Symptoms of neuralgia on the left side of the heart
Intercostal neuralgia is closely associated with the manifestation of pain in the chest. This can happen due to a deterioration in the full functioning of the intercostal nerve fibers against the background of pinching, infections, or hypothermia. This problem can arise at any age, but still the largest percentage of patients is recorded among older people.
Intercostal neuralgia
Such a pathology can also occur due to the presence of pathologies in the patient such as osteochondrosis, hernia of the thoracic ridge or herpes zoster. Often neuralgia is a symptom of more serious diseases - for example, pleurisy or various types of oncology. In addition, neuralgia on the left side of the chest can cause symptoms associated with heart disease.
Neuralgia in the heart area develops as a result of pinching or irritation of the fibers of the intercostal nerves.
Helpful information
The main sign of pathology is pain. It can have a sharp, dull, aching and burning character.
The pain is paroxysmal and localized to the left of the sternum, as a result of which most people think that it is associated with cardiac activity.
Discomfort in the cardiac zone increases with physical activity, breathing, coughing, which is accompanied by a feeling of squeezing of the ribs. The patient may also experience local hyperemia or blanching of the skin, as well as involuntary muscle twitching. Often there may be tingling in the chest and numbness of the skin between the ribs.
Symptoms of the disease
Neuralgia of the heart is similar to heart diseases, therefore only a doctor can distinguish neuralgic manifestations from cardiac pathology, guided by the following symptoms:
- sudden attacks of aching pain in the left side of the chest, the pain can be burning, and the attack proceeds in waves, the pain either intensifies or weakens;
- when changing body position, when coughing and sneezing, there is a feeling of compression of the ribs, numbness of the skin in the affected area;
- convulsive twitching of the heart muscle, tingling in the chest, pallor, bluishness of the skin, or, conversely, their sharp redness.
In case of cardiac neuralgia, the pain does not go away as a result of taking Nitroglycerin, and does not affect blood pressure and pulse, unlike disturbances in the functioning of the heart. Painful sensations radiate to the scapular region, spreading to the lower back and subclavian space.
Diagnosing neuralgia in the heart area on your own, much less treating it at home, is unacceptable, because the symptoms may be similar to myocardial infarction, an attack of renal colic, diseases of the digestive system or pneumonia. At the first signs of neuralgia, you should immediately seek medical help.
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia on the left with folk remedies
In most cases, the patient undergoes therapy at home. Moreover, depending on the severity of the disease, the patient is placed on bed rest from three days to a week. The bed must have a flat and hard surface. It is better if the bed is equipped with an orthopedic mattress, but if this is not possible, then you need to put something flat and hard under a regular mattress that can be adjusted at home. If the patient uses a bed during treatment, for example, with a sagging mesh, then his condition will only worsen.
For therapy prescribed:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, Diclofenac or Meloxicam. These drugs have an analgesic effect coupled with an anti-inflammatory effect. In addition, their zone of action affects the problematic nerve and can relieve syndromes of associated ailments. This type of medication is available in tablets, injections or suppositories;
- muscle relaxants - "Mydocalm" or "Sirdalud" - relieve discomfort in the form of spasms of skeletal muscle tissue;
- sedatives based on natural ingredients. These may be medications such as Sedosen, Persen, Novopassit and many others;
- vitamin B complexes, for example, Neurorubin. Their main effect is to restore damaged nerve roots and increase the interconnection between them.
To get rid of the symptoms of thoracic neuralgia, doctors prescribe medications
The main method of local therapy is the application of dry heat to the affected area of the body. It should be noted that this method involves the use of an indirect source. Woolen items or down scarves are perfect for dry warmth. It is strictly forbidden to apply hot objects to the area affected by neuralgia - this can only cause harm to the patient.
Pharmacy medications in the form of ointments and gels without NSAIDs include anesthetics. Such drugs include Capsicam or Finalgon.
For targeted treatment, ointments and gels are used, as well as special patches.
Along with other treatments, special patches impregnated with anti-inflammatory and analgesic medicinal components are also used in treatment. Using this product involves sticking it to the affected area of the body. Moreover, they are designed for a long-lasting effect due to the slow release of beneficial components.
After the symptoms of the acute stage of neuralgia have been successfully eliminated, you can begin to restore the normal functioning of the areas of the body affected by neuralgia. The following methods for restoring the body are non-drug in nature.
- Massage of the paravertebral muscles is aimed at improving the metabolic processes of the patient’s body, as well as toning muscle tissue, relieving swelling and pain.
- Therapeutic exercise allows you to strengthen the muscle structure of the torso. It is prescribed individually for each patient depending on the physical fitness and condition of the patient.
- Manual therapy can relieve the patient of pinched nerves and restore normal relationships between the vertebrae.
- Acupuncture.
- Physiotherapy such as UHF, electrophoresis, magnetic or laser therapy.
- Thermopuncture, the main effect of which is aimed at “cauterizing” biologically active points of the body. It is believed that the stronger the damage to the skin on certain points of the human body, the more effective the treatment result. Impact on one point can occur up to ten times.
Thermopuncture
You can fight neuralgia with the help of traditional medicine recipes, but only in parallel with the main treatment prescribed by the doctor. Below are a number of methods to combat the disease.
- The affected area of the body must be lubricated with fresh radish or horseradish juice. This will help relieve pain.
- During severe pain, a compress of rue tincture will help.
- Wormwood lotion has an anti-pain effect. To do this, you must first steam the wormwood, then grind it to a paste, add sea buckthorn oil to the mass and apply it to the problem area.
- Geranium is also rubbed on the sore spot, and then wrapped in dry heat.
- A gauze compress soaked in flax seed tincture is also used to treat diseased nerves.
- You can rub homemade ointment based on Vaseline and aspen buds into problem areas. To do this, you need to mix the ingredients in a ratio of 1:4, where one part is Vaseline and four parts aspen.
- It is also recommended to take baths with sage and sea salt.
- Chamomile flowers, lemon balm, orange peel and honey are used in the form of a healing decoction. This remedy strengthens the entire nervous system.
Traditional medicine methods cannot completely get rid of the disease, but they can speed up the treatment process.
If it is not possible to prepare special products, you can simply buy ready-made drugs based on natural ingredients at the pharmacy. Such drugs include, for example, pepper patch. The main thing is to carefully read the instructions before use and degrease the skin at the site of future application with alcohol.
Before performing exercises for neuralgia of the thoracic spine, it is important to know how to do it correctly. Otherwise, it is easy to harm yourself and make the situation worse.
Rules for performing exercises
As a preventive measure for immediate treatment, the following exercises are allowed:
- turning the arms from a supine position. The legs are extended and the arms are bent at the elbows. It is necessary to turn your arms in a horizontal position so that they end up along the body. Repeat 7-9 times;
- body rolls. Performed lying on your back with bent legs, raised gluteal muscles and raised arms up. It is necessary to make smooth rolls. Repeat 10-12 times;
- turns are made from a standing position, with the arms raised at the shoulders parallel to the floor. Turn your torso in different directions, while straining the muscles of your sternum and abdomen. Repeat 20-25 times.
A set of exercises to get rid of thoracic neuralgia
Neuralgia - specialists in Moscow
Choose among the best specialists based on reviews and the best price and make an appointment.
Chest pain on the left, which is caused by neurological pathologies, develops due to pinching or irritation of the intercostal nerve fibers. This can be due to a number of factors, the most common of which are:
- chest injuries;
- Bekhterev's disease;
- herniated intervertebral discs;
- prolonged tension of the intercostal muscles;
- curvature of the spinal column.
The development of neuralgia in the heart area is often associated with psycho-emotional stress, hypothermia, the action of infectious agents or intoxication of the body. Rarely, pain syndrome to the left of the chest is observed with herpetic lesions, pleurisy, or taking certain medications.
The tactics of treating neuralgia on the left side in the heart area consists of the integrated use of various techniques, among which the most effective are:
- drug treatment;
- physiotherapy;
- therapeutic massage and exercise therapy;
- alternative medicine.
The main method of eliminating discomfort to the left of the sternum is taking medications. The most effective groups of drugs for neuralgia in the heart area are:
- Painkillers. Acute stabbing pain can be effectively relieved with Analgin, Paracetamol, Tramadol, Baralgin, Piralgin, Pentalgin, Sedalgin.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. To eliminate foci of inflammation, Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Nimesulide, Celecoxib, Diclofenac are used.
- Selective and non-selective muscle relaxants. Most often, doctors prescribe Baclofen, Mydocalm, Sirdalud.
- Cardiac glycosides. Neuralgia of the heart is eliminated by Digoxin, Strofactin, Korglykon.
- Chondroprotectors. For the regeneration of cartilage tissue, the drugs Artra, Alflutop, Rumalon, Structum, Teraflex, and Chondroitin are used.
In case of acute heart pain, as first aid it is worth taking a supine position and placing your legs below body level. After this, it is recommended to remove thick clothing and provide the patient with fresh air. This is done so that a person can breathe normally and receive the necessary amount of oxygen for the functioning of organs.
Next, you need to take a Nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue. If there is no effect, you need to take another one. It is not recommended to take more than two tablets of the drug, as this can lead to a sharp decrease in blood pressure, which will aggravate the situation.
Physiotherapy
Along with drug therapy, the doctor may prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures. For cardiac neuralgia the following are used:
- electrophoresis;
- water and mud procedures;
- laser treatment;
- magnetic therapy;
- acupuncture.
In the conservative treatment of some diseases, therapeutic exercises and massage are prescribed. With their help, they improve blood circulation in the affected area and relieve spasms of muscle fibers. An experienced massage therapist should select a set of exercise therapy exercises. This will avoid the development of complications and make the treatment safe for the patient’s health.
Features of pain with intercostal neuralgia
Pain with interchild neuralgia is caused by pinching of one or more spinal nerve roots at the level of the thoracic spine or spasm of the intercostal muscles. An attack can be triggered by a sudden movement such as coughing, sneezing, or lifting heavy objects.
The pain is very intense, shooting, burning, localized along the intercostal nerve, intensifies with a deep breath, coughing, sneezing, and turning the body. The attack may be accompanied by vegetative symptoms - increased sweating, redness or paleness of the facial skin.
Pain is a subjective sensation, so interpreting the characteristics of pain syndrome based on complaints presents certain difficulties.
In practice, it is not always possible to distinguish heart pain from neuralgia based solely on complaints. In all cases when there is persistent pain in the left half of the chest, you must consult a doctor; if the pain does not go away for more than 15 minutes, you must call an ambulance.
The term neuralgia defines a pathological process characterized by the development of aseptic (non-infectious) inflammation in the peripheral nerves. The main reason for the development of the inflammatory reaction is local hypothermia (a person being in a draft), which mainly affects the back area.
The severity of pain depends on the severity of the inflammatory process. Since nerve fibers are displaced when the chest moves, the intensity of pain increases during breathing.
In order to be able to distinguish unpleasant pain in the heart from neuralgia, you should pay attention to several features associated with aseptic inflammation of the intercostal nerves:
- The pain spreads along the intercostal arch.
- The discomfort is a tingling or aching sensation.
- The pain does not radiate to the left arm or shoulder girdle.
- Unpleasant sensations intensify during inhalation or exhalation.
- Discomfort can be easily relieved with the help of drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ketanov, analgin).
- The development of pain is usually preceded by local hypothermia.
- The pathological condition can develop equally often in young and elderly people.
The presence of more than 3 characteristics of pain increases the likelihood that a person has intercostal neuralgia.
The possible development of heart pathology with the appearance of corresponding clinical subjective symptoms is indicated by several specific features of pain:
- Unpleasant sensations are predominantly localized on the left side of the sternum (the area of the projection of the heart), they often radiate to the left shoulder girdle and shoulder.
- Mostly, there is a clear connection between physical or functional stress and the occurrence of pain (with the exception of cases of unstable angina, as well as myocardial infarction).
- Painful sensations usually have a pressing, squeezing nature, they are accompanied by shortness of breath. In the event of myocardial infarction, as well as unstable angina, the pain becomes acute.
- Heart pain predominantly develops in older people with cardiovascular pathology.
The main signal of intercostal neuralgia is pain. Firstly, as mentioned above, the main symptom of intercostal neuralgia is pain in the heart area. This pain, in principle, differs from pain in heart disease, since with intercostal neuralgia it is neuropathic.
Pain in the rib area occurs because the intercostal nerves are compressed or irritated. This can be clearly seen in the picture. Although such pain is called neuropathic due to its nature of origin, it can be varied.
For example, both aching and burning; both sharp and dull. It happens that people with intercostal neuralgia complain of constant pain, and in some cases it is episodic. Of course, due to the fact that pain occurs when there is damage, pain caused by irritation of nerve fibers begins to intensify with increased motor activity.
For example, if you suddenly moved your body, coughed, sneezed, spoke loudly, or even just changed the position of your body, if you have intercostal neuralgia, be prepared for the pain to become stronger, and therefore do not hesitate to treat intercostal neuralgia.
In addition, pain is also noted during palpation, that is, palpation of certain areas of the body. This may be the intercostal area, an area along the chest or spine. The part of the chest where sharp pain is observed is the area of the damaged segment of the nerve.
Often with this disease there is pain, which intensifies when exhaling and inhaling. In such cases, during a painful attack, it becomes so painful for the patient to breathe that his breath even stops, and the slightest expansion of the chest during inhalation causes sharp pain.
Also, it should be understood that the pain cannot last forever, so the death of the nerve root occurs. With this process, it will seem that the disease has passed, because the pain begins to go away, but in this case the tidal volume decreases, and the person experiences shallow breathing, and also a feeling of heaviness in the chest.
Of course, pain with intercostal neuralgia is localized in the areas between the ribs, but pain can also be felt in other places. For example, in the lumbar spine or under the shoulder blade.
Pain in the chest area with intercostal neuralgia very often has what doctors call a girdling character. This means that it occurs along the spaces between the ribs.
In addition to pain, the processes of irritation and compression of the intercostal nerves can cause other unexpected and even unpleasant symptoms. Along with the pain of intercostal neuralgia, you may feel distinct muscle contractions or twitching.
Intense sweating is also observed, and the color of the skin may change - it will turn red or, conversely, become unhealthy pale. Also, the skin in the area of direct damage to the nerve fibers, which caused the symptoms of intercostal neuralgia, or along the damaged nerve trunk, can burn, tingle or completely lose its sensitivity, that is, become numb.
Yes, in some cases, a person who suffers from intercostal neuralgia may be in the so-called antalgic position. It looks like this: the patient bends his body in the healthy direction, trying to maintain this position.
Why is this happening? Thus, the intercostal spaces are stretched, and pressure and irritation on the nerve endings are reduced, which reduces pain. And psychological fear of new painful sensations forces patients to be in this position.
So let's summarize. Due to the fact that chest pain is characteristic of both intercostal neuralgia and a variety of diseases of the cardiovascular system, determining the nature of the pain can make it possible to distinguish between these diseases and accurately determine the cause.
Remember that although pain is the main symptom of neuralgia and heart disease, the nature of the pain is completely different in these two cases.
With intercostal neuralgia, the pain is constant, observed over a fairly long period of time, is not relieved by nitroglycerin, and intensifies with any body movements.
DETAILS: What are moxonidine tablets for?
But in diseases of the cardiovascular system, pain is characterized by a short-term, periodic nature and can be suppressed by certain medications (for example, nitroglycerin).
Also, heart pain is accompanied by an irregular pulse, an increase or decrease in blood pressure, and in the presence of intercostal neuralgia, both blood pressure and pulse rhythm remain normal.
Well, I think that after reading this article, intercostal neuralgia symptoms, you will already be able to distinguish and identify intercostal neuralgia not only in yourself, but also in your relatives or colleagues. Of course, we should not forget that if pain occurs in the chest area, it is strictly forbidden to self-medicate.
Be sure to watch this interesting video about intercostal neuralgia.
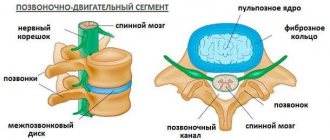
Structure of nerves
Intercostal nerves consist of several types of fibers: motor, sympathetic and those responsible for sensitivity. Each of these nerve endings is located in the intercostal space and runs along the lower edge of each rib. The closing pair of nerve roots is called “subcostal” and is located under the 12th rib.
Each pair of nerve fibers is covered by a special pleura, starting from the spinal canal to the corners of the ribs. The intercostal nerves are responsible for the sensitivity of the muscle tissue of the chest, abdomen and mammary glands, and also innervate the skin in these areas of the body.
Causes of neuralgia on the left
There are a huge number of prerequisites for the diagnosis of “intercostal neuralgia of the thoracic region”. But all the reasons ultimately come down to two main conditions: irritation of nerve fibers in the intercostal space or pinched nerve in the thoracic region.
Pinched nerves can occur due to osteochondrosis, kyphosis, hernia
Pinched nerves in the chest often occur against the background of osteochondrosis in this area. Also, causes of discomfort can be ankylosing spondylitis, herniated intervertebral discs, spondylitis, and kyphosis.
Irritation of the nerves in the area between the ribs can occur as a result of trauma of various etiologies, overexertion during excessive physical activity, or even as a result of psychological stress.
Intercostal neuralgia in rare cases can result from the following ailments:
- acute gastroenteritis;
- spondylopathy;
- allergy;
- damage to nerve fibers due to regular alcohol intake;
- diabetes of various types;
- aortic aneurysm localized in the sternum;
- hepatitis;
- gastritis or ulcer;
- diseases of the duodenum.
Oddly enough, gastrointestinal diseases can also cause thoracic neuralgia
Pain associated with heart disease
Symptoms depend on the location and extent of nerve damage. Most often the pain occurs on one side, but sometimes it is symmetrical. Discomfort radiating to the sternum area gives the feeling that the heart hurts.
Symptoms of intercostal neuralgia:
- The temperature at the site of the lesion rises (hyperemia of the skin).
- The skin in the area of inflammation changes color (slightly reddens or turns pale) and looks drier.
- Muscle tone limits mobility (a common symptom of neuralgia).
- The inflamed nerve loses sensitivity.
- It's hard to take a deep breath.
- The pain radiates to the heart when the left side is affected.
- Increased sweating.
- Attacks of discomfort, which are periodically repeated, intensify at night.
- Pain radiating along the intercostal arch.
The concept of neuralgia is defined as the spread of pain along the course of a nerve. With the development of intercostal neuralgia, such unpleasant manifestations are felt in the area between the ribs, in the places where the nerve endings pass. Cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack and angina are also accompanied by pain in the same area.
Therefore, it is difficult for a non-specialist to distinguish whether it is pain in the heart or neuralgia. Infringement of the spinal root that occurs in the thoracic region can be caused by a sudden movement or cough. This disorder often occurs when lifting heavy objects. It manifests itself as a pronounced shooting and burning pain. The feeling intensifies when you turn your body and take a deep breath.
Neuralgic pain syndrome is accompanied by painful manifestations that can move from a point in the chest to the spinal column, and sometimes to the scapula. At the same time, the patient himself is not always able to accurately indicate the location. Sometimes the pain is referred. In these cases, it is difficult to determine the source of the discomfort.
In addition to pain, when intercostal nerve endings are compressed, unexpected, but this makes even more unpleasant symptoms appear. Clearly noticeable muscle contractions, accompanied by twitching, are possible. At the same time, intense sweating begins, the skin changes its color, becoming red or becoming painfully pale.
Often, with intercostal neuralgia, a person has to remain in a special antalgic position. The patient takes a position bent towards the healthy part of the body, trying not to change it. At the same time, the intercostal spaces are stretched, which reduces pressure on irritated nerve endings. The pain is relieved. Because of the fear of new unpleasant sensations, the patient maintains this position for a long time.
Pain in the heart or neuralgia - only a doctor can accurately distinguish it based on the results of the examination. But to provide emergency assistance, you need to know what the distinctive features of ailments during heart attacks are. With different lesions of the heart muscles, the localization, intensity and frequency of spasms will be different.
1. Angina pectoris.
This pathology is characterized by cutting or squeezing pain directly in the heart area, spreading throughout the sternum and radiating under the left shoulder blade, neck and arm. The frequency of spasms can range from 2 to 20 minutes. Changing body position does not bring relief. The pain is accompanied by a panicky fear of death, oxygen starvation, and asphyxia.
2. Heart attack.
This condition is accompanied by acute compressive pain in the chest, radiating to the spine. Pale skin, severe sweating, and rapid breathing appear. There is a fear of death, the person cannot move, and loss of consciousness is possible.
3. Pericarditis and myocarditis.
These diseases are characterized by moderate to severe pain. A pulling or cutting painful sensation appears. With pericarditis, their localization in most cases is in the upper section of the organ and the right arm. For myocarditis - under the ribs or under the left shoulder blade, slightly above the upper part of the heart. Both diseases are also accompanied by shortness of breath, fever, and arrhythmia.
4. Aortic aneurysm.
This pathology may be accompanied by prolonged pain in the upper section of the chest. The strength of the spasms increases with any attempt to move.
5. Pulmonary embolism.
The pain with this disease is the same as with angina pectoris, the only difference is that it does not radiate to other parts of the body. In addition, thromboembolism is characterized by:
- pronounced cyanosis of the lips and skin;
- a sharp decrease in pressure;
- cardiopalmus;
- shortness of breath.
6. Hypertension.
Acute pressing pain in the heart and head appears with a sudden increase in pressure, which is characteristic of hypertension. Associated symptoms will be redness of the face, vision problems (“goosebumps” and spots before the eyes), dizziness.
Symptoms of neuralgia
The most common symptom of neuralgia is pain attacks. They can appear in the patient in conditions of complete rest and seemingly excellent health. However, the highest percentage of pain occurs after a sudden change in body position, for example, when turning or bending the body.
The duration of pain attacks varies from several minutes to a couple of days. In this case, there may be a prolonged numbness of the torso area located above the inflamed nerve roots.
An attack of pain caused by thoracic neuralgia can last from several minutes to several days.
Having felt paroxysmal pain, the patient often tries to reduce its intensity by holding his breath or changing his body position to a more relaxed one. Often the patient may think that the nature of the pain is caused by heart problems. However, this can often be misleading.
The table below shows the differences between the symptoms of neuralgia and heart pain.
| Heart attack, angina, other coronary pain | Non-coronary pain | Intercostal euralgia of the thoracic region | |
| The sensations experienced, the nature of the pain | Very strong, accompanied by a feeling of squeezing | Dull, aching | Strong, with “lumbago” |
| Associated symptoms | Feeling of lack of air, pale skin, feeling cold | Sweating, sudden increase or decrease in blood pressure, redness or paleness of the skin. If a person tries to move suddenly, the pain intensifies. | |
| Place of manifestation | On the left side of the chest | On the left side of the chest | Along the intercostal nerve |
| The most common causes of manifestation | Excessive nervous and/or physical stress | Excessive nervous and/or physical stress | Sudden movements |
| What happens when you take medications? | Heart attack - no reaction; Angina pectoris - pain relieved with nitroglycerin | The pain becomes weaker if you take a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug - Nurofen, Diclofenac, etc. |
Often the symptoms of thoracic neuralgia are confused with manifestations of heart disease
Herpes zoster often “gives” symptoms of neuralgia of the region, additionally accompanied by the appearance of bubbles with fluid along the path of the nerve fiber. This disease is not contagious, but requires additional treatment.
Symptoms of intercostal neuralgia
The cause of intercostal neuralgia or thoracalgia is damage to the nerve fiber, caused by pinching it in the area where it exits the spine. Risk factors for the development of pathology are:
- hypothermia;
- arthrosis;
- curvature of the spine and displacement of its components;
- osteochondrosis;
- metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus);
- prolonged stress;
- wearing compressive garments (eg, corsets, bras with metal underwires);
- chest area injuries;
- regular physical overexertion;
- hereditary predisposition.
The listed signs may increase the likelihood of the disease occurring, but do not determine the exact cause of the lesion. Nerve fiber pathology does not have a single clear clinical picture and characteristic conditions, so the question “how to distinguish heart pain from neuralgia” is quite acute in cardiological and neurological practice.
Thoracalgia is most characterized by girdling pain at the level of the affected tissue. This is the first, and often the main symptom of intercostal neuralgia. The intensity and duration of the manifestation of painful sensations can vary from barely perceptible aching, but constant and intensifying with movement - to shooting for a second. In the latter case, the patient’s mobility is significantly limited: he cannot bend over, turn his head, or freely use his hand on the side of the affected nerve.
Exacerbation of pain occurs not only with turns and active movement of the arms, but also with any movement of the sternum - coughing, sneezing, laughing, deep breaths.
With external pressure on the area of the pinched nerve and palpation of the ribs, the discomfort also increases.
Another answer to how to distinguish neuralgia from heart pain is hidden in the appearance of the skin over the affected area. In most cases, with intercostal nerve pinching, the outer covering turns pale or, on the contrary, turns red. A rash may appear at the pinched site. A clear manifestation of thoracalgia should be considered the presence of several points, especially sensitive to movement and pressure.
Features of symptoms in pregnant women
Intercostal neuralgia is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The pain is aching, dull, burning. It can radiate to the ribs, back, lumbar region, neck and shoulder blades;
- The pain may be stabbing in the sternum area;
- The pain intensifies when inhaling;
- The pain is cyclical, it decreases until it disappears completely, and then appears again;
- Certain areas of the skin may become numb;
- Sweating increases;
- Tingling of the skin;
- Possible redness of the skin;
- Increased temperature with bouts of heat or cold;
- Muscle cramps.
Since this disease can easily be confused with a heart attack, you can take drops of Corvalol or Valocordin. If the attack passes, then first of all, you need to check the heart.
Neuralgia in the heart area during pregnancy is associated with the characteristics of the woman’s body during this period. The figure is subject to significant changes, which consists of a shift in the center of gravity and an increase in body weight. In combination with hormonal imbalance, these factors can lead to chest pain on the left.
The unpleasant sensations are nagging in nature. They intensify as pregnancy progresses. If pain occurs in the intercostal spaces, you should seek help from a doctor so that the pathology does not interfere with the course of pregnancy.
Consequences of heart pain
In some cases, the heart hurts due to diseases that have nothing to do with this organ:
- Aortic aneurysm. Aching pain is felt at the top of the chest. It intensifies when moving. As the pathology progresses, the sensation increases, the pain becomes sharply bursting. Possible loss of consciousness.
- Acute blockage of the pulmonary artery. The pain is similar to that felt with angina pectoris, but does not radiate to other parts of the body. The heart beats very quickly, the lips turn blue, and the blood pressure drops sharply.
- Thoracic radiculitis. In this case, pain sensations change when turning the body, moving the chest while inhaling or exhaling. The intensity of their manifestation is not affected by the use of such generally accepted cardiac medications as Validol, Nitroglycerin and others.
- Osteocondritis of the spine. When a nerve is pinched, pain can occur in completely different parts of the body. It depends on which ending is pinched. There may be difficulty breathing and coughing.
- Pneumonia, pleurisy or bronchitis. Due to improper expansion of the lungs and movement of the ribs, pain in the chest is possible. Breathing is difficult, coughing is tormenting, and severe weakness is felt.
- Diseases of the stomach and pancreas. With intestinal bloating, pressure can be exerted on all organs, including the heart. Also, unpleasant sensations can be associated with eating a certain type of food or fasting.
Pain in the heart is always a consequence of a pathological process that leads to deterioration in the nutrition of myocardiocytes. The lack of timely adequate treatment leads to the development of a number of consequences, which include:
- Death of a section of the myocardium (infarction).
- Violation of the frequency and rhythm of heart contractions with subsequent thrombus formation in the cavities.
- Rupture of the wall of the ventricular or atrium cavity with blood escaping into the pericardium.
- The development of acute heart failure, in which there is a decrease in the speed of blood flow in all vessels.
Angina pectoris is the most common heart disease. At the time of the attack, painful sensations of a pressing or squeezing nature occur. The pain is localized in the area of the projection of the heart on the sternum.
It can radiate to the left arm, neck, between the shoulder blades and sometimes to the jaw. Patients characterize it as dull and aching. Its intensity does not change depending on body position or breathing. The duration of the pain syndrome ranges from several to 15–20 minutes.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Nervous and emotional shock.
- Large meals.
- A sharp change in ambient temperature when a person moves from a warm room to the street in winter.
The attack stops quite quickly immediately after taking the drug Nitroglycerin.
Myocardial infarction is an acute ischemic disease of the heart muscle. This pathology occurs when any part of the myocardium is left without nutrition (the flow of blood to it stops).
If this condition lasts more than 20 minutes, then the portion of the myocardium dies. At this moment, the person feels a strong, intense pain of a burning nature. Patients describe it as sharp and piercing. It radiates (gives) to the left side of the back and sternum.
DETAILS: What are heart defects signs
Unlike an attack of angina, in this case the pain sensations may change (intensify) with movement. The person experiences pallor of the skin, frequent shallow breathing and fear. When lying down, he gets worse and tries to take a sitting position, but he cannot find a place for himself.
It is easy to distinguish an attack of angina from a heart attack; it cannot be stopped with Nitroglycerin (1 tablet 3 times with an interval of 5 minutes). If such a clinical picture is observed, then the patient needs urgent medical attention.
Myocarditis is inflammation in the myocardium. In this case, the patient complains of pain and compression in the chest. It is aching in nature and radiates to the left side of the neck and shoulder. The pain is quite long-lasting and can intensify with physical activity.
Pericarditis – foci of inflammation in the pericardium. With this pathology, there is a dull pain that can intensify when lying down, when changing the location of the body in space, coughing and deep inhalation and exhalation.
An aortic aneurysm is a sac-like protrusion of a section of the aorta; in the unfavorable course of the pathological process, thinning and rupture of the aortic wall occurs. This pathology may not manifest itself for a long time. Characteristic signs of a thoracic aortic aneurysm:
- Pain in the upper chest that is constant, throbbing and aching. She often gives it to the back. The duration of pain is several days. The cause is excessive physical activity.
- When swallowing, there is a sensation of a foreign body in the throat, a lump in the throat.
- Cough, breathing problems, which leads to snoring during sleep.
When the aorta ruptures, a bursting, “dagger” pain occurs, from which the person loses consciousness. This is an emergency condition that requires emergency care and urgent hospitalization.
PE (pulmonary embolism). The pain is quite strong, it intensifies when breathing, or rather, inhaling. PE is similar to angina pectoris; they can only be distinguished by the irradiation of pain. With pulmonary embolism, it does not radiate anywhere and is not relieved by Nitroglycerin.
Complications of the disease
Complications arising from neuralgia can be successfully treated in the early stages of the development of the disease. But in advanced cases, when the patient experiences pain for quite a long time, the “problem” nerve may even die. Then the excruciating pain disappears, but this is the first sign of the disease moving to a new stage, for which the characteristic symptoms are shortness of breath and the appearance of a feeling of heaviness in the chest.
Finding a person in a constant sitting position or other static position can result in dysfunction of the spinal canal and the development of osteochondrosis and other related pathologies. The occurrence of complications can only be prevented by timely treatment and prevention.
Consequences
The consequences of the disease do not pose a danger or threat to the patient’s life. The negative impact can have indirect consequences in the form of constant pain, lack of sleep against its background, and disruption of the usual rhythm of life.
Since the cause of intercostal neuralgia is usually some more serious disease of the spine, it can worsen its course. Since the pain is especially severe when inhaling, a person reduces the frequency and depth of his breaths, this can lead to oxygen starvation.
Diagnostic methods
To diagnose this disease, the following studies are required:
- Ultrasound diagnostics of the heart and kidneys, to exclude diseases with similar symptoms;
- In case of an inaccurate diagnosis, computed tomography may be used;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- Chest X-ray;
- Examination by a doctor;
- Electroneurography;
- General urine analysis;
- General blood analysis.
If after several studies the diagnosis is confirmed, then a whole range of studies is not required. This will save both time and money for the patient.
Attention! Only a specialist can establish an accurate and correct diagnosis!
If the patient has unpleasant sensations to the left of the sternum, the doctor collects complaints. During this, he determines the nature and location of pain, as well as the presence of accompanying symptoms.
After this, the doctor begins to collect an anamnesis of the disease and life. This procedure makes it possible to obtain the necessary information about the onset of pathological processes, their possible cause, as well as the characteristics of the course of clinical symptoms.
To confirm the diagnosis, instrumental and laboratory research methods are used. For the differential diagnosis of neuralgia of the heart with intercostal attacks, the following is used:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- X-ray diagnostics;
- ultrasonography;
- ECG;
- EchoCG;
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging.
Using an electrocardiogram, the doctor evaluates the functioning of the heart. This method, in combination with x-ray diagnostics, makes it possible to identify pathological foci that can cause acute, severe pain to the left of the sternum.
A timely and adequate examination eliminates the possibility of establishing an incorrect result. It also significantly reduces the likelihood of disease progression and the development of severe complications.
A neurologist will help the patient identify the presence of thoracic neuralgia. A specialist can make a diagnosis based on examination data and a survey for complaints. During the examination, special attention is paid to the patient's posture. Indeed, with neuralgia, a person, trying to reduce discomfort, involuntarily tries to change the posture of the body in a “painless” direction.
An important task in diagnosing neuralgia is to determine the nature of pain, which is specific to thoracic neuralgia. In this case, the goal of a neurologist is to exclude heart diseases - for this, an electrocardiogram is prescribed and, if necessary, a consultation with a cardiologist is held.
To rule out heart disease in a patient, doctors perform an electrocardiogram.
In addition to the fact that the symptoms of neuralgia are similar to the manifestations of heart disease, they can often be put on a par with the manifestations of stomach diseases. For example, the symptoms of gastritis or stomach ulcers, as well as manifestations of acute pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) are very similar to the symptoms of thoracic neuralgia.
However, there are some nuances in the nature of the pain. In gastrointestinal diseases, the painful condition is more prolonged and less severe. It is also often associated with food intake. With pancreatitis, pain has a pronounced bilateral manifestation and also mainly appears after eating.
To exclude radiculitis from the possible causes of neuralgia, an x-ray is prescribed, and if a spinal hernia is suspected, an MRI is prescribed.
MRI and thoracic x-ray results can help determine the diagnosis.
Intercostal neuralgia of the thoracic region may be similar in its manifestations to pathologies of the respiratory system, such as pneumonia, pleurisy or lung cancer. To detect these diseases, radiography or computed tomography is used.
How to distinguish neuralgia from heart pain
There is a rather thin line between ordinary heart pain and neuralgia, but if we roughly generalize these two conditions, we can identify the main aspects by which they can be distinguished from each other. How to determine whether the heart hurts or neuralgia without knowing the specific location of the pain?
Where does your heart hurt?
Acute ischemic processes in the heart are manifested primarily by anginal pain, which occurs due to insufficient blood supply to the myocardium due to a hemodynamically significant obstruction in the coronary arteries.
Most often, pain in a diseased heart is localized behind the upper or middle part of the sternum, less often - to the left of the sternum, in the area of the xiphoid process, in the epigastrium. Angina pectoris is characterized by irradiation to:
- left upper limb;
- spatula;
- lower jaw and other areas.
However, irradiation does not always help in the question of how to determine whether heart pain or neuralgia is present, since it can occur with both pathologies.
This pathology itself occurs due to irritation of the intercostal nerve. The main clinical manifestation of neuralgia is pain in the region of the heart, which may not be localized, but still causes alertness.
This irritation can occur both due to banal osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, and due to its inflammatory, autoimmune, tumor diseases, which can only be distinguished from each other through careful diagnostic measures.
Consequently, if irritation occurs, the pain is observed along the affected nerve and is “shingles,” which makes it necessary to distinguish it from herpes zoster and acute pancreatitis.
The most common localization of intercostal neuralgia is the area on the left from the 5th to the 9th rib.
Pain in other parts of the chest of a neuralgic nature does not exclude intercostal neuralgia. Intercostal neuralgia is characterized by irradiation to:
- upper limb;
- spatula;
- inside the chest.
This often makes it impossible to try to distinguish neuralgia from ischemic heart pathology, but this is not always the case.
help relieve an attack,
help you switch.
Causes increased pain, shortness of breath and cold sweat.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MmJE_QtCbiQ
WHY DONT PILLS HELP?
All heart medications are divided into two groups: those that lower blood pressure and those that normalize the level of fats and cholesterol in the blood.
Getting used to pressure. A person who is accustomed to high blood pressure at first, when taking medications that lower it, very often feels worse, for example, begins to get sick and dizzy. Having decided that the pills are not suitable, he independently decides to stop taking them.
But in fact, living with high blood pressure is not just bad, but dangerous. Therefore, you cannot refuse treatment; you just need to adjust the dosage of the drugs with your doctor so that the pressure decreases more slowly and without side effects.
Self-medication. Very often, without consulting a doctor, a person begins to take the wrong medications on his own. For any pain in the chest, many people suck Validol or drink Valocordin, although if the pain is caused by angina pectoris, neither one nor the other will help.
Details Created 06/25/2012 16:20
To get an answer to a particular medical question, of course, it is better to consult a specialist. True, before going to the doctor, you can look on the Internet, where there is plenty of information regarding a variety of topics, be it chronic diseases, medications or medical vacancies.
As at all times, today one of the hot topics is the heart and everything connected with it. Currently, many people are interested in how to distinguish heart pain from neuralgia - fear of a heart attack often leads to panic and unjustified fears.
First of all, you need to understand the concepts. Neuralgia is paroxysmal or aching pain, accompanied by tingling, burning and numbness. Usually, such ailment spreads along the trunk of the nerve and its branches, and therefore radiates not only to the heart, but also under the shoulder blade, in the lower back, and in the back.
There are many reasons that cause neuralgia. This may be taking certain medications, bacterial toxins and infections, injuries, diseases of the nervous system, allergies, congenital vertebral pathologies, decreased immunity.
Intercostal neuralgia is often caused by hormonal disorders in women during menopause, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, metabolic disorders of B vitamins, as well as bad habits, such as alcohol abuse.
Unlike neuralgia, heart pain is short-term. As usual, such pain goes away within a few minutes after taking nitroglycerin or another specialized drug. When you inhale and exhale deeply, change body position, or move, the unpleasant sensation in the heart does not change its character.
Heart disease is a cause for concern. Any qualified doctor or professional medical website will recommend carefully monitoring your own condition. If necessary, a cardiogram should be done, and for a more detailed diagnosis, an x-ray and magnetic resonance imaging should be performed.
| № | Criteria for distinction | Characteristics of heart pain | Characteristics of neurological pain |
| 1. | Pain intensity | Strong, pressing, aching, short-term action and quickly disappearing after taking the medicine | Very strong, intensifying when performing movements, the duration of which can be calculated in days |
| 2. | Localization location | Behind the sternum or at the level of the 5th intercostal space | Along the location of the intercostal nerve |
| 3. | Additional symptoms | Pale skin, cold sweat, lack of air, swelling | Increased pain with sudden movements |
| 4. | Factors provoking pain syndrome | Emotional or physical stress | Sharpness of movements |
| 5. | Pain relief medications | Nitroglycerine | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Diclofenac, Nimesil, Nurofen, etc. |
The appearance of any type of pain in the chest area signals the need to seek qualified medical help. Timely treatment eliminates the aggravation of any type of disease and the risk of developing serious complications.
Neuralgia is pain that occurs along the injured nerve. These sensations spread between the ribs, where these endings are located. In this case, long-term pain is felt, occurring equally often both during the day and at night.
They get worse when coughing, trying to take a deep breath, or when moving around the room. Medicines that help with heart disease have no effect. The performance of the organ does not change.
The pain caused by cardiovascular diseases is short-term and periodic. Most often they last no more than 10 minutes. Treated with Nitroglycerin or Validol. Taking a deep breath or changing position does not increase pain. Cardiac dysfunction also occurs.
Need to remember. If you experience pain in the chest area, you need to pay attention to such a fact as the presence of risk factors for the development of heart disease. The pain may be atypical for angina, but the following factors are present:
- the patient is already 45 years old;
- one of the direct relatives suffered a stroke or heart attack;
- the patient smokes;
- there is constant high blood pressure;
- tests indicated elevated sugar levels.
DETAILS: ASD of the heart in children: what is an atrial septal defect, cardiac aneurysm in newborns, is surgery necessary
If these factors are present, then any pain in the sternum area must be treated as a potential danger. No need to guess what it could be. It is necessary to provide immediate assistance and then call a medical team.
During pregnancy
Intercostal neuralgia is a common occurrence among pregnant women. During this wonderful period, the load on the spinal column increases, and the growing uterus increases pressure on the internal organs, which leads to pinching of the intercostal nerve.
In this case, the pain is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- The pain radiates to the heart area, stomach and shoulder blades;
- Painful, localized in the intercostal space on the left;
- As pregnancy progresses, the course of the disease worsens.
Treatment in this case is symptomatic and only after consultation with a doctor. Often, the disease goes away on its own after childbirth.
Causes and symptoms of pain due to neuralgia
The heart and nerves are closely connected to each other. In accordance with the activation of the sympathetic or parasympathetic part of the nervous system, the myocardium changes the pace of its work: sympathy increases the heart rate, parasympathetic decreases it.
The mechanism of chest pain of neurological origin is as follows: stress negatively affects the sympathetic nervous system, through mediators it increases the level of adrenaline, norepinephrine, cortisol, which in turn aggravate stress.
It turns out to be a kind of vicious circle, the essence of which is vasospasm. If the strength of stress hormones is so great that the coronaries are involved in the process, there is a feeling of heaviness behind the sternum, aching, pressing pain in the left half of the chest. Frequent attacks lead to hypertension, angina pectoris, myocardial ischemia resulting in a heart attack with cardiac arrest.
There are several reasons why your heart hurts after another stress. The main ones are presented in a table.
| Cause | Characteristic |
| Heartfelt | |
| Cardioneurosis | The standard vegetative-somatic reaction of the body to fear, overwork, stress, insomnia, business trips, depression, alcohol, smoking, drugs, due to the individual characteristics of a person’s psychotype, is perceived acutely by a person and provokes panic attacks. If the sensations resemble a fire in the heart or shackles of ice, if it freezes or is pinched in a vice, if a lump appears in the throat, you should urgently consult a doctor, as these are harbingers of life-threatening conditions. |
| Hypertension | With constant stress, there is a risk of developing hypertension: vascular spasm leads to an increase in blood pressure, disrupts normal nutrition, oxygen supply to tissues and organs, which is accompanied by arrhythmia, shortness of breath, and pain in the heart area. |
| Angina pectoris | Myocardial ischemia, which occurs against the background of narrowing of the lumen of the coronary vessels due to physical effort or stress, is the cause of angina. Discomfort usually goes away without additional effort after a short rest, but frequent attacks indicate myocardial decompensation and the development of a pre-infarction state. The work of the heart against a background of stress should be treated with great caution, since any ischemia precedes a heart attack. |
| VSD | Vegetative-vascular dystonia is the cause of fluctuations in blood pressure due to impaired vascular innervation. Constant changes in blood pressure lead to circulatory disorders, hypoxia, and hemodynamic disorders, which manifest themselves as chest pain after stress. |
| Arrhythmias | Disruption of sinus rhythm of any origin (including due to stress) leads to disruption of the blood supply to internal organs, primarily the heart and brain, which can lead to a heart attack or stroke. |
| Extracardiac | |
| Hormonal changes: puberty, menopause, pregnancy, menstruation | An imbalance of sex hormones: estrogens, progesterones against the background of stress, changes in the functioning of the nervous system leads to metabolic dysfunction, the development of hypoxia, insufficient nutrition of heart tissue with the development of pain. |
| Infections | Bacteria or viruses cause inflammation in the body, which automatically worsens a person’s general well-being and makes him nervous, while microbial toxins spasm blood vessels, causing increased blood pressure and poor circulation with all the attendant consequences. |
| Occupational hazards | Vibration, varnishes, paints, toxic chemical compounds, vapors, poisons, fertilizers - everything affects the functioning of the nervous system and toxically paralyzes blood vessels, causing metabolic imbalance, disrupts hemodynamics with a response in the form of pain in the heart of a different nature or neuralgia. |
| Sexual disorders: decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, impotence, frigidity | Sexual dysfunction is one of the main causes of constant stress, which causes spasm of the arteries, deterioration of blood supply to tissues, and hypoxia. Such experiences often cause heartache. |
Stress affects the sympathetic nervous system, therefore, when chest pain begins against this background, the following symptoms appear: shortness of breath, aggravated by cough; dry mouth and viscosity of saliva; blood pressure surges; hyperhidrosis of the palms; "goose pimples"; tachycardia.
Many people feel pressing pain in the heart area, tremors in their hands, and their pupils dilate. Depending on the clinic, there are:
| Type of pain | Characteristic |
| Classic (typical) | Moderate pain, long-lasting, displaced to the apex of the heart, does not require restrictions |
| Sympathoadrenal | The essence is the effect of stress hormones, the pain itself is protracted, intense, and can be relieved with sedatives (Persen, Novopassit) |
| Vegetative | The heart begins to ache after stress, a diffuse feeling of discomfort occupies the entire chest, muscle tremors, sweat, and frequent urination appear; treated with tranquilizers (Mebicar, Phenazepam) |
| Angiospastic | Short-term pain, non-localized, gives almost no negative sensations, relieved by Valerian |
| During physical activity | The pain occurs when walking, does not stop after stopping, but does not affect the general condition |
Let's sum it up
With proper and timely treatment, thoracic intercostal neuralgia is completely curable. Prevention of this disease is to prevent the development of “root cause” diseases, as a result of which neuralgia subsequently occurs. It is also necessary to constantly lead a healthy lifestyle in order to strengthen the immune system and maintain a healthy state of the body.
It is possible to get rid of such a disease, but it is worth starting treatment on time - this will help you forget about the discomfort as early as possible. You should not prescribe treatment methods on your own, so as not to worsen your health condition even more.
Prevention measures
To prevent the development of neuralgia in the heart area, you need to give up bad habits, lead an active lifestyle, eat a balanced diet and exercise. Compliance with these rules will significantly reduce the likelihood of developing pathological changes in the human body.
Neuralgia in the heart area manifests itself as a result of damage to many organs and systems. If they are present, it is recommended to go to a clinic or hospital for consultation with a specialized doctor. He will help diagnose the underlying disease and also prescribe effective treatment tactics, which will preserve the patient’s health.
There are a number of preventive actions that reduce the manifestations of the disease to a minimum.
In this case:
- It is necessary to avoid hypothermia, drafts, heavy lifting, and alcohol consumption.
- Regular examinations by a doctor are required.
- Hardening the body and strengthening the immune system will also be a good help in the prevention of intercostal neuralgia.
Despite the fact that the disease is not dangerous, quality treatment is required when the first symptoms appear. Thanks to this, it is possible to avoid many unpleasant consequences.
18.01.2020
Difference from cardiovascular pathologies
Here, a special role belongs to determining the nature of the pain. It is a thorough analysis of the patient’s condition that allows us to identify its cause. It should be noted that, despite the fact that pain is the main manifestation of both neuralgia and cardiovascular pathologies, its nature is different in different cases. So, in the first case, the condition differs in duration. The pain in most cases is constant, lasting for a relatively long time. Accordingly, it cannot be eliminated using traditional means, such as Nitroglycerin. If we talk about any cardiovascular disease, the pain is most often short-term and periodic. When taking the same drug “Nitroglycerin” it is usually suppressed. In addition, pain in cardiovascular pathologies does not increase during body movement. At the same time, there is a change in pressure and rhythm. Neuralgia in the heart area, the treatment of which will be described below, is not accompanied by these manifestations. Pulse and blood pressure remain normal.