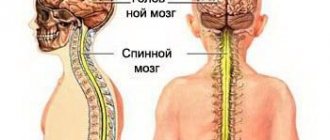
The human body has two movement control systems that work in concert with each other.
The pyramidal system controls voluntary movements and has evolved in connection with upright posture and speech.
Man inherited the extrapyramidal system from the animal world.
It appeared in fish and improved with evolutionary development, retaining great importance in the functioning of the brain.
The human extrapyramidal system consists of clusters of neurons (gray matter, nuclei), which are located in different parts of the brain, but are interconnected. These are the basal ganglia, as well as the red nucleus and substantia nigra, which influence the entire variety of movements of the human body.
The red nucleus is one of the main centers of the extrapyramidal system.
Midbrain. Structure
Its size is only two centimeters.
The midbrain consists of the peduncles and quadrigeminalis. It is responsible for the following functions: visual, auditory, spatial orientation. The peduncles of the midbrain are red (due to the many blood vessels). Connecting with the cerebellum and vestibular apparatus, they provide balance to the body. The quadrigeminals connect the temporal lobe of the brain with bundles of auditory conductors. The red nucleus is involved in regulating muscle tone. The substantia nigra “turns on” the forebrain and helps with reflexes such as chewing and swallowing. The nuclei of the superior colliculi are responsible for turning the eyes and head to the sides. The lower ones - for hearing. Without reflexes, a person cannot survive, so the midbrain is an integral part of the human body.
The two-centimeter element of the brain stem, according to anatomists involved in the study of brain stem, is not complicated at all. For visual study, it is usually suggested to study its cut, and mnemonic techniques recommend memorizing it as the face of a bear, turned upside down with the ears.
A cross-section helps to visualize all the sections from which it is formed, but connections with the upper and lower structures passing through the mesencephalon, communications and tracts, significantly complicate the idea of a small part of the brain.
The structure is very roughly divided into seven segments, but if you delve into its structure, it turns out that everything is much more complicated than one might imagine. This is due to the multifunctionality of education, for the implementation of which nature has provided such a whimsical architectonics.
Four Hills
The structural formation in the upper part of the mesencephalon, which is responsible for processing information that has not yet reached the rest of the brain nuclei, the number of which in the human brain is quite significant, is represented by paired tubercles (posterior and anterior), but not in all creatures inhabiting the Earth.
For example, fish and reptiles have only two. In higher chordates it plays the role of a sentry center, which is extremely important for the preservation of the biological species. The anterior ones are configured to receive visual information from the retina or geniculate nuclei, and the posterior ones are configured to receive information supplied by hearing and the nuclei responsible for auditory and vestibular signals.
Biological expediency consists in the primary processing of unconscious information, its processing before it comes further, and the formation of a sudden defensive reaction faster than other NM structures process it and send signals.
Hence the ability of higher chordates to perform unexpected but necessary actions - scream, jump up, run, while simultaneously forming a chain of signals for transmission to other centers that form a more conscious reaction.
Initially there were two of them, but as they developed they transformed into four tubercles, visualized as protrusions on the back of the SC.
In anatomy, they can be described as the superior and inferior colliculus, since they differ in structure and function, but are considered a complex structure located on the roof of the midbrain.
The location of the quadrigeminal structure is the reason why the roof of the SC is sometimes called the lamina quadrigeminal.
Periaqueductal, or central gray matter is a component of the tegmentum, which is found under the cerebral aqueduct.
The structural features of this segment of the SC suggest that the conductive function is carried out both upward and downward.
The ascending nerve fiber of the spinothalamic tract carries pain and temperature signals to the thalamus, to the line of the medulla oblongata and the locus coeruleus, and the descending one delivers information through it to the spinal cord.
White and gray matter are also the material for the construction of the striatum, in which they alternate in the form of stripes.
Red core
The nuclei of the midbrain are presented in variable forms, for example, the neural structures of the same name on the suture at the border of the medulla oblongata or the quadrigeminal, also sometimes classified as geniculate.
The red kernel, shaped like a sausage, is not round. It consists of two parts - caudal and rostral.
Through it, important signals are transmitted by the regulatory centers of skeletal muscles, the spinal cord (more precisely, its motor nuclei), the extrapyramidal system, the cerebellum, the aqueduct and the globus pallidus.
The activity of the rubrospinal and corticorubral tract would also be impossible without the caudate nucleus, which is conventionally red.
Black substance
The second name is black substance. Regulates autonomic and statokinetic functions, takes an active part in vegetation - the work of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, and is responsible for part of the work of maintaining the tone of the walls of blood vessels.
Located in the space between the pons and the diencephalon, next to the legs, located on the right and left (according to the location of each leg.
It has been proven that neuromelanin is involved in the synthesis of dopamine, and the substance itself projects neuroleptics to important parts of the central nervous system.
Even during the discovery of the structure, it was noted that it was abundantly permeated with vessels, which indicates its ancient origin and importance for the work of the SM.
The literal translation from Latin means “mesh formation.” A complex complex localized throughout the GM trunk, activating its cortex and controlling spinal reflex functionality.
The RF nuclei are responsible for the production of norepinephrine, acetylcholine and serotonin. The importance of this structure of the midbrain formation is undoubted. It is responsible for certain types of behavior, the functions of internal organs, takes part in the initiation and maintenance of wakefulness, attention, thanks to it, a person has indicative reflexes.
Starting from the thalamus and down to the lower part of the medulla oblongata, it directs its processes to other areas, cavities and zones, and communicates with them through paths of different directions.
Located near the substantia nigra and red nuclei, they are a collection of numerous nerve pathways, from here the mesocortical, mesolimbic and dopamine pathways start.
Ventral interacts with reward systems. The structures of the midbrain tegmentum include: the substantia nigra, the reticular formation in its spinal part, the red nuclei and all areas, including the central, dorsal and ventral. It enters, according to some researchers, into the peduncles of the brain, and according to others, it is adjacent to them and limits the structure.
The tegmentum, or tectum of the brain, is the basal or plantar part of the SC; it includes the ventral and dorsal regions, while the tectum (roof) opposed to it is located in the opposite direction.
Brain stems
The most important anatomical formation, responsible for visual orientation, postures adopted by a person, reflex muscle tone and connected in variable ways with other areas and formations of the brain.
The autonomic centers of the spinal, medulla oblongata and midbrain, located in different areas, communicate through the legs with other important structures and cannot work if there is even a bruise of the formation.
And if atrophy occurs, a person loses the ability to respond to external stimuli, cannot provide for himself and literally turns into a vegetable.
Anatomy
The red nucleus (nucleus ruber) is a large collection of neurons along almost the entire length of the midbrain. Its color is explained by the large number of capillaries or the presence of iron-containing pigment in neurons.
The structure is divided into an anterior small cell (parvocellular) and a posterior (magnocellular) large cell part.
| Part of the red core | Parvocellular nucleus ruber | Magnocellular nucleus ruber |
| Neurotransmitters | GABA, glutamate | Glutamate |
| Meaning | Connected to the cerebellum Gives rise to the red nuclear olivary tract | Gives rise to the rubrospinal tract |
| Evolution | Associated with motor learning processes, developed in humans | Ancient motor center |
There are several pathways connecting the structure with other parts of the brain. The main ones:
- The corticorubral tract (corticorubral tract, tractus corticorubralis) stretches from the cortex to the nucleus. It runs parallel to the corticospinal tract of the pyramidal system. This shows parallels between the pyramidal and extrapyramidal systems.
- The cerebellorubrospinalis tract (tractus cerebellorubrospinalis) follows the motor neurons of the spinal cord, but before that it passes through the red nucleus. Connections with the cerebellum provide correction of movements.
- The neurons of the magnocellular part give rise to the rubrospinal tract (red nuclear spinal tract, tractus rubrospinalis, rubrospinal tract). Its fibers immediately pass to the opposite side of the midbrain and then descend to the motor neurons of the spinal cord. In humans, the rubrospinal tract largely determines the movements of the limbs.
- Rubroolivary tract.
The structure also receives signals from the basal ganglia and sends impulses to the cortex.
The function of the red nuclei is to integrate information from the cortex and cerebellum and control underlying structures.
Red cores provide:
- Exit of the extrapyramidal system to the spinal cord.
- Determination of the tone of all skeletal muscles of the body.
- Coordination of posture together with the cerebellum.
- Regulation of unconscious automatic movements, such as changing body position.
Location
The Greek term (mesencephalon) clearly indicates its location - inside the head, its etymology - from roots meaning "middle" and "brain". The Greek term enkephalos literally means inside the head.
The Russian language contains maximum information content - an indication of the main belonging to a complex complex of brain structures and its location.
As part of the brain stem, the SC is located between the intermedius (part of the hypothalamic-pituitary system) and the pons (sometimes called just the pons for simplicity).
A description of the anatomy of the midbrain, starting with the exact localization of the object in the complex interweaving of brain formations, indicates its location as follows:
- caudal direction – border with the metencephalon or hindbrain;
- rostral – boundary with the diencephalon (intermediate);
- the trunk of the large GM consists of the nuclei of the middle, bridge and diencephalon, as part of the structures of the trunk, the mesencephalon can be detected by focusing on the area of \u200b\u200bthe 1st and 2nd cervical vertebrae and the occipital fossa;
- an outdated understanding of the middle complex of important components, now separated into a separate structure - a specific layer between the pons and the diencephalon.
Previously, the mesencephalon was not given the same importance as in modern neurology; it was simply called a mound of medulla.
Studies carried out using special devices have shown that the reflex activity of the midbrain, as part of a complex system of interactions, makes it an indispensable part of the entire physiological functionality of the human body.
Without its independent structures, it is impossible to see and hear normally: the neurons of the quadrigeminal tubercles of the midbrain are responsible for eye movement, regulation of the lens and pupil lumen, start reflexes - as a guarantee of the survival of the body. Because they are the ones who react even to those signals that are not recognized by the auditory or visual center.
Cores
Gray matter accumulates inside the quadrigeminal tubercles, clusters of which are called nuclei. The main function of the nuclei is called the innervation of the eyes. They come in the following types.
Reticular formation - takes part in stabilizing the work of skeletal muscles. They activate the cells of the cerebral cortex of the head, and have an inhibitory effect on the spinal cord. Oculomotor nerve - contains fibers that innervate the sphincter and eye muscles. Trochlear nerve - supplies nerves to the oblique muscle of the organ of vision. Substantia nigra - color associated with the pigment melanin. The neurons of this substance themselves synthesize dopamine. Coordinate facial muscles and small movements. Red nuclei of the midbrain - activate neurons of the flexor and extensor muscles
Age characteristics
In a newborn, the average volume is slightly more than two grams, and in girls it is not much less than in boys, but it is formed in approximately the same form as an adult.
In intrauterine development, the nuclei of the oculomotor nerve and the red nerve are already ready, although the specific coloring of the latter appears only by the age of 2 and is finally visualized no earlier than 4 years.
The baby already has myelin in the substantia nigra, but in not a very significant amount; its active development starts at six months and is finally formed only by adulthood (at 16).
It is no coincidence that a person is considered an adult starting at this age: the substantia nigra is responsible for breathing, cardiovascular system, vascular tone, regulates motor and carries out statokinetic functions, this is an important component of the extrapyramidal system.
The midbrain and diencephalon play an undeniably important role in the activities of the human body. They contain important formations and structures whose responsibilities include regulating the functions of the somatic, autonomic and central nervous systems, brain and spinal cord.
In newborn children, the structure of the midbrain is not fully developed. Until four years, all parts develop evenly. The visual tubercle grows slowly, only by the age of 13 does it reach its size. The red nucleus is formed simultaneously with the conducting pathways. By the age of 16, the substantia nigra is almost completely developed.
Organ structure
It is known that the average human brain has different parts, each of which performs its own role. Quadrigeminal - the structure consists of paired hills. The upper ones are visual and the lower ones are auditory.
The legs contain a black substance. Thanks to it, a person not only lies, but can make precise movements with his hands and eat food. At a certain point, the middle region processes information about when to bring a spoon to the mouth, how to chew food, and what function will allow it to be swallowed.
Useful to know: Brain: functions, structure
The ocular motor nerve originates between the crura and exits from there. It is responsible for the constriction of the pupil and some motor functions of the eyeball. To understand the structure of the midbrain, you need to know where it is located. It is composed of the intermediate and cerebral hemispheres of the cerebrum, its structure is simple and has only two sections. Quadrigemole on nearby two paired colliculi, which form the upper wall. They resemble a plate in appearance. Legs - conductive channels are located there, going to the hemispheres of the anterior section and connecting it with the lower parts of the nervous system.