If a person experiences visual disturbances, this does not always mean that he has developed an eye disease. In some cases, symptoms may indicate brain damage. These diseases include atrial scotoma (ocular migraine). It is expressed in the appearance of a sensation of flickering, loss of visual fields, as well as visual hallucinations and severe headache (however, the last two signs may not always be detected).
The reasons for its occurrence lie in vascular disorders of the brain, which lead to improper functioning of the visual analyzer. Some researchers suggest that this disease is inherited.
Most often, ocular migraine is diagnosed in women during pregnancy and in adolescence, which suggests hormonal effects, as well as a significant load on the nervous system and blood circulation during these periods.
The disease was first described by the physician Hubert Airy in the 19th century and called it “ghost castle”, since the scotoma, as seen by patients, often has jagged edges, reminiscent of the plan of a fortress.
The causes of an attack or risk factors may be the following:
- sleep disorders;
- weather dependence;
- stress;
- clinical depression;
- mental and physical stress;
- hormonal fluctuations;
- smoking, alcohol abuse, drug use;
- oxygen starvation;
- vascular and neurological diseases;
- poor nutrition;
- taking medications that dilate blood vessels;
- flickering light;
- menstruation.
Treatment of such migraine should be carried out after excluding other disorders: Tolosa-Hunt syndrome, multiple sclerosis, retinal diseases, preeclampsia during pregnancy, malignant hypertension, pituitary tumor.
Definition and types of ophthalmological diseases of the visual organs
A migraine attack is preceded by a visual aura. This concept means distortion of the image in one or both eyes at the same time. The duration of the aura is from several seconds to 30 minutes. Then comes an attack of throbbing headache, which is not affected by painkillers.
Symptoms and signs of aura
Aura signs:
- glowing dots, lines;
- changing the size of displayed objects and people;
- dark round spots in the direction of gaze.
Terms used to characterize the aura:
- phosphenes
- point reflections that appear in the dark; - photopsia
– false light sensations; - Alice syndrome
- exaggeration or understatement of the image; - scotomas
- dark spots in the visibility zone; - hemianopsia
– narrowing of the field of vision due to blind spots; - homonymous hemianopsia
- simultaneous loss of right or left fields.
The pain is concentrated in the occipital or frontocular part of the head. Its duration ranges from half an hour to several hours. The frequency of pathological manifestations is individual: from once a year to 1-4 times a week.
Cephalgia (headache) with aura is an associated form of migraine.
This will help you understand why red spots appear around a child’s eyes.
The video shows a description of the disease:
Forms and causes of ocular migraine
Types of ocular migraine:
- ophthalmic;
- retinal;
- basilar.
The factors that determine one or another type of cephalalgia are different.
Ophthalmic
In the ophthalmic form, the blood supply to the brain in the occipital region is disrupted. The cause of the spasm is compression of the cranial nerves by venous or arterial vessels.
Retinal
Retinal migraine is caused by reversible retinal ischemia due to decreased cerebral artery tone. There is a violation of light perception by the retina.
For this reason, the retinal form is called retinal migraine. When the blood supply to several areas is impaired, multiple scotomas develop. But this video will help you understand how this happens and what means are most effective in recovery.
If ischemia covers the entire area of the retina, then blindness occurs ().
Basilar form of atrial scotoma
The basilar form is the most severe. Develops against the background of brain stem dysfunction.
Neurological disorders can be caused by:
- lack of oxygen;
- neuro-emotional shock;
- physical and mental fatigue;
- atmospheric pressure difference;
- loud sounds;
- flickering light;
- products containing caffeine.
The disease begins to manifest itself in adolescence. Hormonal changes, traumatic brain and mental injuries are predisposing circumstances for the development of pathology. The age and gender of people most often susceptible to this type of scintillating scotoma are children, adolescents, and women under 20 years of age. You can find out about the causes of dizziness and double vision.
Is ocular migraine dangerous, how to identify and treat it?
With the tightening of the daily rhythm, an increasing burden of problems falls on a person. People increasingly began to complain of headaches, considering migraines to be their usual companion in life. But it happens that during a headache you can go blind for a while. This is how ocular migraine manifests itself.
Definition
Ocular migraine, also called scintillating scotoma, is a sudden onset of visual impairment. At the height of a headache attack, visual disturbances appear, which disappear over time.
Reasons and factors
The main causes of ophthalmic or visual migraine are not eye problems, but neurological ones. They are connected to the vessels of the brain in the area that is responsible for vision. This is predominantly the occipital region.
Before examining why this or that type of ocular migraine develops, let’s consider the general factors of its development:
- existing disorders in the vessels of the brain (underdevelopment, developmental anomalies, aneurysms);
- physical and emotional fatigue;
- imbalance of hormone levels;
- smoking, including hookah;
- food rich in spicy seasonings, smoked meats, alcoholic drinks, chocolate;
- flickering screen, light;
- pungent odors;
- loud noises;
- change of time zones, body biorhythm, lack of sleep.
All of the above becomes a trigger for ocular migraine if the body already has a background of the disease.
Symptoms and periods
Ocular migraine is a separate disease, and not just a symptom, and therefore has certain periods of its occurrence.
This is a prodrome, an aura, which is usually, but not always, followed by a migraine attack, which ends with a post-migraine period (resolution of the attack).
Prodrome
The initial period of migraine develops before the attack; these are its first symptoms. It manifests itself:
- lability of mood (depression, drowsiness, excessive irritability, cheerfulness);
- changes in well-being from increased activity to apathy;
- muscle pain;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (stool upset, nausea, vomiting);
- increased thirst, increased urination.
Each person, depending on his type of nervous system and the functioning of the body, will have his own symptoms.
The second period manifests itself in the form of an aura, if we talk about the classical form. About 25% of people suffering from this disease have it. An aura is a symptom or a group of them that can be used to tell that an attack will soon occur.
Its most common type is a visual aura. The duration of the precursors ranges from a couple of seconds to half an hour, after which a migraine attack appears. Sometimes there may be no headache. This form is called “decapitated migraine.”
You can tell that you have developed a visual aura by the following signs:
- you see flashing flies, lines, zigzags or dots in front of you - these are phosphenes;
- flashes of light appear - photopsia;
- dark areas or spots before the eyes - scotomas;
- objects have changed size - Alice syndrome;
- you cannot see in some areas, for example near the nose or outside in both eyes - hemianopsia;
- vision has become narrow, the feeling that you are looking through a telescope - tubular vision syndrome.
These are also signs of ocular migraine if they appear not before, but during the headache.
Migraine attack
The period of headache in severe cases can take three days. As a rule, pain is localized in one half of the head. The pain is strong, throbbing, growing and intensifying with movement, the slightest irritant: light, noise, heat or cold.
Vomiting may occur during an attack. Migraine status is considered especially dangerous during a prolonged migraine attack. It can even lead to a stroke, as the blood supply to the vessels of the brain is disrupted.
Permission
The resolution phase is characterized by the gradual fading of migraine symptoms and restoration of function. For some time you will feel heaviness in the head, weakness, decreased appetite, blurred vision.
Symptoms of associated migraine
Each form of cephalalgia has its own characteristics and predisposition.
Characteristics of an attack of ophthalmic migraine:
- Signs of photospia, intensifying, last from a few seconds to minutes. The appearance of scotoma of different sizes: from several mm in diameter to homonymous hemianopsia.
- Attack of migraine pain from 30 minutes to 2 hours (less often 6 hours). Nausea and vomiting may occur. The pain center is located in the frontocular-temporal part.
- Restoration of visual function after a few hours.
The pathological process goes through 4 phases:
- compression of blood vessels
(appearance of sparkling dots); - brain hypoxia
(pulsating cephalgia); - relief of spasm and overflow of blood vessels
(pressing dull pain, indicating cerebral edema). - disappearance of symptoms
(dull pain, general weakness).
Information will help you understand what blepharospasm is.
One of the manifestations of ophthalmic cephalgia is Moebius disease (facial nerve paralysis). This is a congenital disease caused by hereditary predisposition and unfavorable course of pregnancy and childbirth.
A migraine attack is accompanied by external manifestations: a dilated and motionless pupil in one eye, a half-lowered upper eyelid,. This condition persists for 1-2 weeks.
Signs of retinal migraine:
- Single, multiple scotomas or amaurosis in one eye appear 1 hour before the attack.
- The headache is concentrated in one half of the head.
- Scotomas are always located on the side where the cephalgia is.
- Sensations when pressing on the eyeball.
- Hypersensitivity to sounds, smells, light.
- Nausea.
The duration of the attack is from half an hour to an hour. Visual acuity returns to normal an hour after the end of the migraine attack.
In the basilar form, the attack lasts no more than 40 minutes.
Previous symptoms:
- tinnitus;
- hearing loss;
- dizziness;
- impaired coordination of movements and speech;
- narrowing of the field of vision in the peripheral part (to the temple or nose);
- partial paralysis of the limbs.
After 20 years, basilar migraine transforms into other types.
Treatment
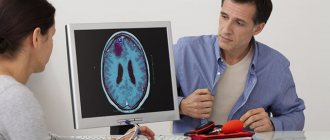
When diagnosing the disease, ophthalmoscopy, angiography, and MRI (CT) of cerebral vessels are used. An eye examination is aimed at excluding ophthalmological causes of visual impairment.
External examination helps to establish:
- line of sight;
- mobility of the eyeball;
- pupil reaction.
A complete examination allows you to confirm or refute the presence of a neurological cause of the disease.
Treatment of atrial scotoma is prescribed and monitored by a neurologist.
In the ophthalmic form, it is suggested to stop the attack at the first signs of an aura. For this, vasodilators and blood thinning drugs (Cinnarizine, Aspirin) are recommended.
Cost from 50 rub.
If the phase of blood vessel overflow occurs, vasoconstrictor medications should be taken. It is necessary to avoid loud sounds, bright lights, and strong odors. For migraine attacks, interictal therapy is carried out more than 2 times a month, which consists of taking nootropics, antidepressants, and muscle relaxants. What types of painkillers and anti-inflammatory eye drops there are, you can find out by.
An attack that continues for several days is called status migraine and requires hospitalization.
The prognosis for ophthalmic migraine is favorable, provided that preventive measures are taken and an attack is prevented in the initial stage. For Mobius syndrome, therapy consists of restoring the functions of the facial nerve.
The selection of medications for retinal cephalgia is carried out on an individual basis. The list of drugs may include analgesics, anti-inflammatory and vasoconstrictors, antidepressants.
There are no effective methods of relief and treatment during the interictal period of retinal migraine.
Migraines are attacks of severe headaches that can last from several hours to several days. A distinctive feature of migraine pain is pulsation during an attack. They may bother you several times a week or a couple of times a year.
Migraines can be with or without aura. Aura is a set of symptoms that occur before the onset of an attack. The effect of the aura often extends to the organs of vision: flickering appears in the eyes, flashes, sparks, and the reaction to light decreases.
Treatment with medications and exercise
When diagnosing ocular migraine, treatment depends significantly on its form and severity. At the first manifestations of an aura, it is recommended to take blood thinning Aspirin, Cinnarizine - to dilate blood vessels. Acute pain is relieved with NSAIDs and analgesics.
In case of mild pathology, the attack is stopped with anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs (Ibuprofen, Analgin, Ketoprofen). If it is moderate, you will need combination medications: Tetralgin, Pentalgin. In severe cases, and especially long-term (migraine status), urgent hospitalization and inpatient treatment are required under the constant supervision of doctors. For severe cephalalgia, painkillers from the class of opiates and corticosteroids are administered. At the same time, the dosage is strictly controlled to avoid side effects and addictive effects. Triptans, which act on special brain receptors, are used only in the treatment of migraine (they are ineffective for other ailments).
A representative of triptans, Antimigraine in the form of a nasal spray quickly helps relieve pain symptoms (15 minutes), in tablet form - after half an hour. But we must remember that its uncontrolled use is dangerous. Only a doctor should prescribe medications and calculate the dose.
Combination therapy during interictal intervals involves courses of nootropics, antidepressants, and muscle relaxants. To relieve inflammatory symptoms (redness, swelling) of the eyes, eye drops (Diclofenac, Indocollir) are used only as prescribed by an ophthalmologist. If migraine attacks recur frequently, it is recommended to regularly take (in courses) medications prescribed by a neurologist in order to avoid subsequent migraine attacks.
Not only medications are used for treatment, a big role is played by: correction of lifestyle, regimen, psychotherapy, autogenic training, physical therapy, swimming, health path. It is important to exclude from the diet foods with large amounts of tyramine, factors that provoke attacks: lack of sleep, stress, any overload. For prevention, use hydrotherapy, massage, acupuncture.
Causes
Factors that can trigger ocular migraine include:
- All information on the site is for informational purposes only and is NOT a guide to action!
- can give you an ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS !
- We kindly ask you NOT to self-medicate, but to make an appointment with a specialist
! - Health to you and your loved ones!
- physical and intellectual overstrain;
- prolonged exposure to stress;
- chronic depression;
- hormonal changes;
- changes in atmospheric pressure;
- taking certain medications;
- non-compliance .
The main cause is disorders affecting the functions of the visual analyzer and disruptions in the blood circulation of the brain.
Ocular migraine is accompanied by a visual aura (flashes, spots). In this case, the following additional symptoms are observed:
- visual hallucinations;
- severe headaches;
- nausea and vomiting;
- violation of pupillary functions;
- ptosis of the upper eyelid;
- strabismus.
Ocular migraine attacks can last up to 2 hours, after which all symptoms disappear without a trace. There are cases of ocular migraine without headache, which are also accompanied by decreased vision.
Risk group
Most often, the disease manifests itself in residents of megacities, since they are the ones who face many stressful situations every day. And those who live in the village are almost unfamiliar with migraines.
This is another confirmation that the psycho-emotional state and lifestyle are of great importance for health. Therefore, it is not surprising that people who are overly passionate about work and career advancement often suffer from migraines.
Often, unbalanced people who are unable to control their emotions, as well as patients suffering from diabetes, experience constant migraines.
Causes of atrial scotoma and risk groups for developing the disease
Atrial scotoma, as we have already noted, is of neurological origin and occurs when a certain area of the cerebral cortex malfunctions.
Various factors can provoke such violations:
- sudden change in weather (for weather-sensitive people);
- hypoxic conditions (lack of oxygen);
- overwork and disrupted sleep patterns;
- hormonal problems;
- diseases that lead to vascular changes in the brain;
- bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol);
- prolonged stress;
- intellectual overstrain;
- eating certain foods in large quantities: smoked meats, cheeses, chocolate, strong coffee and tea;
- taking certain medications;
- exposure to flickering light sources;
- strong odors;
- being in a state of depression.
Also, ocular migraine can be caused by impaired blood supply to those parts of the brain that are responsible for vision, or compression of the vertebral arteries due to instability of the cervical vertebrae or osteochondrosis. It is believed that migraine - ocular and classical - can be inherited, but so far this theory has no practical evidence.
The risk groups for ocular migraine include the following categories of people:
- People over 30 years old, mostly women;
- Residents of cities, especially megacities. Many live in a state of constant stress, eat poorly and regularly experience mental overload;
- Emotional and sensitive people who have poor control over their emotions;
- Suffering from diabetes;
- Women during pregnancy or menopause (when powerful hormonal changes occur in the body).
Symptoms of ocular migraine
| Atrial scotoma |
|
| Retinal migraine |
|
| Migraines arising from visual disturbances |
|
There are other types of migraines. For correct diagnosis, you need to visit an ophthalmologist and neurologist. It is better not to postpone the visit, since not only migraines, but also serious diseases, including tumors, can manifest themselves in this way.
During an attack of ocular migraine, a clear flickering line resembling a zigzag appears in the middle of the resulting scotoma. It persists both with open and closed eyes.
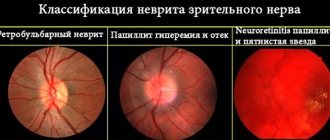
When a scotoma affects the central field of vision, visual acuity drops sharply. When the scotoma moves to peripheral areas, visual acuity returns to normal levels. When studying the fundus of the eye at the time of the attack, no changes are detected.
Types and classifications
- Scotoma that exists in the field of vision of a healthy eye (physiological scotoma);
- Pathological scotoma, which is caused by a number of ophthalmological diseases (for example, glaucoma or retinal detachment);
- Positive scotoma. In this case, the person feels the visual defect as a dark spot;
- Negative scotoma. It can only be detected by eye examination;
- Atrial scotoma, “ocular migraine”.
Depending on the shape of the defect, arcuate scotomas, “auras” with an irregular contour, wedge-shaped, round, oval, and ring-shaped scotomas are distinguished. Also, experts, focusing on the specifics of the development of the pathological process, identify several types of ocular migraine:
- Retinal form of atrial scotoma. In this case, the center of the field of view falls out. This defect in visual perception is so severe that it can cause temporary blindness in both eyes;
- Ophthalmoplegic form of atrial scotoma. This type of painful condition is also called Moebius disease. Ocular migraine in this case is characterized by a disruption of the normal functioning of the oculomotor nerve.
Retinal form of atrial scotoma
Associated basilar migraine also occurs. This condition is characterized by bilateral visual impairment. A number of symptoms suggest damage to the brain stem.
Diagnostics
The following methods are used to diagnose migraines:
- ophthalmoscopy;
- external eye examination;
- identification of neurological disorders;
- analysis of pupillary reactions;
- assessment of motor functions of the visual organs;
- study of the visual field;
- tomography.
Due to the nature of migraines (caused by arteriovenous malformation, and in the ophthalmoplegic form - by arterial saccular aneurysm), the only correct solution may be to visit a neurologist for consultation and examination.
Treatment
As a rule, independent attempts by patients to cure migraine always end in failure.
Effective treatment for ocular migraine should include:
- timely assistance in case of an attack that has already begun;
- preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of an attack.
A person who regularly suffers from headaches should always keep it on hand. This could be paracetamol, aspirin, triptans or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Triptans are most effective for relieving migraine pain. Despite the relative youth of these drugs, they are widely used.
This is due to their spectrum of action:
Medicines that contain caffeine and codeine work well for headaches. At the same time, they must be taken with caution, as they are addictive and can provoke the development of abusive pain. After getting used to such drugs, the brain itself creates pressure, forcing you to drink the medicine constantly and increase the dose.
At the first signs of an approaching attack, you need to lie down and relax. It is recommended to drink a cup of tea with soothing herbs.
If attacks occur more than 2 times a month, it is necessary to carry out a preventive course of treatment.
This course is long-term, it involves changing your lifestyle and following certain rules:
| Physical exercise |
|
| Daily regime |
|
| Healthy lifestyle |
|
| Nutrition |
|
Atrial scotoma in pregnant women
As a rule, during pregnancy this disease manifests itself only in the 1st trimester. In rare cases, attacks may persist throughout pregnancy. The causes include lack of sleep, changes in life schedule, lack of vitamins, and poor nutrition.
Most medications cannot be taken during this time. It is also prohibited to use without consulting a doctor.
- walks in the open air;
- light physical activity;
- control of psycho-emotional state;
- use of alternative medicine methods (only after consultation with your doctor) - yoga, acupuncture.
Ocular migraine is one of the types of the disease, accompanied by a disorder of visual functions due to pathologies that occur in the main vessels of the visual centers. Symptoms typical of a simple migraine are preceded by a visual aura, manifested in the form of glare, flickering, and “blind” spots, which is why this form of the disease received a second name -.
Visual symptoms that precede an attack cause physical and emotional discomfort to the patient. They limit the activities of a person who, in such a state, cannot drive a vehicle, work in production, and sometimes even move around without assistance. To reduce the impact of signs of atrial scotoma on a person’s daily life, it is necessary to find out the reasons for its development, diagnose the disease at an early stage and begin its treatment.
Preventive measures and prognosis
In order to prevent the development of this pathology, it is necessary to do the following:
- Make sure your sleep and alertness patterns are correct. Avoid excessive fatigue during the day or lack of sleep at night.
- Do not subject your body to excessive physical stress. This rule especially applies to heavy athletes.
- Try to exclude caffeine-containing drinks, chocolate and foods containing high levels of tyramine (cocoa, tomatoes, red wine, milk) from your daily diet.
- Yoga and physical therapy classes are shown. Daytime jogging, massages, and cycling are also welcome.
- It is necessary to protect yourself from stressful situations and emotional stress.
- Quitting alcohol, smoking and other bad habits.
The prognosis for atrial scotoma is very favorable. If you follow the above preventive measures, you can completely minimize the risk of occurrence and exacerbation of the disease.
Symptoms of ocular migraine
The main signs of ophthalmic migraine are severe visual disturbances caused by a decrease in blood microcirculation in the posterior cerebral artery. In almost all cases, this type of migraine is accompanied by a visual aura, manifested in the form of flashes, flickering, glare and loss of individual fragments from the field of vision.
Signs of atrial scotoma are:
- The appearance of glare and spots in the central field of both eyes, which subsequently increase in size and spread to the entire peripheral area.
- Spots of different sizes may have a bright color or be colorless. In severe cases, during an attack of atrial scotoma, the patient may become temporarily blind.
- During the aura, the patient may experience visual hallucinations.
- The symptoms do not cause pain and their duration does not exceed 20-30 minutes.
- After the aura, a pain syndrome occurs, characteristic of the usual type of migraine.
- Atrial scotoma does not leave changes in the structure of the fundus during an attack.
Frequent exposure to atrial scotoma is observed in adolescents aged 14 to 16 years, when the vascular and nervous system has the greatest tendency to develop.
Rare retinal migraine
manifests itself in the form of the following pathological signs:
- The presence of single spots in the eyes (scotomas) at the time of the aura, which during severe attacks can cause short-term blindness.
- Pain syndrome, which due to its intensity causes painful nausea and vomiting.
Ophthalmoplegic migraine most often manifests itself in childhood.
, which, against the background of the symptoms described above, has a number of additional signs:
- The appearance of concomitant visual symptoms indicating damage to the oculomotor nerve: strabismus, involuntary drooping of the eyelid, asymmetry of the pupils.
- Development of internal or external ophthalmoplegia - partial damage or numbness of the visual muscles.
- The duration of visual symptoms in ophthalmoplegic migraine can reach several weeks from the end of the pain syndrome.
Visual disturbances associated with headaches may also be due to disorders developing in the brain stem.
Forecast
Ophthalmic migraine has a favorable prognosis, provided that treatment is started at its initial or middle stage. Those who have had Moebius syndrome will require therapy to restore the functionality of the facial nerve. Retinal migraine requires individual selection of a course of therapy.
Atrial scotoma is not a death sentence. Good treatment dynamics and prognosis are possible if all medical recommendations are followed. Unfortunately, even after a long period of remission, migraine attacks can return, especially in a patient who has a genetic predisposition to the disease. Regular examination by a neurologist and neurologist is recommended, and adherence to the preventive recommendations of doctors.
Causes of ophthalmic migraine
Despite the pronounced visual disturbances that appear during ocular migraine, the true reasons for its development are not ophthalmological pathologies, but neurological problems. They are caused by a malfunction of the visual analyzer, located in the brain regions of the back of the head.
Ocular migraine attacks can occur as a result of:
- genetic predisposition;
- vascular disorders developing in the area of the visual center;
- abnormally rapid development of the nervous and vascular system in adolescents;
- sudden hormonal surges.
Ophthalmic migraine can be triggered by one or more factors present in the lives of many people:
- insomnia;
- frequent stress that turns into nervous breakdowns;
- lack of oxygen, asthma attacks;
- overwork due to heavy physical labor;
- mental stress;
- abuse of foods that provoke migraines (chocolate, coffee, citrus fruits, wine);
- smoking;
- flickering of the monitor and other light sources;
- loud music;
- sugary and rich aromas;
- change of weather conditions;
- treatment with drugs that may cause migraine pain as a side effect.
To significantly reduce the number and intensity of visual symptoms during ocular migraine, you need to know the pathological cause of the attacks and methods of its treatment. If external factors have an irritating effect, then it is enough to eliminate them and migraine attacks will be reduced.
Possible complications
The development of complications with ocular migraine is uncharacteristic. Discomfortable symptoms that occur during overwork and stress subside after an attack and eye abnormalities disappear. Most visual abnormalities recover after adequate treatment. Severe pain localized in the area of the eyeball is possible, the eye becomes very watery. In some cases, the skin around the eye turns blue, swelling and redness of the retina occurs. Complex forms of migraine are dangerous if status migraine or stroke develops.
Migraine is capricious and unpredictable, the nature of its manifestations and course is varied. The first principle of her treatment is an individual approach to each patient.
Diagnosis of the disease
Like all types of migraine, atrial scotoma should be diagnosed by a neurologist, while prescribing the patient a mandatory consultation with an ophthalmologist. During the examination, specialists conduct the following studies:
- collecting information about the symptoms that appear and the factors that provoke them;
- examination and tactile tests by a neurologist to identify neurological pathologies;
- visual inspection of the outer surface of the visual organs;
- study of pupil reaction;
- assessment of the condition of the motor optic nerves;
- determination of the boundaries of the field of view;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- examination of the vessels of brain structures on a tomograph.
A comprehensive assessment of the results will allow specialists to diagnose or exclude ophthalmic migraine as a disease.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of ocular migraine is carried out by a therapist, ophthalmologist and neurologist.
Identification of the disease includes a survey, examination, laboratory diagnostics and instrumental examinations:
- Survey. They find out complaints, time of onset of the disease, heredity, injuries and the presence of chronic diseases. Often patients consider themselves absolutely healthy;
- Inspection. Ocular migraine has no specific external signs. Upon examination, you can verify the healthy condition of the fundus, as well as identify cervical osteochondrosis and tortuosity of the veins of the head and neck, which indirectly indicate vascular pathology.
- Laboratory diagnostics help identify anemia, disorders in the coagulation system, and hormonal changes. Ocular migraine does not have specific laboratory symptoms.
- Ultrasound of neck vessels. The method allows you to identify tortuosity, narrowing or underdevelopment of the neck veins and arteries.
- Angiography. Angiography is the introduction of a special substance into the blood, which allows you to obtain a reliable image of any vessels. This method helps to identify all vascular diseases and is the main one for confirming the diagnosis. Angiography is often combined with computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, which can detect minute organic abnormalities in the brain tissue.
IMPORTANT! A common result of the study is the complete absence of any pathology in the brain and blood vessels. In this case, the diagnosis is made based on complaints and interviews.
Treatment of atrial scotoma
If you are susceptible to ophthalmic migraine, it is extremely important to prevent the development of attacks. To do this, if there is a diagnosis during the interictal period, the patient is prescribed a course of treatment, which consists of the following procedures and manipulations:
In case of an acute attack of ocular migraine, treatment consists of its rapid relief. To do this, at the aura stage you should take one of the following medications:
Additionally, the windows in the patient’s room should be curtained and sound sources muffled. He should also be given hot coffee or strong tea with a decoction of chamomile, valerian or lemon balm.
During the entire period of pregnancy, ophthalmic migraine most often manifests itself in the first trimester. This is facilitated by an incorrectly selected diet, a lack of vitamins and minerals, a change in the usual daily schedule and insomnia that occurs due to fluctuations in hormones. In almost all cases, by the beginning of the second trimester, unpleasant symptoms cease to bother you, but sometimes they can manifest themselves throughout the entire period.
In many cases, these simple but effective measures help to significantly increase the period between attacks and get rid of migraine attacks for a long time.
Types of migraine and its phases
The disease can be divided into two main types, namely classic and general migraine. There are other types, but they are relatively rare and are more common in children.
Ophthalmic migraine manifests itself at the age of 6-12 years and, in addition to headache, is characterized by weakness of one of the eye muscles. At the same time, basilar migraine tends to cause dizziness and speech difficulties.
Another rare form of migraine causes weakness in one part of the body but is mostly hereditary. Also, only the aura may appear, without a headache, or the aura appears during pain.
The difference between classic and common migraine is very small. In general attacks, the second stage, called aura, is absent. An aura occurs due to decreased blood flow to certain parts of the brain.
If this decrease is not noticeable enough, the aura does not appear, and the migraine is classified as classic. General migraine is more widespread, and in approximately 80% of cases the headache comes without a preliminary aura.
Having gone through all the phases...
Classic migraine has four phases of development:
- The first one is called prodromal , and most people don't even know about it. It can last from one hour to the whole day. Characterized by decreased dexterity, yawning, feeling tired, stiff neck, thirst, increased sensitivity to light or sound, irritability, cravings for sweets.
- The second phase is the aura , which usually lasts 10-60 minutes. The most common symptom is visual inability, resulting in sparkling, flashing, double vision, or temporary blindness. There may be a decrease in sensitivity in the hands, and sometimes speech difficulties.
- , a moderate to severe headache occurs , which is felt on one side of the head. It is usually accompanied by sensitivity to light and noise, fatigue and drowsiness. Nausea and/or vomiting may be present.
- The fourth phase is the final one, during which deep sleep occurs . After it, a person feels tired, he has no appetite, but there is a feeling of relief.