- General characteristics of the pathology
- Causes
- Symptoms of increased intracranial pressure in infants
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of ICP in infants
- Prognosis, complications
Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) in an infant is quite difficult to diagnose, since the baby, due to his age, is not able to report the symptoms present. This condition is a complex disease that is difficult to treat and causes serious complications.
General characteristics of the pathology
Intracranial pressure changes are characterized by accumulation or insufficiency of cerebrospinal fluid in parts of the cranium. Liquor is the intracranial fluid that circulates through the ventricles in the brain and spinal canals. This creates a healthy pressure, which is considered normal. If there is insufficient amount of cerebrospinal fluid, a decrease in pressure inside the skull occurs, and if there is an excess, it increases, that is, hypertension. In this case, intracranial fluid accumulates in one place, creating a blood clot.
CSF is “born” in the choroid plexus of the ventricles and is then transported to the subarachnoid space through the brain. After each circle, the liquid enters the general bloodstream. The main function of intracranial fluid is to protect the brain and spinal cord from mechanical stress, as well as to provide nutrients and metabolism.
In medicine, increased pressure inside the skull is not an independent pathology. It is considered a symptom that indicates the presence of a particular disease.
Prevention
This pathology can be prevented in infants only by proper preparation for pregnancy. If the mother is healthy, did not abuse anything during the process of bearing a new life, and behaved correctly during the birth process, the likelihood of such a pathology in the baby is minimal.
Screening studies for genetic abnormalities during fetal growth and development should not be neglected. Of course, you should not drink alcoholic beverages, smoke or take drugs, or any medications during pregnancy.
In addition, it is important to pay attention to the baby’s health after birth. Walk more, eat well, do children's gymnastics. Protect your child from hypothermia and overheating, viruses, and get vaccinated in a timely manner.
In essence, the prevention of ICP comes down to preventing the pathologies of which this condition is a symptom. But it is important to understand that no dietary supplements, homeopathic remedies or any other magic pills will help. Only a healthy lifestyle and proper attention to the child will protect against the arrival of such a disaster in your home.
Causes
The causes of high ICP in newborns are:
- Hydrocephalus. Pathology causes the body to produce an excess amount of cerebrospinal fluid, which, after accumulating in one place, stops moving further. In short, intracranial fluid is produced many times faster than it moves and is absorbed into the blood fluid. These clusters increase in size, so the skull begins to move apart, resulting in an enlarged baby's head. The disease is detected immediately after birth.
- Tumors of a benign or malignant nature in the brain. In this case, the tumor puts pressure on the pathways along which the cerebrospinal fluid moves, which leads to increased intracranial pressure.
- Swelling of the brain, which develops against the background of encephalitis or meningitis. The inflammatory process in the brain increases the viscosity of the intracranial fluid, which disrupts its circulation cycle.
- Fetal hypoxia. The problem occurs for the same reason as in the previous case.
- Cerebral hemorrhage - compression occurs.
- Traumatic brain injuries cause cerebral edema. In addition, a large hematoma forms in the skull, which puts pressure on the tissues and circulatory system.
Provoking factors:
- hereditary predisposition;
- chromosomal disorders;
- major prematurity;
- infection inside the womb;
- complex course of pregnancy: constant toxicosis, oxygen starvation, underdeveloped placenta, etc.);
- birth injuries;
- taking certain groups of drugs by the mother during pregnancy.
There is also an unreasonable increase in intracranial pressure. This is noted when weather conditions change, the presence of gas and normal overexcitation (swimming, arrival of guests). This pressure is restored on its own as the baby calms down.
Kawhi Leonard "What's that baby doing?"
ABOUT
"What's It Do Baby" by Cowie Leonard " " is a clip of NBA star Kawhi Leonard enthusiastically saying "What's It Do Baby!" in a video posted by Toronto Raptors teammate Serge Ibaka after the Raptors won the 2020 NBA Championship. The clip gained viral fame in part due to Leonard's reputation for stoicism and odd social behavior, and saw use as a reaction clip on Twitter.
Origin
On June 15, 2020, Toronto Raptors player Serge Ibaka posted a story on his Snapchat featuring him and Kawhi Leonard, whom he calls a "funny guy." When the camera pans to Leonard, he says, "What's he doing, baby!" » The clip was posted on Twitter by user @MSlickk, receiving more than 70,000 retweets and 35,000 likes (shown below).
My guys! Kawhi is killing me pic.twitter.com/oiKFPnlCBX
— M. (@MSlickk) June 15, 2019
Spread
The clip quickly went viral on Twitter, with people joking that Leonard was awkwardly showing off his "funny" side. User @JRoc23 tweeted that it was "Summer of Kawhi 'WHAT DOES IT DO KID'", receiving over 20 retweets and 80 likes (shown below, top). User @OzzyForMayor joked that it looked like Leonard had quit marijuana by typing over 1000 retweets and 5500 likes (shown below, below).
Summer Kaui WHAT'S IT DOING BABY #WhatItDoBabySZN
pic.twitter.com/SDdWGOnnZS
— Jordan Roc (@JRoc23) June 24, 2020
I know a dumb scroll when I see one, Kawhi. pic.twitter.com/dHl82h0hRE
— Osman Noor (@OzzyForMayor) June 16, 2020
Other users began using the clip as a reaction image. For example, Twitter user @MrSoupreme tweeted a joke about Clippy with the clip, receiving over 18,000 retweets and 63,000 likes (shown below, top). User @SheWantsTheVic tweeted the clip as a joke about Apple Music, receiving over 35,000 retweets and 85,000 likes (shown below, below). The jokes were covered by HipHop Wired.
typing essay for windows 97
Paper clip: pic.twitter.com/6oaUoJeGxb
— Stelio Contos (@MrSoupreme) June 24, 2020
Me: Damn my account, I look a little casual
Apple Music: fig.twitter.com/UDxS1NsdhD
— 6'7 Igwe (@SheWantsTheVic) June 24, 2020
Various examples
Wong steps up to fight in Endgam after saving them niggas during the Infinity War
bucks: have COY, MVP and CEO of the year
Kawhi: pic.twitter.com/9D5qDwilgL
— Not my president (@KingFavre) June 25, 2019
When a child hands you a toy and you have no idea what he is doing, pic.twitter.com/75fwWQgy4m
— David Cisneros (@ImDavidSisneros) June 22, 2020
At CVS and from the same cashier you see that for the third time this month you are purchasing plan b pic.twitter.com/lnutTwlixv
— Chubbs Peterson (@macktology101) June 19, 2020
Search for interest
Know Your Meme Store
External links
,
Symptoms of increased intracranial pressure in infants
Despite the fact that the clinical picture is not clearly expressed, there are a number of characteristic signs:
- The first thing that can be noticed by an ordinary person is a significant increase in the circumference of a child’s head. The skull becomes disproportionate to the rest of the body, and the fontanelle protrudes outward. The forehead bones are especially enlarged. With excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the skull, the sutures of the skull bones even separate, which indicates hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome.
- The baby is too irritable and restless, he cries almost continuously, but becomes easier in an upright position. It turns out that if a newborn is lying down, the outflow of venous blood slows down noticeably, which means that the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid also slows down. This leads to additional accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid and venous spasms.
- If you carefully examine the child’s scalp, a venous network becomes noticeable, because large quantities of blood accumulate in the subcutaneous veins.
- The baby constantly spits up, even if he has not eaten before. These regurgitations resemble vomit. This occurs due to irritation of the centers of the medulla oblongata. Therefore, nausea is not associated with eating.
- Graefe's symptom is sure to appear - if the baby's eyes drop down or he is frightened, then a white stripe of the sclera becomes noticeable. It is located between the upper edges of the iris and the eyelids on top. If the child directs his gaze directly, then there is no stripe. This sign is not always a symptom of increased intracranial pressure, since the newborn’s nervous system and visual organs are not yet fully formed.
- The baby has no appetite. This is due to the fact that high intracranial pressure during sucking movements causes pain. The result of this is a decrease in body weight.
- The baby is noticeably behind in development at the physical and mental level.
Features of clinical symptoms
Signs of intracranial hypertension in newborns largely depend on the nature of the underlying disease, which caused the development of symptoms of high pressure in the central nervous system. In infants, ICP manifests itself:
- restlessness, increased irritability and severe crying, especially at night or when in a horizontal position;
- disturbances in normal sleep function, frequent waking up, difficulty falling asleep, etc.;
- regular regurgitation with copious discharge of stomach contents;
- nausea and periodic vomiting;
- an increase in the size of the skull with the appearance of a developed venous network on the scalp;
- swelling of the large fontanel and its non-compliance with age-old norms;
- dysfunction of the visual analyzer, when disturbances occur in the functioning of the optic nerves, a strip of sclera appears between the upper eyelid and the upper edge of the iris, as well as downward deviation of the eyes;
- lack of appetite and lethargy during feeding (the child does not take and suckle well, refuses the bottle, cries);
- slight weight gain or its complete absence;
- delay in psycho-emotional development.
Intracranial hypertension syndrome in children is dangerous due to its complications , which not only significantly reduce the quality of life of a newborn, but can also cause his death. Among these consequences of the disease are:
- severe mental disorders;
- severe forms of visual impairment;
- epilepsy;
- movement disorder syndrome;
- strokes with the formation of foci of ischemia in the head section of the central nervous system;
- hemorrhages in the soft tissues of the brain;
- apnea.
Diagnostics
The following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- Initially, the doctor pays attention to the circumference of the newborn’s head, the dimensions of which should be approximately 30-35 cm. As they grow, the circumference increases by 1 cm every month, so calculating the normal size of the head circumference of a particular child will not be difficult. You can also take measurements at home. All you need is a soft meter. It is applied to the back of the head, where the most convex part is located. Next they wrap it around the head and connect it. At the front of the skull, the meter should be located above the eyebrows.
- The doctor performs neurosonography using ultrasound equipment. This method can be used at any time, even immediately after birth. Neurosonography determines the size of the ventricles. If a pathological process is detected after a certain period of time, this diagnostic technique is repeated.
- The doctor orders a magnetic resonance imaging scan of the brain. The procedure cannot be carried out until the fontanel is completely overgrown. During the examination, the child must behave calmly and not move, which is not typical for infants. Therefore, MRI is done only in the most complicated situations.
The newborn is required to be referred to other specialists. This will eliminate the risk of complications. An examination by an ophthalmologist is very important, because most often you can detect swelling of the optic nerves and varicose veins in the fundus.
Treatment of ICP in infants
Therapy for high intracranial pressure in infants is aimed at neutralizing the causes of development. If there is a mild form of the underlying disease, the child is treated at home, in more severe cases - only in an inpatient setting.
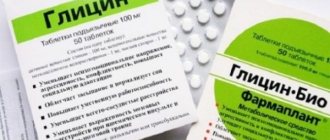
A solution of magnesia , in other words, magnesium sulfate, will help overcome symptoms The drug helps to dilate blood vessels, accelerate blood circulation and outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, thereby stabilizing intracranial pressure. In addition, the baby’s nervous overexcitability decreases and the nervous system generally calms down. Magnesium is administered intramuscularly. Not all pediatricians support this method of treatment: according to the famous pediatrician Komarovsky, the use of magnesia entails pathological disorders in the respiratory center. However, this can only happen with overdoses of the drug.
To remove excess biological fluid, a glycerol solution . It is aimed at eliminating unpleasant symptoms, but does not eliminate the cause of the development of high intracranial pressure. Glycerol, by reducing the volume of cerebrospinal fluid, normalizes not only intracranial, but also intraocular pressure. The drug is taken orally (inside), after diluting it with juice. It is advisable to use natural juice; adding sugar, honey and other sweeteners is prohibited. Freshly squeezed juice is diluted with water in accordance with the requirements of the baby's infancy. The drug acts slowly and gently, is safe for infants, and the results last for a long period of time. There is also a disadvantage of using it - an allergic reaction may occur or stool may be disrupted.
Parents should take care of the baby’s peace of mind - they should not show any negative emotions or aggression in the presence of the child. Hold him in your arms more and give him affection, sing songs and smile. All this calms children, and in a calm state their general well-being improves. Try to saturate your child’s body with vitamins; if you are already introducing complementary foods in the form of purees, limit salt intake. When you put your child to sleep, be sure to place a higher pillow under the head so that the head is not only horizontal. You need to learn how to do special massage manipulations.
The Russian Union of Pediatricians provides useful material about increased intracranial pressure in infants in our video:
What are they and how to say them
During pregnancy, the developing baby moves into several different positions. As you get closer to work, some jobs become safer than others.
The ideal position for the fetus before birth is an anterior position. In this position, the fetus's head is towards the ground and they are facing the woman's back.
Most fetuses reach this position by the last month of pregnancy. The anterior position is also known as the apex, cephalic or occipital anterior position.
An anterior position may reduce the likelihood of complications during pregnancy. Learn more about this and other fetal positions in the womb in this article.
Possible positions of a developing baby in the womb:
Forward position
The best position for the fetus before the baby is born is the anterior position. Most fetuses reach this position before labor begins.
This position means that the fetus's head is at the bottom of the pelvis, facing the woman's back. The fetus's back will be facing the woman's stomach.
This position means that the fetus's head can be tucked in, allowing the top to press against the cervix, which helps open it during labor.
A doctor or midwife may describe a fetus that lies slightly to the left as a left occiput anterior, or LOA, and a fetus that lies a little to the right, as a right occipital anterior, or ROA.
Back position
The back position is also called back to back. Here the fetus's head is directed downwards and the back rests on the woman's back.
This position may make it difficult for the fetus to position its head, which may make it difficult to pass through the small part of the pelvis. This may result in a slower and longer labor than the anterior position and may also cause back pain.
The fetus is more likely to end up in this position if the mother spends long periods of time sitting or lying down, such as if she lies on a bed.
The back of the fetus's body is heavier than the front, so pregnant women can push the fetus into the ideal position by leaning in the direction they want it to move.
Transverse lie position
A transverse lie is when the fetus lies horizontally in the uterus. Most fetuses will not remain in this position in the weeks and days leading up to delivery.
If the fetus is still in a transverse lie position just before delivery, a caesarean section will be necessary.
Without a C-section, there is a risk of a medical emergency known as umbilical cord prolapse.
When umbilical cord prolapse occurs, the woman delivers the umbilical cord into the birth canal before the baby is born.
Buttock position
The buttock position is when the fetus remains with its head up rather than down in the woman's pelvis. There are different types of breech position, including:
- Breech : In this position, the fetus's legs lie straight up in front of their body, so the feet are near the face.
- Full buttock : In this position, the fetus "sits" with its legs crossed in front of the body, so the legs are close to the buttocks.
- Hip bone : In this position, the fetus has either one or both legs hanging below its lower part. If a woman gave birth vaginally, one or both legs would come out first.
Reasons why a fetus may remain in the pelvic position include:
- too much or too little amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus
- uterine fibroids
- irregularly shaped uterus
- several fetuses in the uterus
If a woman is carrying twins, one fetus may be in the anterior or posterior position and the other in the breech.
It is safe for the fetus to be in any of the above breech positions while it is in the womb. However, there are some risks if the fetus is still in the pelvic position when labor begins.
The best way to find out what position your fetus is in is to talk to your doctor or midwife.
At every appointment during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, the doctor or midwife should feel the woman's abdomen to check the position of the fetus.
At the 35–36 week appointment, they will check to see if the fetus has moved to an anterior or posterior position. If the doctor is unsure whether the fetus is in the correct position after the physical examination, they may request an ultrasound scan.
A woman can also determine the position of the fetus at home.
When the fetus is in a back-to-back or posterior position, pregnancy kicks may feel soft. A woman may also notice kicks around the middle of the abdomen, and some people may also see a dimple around the navel.
When the fetus is in an anterior position, a woman may feel more bumps under her ribs. Their belly button may also "pop out."
Most fetuses move into the head-down position at 36 weeks. If the fetus is in the breech position at 36 weeks, your doctor or midwife may suggest an external cephalic version (ECV).
ECV is a procedure in which a doctor or midwife attempts to rotate the fetus manually.
For this procedure, they will first insert a small needle into the woman's arm to relax the uterus.
Using their hands on the outside of the pregnant woman's abdomen, the doctor or midwife will gently manipulate the fetus from the pelvic position to the transverse recumbent position and then to the head-down position.
Some fetuses turn on their own after 36 weeks, and some even turn during birth.
Some people recommend moving into certain positions, taking herbal remedies, and doing certain exercises to help breech babies move into a more favorable position for birth. However, there is no reliable evidence that any of these methods work.
If a person wants to try these medications or methods, it is important to consult with a doctor first.
The baby will move in many different positions throughout pregnancy. During the last few weeks of pregnancy, most babies move into the anterior position, which is the best position for vaginal birth.
If the baby is still in the transverse recumbent or breech position immediately before birth, the doctor or midwife will take medical interventions to ensure the safety of the woman and baby during labor.
Prognosis, complications
In the future, a child who suffered from increased intracranial pressure in infancy can expect:
- dementia and developmental delays;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia, cerebral edema;
- impaired concentration and memory;
- drop in visual acuity;
- persistent headaches and dizziness;
- fast fatiguability;
- ischemic brain disease;
- partial or complete paralysis;
- cessation of blood circulation.
In the best case, a person will have to use medications for life, in the worst, he will die. If treatment is started in a timely manner, the prognosis will be quite favorable.
The main cause of high intracranial pressure in infants is an excess of cerebrospinal fluid production. This is facilitated by oxygen starvation, which develops even inside the womb or immediately after childbirth. Pay close attention to your baby's symptoms of ICP and visit your pediatrician promptly for monthly checkups during the baby's first year of life.