Development mechanism
The term refers to a persistent or temporary increase in blood pressure (above 140/90 mmHg) after the occurrence of a stressful situation.
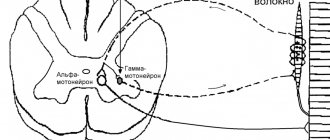
The main mechanism of occurrence is the accumulation of oxidants in tissues under the influence of stress. This is manifested by free oxidation of lipids in cells. This condition especially concerns neurons of the nervous system.
The main centers regulating blood pressure are the medulla oblongata and the cerebral cortex. In the listed structures, the sensitivity of neurons to the action of certain substances (neurotransmitters) changes. This is manifested by the formation of emotional arousal in the brain, which leads to a persistent change in the mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. As a result, temporary nervous hypertension appears, which without treatment can become chronic.
Stress and blood pressure are inextricably linked, thanks to the participation of nitric oxide in this process. Its deficiency is explained by the narrowing of blood vessels, as a result of which persistent nervous hypertension is formed. This causes disturbances in the normal functioning of the heart and kidneys.
Increased stress results in increased release of renin (an enzyme in the kidneys that regulates blood pressure) and angiotensin (a hormone that causes blood vessels to constrict). Nervous excitability is increased. This is due to the adverse effects of these hormones. An increased level of angiotensin in the blood leads to an increase in the formation of adrenaline and norepinephrine. They are stress hormones that protect the body. Adrenaline causes the heart muscle to contract more frequently, which simultaneously constricts the blood vessels. Therefore, people with blood pressure at the borderline of normal have hypertension due to nervousness and during complete calm.
High levels of adrenaline are considered dangerous to the body. Normally, it increases blood pressure and therefore must be completely consumed. If this does not happen, then there is first a temporary increase, and then a permanent one. Long-term stress disrupts the normal functioning of the heart, which over time increases the risk of developing chronic diseases.
Psycho-emotional stress provokes the release of catecholamines - adrenaline and norepinephrine. These hormones increase blood pressure. Arterial hypertension from nerves is caused by the following reasons:
- surgical intervention;
- hypoglycemia (a decrease in blood glucose concentration below normal);
- injury;
- alcohol withdrawal;
Approximately 2 hours after surgery, many patients notice an increased level of blood pressure, this is a manifestation of hypertension. The main mechanism that can increase it is the activation of the nervous system. The level of catecholamines in patients during stress significantly exceeds normal values. Postoperative nervous hypertension most often persists no longer than 24 hours.
The most excitable group of patients are people with hypoglycemia. After emotional stress, high levels of adrenaline significantly increase systolic blood pressure. It is affected to a lesser extent by norepinephrine.
The occurrence of acute stress is possible even after alcohol withdrawal, and increased activity of the nervous system becomes its result. This condition develops 3-4 hours after the last drink. Higher levels of catecholamines are also observed after injury. This happens especially often when the renal artery, kidneys and adrenal glands are damaged.
A large number of factors increase blood pressure. To treat nervous hypertension, drug and non-drug methods are used. Complex therapy is most effective compared to monotherapy (use of one drug).
A way to treat nervous hypertension that improves quality of life while reducing the risk of premature mortality is to take medications. It is known that until 1950 they did not use medications to solve this issue. In the absence of an additional method of treating nervous hypertension, patients were at high risk of developing chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system and complications from other internal organs.
Basis of therapy
If nervous hypertension occurs, the first step will not be to take medications. The basis for further successful treatment should be provided by:
- Limiting the consumption of table salt.
- Refusal to drink alcohol. It is noted that taking 80 g of the drink every day can increase the risk of hypertension several times.
- Loss of body weight.
- Active lifestyle.
To prevent nervous hypertension, playing sports for 30-40 minutes, 3 times a week is enough. Physical exercise is especially recommended for people leading a sedentary lifestyle. The most favorable is the following exercise regimen: daily walking of about 6 km and light jogging. Exercises in the pool effectively help cope with high blood pressure. With constant training in combination with proper nutrition, blood pressure levels for nervous hypertension are reduced by 7-9 mmHg.
In addition to playing sports, it is important to review your diet: add healthy foods and eliminate harmful ones. Some are able to calm the nervous system and have a relaxing effect on the heart and blood vessels.
Arterial hypertension and hypertensive crisis can be prevented by potassium, B vitamins and calcium. Meat products, egg yolk, spinach, nuts, bananas and dried fruits are rich in these substances. Iodine is required to maintain normal regulation of hormonal levels. Therefore, patients should eat seaweed and seafood. It is recommended to limit fatty, smoked, salty foods.
Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages reduces the effectiveness of antihypertensive drugs. When the desire to drink appears, it is allowed to take a drink (wine) without harm to health in an amount not exceeding 140 ml.
It contains natural antioxidants (vitamins A, C and E), substances that reduce cholesterol levels. Therefore, natural wine helps reduce nervous system excitement and the risk of high blood pressure or hypertensive crisis due to stress. At the first signs of arterial hypertension, you need to start moving more rather than lying down. This will calm the excited nervous system and allow high blood pressure to slowly normalize.
Many patients with a tendency to nervous hypertension practice breathing exercises. Thanks to special equipment, it will be possible to reduce blood pressure by 10-15 mmHg. Before you start breathing, you need to calm down. Exhale slowly and deeply, holding your breath for a short time. Next, inhale slowly. This technique has a calming and hypotensive effect within 10-15 minutes from the start of breathing exercises.
A warm bath is considered an effective and simple remedy for nervous hypertension. To do this you will need warm water with a temperature of 35-39˚C. You can add sea salt and essential oils to it. Additionally, after taking a warm sitz bath, you can do the same procedure for your feet. The duration should not exceed 20 minutes.
Home aromatherapy sessions will be useful to help you relax after a stressful situation. It has a beneficial effect on blood vessels, which leads to a decrease in pressure during nervous hypertension. The following oils are suitable for the procedure:
Before aromatherapy, add no more than 3 drops of oil to the bath. If desired, they can be mixed to obtain different scent compositions. During the procedure, you can lubricate the skin along the spine and back of the neck with oils.
Stress and high blood pressure
Five facts about hypertension: when stress is good for your health, why habitual headaches are dangerous and what to do if your blood pressure suddenly rises
We, residents of big cities, are always in a hurry and don’t even notice that we expose our nervous system to harmful stress every day. It seems that we are not doing anything dangerous: we wake up, go to work, communicate with colleagues. In the evening we go to the store... But then we got into a traffic jam and realized with horror that we would be late. Or they decided to cross the road three seconds before the red traffic light. Or you had a fight with someone. The situations are different, but the result is the same: headache, tinnitus, insomnia. In a word – stress. What does it threaten us with and do we need to fight it?
When we experience discomfort, the body turns on its defenses and begins to produce stress hormones: adrenaline, norepinephrine, cortisol. The level of heart rate increases, and with it blood pressure (BP) and metabolism in general. Result: at such moments we feel a surge of strength, a rapid heartbeat - we are overwhelmed with determination and a thirst for action.
When the situation is resolved (we still managed to get to work on time or run across the road in front of a speeding truck), the body gradually switches from combat mode back to normal. This “training regime” is useful because it helps us gather all our strength at the right moment or find a second wind. So we need stress? Yes, but...
First: Stress is not good for everyone.
Unfortunately, not all people are built the same. Some people endure extreme situations with fortitude, while others, on the contrary, are very worried about every occasion. And if chronic fatigue or congenital diseases are added to the worries, the result will be increased blood pressure. At risk of hypertension due to stress are healthy young people who are overweight, smoke, or abuse energy drinks and salty foods.
Second: if you have a headache after stress, then you need to remember about high blood pressure, not painkillers!
High blood pressure is one of the most common forms of overreaction to stress. Its companions are headache, rapid heartbeat, dizziness and nausea. Moreover, blood pressure, like an uninvited guest, can linger for several days. You can take handfuls of painkillers, but there will be no effect!
Third: pressure “like an astronaut” is not the norm for everyone!
Blood pressure above 140/90 mmHg is considered high. But young and at the same time quite healthy people can experience severe headaches and other symptoms mentioned above even at lower pressure, for example 135/85, 130/80.
This happens if their usual blood pressure is normal, i.e. 120/80 mmHg, or even the usual low (90/60 mmHg). This is because they do not yet have a “habit” to an increased level of pressure, and their body reacts painfully to any surge in pressure. For some, poor health may persist for several days or weeks.
Fourth: even young people need a tonometer
How to recognize increased blood pressure caused by stress? Very easy! This is done using a regular tonometer, on both hands, in a sitting position. After 5 minutes, the measurement should be repeated, and if the pressure remains elevated, it’s time to take action. Many people neglect this simple diagnosis: they say, why do I have pressure, I’m young. Although if there are hypertensive patients in the family, then the chance that a person will use a blood pressure monitor is still higher. In any case, this device is as necessary a thing in your home medicine cabinet as a thermometer for measuring temperature. The main thing is to decide which blood pressure monitor is best for you.
Video on the topic
How stress affects heart disease and how to cope with it:
Hypertension and stress are inseparable companions. In the modern world, the question of why your blood pressure rises when you are nervous does not lose its relevance. Nerves are one of the most common causes of hypertension. As the disease progresses, kidney and heart failure become involved. Therefore, hypertension is a very serious pathology, the treatment of which should only be carried out by a qualified specialist.
Why does blood pressure rise with excitement?
this increases vascular tone, blood pressure on the walls of the vascular network increases, and the heart begins to work with greater intensity. In a healthy person, this condition develops quickly, but quickly passes. That is, the pressure rises quickly from excitement, but just as soon it returns to normal. When such cases are episodic, they do not pose a threat.
But with hypertension the picture will be different. Any stressful situation against the background of illness increases the cardiac load, but the heart is already working in a different mode, trying to cope with the pressure of blood on the walls of blood vessels.
A jump in blood pressure during stress in hypertensive patients can result in a hypertensive crisis. This is extremely dangerous for the so-called target organs.
Providing first aid for a sharp rise in blood pressure
In a stressful situation, a hypertensive crisis may occur.
In case of a hypertensive crisis, it is necessary to call an ambulance and carry out some first aid measures:
- first, sit in a comfortable chair or armchair;
- secondly, put something warm on your feet to warm them up. Mustard plasters or a heating pad are suitable for this;
- thirdly, do not eat anything, otherwise your general condition may worsen, possibly causing nausea or even vomiting;
- and finally, before the ambulance arrives, if there is pain in the heart area, put a nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue.
After examination by an emergency doctor, if hospitalization is required, do not neglect the advice of a specialist and refuse this.
What is hypertension
Statistics show that in almost 70% of cases, people’s blood pressure rose due to nerves and certain stress factors. Often, strong emotional shocks can result in a hypertensive crisis. Nervous pressure occurs due to the fact that a fairly powerful release of adrenaline occurs in the body. In this case, the person feels pulsating shocks in the temples, the face turns red (a manifestation of a hypertensive reaction).
Some people are predisposed to hypertension. So, even the slightest worries can cause blood pressure disorders. The reason for this is hereditary vascular weakness. Against this background, a disorder of the autonomic nervous system (vegetative-vascular dystonia) is often diagnosed, which has an extremely negative effect on the functioning of all organs. Such disturbances are caused by constant experiences.
Dystonia is divided into several types:
- hypotonic type;
- by mixed type;
- according to the hypertensive type.
The hypotonic type of disease is typical for people leading a sedentary lifestyle. Violations appear if the energy that accumulates throughout the day remains “inside” (that is, it is not spent anywhere). The disease makes itself felt in the form of a feeling of constant fatigue and depressive disorders.
VSD of mixed type occurs due to internal “conflict”. The parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for rest, “fights” with the sympathetic one. The latter determines emotional factors, physical activity, state of wakefulness and activity.
The hypertensive form of the disorder is the most common. The disease of the hypertensive type appears against the background of severe emotional upheaval. Patients in such cases complain of sleep problems and a persistent feeling of anxiety and fear. They get tired quickly, cannot concentrate on one thing for a long time, and become inattentive.
Hypertensive type disorder most often occurs in emotionally unstable people. If you conduct observations, you will notice that such people very often use the expressions “I’m worried,” “I’m scared,” “I’m very worried,” while there may be no reason for such emotions. Even the most ordinary situations, which most people tolerate calmly, can cause severe anxiety and even panic attacks in sensitive patients. Usually, with a hypertensive type of disease, the pressure increases greatly, and sudden headaches and dizziness may appear.
A small educational program: arterial hypertension or hypertension (as this disease is called “in the old fashioned way”) is a disease that has not been fully studied, is dangerous and practically irreversible. The word “irreversible” must be used with caution: if the disease is no longer in a mild form, it is impossible to get rid of it.
Hypertension is characterized by a persistent increase in pressure, i.e. blood pressure in arterial vessels. It grows due to a complex mechanism, which drug therapy tries to correct. It is almost never possible to say absolutely exactly what became the trigger and launched the disease in the body.
But if the root cause cannot be determined for certain, we can say with confidence what factors can become provocateurs of the disease.
Among the provoking factors today, the following are confidently identified:
- Heredity – it’s difficult to compete with genetics, but it is still possible to prevent the disease.
- Negative habits are a chemical addiction (alcohol, nicotine, drugs), all this undermines the body’s resources, triggers various dysfunctions and deformations in it, and quite quickly, addictions turn into organic lesions and diseases, including arterial hypertension.
- Nutrition - from unhealthy eating behavior to specific harmful eating habits: this includes adherence to fried, fatty foods, overeating, and a large amount of salty and pickled foods in the diet.
- Obesity - in the wake of body positivism, some supporters of “natural beauty” even threaten the medical community with lawsuits for allegedly blaming body features for all diseases. Despite the initially constructive messages of body positivism, the popular movement has become simply dangerous - people are losing the distinction between the concepts of “features of body constitution” and “obesity.” Everyone must clearly understand for themselves where individuality ends and illness begins. Obesity always (some earlier, some later) threatens diseases. Hypertension is a variant of the negative scenario of obesity, the frequency of which can be called frightening.
- Stress is the very case when frequent psycho-emotional stress leads to the body “getting used” to triggering a natural physiological reaction to irritation; certain mechanisms that trigger the disease occur in it. Stress and pressure are clearly linked, and when doctors tell you “don't worry, stay calm”, these are not just words of encouragement, but a medical warning.
How to eat to avoid stress
Nutrition really plays a huge role in how our body interacts with the world around us, including stress. Someone with an incorrect diet only “stirs up” this conflict, making himself more irritable and less flexible. Some people try to eat in such a way as to never cease to feel inner lightness, mobility, and readiness for active action at any moment.
It's not just about what you eat, but how you eat. One of the main problems of modern man related to nutrition is overeating. By the way, this factor can also be called a provocateur of hypertension.
How to understand that you are overeating (mini-test):
- Can you always stop? Do you often add food to a plate that originally contained a whole portion? If this happens often, you are definitely overeating.
- What feelings do you have after eating (after, not during)? Lightness, a surge of strength, and high spirits are a normal reaction to eating. If you feel “full belly”, drowsiness, lethargy, general heaviness in the body, you don’t eat - you overeat.
- Do you feel the taste of your favorite dishes 100%? If this is the case, then everything is normal. But for those who overeat, the taste of food becomes dull over time.
- Are you full of energy after eating? Are you ready to get things done, do you feel capable of multitasking? If yes, then everything is normal. But if food simply “masks out” stress, but does not move you towards solving problems, it is overeating.
Finally, everything can be calculated using nutritionist formulas. As already noted, obesity is one of the main provocateurs of hypertension. Therefore, it’s never too late to take care of your diet and normalize everything. To do this, you need to calculate your daily diet in calories and follow it, without allowing yourself any indulgences. At the same time, one day a week you can allow yourself to eat something sweet or starchy, in a word, not dietary. But this will not be a breakdown, but an acceptable relaxation.
How are stress and pressure related?
The relationship between stress and pressure is two-way. Against the background of a traumatic situation, blood pressure rises. Arterial hypertension increases the load on the nervous system, exacerbating stress. Therefore, normalization of pressure is impossible without eliminating the traumatic factor.
High blood pressure from stress
Nervous hypertension develops under the influence of the following factors:
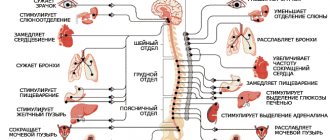
- Stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system. As a result, the production of adrenaline increases, vascular tone increases, and blood pressure on the walls of the arteries changes. Heart contractions accelerate. In a healthy person, such attacks occur rarely and do not pose a threat to well-being. In patients suffering from chronic hypertension, the slightest stress causes an increase in blood pressure.
- Development of specific reactions of the body. During stressful situations, increased amounts of thyroid and adrenal hormones are released. Substances affect target organs, causing a number of pathological changes.
- Features of the psyche. People suffering from hypertension are irritable, hot-tempered, and impatient. Any conflict situation throws such a person out of balance, triggering reactions in the body that lead to the release of increased amounts of adrenaline.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system. In these cases, blood pressure rises immediately after stress; signs of hypertension persist for several days.
Low blood pressure during stress
Reducing nervous pressure is facilitated by:
- predominance of activity of the parasympathetic nervous system;
- decrease in the volume of blood ejected by the heart;
- drop in peripheral vascular resistance;
- reduction in the volume of blood entering the heart through the venous system;
- decreased renin activity in blood plasma;
- accelerated fluid removal;
- decreased sensitivity of vascular wall baroreceptors to the influence of stress products;
- the predominance of inhibition processes in the brain.
Bidirectional communication
According to statistics, hypertensive patients have a special psychological portrait.
- They are irritable and impatient.
- Everything is taken too literally.
- They often suffer from melancholy or apathy.
Hypertension is characterized not only by pressure surges, but also by redness of the skin, tinnitus, and increased sweating. All these symptoms are completely identical to the manifestations of stress. It's all about the bidirectional relationship between nervous tension and hypertension.
The pressure may rise from the nerves, and the disease progresses faster, but at the same time, hypertension has a strong effect on the nervous system, which aggravates any manifestations of stress. You should fight stress, because there is no chance to cope with hypertension in any other way.
It is important to consider that this disease may appear after prolonged stress, and not be independent.
Treatment methods
What to do if a hypertensive crisis develops due to stress:
- take a lying position and try to distract yourself from the traumatic situation;
- take slow, deep breaths in and out;
- drink lemon balm or linden blossom tea;
- close your eyes and lie in silence.
To provide first aid for an acute attack, the following drugs are used:
- Sedatives (Corvalol, Novo-Passit, Persen). The preparations contain herbs for blood pressure. They normalize the functioning of the nervous system and increase the body's stability.
- Tranquilizers (Afobazol, Gidazepam). Used when sedatives are ineffective. Helps quickly cope with the manifestations of stress hypertension. The dosage and regimen for taking tranquilizers is selected by a psychotherapist.
- Beta-blockers (Atenolol, Anaprilin). They weaken the reactions of vascular receptors to stress hormones, lowering blood pressure.
- ACE inhibitors (Capoten). Normalize blood pressure and reduce vascular resistance.
- Diuretics (Hypothiazide). They remove excess fluid, preventing the expansion of arteries.
When blood pressure in the vessels decreases, the following is prescribed:
- Psychostimulants. They increase the sensitivity of receptors to renin, helping to adapt to stressful situations. Herbal adaptogens (tincture of Leuzea, ginseng, aralia) are considered the safest. 30-40 drops of the pharmaceutical preparation are dissolved in 100 ml of water. The medicine is taken 2 times a day.
- Anticholinergics (Atropine). Suppress the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system, increasing blood pressure.
- Sympathomimetics (Dopamine, Mezaton). They are administered for severe hypotension that threatens the patient’s life.
- Saline solutions. Help restore circulating blood volume.
- Auxiliary means. Nootropics (Nootropil, Glycine) are used to improve the condition of the nervous system. Antioxidants and vitamins strengthen the walls of blood vessels (Neuromultivit, Mildronate).
Inhibitors
The most popular group of drugs for reducing high blood pressure from nerves are ACE inhibitors. The presented group of drugs helps to qualitatively control blood pressure levels. Taking them reduces the risk of heart complications.
Inhibitors suppress the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. This process is accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure and a decrease in the risk of developing left ventricular myocardial infarction.
At the very beginning of the course, small doses of the drug are used. A stable effect is observed after 2-4 weeks. Contraindications for use are pregnancy, excess potassium, renal artery stenosis, allergic reactions to previously used hypertensive drugs.
How to avoid pressure during stress?
Regular moderate exercise helps prevent the development of nervous hypertension and improve the general condition of the body. Walking in the fresh air, swimming and gymnastics are useful. The nervous system receives relaxation, the walls of blood vessels are strengthened, and tension gradually recedes. Special medications, such as this one, also have an effect.
Compliance with the work and rest schedule has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the nervous system. Night sleep should last at least 8 hours. When engaging in intellectual and physical labor, you need to take regular breaks. Proper nutrition plays an important role. The body must receive sufficient amounts of vitamins, minerals and nutrients.
Dear readers! We strongly recommend that you consult a doctor before taking medications or self-medicating. There are contraindications.
Causes of nervous excitability
Factors that provoke a stressful state are the following:
- constant lack of sleep;
- emotional outbursts;
- alcohol/tobacco abuse or abrupt withdrawal;
- increased conflict during contacts with people;
- excessive suspiciousness, anxiety;
- mental stress, for example, at a particularly responsible job, strong emotional experiences.
As a rule, hypertension of the nervous system is a consequence of several factors simultaneously.