Ivan Drozdov 07/27/2019 3 Comments
Pressing pain in the head can appear in any part of it. It covers the back of the head and eyes, extends to the temples and frontal lobes. The pain feels like squeezing the head with a steel hoop or a tight hat; the duration of the attacks is mostly long-lasting. The appearance of a pressing headache can be caused by temporary non-pathological factors and serious diseases. In the latter case, it is necessary to contact specialists to identify the cause of pain and undergo drug treatment.
Types of pain syndrome
Why is there a pressing pain in my head?
This symptom can indicate a variety of pathologies. Only a doctor can identify the exact etiology of the pain syndrome. However, if you listen to your feelings, you can roughly guess the possible cause of the discomfort. Pressing pain in the head can be divided into several types depending on their etiology:
- neuralgic;
- vascular;
- associated with impaired outflow of cerebrospinal fluid;
- infectious;
- pain of tension.
Next, we will consider in detail the different types of pain syndrome.
Reasons for appearance
You can give a whole list of reasons why a pressing headache may occur. If you feel pressure on your head, this may be due to the following factors:
- Problems with hormones in the body, various hormonal imbalances, menopause, menstruation (pregnancy, exacerbation of a chronic disease, age-related changes, etc.).
- Getting a head injury. This can be not only a traumatic brain injury, but also any other types of trauma to the skull and head. With the same TBI, pain in the head will not develop immediately after the injury (sometimes after several days or even weeks).
- Depression, constant stress, neuroses, panic attacks, negative psycho-emotional states. Many people suffering from mental illness complain precisely about the pressure in their head.
- Alcohol abuse. In alcoholism in men and women, pressing headaches are one of the most common signs of the disease.
- Incorrect/poor nutrition. Due to an incorrectly formulated or insufficient diet, the brain structures cease to receive the required amount of nutrients and microelements, which often leads to headaches. This category also includes eating junk food in large quantities (fatty, high in food additives and preservatives).
- Overstrain of one or more internal organs. Headaches often occur against the background of overly active work of some internal organs (heart, liver, kidneys, pancreas), so during diagnosis their condition is also checked by doctors.
- Use of certain medications. Many strong medications have a line in their list of side effects about the possible development of headaches. This must be taken into account when taking medications.
- Sleep problems. The lack of a clear sleep-wake schedule almost always leads to headaches (especially after the age of 35-40).
- Influence of weather conditions. Worsening weather, increasing or decreasing atmospheric pressure, precipitation - all this can potentially lead to the development of pressing headaches (especially for those who suffer from VSD, hypertension, osteochondrosis, etc.).
This is not a complete list of reasons why you may have a constant headache. The problem of pressing headaches is quite relevant. It is faced by all segments of the population, regardless of age, gender and other characteristics. According to statistics, women over the age of 30 are most susceptible to such pain. Often a similar syndrome develops in pregnant women and during menopause.
Pressing headache
Pressing pain in the head can be a symptom of more than 50 diseases. Pressing, painful sensations in the head are the most common (85% of cases) complaint of patients, which necessitates the need to seek medical help. A neurologist will help you find out the exact cause of cephalalgia.
Characteristic
A pressing headache is a subjective sensation that occurs due to irritation of intracranial nociceptors or pain receptors located outside the cranium. The feeling of pressure on the head reflects damage (stretching, compression, displacement) of the structures:
- The hard membrane covering the brain.
- Cranial nerves.
- Arteries supplying the medulla.
- Soft tissues covering the skull (tendons, muscles, skin).
A feeling of fullness in the head, with or without pain, occurs without the participation of the brain matter and bone structures of the skull, which are not conductors of pain impulses.
Kinds
There are primary and secondary pressure headaches. In the first case we are talking about migraine, cluster cephalgia, tension pain. In the second, painful sensations are associated with injuries in the neck and head, vascular pathologies, impaired cerebral blood flow, and the use or refusal of pharmaceuticals.
Secondary forms, which are accompanied by a feeling of constriction in the head, include pain caused by infectious and mental diseases, damage to the organs of vision, hearing, nose, and elements of the oral cavity. Taking into account etiological factors, the following types of headaches are distinguished:
- Physiological. Associated with vegetative-vascular dystonia, a violation of neurohumoral regulation of the tone of the vascular wall. They are often combined with pain in the abdominal area and occur after excessive sleep.
- Symptomatic. Correlate with the primary disease, which manifests itself with similar symptoms. These include somatic diseases, vascular pathologies, infectious lesions, and neurological disorders.
- Psychogenic. They occur as a result of physical and nervous overstrain, stress, or in a state of passion (severe excitement).
The share of symptomatic forms is about 20% in the general structure of cephalgia. The success of treatment of symptomatic forms depends on the early detection of the primary disease and the causes of the development of painful sensations.
Causes
If the head is compressed like a hoop and dizzy, this may be due to an intracranial infectious process, which is usually accompanied by characteristic symptoms (fever, meningeal symptoms, paresis and paralysis, convulsive attacks, speech dysfunction).
In these cases, conditions where there is severe compression of the head and dizziness occur require emergency medical attention. Angiospasms in the area of small branches of the main intracranial arteries (carotid, vertebral) lead to stagnation and an increase in the volume of venous blood within the cerebral bed, which provokes the appearance of painful sensations.
Inflammatory processes localized in the head area, including respiratory viral infections, influenza, diseases of the ear (otitis and labyrinthitis), throat (pharyngitis and laryngitis), nose (rhinitis and inflammation of the paranasal sinuses), eyes (conjunctivitis and endophthalmitis) often cause pain and feeling of fullness in the head area. Common causes of the sensation of pressure on the inside of the head:
- Hypertonic disease.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Migraine, tension pain.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Stressful influences.
- Osteochondrosis.
- Disturbance in sleep and wakefulness.
- Volumetric intracranial formations (tumors, cysts).
Neurasthenia is a disease that reflects weakness and decreased functionality of the elements of the nervous system. Often neurasthenia is combined with a disorder of cerebral blood flow and chronic ischemic processes in the brain tissue. The disease is manifested by a feeling of squeezing, tightening, and pulsation in the head.
The feeling of pressure on the head is often associated with pathologies of the spine. Vertebrogenic (associated with the spine) pain and a feeling of compression in the head area develop according to the principle of compression-irritation or reflex-angiospastic course.
In the first case, the mechanism of development of cephalgia is associated with irritation and compression of the nerve roots in the spinal column, in the second - with a reflex spasm of the vascular wall of the vertebral arteries.
The feeling of squeezing the head occurs as a result of many of the primary diseases discussed below.
Arterial hypertension
If the head is bursting from the inside with or without pain, this may indicate a sustained increase in blood pressure, which correlates with diseases of the heart (heart failure, atrial fibrillation) and blood vessels (atherosclerosis, developmental abnormalities). Acute encephalopathy of hypertensive origin leads to disruption of neurohumoral regulation of cerebral blood flow and cerebral edema, which causes a feeling of constriction in the head, but not pain.
It is believed that the feeling of squeezing and squeezing the head, as if in a vice, is caused by a reflex contraction of the muscles lying next to the skull, difficulty in venous outflow, and increased pulsation of the main cerebral arteries. Provoking factors: alcohol consumption, excessive physical activity, strong emotional experiences.
Cerebral blood flow disturbance
The head hurts, as if it were pressing and bursting from the inside, often due to an acute disturbance of cerebral blood flow, which is more common among elderly patients. Any form of ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke causes a headache.
Less commonly, such sensations occur in the prodromal (preceding) period or for 2-4 weeks after stroke. If the feeling of tightness and cephalalgia last longer, there is a high probability of the influence of psychogenic factors, for example, depression. Associated symptoms: speech impairment, motor dysfunction, nausea, vomiting.
Arterial hypotension
If the pressure is 100 to 70 mm. Hg Art. or lower, patients are often haunted by the feeling that the head does not hurt, but there is pressure inside, which is due to a persistent decrease in the tone of the walls of arterioles and cerebral arteries. In this state, pulse stretching of the arterial walls and sustained expansion of the vascular bed occurs. The nature of the pain is dull, generalized.
In this case, the skull seems to shrink and tighten under the influence of provoking factors - physical and mental fatigue, stress, oxygen starvation of brain tissue. Associated symptoms: lethargy, a feeling of heaviness in the area of the skull, as if it were pressing and pulled from the inside.
Giant cell arteritis
Systemic inflammation of the blood vessels begins with damage to the temporal arteries. Usually combined with myalgia of the rheumatic type. It is more often detected among women over 50 years of age. Pain, sometimes throbbing, localized in the forehead and temples with irradiation to other parts of the head is the first symptom of the disease.
Painful sensations often intensify while eating. Associated symptoms: loss of appetite, soreness in the jaw muscles, reflex tension of the spinal muscles, aching pain in the joints and skeletal muscles.
Cerebrovascular diseases
The feeling of constriction and pressure in the head in cerebrovascular pathologies is caused by a constant lack of blood supply to the brain tissue. Associated symptoms: sleep disorder, muscle and general weakness, increased fatigue.
Increased intracranial pressure
A feeling of pressure in the head from the inside, with or without pain, often occurs as a result of increased intracranial pressure. More often, painful sensations appear in the morning or at night, which is due to a deterioration in the outflow of venous blood. The nature of the pain is intense, bilateral, bursting.
Associated symptoms
A common cause of the condition when there is pressure on the head from above is physical stress, effort, coughing.
In this case, the compressive pain in the head is often bilateral, of moderate intensity, and can be combined with symptoms - photophobia, increased sensitivity to noise, nausea.
Tension pain is often monotonous and dull, localized in the forehead, occipital or temporal part of the skull. Symptoms that may accompany a feeling of fullness in the head:
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Increased sensitivity to light and sound stimuli.
- Soreness in the muscle area.
- Lacrimation, conjunctival hyperemia (redness of the membrane of the eye), swelling in the eyelid area.
- Hyperemia of the skin of the face.
- Rhinorrhea (copious discharge from the nasal cavity).
- Anxiety, restlessness.
With neurasthenia, the head hurts, as if it were squeezing the skull, and other symptoms of the disease appear - emotional lability (mood swings), obsessions, sleep disorders, inability to concentrate. Other signs of neurasthenia: paresthesia (sensitivity disorder - numbness, feeling of heat or chills, crawling in the limbs and body).
Movement disorders include muscle weakness and increased fatigue. With migraine, a feeling of constriction in the head is combined with symptoms such as nausea; after attacks, signs are observed - drowsiness, lethargy. The pain is often one-sided, throbbing, and is characterized by repeated attacks.
In the cluster form, painful sensations shoot, drill, and are localized in the orbital and temporal zones. The attack is often accompanied by psychomotor agitation, nasal congestion, lacrimation, and heart rhythm disturbances (bradycardia - decreased heart rate).
In the vertebrogenic compression-irritative form of cephalalgia, the head is compressed and pressed when the neck is turned or when the patient bends over.
The condition is characterized by a decrease in the volume of cerebral blood flow, which is manifested by nausea, photopsia (the appearance of moving, often luminous dots, lightning, spots in the field of view), blurred vision.
The patient becomes dizzy, hearing acuity deteriorates, noise, hum, and whistling appear in the ears.
With forced head tilts, loss of balance and unsteady gait are observed.
With the vertebrogenic reflex-angiospastic form of cephalgia, the skull bursts from the inside, causing painful sensations in the neck, shoulders, and upper vertebrae.
Typically, symptoms worsen with rapid turns of the neck or as a result of prolonged stay in a static position (sitting at a table, playing the piano).
Diagnostics
Due to the many possible causes of head compression, correct diagnosis is important. In 35% of cases, it is not possible to establish the exact causes of pain. If the patient complains of bursting pain in the head area, the doctor collects an anamnesis and prescribes instrumental and laboratory examinations to identify etiological factors.
During the consultation, the nature, intensity, exact localization of pain, and factors provoking the development of an attack of cephalgia are clarified.
A blood test shows the presence of an inflammatory process, metabolic and endocrine disorders (hemoglobin deficiency, changes in the concentration of hormones, glucose, lipids), which makes it possible to suspect the disease that provoked the symptom - cephalgia. During an ophthalmological examination, the following characteristics are revealed:
- Condition of the fundus and blood vessels.
- Visual acuity.
- The presence of a spasm of accommodation.
- Signs of visual dysfunction (loss of visual fields, appearance of foreign objects within the boundaries of vision - dots, spots).
A neuroimaging examination (CT, MRI) shows the presence of space-occupying formations in the medulla. Angiography and Doppler ultrasound are performed to identify the condition of the elements of the circulatory system of the brain, including to detect abnormalities in the development of blood vessels - arteriovenous malformations, aneurysms.
Using electroencephalography, features of the bioelectrical activity of the brain and the presence of convulsive foci are revealed. If the compressive pain in the head is severe, acute, a lumbar puncture is prescribed to rule out infectious brain damage (meningitis, encephalitis) and subarachnoid (in the space between the meninges - soft and arachnoid) hemorrhage.
Neuralgia
Unpleasant sensations may be associated with inflammation or pinched nerve endings. Constant pressing pain in the head is often observed in patients with cervical osteochondrosis and trigeminal neuralgia. In this case, patients also experience other symptoms:
- numbness of the fingers, face or neck;
- muscle stiffness in the morning;
- soreness in the jaw, temples or neck.
The feeling of squeezing most often occurs in the back of the head and then spreads to the parietal region. The pain can be either unilateral or bilateral.
Factors and accompanying symptoms of pain syndrome
Each type of headache has its own characteristic symptoms. When there is pressing pain in the head, a person has the feeling that there is strong pressure on a certain area. It may feel like your head is being squeezed and squeezed from the inside. Typically, this type of pain is localized in the back of the head, forehead, and temples. Moreover, similar sensations in these parts of the head can appear either in turn or simultaneously.
If the pain occurs for a long time, but the person does not treat it in any way, then in the future it will gradually begin to spread to the cervical region, eye sockets, teeth, gums, throat, ears, and so put pressure on other parts of the head. Typically, pain occurs on either the left or right side. There are rare cases when pressing pain simultaneously develops on both sides.
During attacks, pressing headaches are monotonous, have a pronounced dull and aching, not acute character. Immediately after the onset of pain, you may feel dizzy, nausea and vomiting. It is also possible that more dangerous symptoms may occur: fainting, temporary loss of consciousness, blurred vision, increased excitability, etc.
Pressing pain in the head usually accompanies the following pathological processes, being their symptoms:
- Encephalitis and brain abscess. In such situations, patients experience severe and severe headaches that are constant and do not go away after using standard painkillers. Almost always, the patient also experiences nausea, pulsation of the veins in the neck, and his health is extremely poor. In this case, headaches can be reduced only with the help of potent drugs.
- Inflammation in the ear area. With the development of an inflammatory process in the ear area, a pressing headache usually begins to develop, localized in the temporal zone.
- Increased intracranial pressure. With intracranial hypertension, headaches are also of a pressing nature. But they are usually localized in the frontal part and in the orbits.
- Diseases of the temporomandibular joint, severe stress conditions. In these cases, pain also develops in the forehead and eyes.
- Vascular pathologies. If there are certain problems with the condition of the blood vessels, then one of the symptoms of vascular diseases is a pressing headache. In this case, the person also often feels sick. The pain in this case is sometimes localized at the top of the head, after which (if nothing is done) it begins to gradually “spread” throughout the entire head.
- Colds, sinusitis, chronic rhinitis (runny nose). If a child or adult’s cold is left untreated for a long time and a pathological process starts, then there is a high probability that symptoms such as headaches in the eye area and bridge of the nose and the development of an inflammatory process will soon begin to appear. In this case, the ears may become blocked and the nose may become completely clogged with secretions.
Many people cope with pressing headaches at home, without rushing to treat them with specialists (especially if the pain syndrome is infrequent and short-term). The duration of attacks varies significantly from person to person - everything will depend on the reasons that caused the pain, the age of the patient and other factors.
A pressing headache can be rare or regular. If an uncomfortable feeling of squeezing occurs occasionally after physical, mental stress or stressful situations, then the reason lies in spasmodic tension of the blood vessels.
Factors that cause regular squeezing sensations in the head are:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- intracranial hypertension;
- weakened blood circulation in the brain;
- oxygen deficiency;
- vascular spasm;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- damage to the body by viral infections;
- increased body temperature;
- muscle strain;
- dysfunction of the central nervous system;
- heart diseases;
- ailments that impair respiratory function - sinusitis, sinusitis, ethmoiditis, polyps;
- disruptions in the endocrine system;
- nervous overstrain;
- poor nutrition – lack of nutrients;
- alcohol poisoning.
The feeling of tightness may spread to a specific area in the head:
- temporal lobe;
- frontal part;
- eyeballs;
- one or both halves of the head;
- occipital region.
In addition to the sensation of pain in the head, accompanying symptoms may occur:
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- vomiting reflex;
- darkening of the eyes;
- lack of coordination;
- noise in ears;
- loss of consciousness.
Causes of pressing sensations in the head
According to statistics, every person experiences a pressing pain in the head at least once in their life. It can have different localization and degree of intensity, and is often accompanied by additional symptoms. The reasons why the head is compressed can also be different.
The sign is not always pathological in nature, but must be assessed by a specialist. In most cases, it can be eliminated by adjusting your daily routine or switching to a healthier lifestyle. Conservative therapy provides good results for a number of diseases.
Ignoring a symptom can lead to the development of emergency conditions.
Types of pressing headaches
Based on the pressure in the head, where the symptom is concentrated and what manifestations it is accompanied by, an experienced doctor is able to make a preliminary diagnosis. Unpleasant sensations can be caused by various pathological and physiological processes, so specific therapy is required in each case.
When experiencing a pressing headache, it is better not to take independent action, but to consult a specialist. In some cases, inadequate therapy will worsen the condition and increase the risk of complications.
Neuralgic
In this case, a compressive headache becomes the result of pinched nerve endings. It usually appears in the back of the head and spreads to the crown. It can be unilateral or symmetrical.
It is often accompanied by numbness in certain areas of the face or fingers. It is often mild or moderate in severity, but can be intense. Sometimes accompanied by characteristic painful lumbago in the neck, temples, and jaws.
Vascular
The result of a spasm of the wall, expansion, narrowing or blocking of the lumen of the blood channel. Depending on the type of cerebral vascular damage, the patient’s head bursts or presses from the inside.
This may be accompanied by painful pulsation in certain areas of the skull or over the entire area. The squeezing sensation is accompanied by dizziness, restlessness, irritability, or weakness.
Liquorodynamic
The brain is surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid, which protects the organ from negative external influences. Liquid is constantly formed, circulates in a confined space and is absorbed into the blood.
As a result of damage to internal organs, infectious diseases, traumatic brain injuries and a number of other issues, these processes can be disrupted, which leads to an increase in the volume of cerebrospinal fluid.
Due to increased intracranial pressure, a person experiences a pressing, bursting pain that does not respond to taking antispasmodics and analgesics. Often it is encircling, like a hoop that covers the entire skull.
Infectious-toxic
In this case, the patient’s head is compressed against the background of fever and deterioration in general health. The phenomenon is the result of poisoning the body with toxins or other harmful substances.
Cephalgia is constant, obsessive, persistent, without specific localization. She responds poorly to taking medications and using improvised means to relieve symptoms. You can completely get rid of it only by eliminating the cause of the disease.
Voltage
The most common type of cephalalgia, which occurs as a result of prolonged tension in the neck muscles due to stress, after physical and mental stress, is a tension headache.
In this case, the head feels like it is in a vice, sensations are concentrated along the entire circumference of the skull, accompanied by weakness, irritability, and decreased performance. You can even find the most painful places on your head by feeling the skin. The symptom goes away on its own after rest, relaxation therapy, massage.
Why can pressing, squeezing pain occur?
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is not enough to assess the nature of the pain; one must also take into account the presence of additional alarming signs. You should not try to figure out on your own why this type of cephalgia occurred.
You should contact a therapist who will conduct an initial survey and examination, prescribe treatment or refer you to a doctor of a narrow specialization. If the pressure on the head is only occasional and the symptom does not cause much concern, there is no reason to panic. It is enough to adjust your lifestyle and daily routine.
The systematic occurrence of the problem may be due to circulatory disorders, which requires immediate medical intervention.
Hormonal imbalance
Compression in the head can be accompanied by physiological conditions such as PMS, menstruation, menopause.
At the same time, the woman feels as if her head has been tightened; even touching the skin can be painful. Also, the symptom can occur when the functioning of the endocrine glands is disrupted, in particular the parathyroid and thyroid glands.
Migraine
Women of reproductive age especially often suffer from this disease. A painful attack occurs on its own or in response to irritants. It can develop without warning or after an aura (a set of specific symptoms).
The pressing sensation during migraine is often accompanied by pulsation or bloating. It usually originates in the frontal part, radiates to the eyes, temples and back of the head from the problematic side, and gradually spreads to the entire hemisphere. The attack lasts from several hours to 3 days. It is often accompanied by dizziness, nausea and vomiting, which brings relief.
Traumatic brain injuries
Head injuries rarely occur without pain. The symptom occurs immediately after the blow or some time after it.
In some cases, there is a lot of pressure on the head from above, in others, patients feel as if their skull is splitting due to the pressure coming from inside.
The condition is usually accompanied by symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, fainting, problems with perception or speech, nausea and vomiting. Even minor cephalgia that appears after a head injury is an indication to see a doctor.
If you miss the development of cerebral edema, rupture of a vessel or the formation of a hematoma, this can lead to death.
Hypertonic disease
With high blood pressure, patients feel not so much squeezing as bloating in the head. It does not allow you to rest or even close your eyes. The sensation occurs in the back of the head and can spread throughout the entire skull. At the peak of pain, pulsation occurs.
The patient's face turns red, his pulse and breathing quicken. Any external irritants intensify symptoms. After a while, they are accompanied by nausea and dizziness. A person who has high blood pressure should monitor any changes in their condition.
Hypertension significantly increases the risk of developing stroke and cardiovascular pathologies.
Tension headache
A persistent and pronounced feeling of fullness in the head is often classified as an occupational disease. Tension headaches are typical for people engaged in mental work and those who are forced to remain in a position for a long time in which the neck muscles are tense.
This leads to impaired blood circulation in the collar area, hypoxia of the brain, and its poisoning with toxins due to a failure of the outflow of venous blood. Soreness often occurs in the forehead or back of the head and gradually spreads along the entire perimeter of the skull.
As a result, the patient feels as if he has a tight headdress or hoop on his head.
Stress
Another common cause of non-pathological cephalgia, which is characterized by pressing sensations. Anxiety leads to increased muscle tone and disruption of metabolic processes in the tissues of the neck and skull. The result is a tightening pain.
It can occur in different areas of the head. Local manifestations gradually merge into more massive zones, but the severity of the symptom does not increase.
This hoop-squeezing cephalalgia can be relieved by using relaxation techniques and taking sedatives.
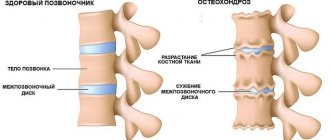
Osteochondrosis
Due to a sedentary lifestyle, refusal of physical activity and a number of pathological reasons, the structure of the cartilage in the cervical spine changes. This leads to a narrowing of the lumen of the canal through which large blood vessels and nerves pass.
The brain begins to experience a deficiency of oxygen and nutrients, and the veins cannot cope with the removal of blood saturated with toxins. As a result, a person feels compression of the head, which occurs in the back of the head and radiates to the crown. This is accompanied by stiffness in the movements of the upper shoulder girdle and a crunch in the neck when turning the head.
Weather changes with changes in atmospheric pressure
Dizziness, nausea, headache, weakness and general deterioration in health are typical for weather-sensitive people. The more abruptly the atmospheric pressure changes, the more pronounced their symptoms are. Sometimes the intensity of the manifestations is such that a person cannot do his usual activities.
The symptoms are poorly responsive to medications. They often develop suddenly and go away on their own within a few hours or days.
Human lifestyle
Alcohol abuse, smoking and refusal to get a good night's rest are factors that lead to a decrease in the functionality of cerebral vessels.
Additionally, toxins that the body does not have time to neutralize and remove have a negative effect on the organ.
Pressing pain in the head is complemented by dizziness, muscle weakness, apathy and loss of appetite, nausea and fatigue, and sleep problems.
Ignoring the signs and refusing to adjust your lifestyle can lead to the development of organic problems and chronic diseases.
Treatment
After the diagnosis of the disease has been made and the causes of cephalgia have been established, appropriate therapy is carried out. The list of treatment measures is established by the doctor. Even the use of traditional medicine is best coordinated with a specialist, so as not to aggravate the situation or neutralize the effect of the drugs.
Methods for eliminating the symptom depend on the factors that provoke it:
- for migraines, the doctor selects the optimal painkillers - triptans, ergotamines, analgesics, NSAIDs;
- in case of hypertension, it is necessary to reduce blood pressure to normal levels - antihypertensive drugs, diuretics and herbs are used;
- headaches due to tension and stress are treated with massage, taking sedatives, physical therapy and, if necessary, antispasmodics;
- for hormonal problems, therapy is coordinated with an endocrinologist;
- one-time manifestations of cephalgia are relieved by taking NSAIDs, antispasmodics or analgesics;
- for osteochondrosis, massage and exercise therapy methods are used. Drug therapy is carried out aimed at relieving pain and restoring the structure of cartilage tissue.
Even if it seems that the cause of the headache is obvious, it is necessary to undergo a full diagnosis under the supervision of a specialist. It will confirm or refute suspicions, eliminate the risks of complications and the transition of an acute disease to a chronic one, and will identify concomitant diseases.
Preventing pressing headaches
Regular medical examinations and timely treatment of diseases will prevent you from encountering regular or prolonged attacks of pressing cephalalgia. Elderly people and people leading a sedentary lifestyle should pay special attention to their condition.
Effective prevention of pressing headaches:
- daily ventilation of working and living spaces;
- long walks in parks, which allow you to saturate the body with oxygen;
- introducing an age-appropriate level of intensity into the physical exercise regime - it is better to spend time in the fresh air rather than in the gym;
- performing self-massage of the head and collar area when stiffness appears in the neck;
- a full night's sleep of 8-9 hours, refusal of daytime rest;
- prevention of stress, taking natural sedatives if necessary;
- quitting smoking, alcohol, and unhealthy foods that increase blood cholesterol levels.
The listed rules of prevention must be followed constantly, and not just when the first alarming symptoms appear. Additionally, it is worth strengthening the immune system by hardening the body and seasonally taking vitamin complexes. You should check your blood cholesterol levels at least twice a year, and measure your blood pressure at least once a week.
A situation where there is pressure on the head knocks you out of your usual rhythm, even in the absence of additional symptoms. A one-time occurrence of a problem indicates that you need to pay attention to your usual lifestyle and eliminate potentially dangerous factors. The systematic occurrence of a symptom is a signal about the presence of serious problems in the body and the need for specialized therapy.
Source: https://insultinform.ru/bolezni/golovnye-boli/prichiny-sdavlivaniya-golovy
Prevention and treatment
Treatment for compressive pain syndrome depends on its cause. Analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used as symptomatic therapy:
- “Analgin.”
- "Pentalgin".
- “Ketanov.”
- “Ibuprofen.”
- “Nise.”
- “Spazmalgin.”
However, such medications do not help relieve pain in all cases. For example, with increased intracranial pressure, the patient's condition does not improve after taking painkillers. Therefore, it is necessary to undergo a course of therapy aimed at eliminating the cause of the pain syndrome. The choice of treatment method depends on the type of pathology. The most commonly used groups of drugs are:
- Antispasmodics. Used for pain caused by neck muscle tension and vasoconstriction.
- Diuretics. They are prescribed for intracranial hypertension. They remove fluid from the body and reduce the pressure of cerebrospinal fluid on brain tissue.
- Antihypertensive drugs. These drugs are indicated for pain associated with high blood pressure.
- Sedatives and antidepressants. They help relieve pain in stressful situations.
- Antibiotics and antiviral drugs. These medications are effective for pain of infectious-toxic etiology.
- Iron supplements. Such drugs are prescribed for pain of anemic origin.
- Triptans. These medications are used for migraines and also for trigeminal neuralgia. They stimulate the production of a special pain-relieving protein.
Non-drug treatment methods are also used. For cervical osteochondrosis and tension pain, massage sessions, physiotherapy, therapeutic exercises, and manual therapy are indicated. If the pain syndrome is associated with frequent stress and emotional instability, then patients are recommended to practice yoga and attend psychotherapeutic sessions.
If you constantly have pressure on your head from the inside, then this is a reason to see a doctor. You cannot tolerate any pain and hide it with painkillers - you need to get rid of it completely by treating the disease that caused it. According to statistics, about 60% of the adult population of the planet systematically suffer from certain headaches.
However, not everyone seeks qualified medical help. It is strongly recommended to visit a specialist as soon as possible, because... pressing headaches will almost always indicate the development of a complex pathology.
The principles for eliminating pressing headaches will directly depend on the disease or factors that cause them. For example, for intracranial hypertension, therapeutic measures are carried out aimed at reducing intracranial pressure (the headache goes away along with it), and for an inflammatory process localized in the ear, bridge of the nose and other parts of the head, anti-infective therapy is carried out.
To temporarily relieve pressing headaches, you can take certain medications. The modern pharmaceutical market offers a huge number of drugs that have good antispasmodic and analgesic effects:
- Ibuprofen.
- Ketoprofen.
- Acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin).
- Paracetamol.
- Nimesulide.
- Naproxen sodium.
Taking these drugs should potentially reduce pressing headaches. But you need to understand that these medications are aimed at only temporarily eliminating the pain syndrome, alleviating the patient’s condition.
It is quite difficult to talk about the treatment of headaches, regardless of their type, because they can be caused by various pathologies, the treatment of which is significantly different.
As preventive measures that can partially eliminate pressing headaches, the following is recommended:
- Daily walks in the fresh air (in a park area, in the forest, across a field, in the mountains, etc.). The duration of the walk should be at least 40-50 minutes (especially important for those who work indoors all day).
- Periodic ventilation of the work area and rooms in your own home. When the air is stale, your head may start to hurt on its own.
- Sports, daily physical activity (you shouldn’t strain yourself too much, but morning exercises and short exercises on the simplest exercise equipment will have an excellent healing effect).
- Visit to the massage room. Massage is an excellent solution for those who suffer from osteochondrosis, which often causes severe headaches. Many massage parlors also offer a relaxing head massage.
- Reducing the number of stressful situations. You need to be as nervous as possible at home and at work, to react more easily to conflict situations, and not to take anything too personally.
- Normalization of sleep patterns. If there is no clear pattern of sleep and wakefulness, then getting rid of headaches will be extremely difficult.
- Proper healthy eating. The diet should be varied, but without harmful and useless food.
- Quitting all bad habits (cigarettes, alcohol, drugs).
If you are at home, you need to open the window and ventilate the room thoroughly (despite the temperature outside).
The consequences of pressing headaches, if nothing is done, can be very different. Firstly, a person will have a chronic headache, and the pain itself will most likely become migraine, which is more pronounced. Secondly, the pathology that caused the pain in the head will also continue to develop, manifesting itself in other symptoms.
Thirdly, it will be much more difficult to cope with an advanced pathological process - it will be almost impossible to get rid of pain with the help of conventional painkillers. Unfortunately, many people only at this stage, when nothing helps, turn to a doctor, and the underlying disease at this time is already at serious stages of development.
What causes pressing, squeezing pain?
Combined complaints such as headache and high blood pressure are quite common in the medical histories of patients in the cardiology department. These symptoms are characteristic of hypertension.
Patients note that conditions arise as if the systolic pressure is significantly and constantly high (more than 200 mm Hg. Based on the nature of the pressing pain, localization and accompanying symptoms, an experienced specialist can diagnose a developing disease. Signs can be determined by physiological characteristics, so in different situations it is necessary to use special therapy .
When attacks occur, no independent decisions can be made; you need to consult a doctor. Inadequate treatment in this situation will complicate the condition and increase the likelihood of complications.
To make a diagnosis, it is not enough to determine the nature of the pain; attention must be paid to other alarming symptoms. There is no need to try to decide on your own why this type of cephalgia occurs. You need to contact a therapist for examination and an initial examination, prescribe the necessary treatment procedures and refer you to a suitable doctor.
There is no need to panic, if symptoms appear periodically, there is no concern. You need to determine a suitable daily routine for yourself. The constant occurrence of the problem may be due to problems with blood circulation. Therefore, medical intervention will be required.
The reasons why the head is compressed vary from relatively trivial stress, typical of a modern person, weather sensitivity, to the consequences of a head injury, hypertension. Determining the causative factor of the tightness is the first step to successfully treating the problem.
Many women with the onset of menstruation experience pain in the crown and other parts of the head due to hormonal changes. During this time, it is recommended to avoid food allergens. Rest in a dark room and cold compresses help.
It often puts pressure on the head from the inside when using hormonal contraception. Other side effects may occur:
- mood swings;
- vomit;
- weight gain;
- chest tension.
Migraine
The next reason why the upper part of the head hurts or there is pain on one side is migraine. The disease most often affects people aged 25–55 years, and its symptoms are more common in women. Migraine triggers include:
- stress;
- weather changes;
- food;
- hormonal factors;
- exhaustion;
- lack of sleep.
A person with migraine cannot continue to work and needs peace and quiet. If you have frequent migraines, you should definitely consult a specialist and treat the disease.
When a concussion occurs, a person experiences a pressing headache, nausea, vomiting, sometimes dizziness, orthostatic tachycardia, and hypotension.
Some patients develop problems associated with post-concussion syndrome after traumatic brain injury. Pressing headaches, dizziness, fatigue, decreased performance, and sleep disturbances dominate.
Presses the head from the inside also with an epidural hematoma. At the same time, unilateral mydriasis develops with a photoreaction disorder and, as a rule, contralateral hemiparesis.
Acute subdural hematoma is mainly associated with contusion and impaired consciousness, so cephalalgia is difficult to detect. Warning signs are anisocoria and hemiparesis.
Chronic subdural hematoma usually appears weeks or months after the injury. The symptoms are dominated by pressing headaches (often pressing on the bridge of the nose, it is painful for a person to bend over), mental symptoms (drowsiness, confusion), hemiparesis.
Hypertension
Some people experience pressure on the top of their head due to high blood pressure. In addition, they complain of fatigue and decreased productivity. Most people, however, do not feel the presence of hypertension, so they do not cooperate enough with their doctor in treating the disease. But long-term high blood pressure, if left untreated, can lead to serious health problems.
Tension headache is the most common cephalalgia, in which there is pressure in the head. The pain is diffuse, the onset of the attack is gradual. The pain is constant, easily changing in intensity throughout the day. Sometimes it can be defined as a tightly compressed hoop around the periphery of the head. Usually the problem is caused by stress and psychological factors.
Sometimes the pain does not manifest itself in the head (pressure in the sides of the neck) or is one-sided and occurs locally. If pain occurs only with movement or touch (for example, when tilting the head down, there is pressure on the head), there may be a local cause. It happens that cephalgia comes from the back of the head. If fatigue or vomiting is present, be sure to visit a doctor.
Stress
The definition of stress, in which the head is compressed from above, is quite complex, it strongly depends on the way it is assessed. This state is understood as experiencing difficult, unpleasant, threatening situations, important life events, everyday worries, and anxiety.
Tension and nervousness are involved in the appearance of cephalgia. Stressful states can be divided into unexpected life situations and everyday life events.
Osteochondrosis
If you have a headache from the inside due to osteochondrosis, the problems also affect other parts of the body. This is due to the fact that the cervical spine area is rich in nerve canals connecting the brain and spinal cord. Due to deformation of the disc or connecting tissue, the nerve endings are pinched, resulting in pressure on the ears and the back of the head.
Weather sensitivity most often manifests itself as discomfort (as if there is pressure in the head), joint pain, breathing or heart problems. Changes in weather not only affect human health, but can also manifest as changes in mood.
Cephalgia can have a number of causes, but many of them stem from modern lifestyles. They are often associated with high workload and psychological stress. These factors cause tension in the muscles around the neck, causing discomfort that makes it difficult for a person to bend forward. Soreness can also be a reaction to some medications.
Disturbances in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid
There are cases when patients experience pressing pain in the head that does not go away even after taking potent analgesics and antispasmodics. This may be due to increased intracranial pressure.
CSF constantly circulates in the brain. This fluid is constantly produced by ependymal cells, passes through the meninges, and is then absorbed into the bloodstream. It is necessary to protect nerve tissue from harmful influences.
With various diseases of the central nervous system and head injuries, the amount of cerebrospinal fluid increases sharply. The fluid begins to compress the brain tissue. This condition is called intracranial hypertension. It is accompanied by severe pressing pain in the head. Patients feel as if their skull is being pulled together with a tight hoop. This is often accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Muscle tension
Tension headaches are very common. It occurs after heavy physical or mental work, as well as against a background of stress. The cause of pressing pain in the head is overstrain of the neck muscles.
Painful compression is felt over the entire surface of the skull. It has no specific localization. At the same time, the person feels weak, restless, and his activity and performance decrease. The discomfort usually goes away after rest or a light massage.
Next, we will consider possible causes of pain depending on its location.
Treatment
After the diagnosis of the disease has been made and the causes of cephalgia have been established, appropriate therapy is carried out. The list of treatment measures is established by the doctor. Even the use of traditional medicine is best coordinated with a specialist, so as not to aggravate the situation or neutralize the effect of the drugs.
Methods for eliminating the symptom depend on the factors that provoke it:
- for migraines, the doctor selects the optimal painkillers - triptans, ergotamines, analgesics, NSAIDs;
- in case of hypertension, it is necessary to reduce blood pressure to normal levels - antihypertensive drugs, diuretics and herbs are used;
- headaches due to tension and stress are treated with massage, taking sedatives, physical therapy and, if necessary, antispasmodics;
- for hormonal problems, therapy is coordinated with an endocrinologist;
- one-time manifestations of cephalgia are relieved by taking NSAIDs, antispasmodics or analgesics;
- for osteochondrosis, massage and exercise therapy methods are used. Drug therapy is carried out aimed at relieving pain and restoring the structure of cartilage tissue.
Even if it seems that the cause of the headache is obvious, it is necessary to undergo a full diagnosis under the supervision of a specialist. It will confirm or refute suspicions, eliminate the risks of complications and the transition of an acute disease to a chronic one, and will identify concomitant diseases.
In the back of my head
Pressing pain in the head, localized in the back of the head, may be a sign of the following diseases:
- Anemia. Brain tissue is primarily affected by a decrease in hemoglobin. The central nervous system experiences a sharp lack of oxygen. Pressing pain first occurs in the back of the head, and then moves to the frontal and temporal region. This is accompanied by weakness, increased fatigue and dizziness.
- Cervical osteochondrosis. Deformed vertebrae can compress the nerve endings and blood vessels of the head. As a result, the outflow of blood is sharply disrupted. Because of this, pain occurs that spreads from the back of the head to the neck area. This is often accompanied by severe muscle stiffness, especially in the morning.
- Injuries to the occipital part of the head and neck. After severe bruises, tissue swelling and compression of blood vessels are observed. This is accompanied by a headache and a feeling of fullness in the skull. Severe injuries also cause dizziness, vomiting, confusion, and fainting.
Medicines that relieve pain attacks
Pressing headache is the most common complaint in 92% of the population. It can occur even in young children and at absolutely any age. According to statistics, women suffer more often from this type of pain.
The main causes of attacks of pressing headaches:
- changes in the body's hormonal levels;
- received head and brain injuries;
- stress and depression;
- excessive tension of any organ;
- unhealthy diet and alcohol;
- excessive consumption of fatty, salty foods, foods with food additives and preservatives;
- fasting and sleep disturbance;
- change of season, changes in atmospheric pressure, sudden climate change;
- taking medications.
As for the symptoms of a pressing headache, a person’s sensations are approximately the following:
- a feeling as if something is pressing on the source of pain from within;
- pain affects the temporal, frontal and occipital parts simultaneously or alternately;
- pain spreads from the neck to the back of the head, eyes, temporal part;
- an attack of pain often affects one side of the head, less often – both;
- the attack of pain is monotonous, it does not increase, but is aching in nature.
The localization of a pressing headache manifests itself differently for different reasons for its occurrence, for example, against the background of an inflammatory process in the ear, the pain spreads more to the temporal part of the head.
If intracranial pressure increases, the pain puts most pressure on the eyes. The pressing pain is different from the pain that usually accompanies a cold or flu.
To accurately characterize the sensations of a person who has had an attack of a pressing headache, they can be compared to when a person tries on a tight hat and it is very small for him.
Often this type of headache occurs during stress and depression and manifests itself most strongly at the age of 27-37 years; such pain has a pressing nature and is sometimes accompanied by a loud and sharp sound, like an external irritant.
The causes of headaches that put pressure on the eyes can be emotional shocks, frequent stressful conditions, and pathology of the temporomandibular joint.
The use of large doses of analgesics, caffeine (coffee, teas, energy drinks), as well as various tranquilizers, can intensify attacks and make them permanent.
Separately, it is necessary to highlight this type of pressing headache that occurs with cervical osteochondrosis, that is, destruction of the intervertebral discs. With this burning, squeezing, pressing pain, the patient experiences the following:
- dizziness;
- vomiting, nausea;
- visual disturbances;
- loss of consciousness;
- tinnitus.
You will learn about the treatment and prevention measures for pressing headaches in the next part of this article.
The medications prescribed in such cases not only relieve pain and tension during an attack, but also prevent subsequent crises. The doctor can advise and prescribe medications based on the following active ingredients:
- "Acetylsalicylic acid";
- "Paracetamol";
- "Ibuprofen";
- "Napoxene sodium";
- "Nimesulide";
- "Ketoprofen".
It is also possible to take combined analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, however, in most cases they bring only temporary relief or are ineffective.
Much better for pressing headaches are combinations of painkillers and antispasmodics, which enhance each other’s effect. A good example is the drug Spazgo, which is produced in the UK. It contains paracetamol combined with dicyclomine hydrochloride.
Spazmolgon tablets have the same effect. The drug “Nise” will help improve your condition; you should also try the powder for preparing the “Nimesil” suspension.
Everyone is treated with their own methods: pills, coffee, folk remedies, a glass of cognac. However, the effect of such treatment can be unpredictable: either relief or worsening of the condition.
There are cases in which you should contact a specialist as soon as possible:
- the presence of side symptoms - weakness and numbness of body parts, loss of vision, memory problems;
- headaches become longer and stronger;
- headaches that are too severe to bear;
- severe pain in the head even from touching anything;
- In addition to the headache, there is fever, nausea, difficulty breathing, and dry mouth.
Any signs of cephalalgia are behavioral characteristics of a person suffering from this condition. Infants, deaf-mutes, and sick elderly people are unable to explain what is bothering them. Signs of cephalalgia are:
- crying, moaning;
- frequent blinking, squinting of eyes;
- pressing with palms, fingers on the bridge of the nose, back of the head, crown, eyebrows, temples;
- unreasonable rotation of the head or neck;
- unusual facial expressions.
At the temples
Pressing pain in the head and temples is most often a sign of migraine. The pain syndrome is paroxysmal in nature. At first, a person feels drowsy and has visual disturbances: flashing colored zigzags and circles before the eyes. The patient becomes extremely sensitive to sounds and smells.
Pressing pain in the head and temples may be associated with hunger. This feeling is often experienced by people on strict diets. With insufficient nutrition, a glucose deficiency occurs in the body. This leads to compressive pain in the temple area. The discomfort usually goes away after eating.
Pressure in the forehead
A pressing headache in the forehead is most often infectious and toxic in nature. It can be caused by the following diseases and conditions:
- Sinusitis. Inflammation of the frontal sinuses causes severe pain. An unpleasant feeling of fullness appears in the superciliary area. The pain radiates to the eye area. Sinusitis usually occurs as a complication of colds. This pathology is accompanied by nasal congestion and increased temperature.
- ARVI and influenza. With viral colds, the superciliary area swells. Swollen tissue puts pressure on blood vessels. This causes pain in the forehead area. Often this symptom occurs at the very beginning of the disease, when there are no obvious manifestations of a cold.
- Hypothermia. If a person is exposed to the cold for a long time without a hat, he may experience compressive pain in the forehead. This is caused by vasospasm from the cold. The pain syndrome quickly disappears after warming up.
The cause of pain in the forehead can also be increased arterial or intracranial pressure. In this case, the patient feels dizziness, nausea, and weakness. With high blood pressure, a rapid heartbeat occurs and black dots flash in the field of vision. The pain syndrome is bursting in nature.
Diagnostics
Any headache of a different nature cannot be ignored, since this is how the body signals the presence of any malfunctions in the body, which a comprehensive examination will help to identify.
Diagnostic methods:
- clinical blood test - helps to see the presence of inflammatory processes in the body, determine the level of hemoglobin;
- CT, MRI, REG - these hardware examination methods help assess the functional state of the brain;
- Doppler examination of blood vessels - shows the presence of plaques, blood clots;
- ECG – performed for vascular pathologies;
- measurement of intracranial pressure.
An ECG is performed to identify the causes of pain.
If an intense headache is accompanied by severe thirst, a person cannot lower his chin, the nasolabial triangle turns blue, the skin on the face and neck becomes numb, there is a strong increase in temperature, it is necessary to urgently contact an infectious disease specialist. Such symptoms may indicate the development of meningitis, encephalitis, and the person requires urgent hospitalization.
Pressure on the eyes
Patients often complain that they have pain in the head and pressure on the eyes. Most often this is due to severe fatigue of the visual organ. In this case, pressure is felt from the inside on the eyeballs and distension in the forehead. This condition can occur after working at the computer for a long time or doing handicrafts. In such cases, you need to give your eyes a rest, usually after this the pain disappears.
Similar pain can occur if glasses are chosen incorrectly. If the distance between the centers of the lenses does not correspond to the gap between the pupils, then a headache and a feeling of pressure on the eyes from the inside may occur.
However, there are also dangerous causes of pressing pain in the head and eyes. This symptom may be a sign of meningitis. This is a serious infectious disease accompanied by inflammation of the membranes of the brain. The pain syndrome with meningitis is extremely severe. The patient's temperature rises sharply and his health worsens. Photophobia, nausea, confusion, and weakness are observed.
Headache and a feeling of pressure in the eyes can be one of the early signs of glaucoma. The leading symptom of the disease is pain in the eyeballs and deterioration of lateral vision. The headache is secondary. The pathology is accompanied by increased intraocular pressure and, without treatment, can lead to loss of vision.
Why does my head hurt?
To understand what will help with problems with blood pressure, you need to understand why a headache occurs with pressure, when the disease relates to the heart.
Firstly, a headache can appear when there is a sharp jump in blood pressure, more than a quarter of normal. Secondly, this can happen when it is not the upper, but the lower pressure that makes a sharp jump.
Migraine from pressure, in turn, comes in various types:
- muscle tension
- liquorodynamic malaise
- vascular
- neuralgic headache with high blood pressure
The most painful headaches are muscle tension headaches. They develop slowly, and gradually the person begins to feel as if something is squeezing his skull in a vice. Typically, the cause of such a migraine is:
- nervous overload
- stress
- physical exercises contraindicated for the patient
- spending a long time at the computer or TV.
- hormonal instability.
- sudden changes in weather conditions. This is not fiction, as some may think. Weather dependence actually exists and many people suffer from it very much.