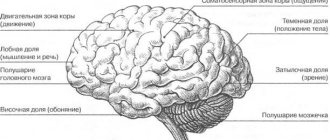
Diseases and disorders
The most common consequences of any stroke pathology are movement disorders (paralysis) of the right or, conversely, left
It is very important for modern medicine to combat brain pathologies in newborns; this task is extremely
Ivan Drozdov 07/27/2019 3 Comments Pressing pain in the head can appear in any of its
Among human diseases, brain diseases remain among the most difficult to cure, and some
Image copyright Getty Are we always in control of our thoughts? As a BBC Future correspondent found out
Perseveration Doctors call perseveration a behavioral disorder expressed in the repeated repetition of certain actions. Repetition can
Reactive psychoses Systematics: affective-shock reactions (F0); reactive depression (F32 single episode, F0); reactive paranoid
A pinched nerve in the calf is not an independent disease, but a symptom that indicates
Reactive meningitis is an extremely dangerous infectious disease that affects the spinal cord and brain.
What is vagotonia? In short, this disease is a dysfunction of the vagus nerve. It is located