Acoustic neuritis (or cochlear neuritis) is an inflammatory disease of the auditory nerve. The main manifestations of this pathology are decreased sound perception and noise in the ear. These complaints can bother the patient on one or both sides.
Most often, cochlear neuritis occurs in people over fifty years of age. The main risk factor for the development of this disease is living in large cities, where the noise threshold is increased. This problem adversely affects hearing function.
Anatomy
The auditory nerve begins in the middle ear. In this area it contains hair cells. This type of cell is responsible for sound perception and sound conduction. The auditory nerve transmits impulses generated by hair cells to the brain.
From the middle ear, vibrations passing along the auditory nerve, through the opening of the temporal bone, enter the stem part of the brain, where the process of primary (unconscious) sound perception occurs. Next, the vibrations move to the cortical part of the brain, where the processes of recognition and processing are carried out - this is how the incoming sound becomes aware.
When the auditory nerve becomes inflamed, damage occurs to one of its three components:
- hair cells;
- the auditory nerve itself;
- subcortical auditory centers of the brain.
Causes
The causes of this pathology can be divided into 5 groups:
- Diseases of infectious origin:
- ARVI and influenza (a viral infection enters the auditory nerve through a hematogenous route);
- meningitis and meningoencephalitis;
- rubella;
- parotitis.
- Somatic pathologies:
- arterial hypertension;
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- stroke.
- Head injuries. In this case, damage to the auditory nerve occurs due to pathological processes that occur after a traumatic brain injury:
- violation of microcirculation in the brain;
- the occurrence of edema;
- development of hemorrhages of varying complexity.
- Toxic factor:
- taking medications that have an ototoxic effect (antibacterial agents; drugs used in the treatment of malignant tumors, etc.);
- toxic substances in production (salts of heavy metals, arsenic, phosphorus);
- consumption of tobacco and alcohol-containing drinks.
- Occupational hazards:
- noise at work;
- trauma of acoustic origin (sharp exposure to a loud sound in the ear);
- vibration disease.
In rare cases, acoustic neuritis may have an allergic etiology, or barotrauma may also cause it.
How to prevent the disease?
Prevention of this pathology is based on the exclusion of all factors that can provoke its development. First of all, doctors recommend timely treatment of all diseases of an infectious nature. It is equally important to avoid contact with toxic substances, use protective equipment when working with them, and take medications only as prescribed by a doctor. Elderly people are recommended to undergo annual preventive examinations, take the necessary tests and monitor blood pressure.
Symptoms
Symptoms of damage to the auditory nerve appear as follows:
- Deterioration of sound perception. Hearing loss progresses gradually; with irrational therapy, the disease can lead to complete loss.
- Noise in the affected ear. This symptom is permanent and does not depend on exogenous factors.
- Pain syndrome. Pain in this case is noted along the nerve (neuralgia).
- Vestibular disorders. Symptoms such as dizziness and loss of balance occur when the vestibulocochlear nerve is damaged, the main function of which is to transmit impulses to the center of balance.
- Intoxication of the body. The patient has complaints of weakness, increased fatigue, and decreased performance.
- Hyperthermia, rhinorrhea, cough. Such symptoms are present with an infectious etiology of the disease.
In most cases, neuritis occurs in an acute form. Chronic neuritis of the auditory nerve is formed due to irrational treatment of acute neuritis, as well as with decreased immunity.
YOU MAY ALSO BE INTERESTED
- BPPV: symptoms and treatment
- Structure of the inner ear
Drug treatment of acoustic neuritis
The treatment algorithm depends on the causes of the disease.
In the case of viral or bacterial etiology of neuritis, treatment with antiviral drugs or antibiotics is selected, respectively. In this case, it is necessary to abandon medications that directly cause toxic neuritis. To enhance the therapeutic effect, high doses of the drug are used.
To maintain the condition, the patient is prescribed vitamins C, as they are antioxidants and prevent cell damage. Drinking plenty of fluids will help quickly remove viral or infectious toxins from the body. In this case, it is necessary to ensure the patient complete rest and provide adequate nutrition.
To detoxify chronic exposure to toxic substances, medications are primarily prescribed to remove toxins from the body. In this case, droppers are prescribed:
- with rheopolyglucin solution;
- ringera;
- saline sodium chloride solution.
Treatment of cochlear neuritis of traumatic origin is preceded by a consultation with a neurologist. Based on an X-ray of the skull, anticonvulsants and medications that improve blood flow are prescribed.
Besides:
- to relieve pain - analgesics;
- to prevent or reduce cerebral edema - diuretics;
- vitamins B and P to maintain the functions of nerve endings.
In a situation where the cause of a sharp decrease in hearing is a tumor process, doctors recommend surgical removal of cancerous tumors.
If the chronic form of the disease has led to complete loss of hearing, then in this case the question of using a hearing aid or hearing aids becomes relevant. Advances in modern medicine make it possible to restore hearing to people who have not heard for many years.
Diagnostics
When the first symptoms of inflammation of the auditory nerve appear, you need to contact a specialist - an otolaryngologist. Based on clinical and additional diagnostic methods, he makes a final diagnosis and then prescribes appropriate treatment.
Clinical diagnosis of cochlear neuritis consists of collecting complaints (disturbing symptoms), anamnesis (information about risk factors, the presence of concomitant diseases is found out), and examination of the affected ear.
Additional diagnostics include the following methods:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- study of thyroid hormones in the blood;
- audiometry;
- tympanometry;
- Weber test (determining the audibility of sounds using a tuning fork);
- Rene's test (comparison of air and bone conduction using a tuning fork);
- X-ray and CT scan of the skull.
Therapy at home
In folk medicine there are many recipes to combat advancing deafness. They are inexpensive, and their effectiveness sometimes exceeds drug therapy.
Recipe No. 1:
- chop three leaves of golden mustache;
- place in a small saucepan and pour in one glass of boiling water;
- put on low heat and cook for no more than five minutes;
- then place the resulting mixture in a thermos and leave for two hours;
- After the time has passed, strain. Take one teaspoon four times a day.
Recipe No. 2:
- Fill a small 100 ml glass container halfway with juniper berries;
- pour vodka and place in a dark place for three weeks;
- shake constantly all this time;
- Place the resulting tincture in each ear, three to four drops twice a day.
Recipe No. 3:
- take two tablespoons of fireweed;
- pour 500 ml of boiling water and cook over low heat for no more than eight minutes;
- Cool the resulting brew to room temperature and strain;
- instill 6–7 drops of infusion into each ear;
- treatment is carried out until the symptoms of the disease are completely eliminated.
Recipe No. 4:
- finely chop one clove of garlic;
- add 3 drops of camphor oil to the resulting pulp;
- fold the finished mixture into gauze and make a small tampon, which must be inserted into the sore ear;
- the time of the procedure is purely individual - until a burning sensation appears;
- course - until complete recovery.
Treatment
Treatment of acoustic neuritis depends on the symptoms and causes that caused it.
Infectious neuritis is treated with antibacterial or antiviral drugs. In the case of antibiotics, the drug is prescribed only by a doctor after receiving the results of bacterial culture for sensitivity to antibiotics. As an auxiliary therapy, treatment includes the following items:
- detoxification therapy (drinking plenty of water);
- vitamin therapy;
- balanced diet.
How to treat neuritis of the auditory nerve that occurs against the background of somatic pathologies? In this case, therapy is aimed at treating the underlying disease:
- antihypertensive drugs for arterial hypertension;
- statins and fibrates in the presence of atherosclerosis;
- drugs that improve microcirculation in the brain during stroke.
For neuritis caused by the effect of toxic substances on the body, treatment is based on the following points:
- administration of an antidote;
- symptomatic treatment (therapy of individual clinical manifestations);
- when the process subsides, it is possible to use physiotherapy methods, treatment with mud and mineral waters.
Neuritis caused by traumatic brain injury is treated with:
- analgesic drugs;
- agents that improve cerebral circulation;
- diuretics.
Patients with head trauma are prescribed a comprehensive examination of the skull (X-ray examination, encephalography) and consultations with specialists (ophthalmologist, neurologist).
The basis of therapy for neuritis, which was caused by occupational hazards, is a change in the field of activity. Further, in the treatment of auditory neuritis, drugs such as adaptogens, dietary supplements, and vitamins are used. Physiotherapeutic treatment methods are prescribed for complete recovery.
Traditional therapy as one of the treatment methods
Is it possible to cure cochlear neuritis of the auditory nerve with medicinal herbs? Unfortunately, traditional therapy methods alone cannot cure this disease. However, they find their effectiveness in combination with drug therapy methods.
The most effective plant used in the treatment of acoustic neuritis with folk remedies is golden mustache. It is recommended to make a decoction from it. To do this, the leaves of the plant must be cut, poured with hot water and allowed to brew for 1 day. You need to use the decoction 1 tsp. 3 times/day. The course of therapy is at least two weeks.
Hearing restoration is carried out through a hearing aid, cochlear implantation, and anti-neurotic therapy.
Ear neuralgia symptoms and treatment of the ear nerve
Neuralgia of the ear is symptomatically similar to purulent inflammation of the middle ear (otitis), which is often associated with difficulty in making a correct diagnosis. Feeling pain in the ear, the patient in vain turns to an ENT specialist, while only a neurologist can select methods for treating this problem.
Features of the pathology
The ganglion of the ear is a complex structure formed by autonomic and sensory nerve fibers. This nerve node performs the following functions:
- responsible for the sensitivity of the temporomandibular joint;
- responsible for the functioning of the salivary gland;
- regulates the sensitivity of the external auditory canal.
This node or ganglion is responsible for the sensitivity of the area, so when it is damaged, pain is felt. With neuralgia of the ear, patients note the following symptoms:
- shooting and sharp pain in the ear;
- excessive salivation;
- feeling of stuffiness in the ear.
Pain is often reflected into the lower jaw, which makes it difficult to make a diagnosis and determine the cause of the pain syndrome.
To make a diagnosis, consultation with three specialists is necessary - an otolaryngologist, a neurologist and a dentist, since the symptoms of neuralgia largely repeat the symptoms of otitis media and some dental diseases.
Causes
More often, neuralgia of the ear node develops due to the presence of a source of infection in the body. The infection spreads throughout the body through the bloodstream and enters the area of the cranial nerves, causing an inflammatory process. The reason may be:
- inflammation of the salivary gland;
- blockage of the salivary glands;
- chronic and purulent inflammation of the middle ear (otitis);
- tonsillitis, including chronic ones;
- sinusitis;
- bacterial and infectious dental diseases.
In some cases, secondary inflammation of the ear nerve is observed. This is typical for diseases such as pneumonia, sepsis and kidney pathologies. Damage to the auricular ganglion may be one of the manifestations of diabetic polyneuropathy.
Symptoms of the disease
Pain with neuralgia of the ear can radiate to the jaw, but more often patients notice pain in the ear and around the auricle, spreading to the temporal region.
The pain is paroxysmal, with a tendency to intensify under certain influences. A factor that provokes increased pain during neuralgia is the consumption of hot food.
Often the pain intensifies and becomes acute with strong psycho-emotional stress or stress. Attacks of pain are short-lived and can vary from a few minutes to one hour.
The eardrum is very susceptible to vibrations, so even a sudden change in atmospheric pressure can trigger a new attack of pain. Particularly often there is an increase in pain in humid weather.
Neuralgia of the ear node is considered a seasonal disease, since in most cases the problem becomes relevant in the fall and spring, when there is predominantly rainy weather and low air temperatures.
Attack of pain
The attack begins suddenly. Its onset is signaled by characteristic ear congestion. The pain has a wave-like character and during an attack it either intensifies or almost goes away. There is increased salivation and special sensitivity to loud sounds.
The attack ends suddenly, just as it begins, and with it the copious secretion of saliva and the feeling of congestion stop.
Establishing diagnosis
To make a diagnosis, you must undergo the following examinations:
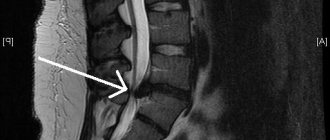
- Brain MRI;
- ultrasound examination of the salivary glands passing near the ear;
- examination by an otolaryngologist;
- dental examination.
Making a diagnosis is the task of a neurologist. The doctor will analyze the patient’s complaints and refer him to another specialist to rule out other pathologies with similar symptoms.
How to distinguish from otitis media
Neuralgia of the ear node is often mistaken for otitis media. To avoid this, you need to know the symptoms of middle ear inflammation:
- increased body temperature;
- fever and general weakness;
- pain when trying to open your mouth wide;
- discharge of pus from the ear canal;
With otitis, there is a prolonged aching pain with high fever. The ear stops hurting after a breakthrough, when pus begins to be released.
With neuralgia, the temperature does not rise. There is no fever or general weakness, but the pain is acute and appears periodically. Discomfort increases when eating hot food, and not when opening the mouth, which is typical for inflammation of the middle ear.
Treatment methods
The basis of therapy is analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs. To reduce pain, taking painkillers with analgin or ibuprofen is recommended.
To relieve inflammation, medications containing diclofenac or ibuprofen are used. These nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs also help relieve pain.
It is important to take antispasmodic drugs. This helps relieve muscle spasm of the auditory tube, which accompanies neuralgia and increases discomfort. Taking such drugs helps to quickly improve the patient's well-being.
To improve the patient's well-being and speed up recovery, taking sedatives is indicated. They help normalize sleep and strengthen the nervous system, which reduces the frequency of pain attacks and speeds up recovery.
Therapy is supplemented with B vitamins to improve the restoration of nerve fibers. Vasodilators, for example, with nicotinic acid, are often prescribed to improve local blood circulation and relieve spasm.
If for any reason drug treatment is not possible, physiotherapy is used - acupuncture, amplipulse, electrophoresis. This helps reduce pressure on the nerve, improve local metabolic processes and relieve the inflammatory process.
Blockade for neuralgia
Drug blockades are a method of long-term pain relief based on the injection of medication directly into the area of the affected nerve. For neuralgia of the auricular nerve, this method is one of the methods for making a diagnosis, since in case of otitis media, administering medication to the area of the nerve does not relieve pain.
Novocaine is usually used for pain relief. This helps relieve pain for several days. The blockade is used when the pain syndrome cannot be relieved with analgesics in tablets. The blockade does not replace therapy with anti-inflammatory drugs.
What to remember
For neuralgia of the ear, traditional methods of treatment based on exposure to heat cannot be used. Warming up in this case can provoke the spread of the inflammatory process.
If ear pain suddenly appears, and there are no symptoms of a cold or general malaise, you should first consult a neurologist. If discomfort is accompanied by an increase in temperature, you need to be examined by an otolaryngologist.
Often neuralgia of the ear becomes a constant companion for the patient. Due to the fact that the pain goes away on its own and the attacks do not last long, patients prefer not to pay attention to the discomfort. This approach is incorrect, since any disease should be treated in a timely manner.
Source: //NashiNervy.ru/perifericheskaya-nervnaya-sistema/simptomy-i-lechenie-nevralgii-ushnogo-uzla.html