Accommodation paresis is a fairly common disease. But in order to understand the essence of the problem, you must first define two terms. Accommodation refers to the ability of an organ (in this case the eye) to adapt to changes in external conditions. It shows how the refractive power of the optical system of the eye changes. This mechanism ensures clear perception of objects. Paresis is a decrease in muscle tone. Patients note that their visual acuity is dulled and it is difficult for them to work with close objects. To read the text, you have to bring it very close to your eyes. This creates serious discomfort. What is the mechanism of accommodation and why does paresis occur?
Why is accommodation impaired?
Intense visual stress is the main cause of accommodation spasm. The ciliary muscle, which is in a tense state for a long time (for working at close range), spasms and can no longer relax. Therefore, at one point, a person with naturally good vision may stop seeing clearly into the distance.
This problem is common among people who interact with digital devices for a long time (web designers, programmers), who work with information at the computer (managers, accountants, journalists). The likelihood of an accommodation spasm increases in those who do not comply with the visual load regime, do not pause during work, does not monitor the health of his eyes, forgetting about gymnastics, taking vitamin complexes and the general health of the body.
For a long time, false myopia, or spasm of accommodation, can go unnoticed by a person, because it usually affects not two eyes, but one. This disorder causes discomfort, which people usually attribute to fatigue. In order to promptly detect a problem such as a spasm of accommodation, you need to pay close attention to its first symptoms.
Treatment
Treatment includes prescription of special lenses to reduce eye strain. Clinics provide therapy for disorders of the physiological mechanisms of accommodation using optometry.
Treatment is carried out using individually selected glasses and laser eye microsurgery. The latter method changes the shape of the cornea using a beam. Laser treatment restores visual perception and slows the progression of pathology.
Drug therapy is useful if used in combination with physiotherapy. Medicines prescribed:
- Irifrin;
- Mydriacyl;
- Lutein;
- Atropine;
- Tropicamide;
- Cyclomed.
Parasympathomimetic drugs (Pilocarpine) induce accommodation, while parasympatholytic drugs (Atropine) block it.
Physiotherapy involves the use of electrophoresis and magnetic therapy. These treatment methods not only improve visual perception and stop the course of the pathological process, they help medications better penetrate the eye tissue, thereby enhancing the effect of their use.
Taking vitamin complexes is mandatory. Initially, it is recommended to supplement the patient’s diet with beneficial nutrients obtained from vegetables and fruits. If they are not enough and recovery is slow, dietary supplements with the required complex of vitamins and minerals will be prescribed.
Paralysis of accommodation: diagnosis and treatment. Delivery of contact lenses and glasses in Moscow and Russia
Depending on the cause, surgery may be required to correct the paralysis.
Accommodation paralysis defines a pathological condition in which the near and far points of clear vision of objects and images merge into one. This pathology of neurogenic origin is not widespread.
Most often it appears in children aged 7 to 15 years. It is very rarely detected in middle-aged and elderly people. The disease has no gender and develops equally in both women and men.
Paralysis of accommodation is accompanied by a loss of the ability of the ciliary muscle to tension. With the development of this pathology in people with normal refraction and farsightedness, the ability to recognize close-up small print disappears.
The disease has a certain classification. In medical practice, the types of paralysis of accommodation are clearly defined.
According to the nature of the lesion, paralysis of accommodation is divided into:
- Unilateral - paralysis develops in one eye.
- Bilateral – characterized by paresis of accommodation with pathological changes in the lens, size of the eyeball and its muscles.
Ophthalmologists also distinguish the following forms of the disease:
- Peripheral - caused by dysfunction of the ciliary ganglion.
- Central - accompanied by an inadequate reaction of the pupils and is associated with damage to the midbrain.
- Isolated – caused by damage to the central nervous system, has a central and peripheral form.
Only an ophthalmologist can determine the presence of accommodation and establish its type, form and stage of development.
Treatment for paralysis of accommodation is carried out in an inpatient or outpatient setting. Throughout the course, a follow-up examination by an ophthalmologist is carried out and, if necessary, additional examination is prescribed. This is necessary for timely correction of the therapeutic course.
To treat paralysis in modern medical practice, two main methods are used:
- Conservative.
- Surgical.
Conservative therapy includes: the use of medications, ophthalmic drops to relax muscles and improve eye mobility; use of lenses with positive diopters; performing special gymnastics for the eyes.
The therapeutic method is selected individually in each case, according to the stage of development of the disease and physiological indicators.
The prognosis for paralysis of accommodation directly depends on the cause of the development of the pathology. If it is caused by intoxication of the body with medications or toxic substances, it is enough to exclude them from entering the body and vision will be restored on its own.
But when paralysis develops against the background of impaired functionality of the ciliary muscle, it can lead to a gradual decrease in visual acuity, which cannot be corrected with contact lenses.
Accommodation is the ability of an organism or organ to adapt to any conditions.
The essence of eye accommodation can be clearly explained. If you press lightly on the eyeball with your finger and after a couple of minutes open your eyes, you will notice that our vision is failing us, and we see everything as if in a fog. After a certain time, we again enter normal visual mode.
The concept of accommodation is usually used to represent disturbances in the refractive power of the optical ocular system, i.e. for a clear identification of observed objects located at different distances from a person.
The disease occurs when the connection between the nerve, muscle and lens is interrupted, resulting in a disruption in the transmission of nerve impulses to the brain.
Eye accommodation is a physiological process of changing the refractive power of the eye during visual perception of objects located at different distances from it.
Two components are involved in the process of accommodation: active - contraction of the ciliary muscle and passive, due to the elasticity of the lens.
With spasm of the ciliary muscle, which is observed with uncorrectable hypermetropia and astigmatism, especially often against the background of a general weakening of the body (overwork, intoxication), accommodative asthenopia also develops, but is accompanied by an increase in refraction - a weakening of the degree of hypermetropia, the appearance of false emmetropia and false myopia. The main sign of accommodation spasm is weakening of refraction at the height of cyclopegia.
Paralysis of accommodation occurs when the parasympathetic part of the oculomotor nerve is damaged due to injury, poisoning or drug exposure.
Classification[ | ]
| This section is missing references to information sources. Information must be verifiable, otherwise it may be questioned and deleted. You may edit this article to include links to authoritative sources. This mark was set on June 6, 2020 . |
- According to the level of damage to the nervous system:
- central
- peripheral
- mixed
- psychogenic
- By severity:
- Easy
- Moderate
- Deep
- Paralysis
- Most common within one limb: Weakness of one muscle
- Weakness of a muscle group (flexors, extensors)
- Parts of the limb (distal or proximal)
- One limb (monoparesis)
In addition to paresis of skeletal muscles, the term is also applicable to the muscular membranes of internal organs: paresis of the intestines, bladder.
There are two scales for assessing the severity of paresis - according to the degree of decrease in muscle strength and the degree of severity of paresis, which are the opposite of each other:
- 0 points “muscle strength” - no voluntary movements. Paralysis.
- 1 point - barely noticeable muscle contractions, no movements in the joints
- 2 points - the range of motion in the joint is significantly reduced, movements are possible without overcoming the force of gravity along the plane
- 3 points - a significant reduction in the range of motion in the joint, the muscles are able to overcome gravity and friction (the possibility of the limb being torn off the surface)
- 4 points - slight decrease in muscle strength, with full range of motion
- 5 points - normal muscle strength, full range of motion
Based on the location of the lesion, two groups of paralysis are distinguished, which differ significantly in clinical manifestations:
- flaccid (peripheral) paresis and paralysis
- spastic (central) paresis and paralysis
- Mixed, having signs of both flaccid and spastic paresis.
The most significant features of peripheral paresis and paralysis are:
- Hypotonia up to atony (decreased tone) of muscles;
- Hypotrophy up to muscle atrophy due to cessation of autonomic innervation;
- Hyporeflexia up to areflexia - decreased severity of reflexes from the affected limb;
- Absence of pathological signs;
- Much less often, in some diseases, fasciculations occur - involuntary contractions of individual muscle fibers, which are one of the symptoms of damage to the large alpha motor neurons of the anterior horns of the spinal cord.
Central paresis is characterized by:
- Hypertonicity (increased muscle tone) of the spastic (or pyramidal) type, the “jackknife” phenomenon;
- No malnutrition;
- Hyperreflexia (increased intensity of deep reflexes), up to the appearance of clonus, as well as a decrease in superficial reflexes;
- Pathological reflexes (extensor: Babinsky, Oppenheim, Schaeffer, Gordon, Chaddock, Poussep; flexion: Rossolimo, Zhukovsky, Bekhterev, Mendel, etc.);
- The appearance of pathological synkinesis (friendly movements), for example, when a patient, voluntarily clenching a healthy hand into a fist, involuntarily repeats this movement with the affected hand, but with less force;
Symptoms of the disease
The first symptoms of eye accommodation are often mistaken by people for a sign of fatigue. A person feels that the eyes become tired after hard work, there is slight redness, burning, dryness of the eyes or watery eyes. Subsequently, eye fatigue becomes more pronounced, objects begin to blur, and viewing small details becomes difficult.
The initial stage of accommodation disturbance is asthenopia, characterized by chronic eye fatigue with redness of the whites of the eyes, the edges of the eyelids and unpleasant symptoms - burning, itching, sand in the eyes. Typically, such manifestations disappear after a night's rest.
Symptoms of accommodation spasm are more prolonged and unpleasant. Painful sensations, pain and burning in the eyes intensify, clarity of vision deteriorates, patients note double vision of objects. For young children, indirect signs are moodiness, irritability, the habit of squinting their eyes, and schoolchildren’s academic performance decreases. Without consulting a doctor, a spasm of accommodation can develop into childhood myopia.
A complex form is a pathological spasm of accommodation. Eye symptoms are supplemented by eyelid tremor and nystagmus. The general condition of the body worsens - migraine attacks, trembling fingers, and emotional lability appear.
Symptoms of accommodation paresis manifest themselves differently in nearsighted and farsighted people. With farsightedness, distant vision also deteriorates. Patients with myopia (myopia) often experience severe headaches, severe itching and burning in the eyes.
Notes[ | ]
- Paresis // Medical terms (Russian). - 2000.
- Paresis // Great Soviet Encyclopedia: [in 30 volumes] / ch. ed. A. M. Prokhorov. — 3rd ed. - M.: Soviet Encyclopedia, 1969-1978.
- Rocco Salvatore Calabrò, Alberto Cacciola, Francesco Berté, Alfredo Manuli, Antonino Leo.
Robotic gait rehabilitation and substitution devices in neurological disorders: where are we now? // Neurological Sciences: Official Journal of the Italian Neurological Society and of the Italian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology. — 2016-01-18. — ISSN 1590-3478. - doi:10.1007/s10072-016-2474-4.
Causes
Children have to constantly “load” their eyes with reading at school, and then at home when doing their homework. Added to this load is the constant use of gadgets, computers, and watching TV. There are many more factors that can provoke a spasm of accommodation in schoolchildren than the reasons that cause symptoms of false myopia in adults.
- unbalanced diet and lack of vitamins in the body;
- incorrect body position when reading;
- poor circulation in the spine, especially in the cervical region, disorder of the cervical and spinal muscles;
- using a table and chair that is not appropriate for the child’s age;
- increased strain on the eyes in the absence of eye exercises;
- improper organization of the workspace: poor lighting, too large or too small a distance from which the child reads, etc.
These are the most common reasons. False myopia can also be caused by head/eye injuries and neurological diseases.
Actually, the above reasons can become factors provoking a spasm of accommodation in adults. It just occurs more often among schoolchildren. In adulthood, false myopia occurs in those people whose work involves excessive eye strain, for example, office workers, jewelers, and seamstresses.
The main stimulus for the accommodation reflex to appear is the defocusing of the image on the retina under optimal lighting conditions - light rays from a nearby object are not focused on the retina (defocusing on the retina), this defocusing, perceived by the brain, is an impulse to turn on the accommodation mechanism.
A nerve impulse passing along the oculomotor nerve gives a signal to contract the ciliary muscle. The muscle contracts, the tension of the ligaments of Zinn decreases, and as a result the lens changes its curvature. As a result, the focus of the image moves to the retina. If the gaze is moved into the distance, the focus of the image will return to the retina, there will be no defocus signal, there will be no nerve impulse, the ciliary muscle will relax, the tension of the zonules of Zinn will increase, the lens will eventually reduce its curvature and become flat again.
The development of accommodation spasm is promoted by:
- excessive visual stress (TV, computer, doing homework in the evening);
- poor workplace lighting;
- non-compliance with the daily routine (lack of walks in the fresh air, playing sports, insufficient sleep);
- the desk and chair do not match the child’s height;
- failure to maintain the optimal distance to the book (30–35 cm);
- weakness of the neck and back muscles;
- impaired blood supply to the cervical spine;
- poor nutrition, hypovitaminosis;
- insufficient physical activity.
The picture clearly shows the mechanism of accommodation of the eye in accordance with the distance of the object focused by the eye.
Most often, paralysis of accommodation occurs against the background of excessive psycho-emotional stress. The relationship between the occurrence of pathology and metabolic disorders and diabetes mellitus of any type is also noted.
Since this disease is very rare, medical scientists are constantly studying its triggering factors. As a result of this work, the main causes of accommodation paralysis were established. These include:
- Diseases of infectious etiology: botulism, diphtheria, syphilis, influenza.
- Frequent exposure to cycloplegics and mydriatics.
- Traumatic injury to the ciliary muscle.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Eye contusion.
- Brain pathologies: neoplasms, cysts, abscess, meningitis, encephalitis.
- Damage to the ciliary nerves during surgical treatment with a laser.
These causes cause constantly developing paralysis. A temporary paralytic phenomenon can occur against the background of severe alcohol intoxication.
The reasons for the development of the disease may be different. Most often, paralysis of accommodation occurs due to injuries and microtraumas. A temporary spasm may occur when the brain is contused or when looking at the sun. If severe damage occurs in the form of a burn, then the disease develops on an ongoing basis.
When neurological pathologies occur, paralysis of accommodation is a sign and can be treated if the root cause is eliminated.
There are the following causes of paralysis of accommodation:
- age-related changes;
- tumors;
- inflammation;
- tuberculosis;
- meningitis;
- previous injuries;
- infectious diseases;
- poor nutrition;
- intoxication with drugs or chemical elements;
- diabetes;
- constant physical overload.
The development of paralysis of accommodation also occurs naturally with aging. After forty-five years, the lens becomes inelastic and takes on an irregular shape. Eye strain and physical strain also influence the development of pathology. In order to avoid unpleasant manifestations, it is necessary to visit the doctor more often.
Diagnostics
At the first stage of the ophthalmological examination, vision is checked using a letter table and special equipment. First, the results are recorded without instilling drops that dilate the pupil, and then studies are carried out with a dilated pupil, the fundus is examined using a slit lamp, intraocular pressure is measured, refraction, volume and accommodation reserves are determined.
Causes of accommodation disturbance:
- disturbance of sleep and rest patterns;
- lack of necessary physical activity, sedentary lifestyle;
- excessive visual stress;
- unbalanced diet;
- injuries, tumors, vascular disorders.
Accommodation disorders also have physiological causes. Due to the natural aging of the lens, which can no longer perform its accommodative functions, vision deteriorates. In young people, problems with accommodation are more often associated with abnormal eye strain. Spending a long time at a computer in a forced position leads to disruption of the blood supply to the cervical spine and organs of vision, which negatively affects eye health.
The disease most often manifests in adolescence
The clinical symptoms of paralysis of accommodation have common features with other diseases such as: optic neuritis, infiltration of the optic nerve in glioma and sarcoidosis, Chiari syndrome, Foster-Kennedy syndrome, Lyme disease, drug intoxication, medulloblastoma, lymphoblastic leukemia.
To exclude these pathologies, a differential diagnosis of paralysis of accommodation is carried out. It includes a complex consisting of:
- Hardware refractometry.
- Rheophthalmography
- Ophthalmoscopy.
- Perimetry.
- Sonography.
- Visometry.
- Microscopic examination with a slit lamp.
- Computed tomography of the brain.
- MRI of the eyeball and brain.
- Accommodation studies using sets of negative and positive lenses.
Based on the results of this examination, the ophthalmologist will be able not only to accurately determine the presence of paralysis of accommodation. Such an examination will also help to establish the reasons for its development.
If paralysis of accommodation is suspected, an examination is carried out by a specialist and a medical history is collected. You should not wait until the symptoms go away on their own, this can lead to consequences. It is best to visit a medical facility immediately to avoid complications.
The following research methods are carried out:
- accomodometry is carried out with a special device to study the reaction of the eyes;
- biomicroscopy using this procedure examines the patient’s fundus;
- viziometry reveals visual acuity thanks to special plates;
- pachymetry makes it possible to find out the thickness of the cornea of the eye;
- Ergography This research method checks the mobility of the ciliary ligament.
It happens that a specialist may prescribe an ultrasound or MRI. If there are suspicions of neurological changes, the doctor will refer you for a consultation with a neurologist. In order to prevent further development of paralysis of accommodation, you need to consult a doctor at the first sign.
| Type of medical service | Service price in rubles |
| Complete ophthalmological examination | 1000 |
| Complete ophthalmological examination of children | 1100 |
| Consultation with an ophthalmologist for eye disease in an adult | 500 |
| Consultation with an ophthalmologist for eye diseases in children over 3 years of age | 700 |
| Selection of simple glasses with a prescription | 500 |
| Selection of progressive, office glasses with prescription | 700 |
| Selection of contact lenses with training and prescription | 1000 |
| Selection of contact lenses without training | 600 |
| Training in the use of contact lenses | 400 |
Treatment methods
Treatment with ophthalmological devices makes it possible to achieve a lasting therapeutic effect in young patients. In some cases, it is possible to completely get rid of pathologies such as amblyopia, impaired binocular vision, and false myopia.
The lenses have a corrective effect for myopia. Perifocal models are aimed at correcting central and peripheral vision, which provides excellent visibility and a pronounced therapeutic effect.
The device is a system in which light emitters are located at different distances from the patient’s eyes. Training is carried out by adjusting the image position and the speed of changing “pictures”.
Impact on the visual function of the eyes with light and color stimuli that dynamically move over a certain distance in a closed tube. Particularly effective for accommodation disorders and restoration of binocular vision.
The ophthalmic myotrainer relaxer has a complex effect on the organ of vision and oculomotor muscles. Particularly effective for eye accommodation disorders, as well as during myopia, hypermetropia and computer syndrome.
How to relieve spasm of accommodation
Treatment of spasm of accommodation should be comprehensive. The effectiveness of therapy depends on how responsible the approach of the person diagnosed with such a problem is. In order for the ciliary muscle to relax, special eye drops are used to dilate the pupil. The drug is prescribed by the doctor depending on how long ago such a spasm formed.
False myopia - treatment:
- It is recommended to reduce visual load as much as possible;
- daily, in doses prescribed by the ophthalmologist, instill eye drops with medications that dilate the pupil;
- regularly perform eye exercises by choosing the appropriate technique;
- increase physical activity: play tennis, swimming, dancing to improve blood supply to all organs, including the visual system;
- enriching the diet with foods rich in selenium, vitamins A, B, zinc - include leafy greens, seaweed, egg yolk, salmon, spinach in the menu.
After two weeks of drug therapy, visual acuity improved. In most cases, vision increases by two to three diopters. To achieve a sustainable result, it is necessary to control the visual load regime and constantly do exercises aimed at improving accommodation.
Treatment
Special exercises and physical therapy
Gymnastics for the eyes is carried out in combination with exercises and massage for other parts of the back, as well as the head and temples. It allows you to restore the muscle frame.
Gymnastics for the eyes strengthens the ciliary muscle, allowing the eye to adapt faster. Special exercises help adjust the level of curvature of the lens.
Physiotherapy is carried out after relief of the signs and causes of the disease. It allows drugs to better penetrate tissues.
Eye drops
Medicines relieve spasms. Prescribed:
- Cyclomed;
- Atropine.
Medicines dilate the pupil. Sometimes Irifrin is used, which relaxes the ciliary muscle as much as possible.
The course of treatment and dosage is determined by an ophthalmologist after a comprehensive examination of the patient’s eyes and determining the cause. Sometimes it is enough for a patient to use eye drops for 1 week to obtain a positive effect.
Treatment is carried out in combination with exercises and physiotherapy, since eye drops provide short-term results.
Surgical intervention
The operation is performed if the disease has led to myopia, which is difficult to correct with glasses or lenses and the patient constantly has to use vision correction devices.
Possible complications
Spasm of accommodation, if untreated, can lead to asthenopia. It will be quite difficult to work or study with constant fatigue, headaches and decreased visual acuity. Due to false myopia, true myopia can develop. Myopia and accommodation spasm, although they are different ailments, often cause the same symptoms. It is better to eliminate a symptom such as a spasm than to treat myopia for a long time.
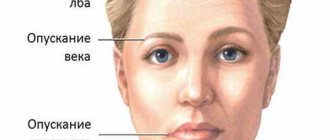
One of the early symptoms of paralysis of accommodation is a decrease in the clarity of perception of objects near
In the initial stage of development, paralysis of accommodation is successfully treated. But in the absence of timely therapy, certain complications may develop.
If initially vision was normal or paralysis appeared against the background of farsightedness, an irreversible weakening of the clinical refraction of the eye may occur. In this condition, the ability to clearly see objects at close range is lost.
Signs of illness
For a disease such as accommodation paresis, there are distinctive symptoms:
- Visually the pupil is dilated;
- Eyes are constantly red;
- Unpleasant sensations in the eye area, which makes you want to rub them;
- Difficulty reading text (if you tilt your head);
- When it is necessary to look at something in the distance, the eyes squint.
The disease occurs suddenly on one or two eyeballs at the same time.