair and is fed with a special spoon. Dementia and severe depression often develop, and suicidal thoughts arise. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital are successfully removing patients from this condition. Doctors use modern treatment regimens for the disease with effective drugs that reduce the severity of symptoms and prolong life expectancy.
Life expectancy with Parkinson's disease primarily depends on the stage of the syndrome. Each stage of pathology development is characterized by certain symptoms.
You can familiarize yourself with the stages of the disease and their symptoms using the following table: Each stage of the syndrome requires immediate intervention by a neurologist. Therefore, if any symptoms are detected, you should immediately contact a medical facility.
Although there are typical symptoms of Parkinson's disease, they can vary significantly from person to person—both in terms of their intensity and how they progress. Motor symptoms are usually associated with movement, while non-motor symptoms are not.
Movement symptoms typically include tremor (shaking), rigidity (muscle stiffness), bradykinesia (slow movements), postural instability (balance problems), and walking/gait problems. Non-motor symptoms include sleep problems, decreased sense of smell, fatigue, depression/anxiety, mental disturbances, gastrointestinal problems and others.
The last stage of Parkinson's disease implies the onset of the most difficult period of patient care due to his immobilization. The patient is completely immobilized, which increases the risk of developing bedsores, intercurrent diseases, and difficulty performing hygienic procedures, especially with high weight.
Additional equipment is required in the form of a special medical bed, in which the foot or head end can be raised, and an anti-decubitus mattress. The patient is turned from one side to the other every two hours, diapers are changed as needed, and the skin of the intimate areas is left open for several hours a day to avoid diaper rash. It is also necessary to ensure that there are no folds on the bed - this provokes the development of bedsores.
Liquid food, pureed in a blender, if possible, up to 5 times a day. It is important to maintain water balance, since in the last stage of Parkinson's the patient is often dehydrated, which can lead to a decompensatory breakdown. Hygienic procedures are carried out regularly, the room where the patient is located is ventilated twice a day, and if necessary, the room is quartzed with a home apparatus.
There are several classifications of the stages of Parkinson's disease, but the Hoehn-Yahr rating scale is considered the simplest and most convenient. It was developed by English doctors Margaret Hen and Melvin Yahr in 1967.
The Hoehn-Yahr system is an international criterion that allows one to determine the intensity of disease progression and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
At first, the Hen-Yahr classification contained 5 stages, but later 2 more were added:
- zero;
- first (unilateral lesion);
- intermediate, or transitional;
- second (bilateral lesion with preservation of balance);
- third (bilateral lesion of moderate severity)
- fourth (severe immobility with impaired ability to maintain balance);
- fifth (loss of ability to move).
If it is possible to identify signs of the disease in the initial stages, then individually selected treatment for Parkinson’s will significantly slow down the progression of pathological processes. But, unfortunately, it is impossible to completely defeat the disease.
Zero stage
How does Parkinson's disease manifest in the early stages? The disease does not reveal itself in any way, there are no symptoms. But structural changes are already occurring in the brain, which can sometimes be noticed during a diagnostic examination.
Many people worry about the health of their elderly relatives and ask how to recognize Parkinson's disease at an early stage. It is necessary to carefully monitor the behavior of a relative and, if even the slightest deviation from the norm is detected, consult a doctor.
First stage
When the patient is worried, the fingers on one hand begin to tremble a little, which he usually does not pay much attention to. Over time, the trembling intensifies and is observed even during periods of rest. Sleep is disturbed, even with minor exertion, severe fatigue quickly occurs, and there is often a depressed mood.
The tremor covers the entire arm, the shaking stops only during sleep. Handwriting changes and fine motor skills deteriorate. The patient feels stiffness in the neck and upper back. Hands stop moving when walking.
Second stage
The disease affects both sides of the body. Possible tremor of the tongue and lower jaw. Increased salivation is observed. Sweating is impaired, the skin becomes too dry or excessively oily. Facial expressions worsen, speech slows down, and the timbre of the voice changes. Joints become less mobile, walking is slow. The patient often loses his balance. Although he is able to perform usual actions, they take much longer than before.
Third stage
At this stage, the disease progresses and characteristic symptoms appear:
- “doll gait” - steps become small, mincing, feet are parallel, shuffling movements;
- “supplicant pose” - the body leans forward, the head is tilted, the back is hunched, the legs are bent, the elbows are pressed to the body;
- “mask effect” due to limited facial expressions and slow blinking;
- nodding tremor of the head, reminiscent of gestures of agreement and denial;
- monotony and muffled speech, unambiguous answers, repetition of the same words.
The muscles become inflexible, movements are constrained, and the joints work like a gear mechanism. Falls may occur due to clumsiness and loss of balance.
The retropulsion test shows a positive result. If you lightly push the patient's chest, he will slowly move back to restore his balance (a healthy person will only lean back slightly, but will remain in place).
The patient has difficulty caring for himself; simple actions take twice as long. He needs help buttoning buttons, tying shoelaces, getting into sleeves.
Fourth stage
The importance of rehabilitation
In order to prevent complications and prolong the patient’s life, it is necessary to use all the possibilities offered by modern medicine. In addition, it is recommended to include therapeutic exercises, massage and acupuncture in the rehabilitation program. To maintain and improve fine motor skills of your fingers, you can do needlework or drawing.
Life expectancy prognosis improves significantly if physical exercise brings moral pleasure. For example, in some countries, special dance studios have even been created, so-called “dance” studios for patients with parkinsonism.
Care becomes especially important at the last stage, when the patient cannot cope with basic actions. He needs help with literally everything - hygiene procedures, dressing, feeding and walking fall entirely on the shoulders of loved ones.
To make the task easier, adaptive equipment is used - electric beds or mattresses, wheelchairs, handrails, built-in appliances and walkers. A special spoon, created in 2013 with financial assistance, can be a good help. Its owner, Sergey Brin, is a carrier of a gene that can cause Parkinson's disease, so he invests a lot of money in research to find methods of treating it.
Dancing allows you to achieve several goals: music has a beneficial effect on brain activity; Coordination of movements in accordance with musical rhythms stimulates the work of the brain centers - as a result, coordination, mobility and balance are improved
The miracle spoon is called Liftware and is similar to a regular toothbrush. Its scooping part is somewhat elongated, and the handle is quite massive, since it contains touch sensors and a microchip. This mechanism detects the vibrations of the patient’s hand and adapts to them. As a result, a person can eat on his own without spilling or scattering the contents of the spoon! This is confirmed by clinical trials - about 80% of patients cope well with eating.
The Parkinson spoon can be disassembled and can have several attachments - spoons of different capacities (table, dessert, tea), forks and knives. Other attachments are currently being developed, in particular, for a toothbrush and a key holder.
Diagnosis of Parkinson's disease
Before you begin a course of treatment that can increase your life expectancy, you first need to confirm the diagnosis. Parkinson's syndrome can be determined based on the characteristic symptoms of this disease.
However, the disease often behaves unpredictably. Therefore, in order to accurately diagnose the stage of the syndrome and assess the general state of health, a neurologist will need to conduct a series of clinical examinations.
Drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking tobacco products contributes to the progression of Parkinson's disease. Therefore, if the patient wants to live long, he should give up these bad habits.
Clinical examination methods:
- History . During this diagnostic process, the neurologist collects information about the patient’s lifestyle, asks about how the pathology manifests itself, and what could have caused its appearance.
- Differential diagnosis . Here, the doctor, based on diagnostic and logical algorithms, excludes the possibility of the existence of another pathology.
- Topical diagnostics . This research technique, using clinical data and other examination results, identifies damaged areas of the nerve processes, the extent of the pathology and the site of its occurrence.
To obtain more detailed information about the course of the disease, computed tomography and MRI of the main organ of the nervous system are performed.
Gamma knife against tremors
Cyber knife, gamma knife - until recently, this device was used only during oncological operations. Today, the procedure using them relieves patients from tremors without traumatic incisions. The effect of such treatment is comparable to deep brain stimulation, but the operation is performed in one session and costs several times less. In addition, there is no need to adjust the neurostimulator implanted under the skin or change its batteries.
In Russia, gamma knife operations began to be performed in 2011 at the radiosurgery center of the Leningrad region. The essence of the operation is the destruction of a specific area of the brain with a beam of ionizing radiation. Gamma Knife delivers more precise and targeted radiation than other types of radiation therapy.
The operation lasts about two hours, the target may be the anterior ventral nucleus of the thalamus or other brain structures. This technique is completely non-invasive and is performed on an outpatient basis. If there are no complications, the patient is sent home on the same day or observed for 1-2 days in the hospital.
Studies conducted in Japan have shown that complete or almost complete cessation of tremors is observed in 80% of patients. In this case, no complications arose. It should be noted that in the first few weeks, patients experience euphoria. Motor disturbances disappear, and you can live a normal life, as you did several years before the operation!
Important: despite the undoubted advantages of the gamma knife, the progress of the disease does not stop. However, the quality of life improves and the dosage of levodopa is significantly reduced.
Causes of death
Frequent:
- infectious processes
- aspiration pneumonia
- bedsores
- severe damage to the cardiovascular system
Aspiration pneumonia
According to statistics, aspiration pneumonia is the most common cause of death in Parkinson's disease. It occurs in half of the cases, and in every fourth case, death occurs due to chronic heart disease.
Swallowing disorders lead to the development of aspiration pneumonia. In this case, pieces of food or drops of liquid enter the lower parts of the lungs. The subsequent addition of infection due to weakened immunity contributes to the development of severe pneumonia, from which patients with Parkinson's disease die. Therefore, it is very important to recognize changes in the act of swallowing in a timely manner.
The earliest sign of the development of swallowing disorders is drooling. To prevent the occurrence of profound disorders, it is necessary to start using anticholinergic drugs. They will help get rid of this condition, but have a large number of side effects - dry mouth, hallucinations, constipation. Treatment also involves injections of botulinum toxin into the salivary glands, but the effect lasts only for several months.
Other serious symptoms of swallowing problems include coughing and choking while eating. Coughing is a reflex reaction of the body that helps remove food and liquid from the respiratory tract when it gets there, but sometimes microscopic pieces of food can remain in the lungs or bronchi.
These symptoms should cause concern
- difficulty swallowing medications
- slow chewing
- patient complaints of chest discomfort
- attempts to “clear” my throat
In severe cases, parenteral nutrition via tube may be necessary.
How to avoid pneumonia
- drink liquid in frequent small sips
- bite off small pieces of food, chew them thoroughly and swallow slowly
- after eating, maintain a straight body position for 15 minutes
- eat soft foods to make swallowing easier, avoid dry foods
- while eating, sit slightly leaning forward
- rinse your mouth after eating
- to improve sputum discharge, drink alkaline drinks - milk with soda, mineral water
- sleep with your head elevated
Prevention of other complications
Fractures in patients can be prevented by arranging housing, removing sharp and hard objects from rooms, being attentive to the patient, and helping him in everyday life. To prevent bedsores and sepsis, professional care with careful wound treatment is recommended.
What's the end result?
In drawing conclusions, I would like to note the ambiguity of the issue of life expectancy. It is almost impossible to give an accurate prognosis for Parkinson's disease, since too much depends on the individual characteristics of the person and his attitude towards his illness, as well as on the quality of the treatment provided.
The question of the quality of life of the patient, who must overcome many difficulties, is much more pressing. Support and mutual understanding are the main tasks of loved ones who are able to provide the mental comfort that is so necessary for the sick person. Systematic physical exercise, meditation, auto-training and even folk remedies - all this will help you stay active for a long time and lead a full life.
Ways to extend life
If the patient, at the first signs of the disease, sought help from a doctor and received adequate treatment, then the disease may not progress for many years, and the patient remains able to work.
Therapy for Parkinson's disease consists of medication, exercise therapy, massage, diet, and in some cases surgery is required.
Taking medications still comes first. If the disease is diagnosed early, this does not mean that the patient will be immediately prescribed medication, since the goal of therapy is to restore function using minimal doses.
On this topic
- Parkinson
9 types of exercise therapy for Parkinson's disease
- Natalia Sergeevna Pershina
- June 6, 2020
With progression, drugs are prescribed that promote the synthesis of dopamine and prevent its inhibition, then combination drugs Levodopa (if possible, doctors prescribe them to patients over 60 years of age).
With the help of Levodopa, it is possible to restrain the development of the disease for many years and partially stop its symptoms, for example, tremor. Over time, the body gets used to the action of the medicine and stops responding to treatment, so an increase in its dosage is required.
Daily exercise can help slow down or eliminate muscle stiffness and maintain mobility. Physical exercises are selected individually, so that the patient does not experience too much physical exertion. Handicrafts, drawing, and hand exercises will help maintain fine motor skills for a longer period.
To maintain gross motor skills, American doctors advise dancing. Dance movements require balance, and this activates a part of the brain whose neural connections are impaired by Parkinson's.
In addition, group activities promote social contacts and brighten up everyday life. A case has been described in medicine: a man who has been diagnosed with Parkinson's for more than 20 years remains functional, and, as he says, happy, thanks to dancing.
Prevention
Preventive measures will help reduce the risk of developing pathology. To protect yourself and your loved ones in the future, follow these recommendations:
• Eat nutritiously, eat foods high in omega acids. • Ensure good oxygen saturation of the body: take frequent walks, ventilate your home. • Exercise. • To refuse from bad habits. • Avoid brain damage. • Organize good rest every day and throughout the year. • Have regular medical examinations.
You can live many good years with Parkinson's disease, and you should strive for this. Much depends on the patient himself and the support of his loved ones, which is very important. It is necessary to recognize the disease in time, consult a specialist and follow all medical recommendations. A responsible approach to the problem will give good results. Patients who are treated have good opportunities for a high-quality and long life.