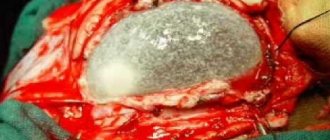
A subependymal cyst in a newborn baby is a benign tumor. Like other similar formations, it is a cavity filled with liquid. The cyst has a dense shell that does not allow fluid to escape.
This formation occurs as a result of changes in the medulla located in the area of the walls of the ventricles (lateral). Its appearance is due to a natural replacement reaction to the death of brain tissue due to hypoxia.
This pathology is quite common. According to statistical data, it is observed in 10 percent of newborns born during a difficult birth. It may be asymptomatic or have severe neurological manifestations. Also, this disease is sometimes combined with cysts located in the vascular plexuses.
How does a cyst form?
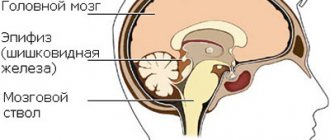
The source of intracerebral cyst creation is ependyma. It is neuroepithelium. Ependymal cells are a thin membrane lining a narrow canal that is central to the spinal cord and the walls of the cerebral ventricles.
During a pathological process that leads to the appearance of a new formation, the activation of cellular hyperplasia begins. Cell division also slows down. The cyst can develop on top of the ependyma (that is, in the gastric cavity) or grow under its layer.
Various negative effects can disrupt the normal blood flow of some brain areas. Lack of nutrients and oxygen leads to the formation of a necrosis zone. As a result, after the tissue dies, a cavity appears that fills with liquid. This is how a cyst is formed.
Causes
This pathology develops due to the lack of oxygen that the child experiences while still in the form of a fetus while in the mother’s womb. Doctors also identify other factors that can lead to the appearance and development of this disease.
A subependymal cyst of the brain can occur for the following reasons:
- the presence of infectious diseases (bacterial and various viruses),
- anemia,
- low amount of iron in red blood cells,
- multiple pregnancy type,
- the baby getting injured during childbirth,
- conflict of Rh factors,
- placental insufficiency,
- powerful toxicosis experienced by a pregnant woman in the early stages.
Also, the impetus for the emergence of such pathologies at any time can be a brain injury, a disease of the central nervous system (encephalitis, etc.) and poor heredity.
Factors that provoke the appearance of cysts in newborns may also include intoxication of the pregnant woman’s body, in particular due to excessive intake of alcoholic beverages and medications, severe stress conditions, terrible ecology and other reasons.
Causes and treatment of pseudocysts in the head of a newborn
A cerebral pseudocyst in newborns is a small round cystic formation that contains cerebrospinal fluid. Pseudocysts are localized at the border of the head of the caudate nucleus and the optic thalamus, in the area of the bodies of the lateral ventricles of the hemispheres or near the lateral angles of the anterior horny parts of the cerebral hemispheres. Why does education appear?
Catalysts for occurrence
Pseudocysts in infants are formed under the influence of various factors. However, in most cases, the cause of the appearance is disturbances during prenatal development of the fetus.
Causes of pseudocyst formation:
- lack of oxygen;
- cerebral hemorrhages;
- deficiency of macro- and microelements, which leads to circulatory disorders$
- infections that a woman suffered while pregnant.
The most dangerous formation is considered to be a subependymal pseudocyst, which is formed as a result of hemorrhage or trauma during childbirth.
How to cure a pseudocyst?
With normal size of the formation, it is not advisable to treat infants with this diagnosis, since in most cases they resolve on their own in the 1st year of life. Pseudoformation does not in any way affect the physical, mental and emotional state of the child.
Children who are found to have a pseudocyst are registered with a neurologist, who will monitor the growth of the formation and prescribe appropriate treatment. In most cases, with this diagnosis, drugs are prescribed to improve blood circulation in the brain and antihypoxants, such as Mildronate, Mexidol.
Hyperactive children are prescribed drugs Pantogam, Glycine. To improve the condition of the neuro-reflex and musculoskeletal system, patients are prescribed massage. The procedure is performed by qualified massage therapists in the absence of contraindications.
If a formation is detected, the neurologist prescribes a repeat examination for the patient in order to determine whether it is growing or not.
If by the second visit to the doctor the cyst remains the same size or has increased, the baby is prescribed therapy, which is designed to prevent headaches and seizures.
At an older age, the pseudocyst is examined using MRI and CT. Thanks to these studies, it is possible to verify the absence of a tumor.
If by the end of the first year of life the baby’s formation has not resolved, it means that the diagnosis was made incorrectly and doctors should examine the child again. For large lesions that put pressure on the brain, medications are prescribed to prevent seizures.
If the formation continues to grow, surgical intervention is resorted to. The cyst is removed through craniotomy, shunting and endoscopy. The best method is endoscopic, however, it is only suitable for some cystic formations. If there is no treatment, the patient begins to have seizures and neurogenic disorders.
Localization and symptoms
Neoplasms of the cystic type appear in areas where tissue necrosis occurs. They can form both in the left cerebral lobe and on the right. Very often, cysts arise in the area of the left ventricle or, conversely, the right. These are cavities located in the brain area filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Symptoms of such a cyst appear depending on its location, rate of increase and current size.
Each area of the brain is responsible for specific functions. When tissues are compressed by a tumor, disturbances occur in the functioning of certain areas:
- The temple area is responsible for hearing. When exposed to a cyst, it may disappear completely or weaken significantly.
- The cerebellum controls overall coordination of movements. If pathology occurs in this area, problems may occur when sitting, moving, holding objects, etc.
- The back of the head area is responsible for vision. If problems arise in it, the baby is at risk of blindness, significant myopia or diplopia.
- The pituitary gland produces various hormones. Among them is growth hormone. It is necessary for infants for their further development. If the tumor affects it, the child may be at risk of dwarfism, especially if there are genes that can affect this factor. In such a situation, the cyst acts as a provoking element that triggers a similar process.
- The frontal lobe is responsible for motor functions. Its defeat can lead to disturbances in this area. Problems with speech formation are also possible: babbling or humming appears late.
If we talk about general symptoms, they include:
- high anxiety,
- lack of weight gain and even weight loss,
- insomnia,
- powerful regurgitation,
- lack of desire to breastfeed,
- pathological processes associated with muscle tone,
- continuous or constant screaming for no reason,
- excessive physical activity. There is tremor in the limbs,
- epilepsy attacks,
- loss of consciousness observed regularly, which can even lead to coma,
- pathologies noticed in the fontanel area. It may feel tense or swollen.
Brain pseudocyst in a newborn: causes and diagnosis
A pseudocyst found in the head of a newborn does not necessarily affect brain function or lead to problems with the psyche or mental abilities. On average, one out of a hundred babies is diagnosed with this pathology.
Most often it is found between the head of the caudate nucleus, the optic tubercle, and the lateral angles of the lateral ventricles of the brain. It is assumed that the formation of a pseudocyst is a consequence of exposure to unfavorable factors on the fetus during embryonic development.
In most cases, pseudocystic formation resolves in the baby without outside help within the first twelve months.
What is a cerebral pseudocyst in newborns?
To understand what a pseudocyst is, imagine a cavity filled with cerebrospinal fluid or other liquid, surrounded by a thin, clear membrane.
This brain pathology is a malformation of intrauterine development. It can appear in vascular tissue or meninges during embryogenesis or as a consequence of complicated childbirth.
The bones of the baby’s skull are still mobile and, when displaced, can compress the brain tissue during childbirth, leading to hypoxia or small ruptures of blood vessels.
What is the difference between a pseudocyst and a cyst?
There is a not entirely correct idea that differentiation of a cerebral pseudocyst is possible by the presence or absence of an epithelial layer inside it. However, this is a controversial point, since this layer is often absent inside a real cyst.
In addition, ultrasound, which is used to determine the nature of the cystic formation, does not make it possible to carefully examine the membrane and its walls from the inside. Also, shape and size are not indicative of diagnosis: they differ in variety both in the case of a pseudocystic cavity and in a true cyst.
In domestic medical practice, the concepts of cyst and pseudocyst are even used as synonyms in relation to any hollow structure. These two types of pathology differ in structure and area of occurrence.
The main signs indicating that the formation in the lateral ventricles of the brain is a pseudocyst are:
- location. It is found in the following areas: the lateral angles of the anterior horn, the lateral ventricles, the area bordering the optic thalamus and the caudate nucleus;
- the causes of formation, which lie in intracerebral bleeding, lack of oxygen. Hereditary factors are not involved in the mechanism of its development.
Subependymal pseudocyst in infants is formed as a result of birth injuries. It develops under the ependyma, which lines the inside of the ventricles and the spinal canal, in which cerebrospinal fluid accumulates, washing the brain tissue.
The size of this pathology varies from two to ten millimeters. Pseudocysts are found in the ventricles on both the left and right sides.
Small formations resolve on their own after a year. But those that are larger are able to compress the surrounding tissues and do not go away for a long time, up to the age of six. With different locations, the formation can have different effects on the brain, causing a variety of symptoms:
- compression of the occipital area affects vision;
- effects on the cerebellum may impair motor functions;
- exposure to the temporal zones worsens hearing acuity;
- a large pseudocyst pressing on the pituitary gland can cause hormonal imbalances.
Reasons for education
It is still not possible to find out the exact reasons for the appearance of a cerebral pseudocyst in a newborn. Practice and experience make it possible to outline the range of circumstances influencing the formation of cyst-like cavities.
The main factors causing the appearance of a bubble are injuries and various adverse consequences of childbirth. The reasons for the formation of pseudocysts include the following:
- intracerebral hemorrhage or brain hypoxia in the fetus;
- stress, excessive physical and emotional stress of a pregnant woman;
- infectious diseases caused by herpes virus, chlamydia, cryptococci and other pathogens;
- deficiency of some elements important for the normal development of the embryo, impaired blood circulation in the brain.
If the anomaly does not affect the lateral ventricles and periventricular region, the pathology usually does not manifest itself in any way.
The development of neoplasms of the choroid plexus is recorded by ultrasound, starting from the ninety-eighth day of embryogenesis.
Such a pseudocyst does not pose any threat to the fetus. Essentially, this is a temporary stagnation of cerebrospinal fluid that nourishes brain tissue.
Liquor is retained and forms bubbles in the rudiment of the central nervous system, where it is produced. The cavities disappear on their own over time, mainly by the one hundred and ninety-sixth day of pregnancy.
There are versions according to which the cause of their development is a hereditary factor. Mutations in genes lead to stagnation of fluid in cyst-like blisters.
At the same time, the baby is found to have congenital genetic pathologies that have a much greater significance and impact on the baby’s development than a pseudocyst, which does not pose any danger.
You need to take the situation seriously if, along with a pseudocystic cavity, the baby is diagnosed with the following disorders:
- hernia, hematoma of the diaphragm;
- Edwards syndrome;
- delays in the development of the upper jaw;
- disruption of the formation of the anterior peritoneal wall;
- hydrocephalus;
- neural tube pathologies;
- disorders in the development of the foot.
Be that as it may, you should remain calm and observe how the baby develops, intervening only if the formation grows and does not resolve.
Is a cerebral pseudocyst dangerous for a child?
The origin of a cerebral pseudocyst in a newborn is not related to genes. It is most often caused by birth trauma, which affects the walls of the baby’s skull and brain tissue, and oxygen starvation.
As a rule, pseudocysts do not pose a threat to the child’s life and normal development. Usually it is enough to be observed by a neurologist to eliminate the consequences of birth injuries. Within twelve months, as a rule, the formation in the baby’s brain resolves on its own.
Otherwise, a true cyst is diagnosed (no more than in five percent of cases), which can already pose a certain danger to the child.
Depending on its location, type, and growth tendency, the doctor selects a treatment method. Particular attention should be paid to subependymal cavities that arise after extensive intracerebral bleeding.
What to do if a pseudocyst is detected in a newborn
In view of various controversial information regarding the need for some kind of therapy for a cerebral pseudocyst in a newborn, it is important to figure out whether something needs to be done.
Usually, during the first year of life, the child is periodically examined to make sure that there is no tendency for the cavity to increase, it decreases gradually, and there are no signs of pathology.
In most cases, pseudocyst does not affect the development of the baby; there are no specific medications for brain pseudocyst. To improve cerebral circulation, the doctor may prescribe a course of treatment with appropriate medications.
A year later, the condition of the pseudocystic structure is checked. If it is discovered that it has grown, intracranial pressure has increased, it is necessary to begin treatment.
This can be medication, manual therapy, and in rare cases, when the size of the formation is significant and there are pronounced symptoms, endoscopic surgery or bypass surgery.
In this case, we are dealing with a true cyst that does not disappear on its own. Anticonvulsants, enzymes to normalize metabolism, vasodilators, and nootropics can be used. To improve neuro-reflex reactions and the development of the musculoskeletal system, a course of therapeutic massage is carried out.
It should only be performed by a professional massage therapist. It is better not to get carried away with homeopathy and traditional medicine, but to seek professional medical help.
A special case is the cystic cavity in the choroidal plexus, located under the large fontanel, which prevents it from closing on time due to its impressive size (normally, the fontanel in babies closes no later than by one year). The pathology may be accompanied by:
- uncontrollable limb spasms;
- cramps with a sudden change in daily routine or with a cold;
- lethargy, anxiety;
- problems with coordination;
- cephalgia;
- damage to the optic nerve.
Only half of such formations disappear on their own. They are necessarily removed by a neurosurgeon after a comprehensive examination.
Source: https://golovnie-boli.com/deti-i-beremennye/psevdokista-golovnogo-mozga-u-novorozhdennogo.html
Types and forms
Based on its size, the subependymal cyst is classified into:
- small. They are less than 3 cm. Usually such neoplasms do not threaten the child. They often resolve on their own and only rarely require treatment. It is quite enough to be examined regularly to monitor the development of such formations,
- big. The larger the tumor, the higher the risks for the baby. Such cysts require active treatment, and in some cases, surgery.
These tumors can also be:
- not increasing. If they are small and do not grow, then the chance of independent recovery is very high,
- increasing. In such cases, intensive treatment and even surgery may be necessary.
Also, such formations differ in the number of chambers:
- single-chamber. They pose less danger and are easier to treat than others,
- multi-chamber. These cysts are more difficult to diagnose (symptoms may resemble other diseases) and much more difficult to treat.
Features of differentiation
Since it is difficult to distinguish a cerebral pseudocyst in newborns from a true tumor, doctors carefully examine each tumor in order to identify the most characteristic common signs for one and the other disease.
Signs of a pseudocyst:
- typical localization is located in the ventricle of the brain. In rare cases, pseudocysts in the head of newborns can be found between the caudate horn and the center responsible for visual function. All other localizations indicate the presence of a true cyst, since it is located in other parts;
- the origin of the cyst - it is always an acquired defect, is not inherited and is not congenital. If a baby is diagnosed with a multi-chamber pseudocyst of the brain, then it usually indicates a ruptured vessel and hemorrhage, and with oxygen starvation during childbirth, a tumor appears in the ventricles of the medulla.
A more accurate diagnosis can only be made after an ultrasound examination.
The concept of pseudocyst
With intensive development of the brain inside the womb, the vacated zone in the area of the vascular plexuses is filled with a certain fluid (it is called spinal fluid).
It is as a result of these processes that a subependymal pseudocyst appears. It is absolutely safe. Most often, such a formation is diagnosed during an intrauterine ultrasound, when the condition of the fetus is examined.
In most cases, it resolves on its own before birth. Otherwise, as doctors explain, the mother experiences a herpetic type infection.
Pseudocyst in the head of a newborn baby
The most valuable thing in the life of each of us is children, which is why their health should be monitored from birth, so as not to encounter numerous problems and complications that worsen the lives of children and parents.
Pseudocyst of the brain in newborns, according to experts, is the safest complication that can appear during childbirth.
Approximately one in 100 cases is diagnosed with this disease.
The appearance of such a formation does not entail serious consequences, but requires close monitoring by doctors. The pathology detected in infants is not reflected in the functioning of the brain. Moreover, it does not affect mental abilities or the appearance of mental problems.
The concept of pseudocyst
Formations of the cystic type are peculiar cavities, characterized by a round shape and having a small size. They are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (exudate or other substances). The bulges are concentrated on one or both sides at the same time.
The mechanism of development of this pathology in infants has not been fully studied to this day.
It may happen that, in the presence of alarming prognosis, a baby is born absolutely healthy, and a second newborn is born with damage to the nervous system, with completely normal prognosis.
With the rather rapid intrauterine development of the brain, the vacated territory located in the area of the choroid plexuses is filled with a special fluid (cerebrospinal fluid). These are the processes that are observed during the development of a pseudocyst. It is safe for the life of the baby and is most often detected during an ultrasound scan of the fetus in the womb.
A large percentage of cystic formations resolve before birth. If this does not happen, then experts explain this by the presence of a herpes infection in the mother.
Reasons for appearance
The causes of a cerebral pseudocyst in a newborn baby can be very different. In most cases, the etiology of the appearance is associated with disorders observed during prenatal development of the fetus.
As a rule, the stimulating factors are:
- hemorrhages in the brain;
- hypoxia;
- disruptions in the functioning of the circulatory system caused by a lack of nutrients for the full development of the baby.
The most dangerous is the subependymal pseudocyst, which appears as a result of hemorrhages. In some cases, pathology occurs due to birth injuries.
Symptoms
As a rule, true and pseudocysts in a newborn do not manifest themselves clinically. The pathology does not interfere with the full development of the infant, as well as the adult child. The disease is detected during intrauterine examinations, as well as during examinations after childbirth.
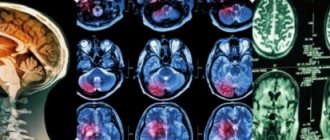
Diagnostics
Ultrasound is most often used to confirm the presence of a false mass in the brain area. This method is the most popular, but it does not provide the opportunity to conduct a thorough inspection of the walls, as well as the internal space of the existing cavity. The emphasis is on specific areas where false benign formations most often form.
Particular attention is paid to the cerebral hemispheres. Also, emphasis is placed on the lateral ventricles, the area where the head of the nucleus (caudate) is located and some other areas. Features of the location of the pathology make it possible to distinguish it from a true cyst.
The presence of formations is confirmed by echo signs of a subependymal pseudocyst in the area of the right as well as the left ventricle. The use of ultrasonic waves is effective only in cases where the baby’s age has not reached 1 year. In this case, the fontanel located on the head is not covered by bones.
A newborn is examined for the presence of a pseudocyst if:
- the child was born prematurely;
- the birth was accompanied by serious complications;
- observation of insomnia, excessive tearfulness and anxiety in a newborn;
- the presence of convulsive muscle contractions, dizziness and other neurological signs.
When conducting research, the following methods for identifying the disease can be used:
- Doppler encephalography.
- Neurosonography.
- MRI and computed tomography.
- Cerebral scintigraphy and some other techniques.
If there is a suspicion that the fetus has genetic disorders, a chromosomal analysis of the fluid (amniotic fluid) may be prescribed. This intervention is invasive and is therefore used in very rare cases.
Difference between cyst and pseudoplasm
False formations that appear in the brain area have significant differences from the true ones. They are distinguished by:
- Place of appearance. In most cases, pseudoformation is located in the zone of the subcortical nuclei, or rather between them. The pseudocyst is localized near the lateral ventricles or in the area of the cerebral hemispheres.
- Reason for appearance. The disease can be secondary or acquired. An accurate diagnosis is made through instrumental diagnostics. If a specialist has directed you to undergo an examination, you should not abandon this step, since timely detection of pathology will prevent the occurrence of serious violations.
Is a pseudocyst dangerous and why?
The existing pseudocyst in the head of a newborn in all cases has a second cause of development. The following reasons may act as a catalyst for the appearance:
- lack of oxygen;
- problematic childbirth;
- presence of injury.
A false cyst in an infant is not dangerous to health. This pathology should cause alarm in cases where the formation rapidly increases in size.
There is no need to perform any specific therapeutic procedures in the treatment of pseudocysts in infants. All that is necessary is to regularly visit a neurologist and carry out restorative therapy designed to combat the emergence of possible complications that often appear against the background of injury.
If after 12 months the formation and the baby have not gone away, doctors diagnose a true cyst. In such situations, you should be observed by a neurologist throughout your life.
Treatment
The course of pathology observed in a newborn child should be monitored by a pediatric neurologist. The following techniques can be used during therapy.
Medicines
As a rule, doctors prescribe a number of drugs to children, the action of which is aimed at improving blood circulation in the brain, and also prescribe antihypoxants:
- Mexidol;
- Cytoflavin;
- Vitamins belonging to group B;
- Mildralex.
If hyperactivity is observed, the use of drugs such as:
- Glycine;
- Pantocalcin, as well as Pantogam.
To strengthen the musculoskeletal system, you should attend massage sessions, but only if they are recommended by your doctor.
If the false cyst was not subject to resorption during the first year of the child’s existence, and it increases in size, surgery will be required. Removal of the formation is carried out through craniotomy using endoscopy and shunting techniques.
Surgery
Endoscopic surgical procedures are by far the best ways to treat tumors in children. But such operations are not carried out in all cases.
If your baby has been diagnosed with a cyst of the septum pellucida developing in the brain area, then this technique is perfect for treatment.
The treatment is not accompanied by complications and avoids excessive trauma to the small patient.
The recovery period after surgery to remove a cyst is different for each case, and depends on the general well-being and state of health of the child.
Folk remedies
To improve the well-being of children with large cystic formations in the brain, in addition to the use of medications, folk remedies can also be used. The most effective are the following recipes:
- a decoction made from hawthorn fruits. The liquid is taken internally to strengthen the nervous system. This product helps improve baby's sleep;
- horsetail, cinquefoil, as well as capitol and violet are distinguished by their ability to lower intracranial pressure;
- Hemlock is endowed with excellent absorbent properties;
- herbal infusions for taking soothing baths.
To prepare a decoction that has a calming effect, you will need to take raspberry leaves, yarrow, as well as chamomile, licorice rhizome and calamus.
The components are used in equal proportions and mixed. Composition in the amount of 2 tbsp. should be placed in a container, pour boiling water (0.5 l) and leave for 8 hours.
After this, the liquid is filtered and added to the baby’s bathtub.
Before using traditional medicine in the fight against pseudocyst, you should consult with your doctor.
Source: https://kistaoff.ru/mozg/psevdokista-u-novorozhdennogo
Treatment methods
Therapy for a subependymal cyst, namely the selection of a technique, will depend on the characteristics of the pathology. The doctor may prescribe resuscitation procedures if disturbances in the functioning of important organs are observed. If children are born in hypoxic conditions, they may need
- artificial ventilation,
- correction of biological constants, thanks to the use of infusion treatment,
- detoxification procedures carried out in intensive care conditions.
If no threats to the life of the newborn are observed, but there are symptoms indicating damage to the brain, the specialist may resort to drug treatment, which includes the use of:
- nootropic drugs (nicergoline, piracetam, etc.), the work of which is aimed at improving metabolism in tissues,
- minerals and vitamins,
- diuretics if there is a risk of brain swelling or intracranial hypertension,
- anticonvulsants in the presence of seizures (Depakine, carbamazepine, etc.).
Treatment for infection involves the use of immunotherapy using immunoglobulin medications (pentaglobin and a number of others). In addition, antiviral pharmacological products are prescribed, which provide positive results in almost all cases.
Observation of an asymptomatic subependymal cyst is usually not accompanied by treatment. It is enough to carry out regular examinations, visiting a neurologist, and also undergo prescribed diagnostic measures (MRI or ultrasound). In some cases, if there is an asymptomatic cyst, specialists may prescribe the use of medications (nootropics and vitamins).
Is a cerebral pseudocyst dangerous in a newborn and how to get rid of it?
There is still no consensus on how a cerebral pseudocyst in a newborn differs from a regular cyst. As a rule, the main criterion is the presence or absence of epithelial lining. However, not all experts agree with this term. What is hidden behind the concept of pseudocyst, is this deviation dangerous for a child?
Why do pseudocysts appear in the brain of a baby?
The causes of cerebral pseudocysts in infants are very different, but basically the etiology of the formation comes down to disorders associated with prenatal development of the fetus. Often the catalyst is:
- Hypoxia.
- Brain hemorrhages.
- Circulatory disorders due to insufficient nutrients for the development of the child.
Particularly dangerous is a subependymal pseudocyst of the brain in newborn infants. The disorder always occurs against the background of hemorrhage, sometimes as a result of birth trauma.
The causes of the formation of a subependymal pseudocyst are always associated with an acquired during pregnancy rather than a congenital factor.
Why is a pseudocyst dangerous?
A pseudocyst always has a secondary cause of development. The catalyst for the occurrence is injury, lack of oxygen, difficult childbirth, and not disturbances in the functioning of the body.
No specific treatment is required for cerebral pseudocysts in infants.
It is enough to regularly visit a neurologist and undergo restorative therapy aimed at combating possible complications due to injury.
If a year after birth, the formation does not go away in an infant, a true cyst is diagnosed. In this case, a lifelong consultation with a neurologist will be required.
In most cases, true and false cysts do not manifest themselves clinically and do not interfere with the normal development of a child or an adult.
The danger arises when there is a tendency towards a rapid increase in formation, which occurs no more often than 1-5%.
How to identify a pseudocyst
The most informative and safe method for diagnosing abnormalities in a baby is an ultrasound of the brain. Indications for an ultrasound examination are birth trauma, fetal hypoxia and any disturbances in the child’s behavior. Excessive tearfulness, lack of sleep, etc.
Having discovered cerebral vascular pseudocysts in newborns, the neurologist will prescribe a repeat examination to monitor the dynamics of growth. During the repeat examination, attention is paid to a decrease in the volume of the tumor.
If the size remains the same or there is a tendency to increase, a course of therapy is prescribed to prevent the occurrence of possible complications: seizures, headaches. As you get older, the diagnostic procedure may be replaced by an MRI.
Difference between a cerebral cyst and a pseudocyst
Although some medical reference books indicate that the main difference between diagnoses is the presence of an epithelial lining, not all experts agree with this.
Pseudocysts of the lateral ventricles of the brain are determined by the following criteria:
- Localization - pseudoformations are always located in the area of the lateral corners of the anterior horn or the lateral ventricles of the brain.
A cavity may develop between the optic thalamus and the caudate nucleus. In other cases, we are talking about a true cyst. - Etiology - the cause is always secondary or acquired in nature and is not determined by genetic predisposition.
Thus, a multi-chamber pseudocyst occurs due to hemorrhage; during fetal hypoxia, the lateral ventricles of the brain are damaged.
Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis and determine a true cyst from a pseudocyst after an ultrasound scan.
How to treat a pseudocyst of the brain of the head
Treatment of pseudocysts in children is not required. Usually education occurs independently during the first year of life. The development of the child: his mental, emotional and physical state is not affected. To be on the safe side, a neurologist may prescribe Actovegin or a similar drug that improves blood circulation in the brain.
But if during the first year the cystic formation remains unchanged, intracranial pressure has increased, medicinal, if indicated, manual therapy will be required. Massage for pseudocyst is prescribed to improve the neuro-reflex and musculoskeletal system. It is carried out exclusively by a specialist.
There are contraindications.
What to do if the pseudocyst has not resolved
In this case, the diagnosis of pseudocyst was made incorrectly. Errors are rare, but they do occur. After determining the exact diagnosis, the doctor determines the symptoms of the formation and determines what consequences the disease led to.
The likelihood of affecting the development of the child, the occurrence of convulsions and seizures is minimal, but if the cystic cavity exceeds the permissible size, anticonvulsants are prescribed. The main task of the specialist is to determine the causes of the formation. Therapy is mainly directed against the catalysts of deviations and combating the symptoms of the disease.
The course of treatment is aimed at improving blood circulation and metabolism. Homeopathy can be beneficial, but it is prescribed with extreme caution.
Consequences
If you do not start treatment of a cystic formation in a timely manner, or if you detect a bulge that is increasing in size too late, you may face serious consequences. For example, an enlarging cyst can put pressure on nearby tissue.
Focal signs will begin to manifest themselves significantly. If a growing formation is detected in the back of the head, minor vision problems may initially appear. As the benign lesion increases, the child may experience vision loss.
A cyst affecting the brain can lead to intracranial pressure, which is accompanied by such manifestations as:
- regular severe headaches,
- a feeling of tightness in the head,
- the appearance of apathy and weakness,
- fast fatiguability
- fainting, etc.
A cystic formation that has reached a large size requires immediate treatment. If it is not produced, the pathology will affect the formation of the cranial bones (ossification of the fontanel in newborns will not occur). In addition, problems with mental and physical development may occur. In some cases, the course of the disease was fatal.
Diagnostics
Ultrasound is recognized as the most accurate and safe diagnostic method for detecting pseudocysts in the head of newborns. Ultrasound diagnostics is performed for all patients who suffered hypoxia during childbirth, were injured, received a low Apgar score, or doctors discovered behavioral defects in the baby. Indications for diagnosis include sleep problems, moodiness, and frequent mood swings.
If a pseudocyst is once detected in a newborn, a specialist neurologist will monitor the neoplasm over time, since it is extremely important to monitor the increase in the size of the pseudocyst in the newborn.
The child’s secondary consultation mainly has one goal – to find out the dynamics of the disease. If the child’s education remains the same or grows, drug support is required. The objectives of conservative care are to eliminate the worsening of the situation , for example, the appearance of migraines and convulsions. As the baby grows, ultrasound diagnostics are replaced by magnetic resonance imaging - this way the head is better visualized.
Prevention
The development of such a pathology as a subependymal cyst can be avoided; to do this, all causes that can lead to hypoxia, as well as a number of other disorders, should be excluded:
- a pregnant woman should wisely diversify her diet, replenishing it with a large amount of vitamins and other useful substances,
- avoid drinking alcoholic beverages,
- quit smoking.
Preventive measures during pregnancy should be as follows:
- begin immediate and timely treatment of any infectious diseases,
- Avoid exposure to various toxic substances on the body.
If you follow these rules, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing this pathology. In this case, the fetus will develop fully and complications will be avoided.
Reviews about pathology
Ekaterina, 25 years old:
“It so happened that my baby was born in hypoxia, as there was a double entanglement of the umbilical cord. She was born, but never cried. Immediately after birth, my girl was taken to intensive care, and she spent three days on a ventilator. Then the machine was turned off, and she was already breathing on her own. Fortunately, this condition did not last too long and did not lead to serious consequences.”
Svetlana, 24 years old:
“I am the mother of two wonderful twins. Unfortunately, when I wore them, I had moderate anemia. I spent half of my pregnancy on pills, but my hemoglobin levels were not really able to increase. The children were born weak, and one was diagnosed with a cyst in the head. So far we haven't seen any deviations. The pediatrician said that after a year I will have to undergo a bunch of specialists and various examinations. But we do not despair and believe in the best.”