Impaired consciousness: mechanism of occurrence
After damage to the central nervous system due to a traumatic brain injury, a person loses the ability to respond to any external stimulus. The psycho-emotional state is completely disrupted, the victim cannot contact the people around him. Coma sets in.
Coma due to TBI is characterized by the immersion of a person in a specific state, which is associated with inhibition of certain areas of the central nervous system. The victim does not respond to pain, bright light and loud sound, and has no reflexes.
Consciousness is impaired when certain parts of the brain that are responsible for speech, thinking, wakefulness, and reasoning are damaged. Based on the degree of damage, loss of consciousness can have different durations:
- mild traumatic brain injury (for example, bruise): loss of consciousness does not occur or lasts no more than 5 seconds;
- moderate injury (for example, open head injury): duration of disturbance of consciousness – 2 hours-2 days;
- severe injury: deep coma and vegetative states occur.
Coma after TBI is not a separate disease, but only a consequence of damage to the central nervous system. If there is a severe general condition that threatens a person’s life, he may be placed in an artificial coma. This condition allows you to cause a controlled decrease in the activity of reflexes and vital functions.
An artificial coma involves the introduction of special medications into the body. In this case, the respiratory function is performed by a ventilator.
What determines the severity of TBI and its types?
All, including long-term types of consequences of traumatic brain injury, are subject to many factors:
- Nature of injury. The stronger and deeper it is, the greater the likelihood of complications and, as a result, long-term treatment.
- Patient's age. The younger the body, the easier it is for it to cope with the injuries received.
- Speed of medical care. The sooner the victim is shown to a doctor and the stage of treatment begins, the easier it will be for him to recover.
As already mentioned, there are mild, moderate and severe forms of damage. According to statistics, there are almost no complications with minor injuries in young people aged 20–25 years.
Consequences in mild form
A mild form of head trauma is the most favorable option of all existing ones. Treatment usually does not take much time, and patients recover quickly. All complications are reversible, and symptoms are either early (acute) or last a short time. The following signs can be noted here:
- dizziness and headaches;
- profuse sweating;
- nausea and vomiting;
- irritability and sleep disturbance;
- weakness and fatigue.
Typically, therapy, after which the patient returns to normal life, takes 2 to 4 weeks.
Consequences in moderate form
Moderate severity is a more serious reason for concern about the patient’s health. Most often, such conditions are recorded with partial brain damage, severe bruise or fracture of the base of the skull. The clinical picture can last for quite a long time and includes symptoms:
- speech impairment or partial loss of vision;
- problems with the cardiovascular system, or more precisely with heart rhythm;
- mental disorders;
- paralysis of the cervical muscles;
- seizures;
- amnesia.
Rehabilitation after a traumatic brain injury can take from 1 month to six months.
Consequences in severe form
Severe injuries are the most dangerous and are the most likely to cause death. Most often, this type of injury is recorded after open skull fractures, severe brain contusions or compression, hemorrhages, etc. The most common type of complication after severe TBI is coma.
According to statistics, every second person in severe cases will experience the following types of consequences:
- Partial or complete disability. In case of partial disability, the ability to work is lost, but self-care skills are retained, mental and neurological disorders are present (incomplete paralysis, psychosis, movement disorders). With complete disability, the patient requires constant care.
- Coma of varying degrees of manifestation and depth. Coma due to traumatic brain injury can last from several hours to several months or years. At this time, the patient is on artificial life support devices or his organs are working independently.
- Death.
Also, even the most effective treatment and a favorable outcome of the measures taken necessarily entail the appearance of the following signs:
- problems with vision, speech or hearing;
- abnormal heart rhythm or breathing;
- epilepsy;
- seizures;
- partial amnesia;
- personality and mental disorder.
They can be combined and appear immediately after a head injury or years later.
It is impossible to give an accurate assessment of the patient’s recovery, because each organism is individual, and there are multiple examples of this. If in one case, even with severe injuries, patients endured rehabilitation with resilience and returned to normal life, then in other situations, even a mild head injury did not have the best effect on the neurological status and health in general. In any case, rehabilitation and psychological support play an important role in cases of traumatic brain injury.
– the most common cause of damage to the structures of the central nervous system. If severe damage to cerebral tissue occurs, coma may occur, which can lead to disability or death.
Characteristic symptoms
Coma after traumatic brain injury is primarily characterized by impaired consciousness. All symptoms of this condition can be divided according to the degree of its severity:
- Superficial disturbance of consciousness. The person falls into deep sleep. When trying to talk to the victim, he may open his eyes and sometimes start a conversation. Speech with punctuation. The patient can make slight movements of the limbs.
- Ordinary coma. The patient is able to make sounds, unintentionally open his eyes and make sudden movements with his hands. The doctor can fix the victim’s limbs with special devices to prevent physical harm.
- Deep coma. Reflexes, mobility and respiratory function are completely absent. There is no reaction to pain, just like there is to the light of the pupils.
Why does coma occur?
Many factors can provoke a coma. The most common and important causes of cerebral coma include:
- traumatic lesions of the head and brain structures;
- severe course, extensive brain damage with ischemic and;
- infections of the membranes (meningitis), substances () of the brain, especially in children;
- pathological effects of poisons, toxins, drugs, alcohol and overdose of certain medications;
- brain damage due to carbon monoxide poisoning and prolonged oxygen starvation;
- endocrine disorders accompanied by hormonal imbalances with hyperfunction or, conversely, lack of hormones (hypocorticoid, diabetic coma).
Treatment during coma
Once a diagnosis of coma due to traumatic brain injury has been made, appropriate treatment is begun. First of all, measures are taken to increase blood flow to the brain. Emergency treatment begins already in the ambulance.
Artificial ventilation is used and medications are introduced into the body to help normalize blood pressure. It requires the introduction of drugs that improve the functioning of organs such as the liver and kidneys.
In case of respiratory arrest, the emergency doctor inserts a special tube into the tracheal cavity, which is a conductor of oxygen air coming from the breathing apparatus.
Since, while in a coma, a person cannot eat on his own, nutrients are administered by tube. To prevent secondary infections of the urinary tract and lungs, powerful antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
Causes
The sources causing damage to cerebral structures can be different.
The main ones are closed or open craniocerebral injuries caused by trauma.
Today, depression of the central nervous system caused by cancer, strokes and hemorrhage of various pathogenesis has become increasingly widespread.
The third most common causes are bacterial and viral infections that provoke inflammation and disruption of brain activity.
Distortion of consciousness can be caused by diabetes, hormonal disorders, abnormal changes in the functioning of the kidneys and liver.
Also, factors contributing to the development of a coma include intoxication and poisoning with potent poisons and substances: alcohol, drugs, medications.
Rehabilitation period
Not all cases of impaired consciousness require a long rehabilitation period. According to statistics, recovery from a coma caused by diabetes, high doses of drugs or alcohol does not last long. In such cases, impaired consciousness is present before the toxic substance is eliminated from the body.
Coming out of a 3rd degree coma after a TBI or 1st degree equally requires rehabilitation measures. First of all, measures are taken to restore brain function. Not in every case, amnesia develops, but there is a deterioration in memory and attention.
How do you recover from a coma after a TBI? During this period, the ability to sit and walk without assistance and available means is lost. Confusion of consciousness is observed, the person loses orientation in space. The following specialists help correct such disorders caused by prolonged impairment of consciousness:
- neurologist (helps restore speech);
- psychologist (normalizes the psycho-emotional state);
- occupational therapist (helps improve motor skills);
- neurologist, physiotherapist, etc.
When recovering from a coma after a TBI, there is no need to immediately subject the patient to physical and mental stress on the first day. Rehabilitation should take place gradually. How many months or years it will take to fully restore the activity of the central nervous system, and what the prognosis will be, depends on the severity of the traumatic brain injury.
Rehabilitation after a coma consists of assisting the patient in all everyday activities: eating, going to the toilet and showering. Developmental games are required to help restore motor skills, memory, and speech. It is important to normalize your diet so that it includes all useful vitamins and microelements.
To restore muscle tone, massage procedures are prescribed, which are carried out in a specialist’s office and subsequently at home. During the massage, you can use any essential oil. The procedure also helps improve blood circulation. The main condition is continuity of therapy, even if the first positive changes are visible.
Traumatic brain injury: coma after head injury – Izvilina
Head injuries themselves pose a health hazard to the victim and can lead to serious complications. In case of serious damage to the structure of the brain substance, the patient may fall into a coma.
With it, the patient loses consciousness, does not respond to stimuli and is literally between life and death. Coma after a traumatic brain injury can manifest itself differently depending on the degree of damage to the cerebral tissue.
The lack of timely professional assistance threatens the death of the victim or the development of severe disability.
After a TBI, the victim may go into a coma.
The mechanism of coma during TBI
The development of coma affects the general condition of the patient, but the central nervous system is primarily affected.
A disorder of its functions leads to changes in consciousness, dulling of reflexes, lack of response to external factors and the ability to contact others.
The pathological phenomenon in its quality resembles very deep sleep, which is caused by inhibition of the work of certain parts of the brain.
Coma due to TBI is not an independent disease, but a consequence of a malfunction of the nervous system.
It is important to understand the mechanism of its development in order to properly treat and eliminate risks to the victim’s life.
Coma occurs as a result of extensive damage to the brain matter, as well as vital centers of the central nervous system.
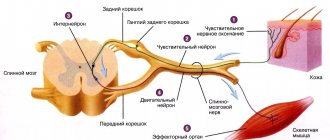
This causes damage to the transmission pathways of nerve impulses to all organs and systems, disruption of processes that are the key to the normal functioning of the body.
Such consequences result from changes in tissue structure and circulatory disorders in certain areas. The loss of communication between the higher parts of the nervous system and functional centers is aggravated by local or general cerebral edema.
In coma, the transmission of nerve impulses to organs is disrupted.
Types and symptoms of coma
Regardless of the cause of coma and its form, the main symptom of the pathological condition is impaired consciousness. Dysfunction of individual areas of the brain can manifest itself in different ways.
Often, the clinical picture of the disorder helps doctors make a preliminary diagnosis and select the best first aid options.
Symptoms that may accompany coma with different types of traumatic brain injury:
- speech disorders;
- inability to perform purposeful actions with the upper and/or lower extremities;
- sudden cramps, involuntary muscle contractions;
- rapid rhythmic movements in the knee and/or ankle joints;
- varying degrees of decrease in consciousness up to its complete shutdown and absence of reflexes;
- paralysis;
- breathing problems;
- fixation of pupils;
- heart rhythm disturbance.
In coma, the heart rhythm is disrupted.
The degree of brain damage is determined using a special Glasgow scale. To use it, you need to evaluate a number of indicators, calculate the points obtained and check which diagnosis their number corresponds to.
Determination of the level of coma
Restoration of impaired or lost functions of the central nervous system is possible only after establishing the cause of the coma and its type. The first assessment of the victim’s condition is carried out before emergency care is provided.
Restoration of the central nervous system is possible only after establishing the type of coma.
Diagnosis of a patient with TBI in a coma includes:
- collecting anamnesis - interviewing the victim’s relatives, witnesses of the accident, collecting data from the patient’s medical record;
- physical examination - examination of the skin and mucous membranes, assessment of the functioning of the respiratory and circulatory system, checking the fundus of the eye and the reaction of the pupil to light. Additionally, the likelihood of spinal injuries is determined, and certain types of palpation and percussion of the body are used. They are necessary to exclude pathological enlargement of organs and the presence of internal bleeding;
- neurological tests - include checking the level of unconsciousness, eye reaction, establishing the degree of motor activity and tendon reflexivity. Muscle tone is assessed, asymmetry of the facial areas is excluded;
- laboratory and hardware tests - X-ray of the skull, MRI, CT, EEG, angiography, lumbar puncture, measurement of intracranial pressure.
If necessary, the attending physician may prescribe additional diagnostic tests. The manipulations are repeated regularly to monitor the dynamics of the patient’s condition.
To diagnose the patient, a lumbar puncture is performed.
How does one come out of a coma?
Depending on how the brain tissue responds to the treatment, the victim's return to consciousness may manifest itself in different ways. Regardless of the specifics of the case, recovery from a coma after a TBI requires increased attention and a number of rehabilitation measures.
Doctors must take measures to restore the functionality of damaged tissues. After restoration of consciousness, the patient may experience amnesia, decreased quality of attention, and memory impairment. This is accompanied by loss of the ability to sit and walk without assistance for any period of time.
The picture is often complemented by confusion and loss of orientation in space.
Rehabilitation period
Depending on the individual and general reactions of the body, the recovery period takes place under the supervision of a neurologist, physiotherapist, or psychologist.
Sometimes a speech therapist, occupational therapist, or physical therapy doctor is involved in the work. The main thing is to avoid significant mental or physical stress in the first days of emerging from a coma.
Rehabilitation after a coma due to TBI can take several months or even years.
The main thing during rehabilitation after a coma is not to overload the brain.
Brain coma and its consequences
Coma, from ancient Greek, means deep sleep, drowsiness. It is characterized by a lack of consciousness, motor activity and reflexes, inhibition of the vital processes of breathing and heartbeat. A patient in a coma is deprived of an adequate response to external stimuli, for example, touch or voice, or pain.
Why does consciousness disorder occur?
The normal functioning of the central nervous system (CNS) is ensured by balancing excitation and inhibition. In the case of an unconscious state, the inhibitory influence of individual brain structures on the cortex predominates. Coma always occurs as a result of extensive damage to brain tissue.
Causes
The causes of unconsciousness are quite varied. Brain coma can occur when:
- infections of the nervous system, meningitis of a viral and bacterial nature;
- injuries to the head and brain matter;
- ischemic strokes or as a result of cerebral hemorrhage;
- toxic damage to the nervous system caused by overdose of drugs, alcohol, as well as exposure to drugs and toxic substances;
- tumors of the central nervous system;
- impaired metabolism (diabetic comas with high or low blood sugar levels, adrenal dysfunction with hormonal imbalance, accumulation of waste metabolic products with depressed liver and kidney function).
Symptoms
When coma develops, disturbances of consciousness always come to the fore.
There are three main types of coma depending on the severity of the patient:
- superficial;
- actual coma;
- deep.
In the superficial form, the patient resembles a deeply sleeping person. Verbal appeal to him is accompanied by opening of the eyes, sometimes the ability to answer questions. Speech disorders manifest themselves in sluggish and incoherent speech. Minimal movements in the limbs are maintained.
While in a state of normal coma, a person may make sounds, suddenly open his eyes and become agitated. Doctors sometimes even have to restrain such patients with special means so that they do not cause physical harm to themselves.
Deep coma is characterized by a complete absence of movements and reflexes. In this state, the patient does not swallow saliva and does not breathe. There is a complete absence of reaction to pain, and the pupils react poorly to light.
Complications
If the central nervous system was affected at the time of the traumatic brain injury, complications are likely to occur. Coma is one of them. With severe TBI, the consequences can be so serious that the patient will no longer be able to care for himself, stand up, or sit. In such cases, outside help and special medical equipment will be required.
Coma is not always accompanied by such severe consequences. In some cases, a person quickly recovers from injury and impairment of consciousness, and basic functions and reflexes return to normal.
The most common consequences of coma include amnesia or incomplete memory loss, impaired concentration, loss of the ability to independently care (eating, taking water procedures, etc.).
Being in a lying position for a long time, a person may begin to suffer from bedsores, which require other specific therapy using medications.
The most dangerous consequences
All traumatic brain injuries are usually divided into three degrees of severity
: mild, moderate and severe traumatic brain injury, the consequences of which are almost always irreversible.
Severe traumatic brain injury has the most dangerous consequences, such as
diffuse axonal damage, contusion and compression of the brain, falling into a coma and a vegetative state.
Severe contusion of the telencephalon is when a person is unconscious for 2 weeks
, while vital functions also change the rhythm of their activity.
From a neurological point of view, the brain stem is especially damaged, as a result of which unclear movements of the eyeballs, a violation of the swallowing reflex and muscle tone may be observed.
Severe injury is often accompanied by a fracture of the skull vault and hemorrhage into the cavity of the cranium.
Nothing more than a consequence of compression of the brain.
Hematomas most often occur epidermal and subdural.
The most important thing in such a situation will be diagnosis carried out on time. If the hematoma is not complicated and has a “light period,” then the victim will begin to come to his senses after some time.
Hematoma against the background of coma is much more difficult to recognize, and it can only be explained by bruise of brain tissue. As hematomas form and grow inside the skull, a tentorial hernia can develop, which is a protrusion of the brain into the opening through which the brain stem passes.
If the compression continues for a long period, the oculomotor nerve is affected, without the possibility of recovery.
The absence of normal physiological functioning of the cerebral cortex is called a vegetative state of the brain.
Only the functions of the brain stem and reticular formation are preserved, so the changes in the phases of sleep and wakefulness continue to work as usual. When awake, a person lies with his eyes open, but is not in contact with the world around him.
If the dysfunction of the cortex is reversible, then the patient’s consciousness can gradually be restored, then psychosensory and psychomotor activity is reintegrated, and after some time the person returns to full consciousness.
Unfortunately, damage is not always reversible. In such cases, a persistent vegetative state of the large brain rapidly develops.
Human life continues only with the help of artificial drugs
, which support the normal functioning of the respiratory, cardiovascular and excretory systems.
Death is almost inevitable.
Traumatic brain injury and coma
Falling into a coma is also a dangerous consequence of traumatic brain injury. In a state of coma, a person is unconscious, the functions of the central nervous system are suppressed, consciousness is lost, and all vital human systems are gradually suppressed.
There are three types of coma: