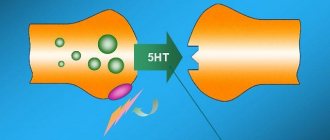
Aminazine is a drug that has a sedative effect on the central nervous system. Included in the group of antipsychotic drugs. This drug is used as an antipsychotic drug. The main component of the drug is clopromazine hydrochloride.
Aminazine is on the list of drugs used to treat nervous disorders, psychosis caused by frequent alcohol consumption, sleep disorders, and paranoid manifestations of schizophrenia. It is also used in the treatment of other mental disorders, which are characterized by a feeling of fear and great muscle tension.
Pharmacological features
What is remarkable about the drug “Aminazin”? Instructions for use, reviews indicate that this is an antipsychotic drug, which in its pharmacological group belongs to antipsychotics. It has hypotensive, antiemetic and antihistamine effects.
The active ingredient of this medicine is a phenothiazine derivative. In addition to the listed properties, this medication has sedative, weak hypothermic, antipsychotic, local irritant, vasodilating and moderate M-anticholinergic effects.
The antipsychotic effect of this drug is achieved by blocking dopamine D2 receptors of the mesolimbic and mesocortical systems. Thanks to these properties, the drug in question is able to eliminate hallucinations, delusions and other productive symptoms of psychosis.
It should also be noted that Aminazin, reviews of which are given below, stops various types of psychomotor agitation, reduces the severity of aggressiveness and psychotic fear.
The sedative effect of this medicine is achieved by blocking the adrenergic receptors of the reticular pharmacy, which are located in the brain stem.
View gallery
Properties of the medicine
What properties are inherent in the drug "Aminazine"? Reviews report that this drug has a depressing effect on conditioned reflex work, relaxes skeletal muscles, reduces the spontaneity of motor activity, and reduces sensitivity to endogenous and exogenous stimuli with stable consciousness. Using large dosages of this medication causes severe drowsiness.
Blockade of the vagus nerve in the gastrointestinal tract and dopamine D2 receptors located in the trigger zone and vomiting center provides the antiemetic effect of the drug. It should also be noted that this drug has a weak effect on M-cholinergic receptors. In addition, its pronounced effect is noted in relation to alpha-adrenergic receptors.
Action of the medication
How does the drug "Aminazin" work? Reviews say that this remedy can completely eliminate the effects that were caused by epinephrine. Its hypothermic effect is due to the blockade of dopamine receptors located in the hypothalamus.
The drug in question lowers blood pressure, increases heart rate, has a weak antihistamine effect and a pronounced cataleptogenic effect, and also reduces the permeability of capillary walls.
When administered intramuscularly, this medication causes a sedative effect within ¼ hour, and when taken orally, after 120 minutes. Patient tolerance to the sedative and hypotensive effects develops after approximately one week.
When this medication is taken orally, its antipsychotic properties become apparent on the 4th or 7th day. The therapeutic effect of this drug lasts about 2-6 months.
View gallery
Overdose
Exceeding the dosage of chlorpromazine prescribed by the doctor can cause many negative manifestations. First of all, a sharp decrease in blood pressure may occur when the drug is administered parenterally. To do this, the dose of chlorpromazine is reduced, prescribing only a small amount of the drug. Also, if the dosage determined by the doctor is not followed, allergic reactions may occur. To reduce the risk of developing such pathologies, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the body, blood pressure, and the condition of the patient’s kidneys and liver.
To stabilize blood pressure, injections are given to the patient lying on his back. And then for an hour he should be in the same position. Sudden rise from a lying position can lead to the development of orthostatic collapse. When drinking alcoholic beverages, use the medicine especially carefully.
For nervous phenomena caused by alcohol intake, the drug is used at a dose of 0.2-0.4 grams per day. If no positive dynamics are observed, the drug is administered intravenously in combination with levomepromazine.
In case of pathological phenomena in the liver or kidneys, taking chlorpromazine is strictly prohibited. The drug is also contraindicated for expectant and nursing mothers. Children can use the drug when they reach one year of age. In this case, the doctor selects the dosage individually for each small patient, depending on the baby’s weight. Children over five years of age take half or a third of the adult dose.
Pharmacokinetics of the drug
Is Aminazine absorbed? Reviews report that when taken orally, chlorpromazine is quickly but not completely absorbed from the digestive system. Its peak concentration in the blood is reached after 4 hours.
This drug undergoes a first pass through the liver. Therefore, its concentration in the blood after oral administration is much lower than the concentration after intramuscular administration.
This medicine is metabolized in the liver with the formation of inactive and active derivatives.
Chlorpromazine is highly bound to plasma proteins. It is widely distributed in the patient's body, penetrating the BBB.
The half-life of the active substance of this medicine is approximately 30 minutes. In this case, the elimination of its derivatives may take longer.
The medication in question is excreted along with urine and bile.
special instructions
Therapy with the drug requires control over the pulse, blood pressure, and the functioning of the hepatic and renal systems. To prevent a sharp drop in blood pressure after intravenous and intramuscular injections, the patient is placed on the couch for 1.5-2 hours.
Due to the fact that the drug can cause photosensitivity , it is recommended to avoid ultraviolet rays and radiation. Ethanol intake is not allowed during therapy. It is necessary to completely eliminate the possibility of chlorpromazine getting on mucous membranes and skin.
The drug affects driving.
Described on Wikipedia as Chlorpromazine.
INN: Chlorpromazine.
Recipe in Latin:
Rp.: Sol. Aminazini 2.5% 1.0 D. td N 10 in amp. S.
The drug "Aminazine": indications for use
Reviews report that this drug is actively used in psychiatric practice. It is prescribed for the treatment of psychomotor agitation in a person with schizophrenia. This medicine is also used for chronic psychosis, acute delusional states, hypomanic agitation, insomnia, psychopathy, mental illness, anxiety, fear and worry.
In addition to the listed conditions, indications for the use of this medicine are: persistent hiccups, alcoholic psychosis, uncontrollable vomiting and severe nausea. In the presence of pain, this drug enhances the effect of analgesics.
View gallery
It should also be noted that the drug in question is prescribed for diseases that are accompanied by increased muscle tone, tetanus (as a combination therapy together with barbiturates) and after suffering disorders in cerebral circulation.
Not long ago, this drug was used for artificial hypothermia as part of lytic mixtures. In anesthesiology, this medication is often prescribed for premedication and potentiation of general anesthesia.
In dermatological practice, Aminazine (patient reviews of this medicine are predominantly positive) is used for itchy dermatoses. In addition, it can be used in the treatment of acute porphyria.
Aminazin (Aminazinum)
Home Medical Encyclopedia Medicines in alphabet A
Synonyms: Chlorazine, Chlorpromazine, Largactil, Megafen, Plegomazine, Chlorpromazine hydrochloride, Ampliactil, Amplictil, Kontomin, Phenactil, Gibanil, Hibernal, Cloproman, Promactil, Propafenin, Thorazine, etc.
Pharmachologic effect. Aminazine is one of the main representatives of neuroleptics (medicines that have an inhibitory effect on the central nervous system and do not cause a hypnotic effect in normal doses). Despite the emergence of numerous new antipsychotic drugs, it continues to be widely used in medical practice.
One of the main features of the action of aminazine on the central nervous system is its relatively strong sedative effect (calming effect on the central nervous system). The general sedation that increases with increasing dose of chlorpromazine is accompanied by suppression of conditioned reflex activity and, above all, motor-defensive reflexes, a decrease in spontaneous motor activity and some relaxation of skeletal muscles; a state of reduced reactivity to endogenous (internal) and exogenous (external) stimuli occurs; consciousness, however, remains.
The effect of anticonvulsants under the influence of chlorpromazine is enhanced, but in some cases chlorpromazine can cause convulsive phenomena.
The main features of aminazine are its antipsychotic effect and the ability to influence the emotional sphere of a person. With the help of aminazine, it is possible to stop (relieve) various types of psychomotor agitation, weaken or completely stop delusions and hallucinations (delusions, visions that acquire the character of reality), reduce or relieve fear, anxiety, tension in patients with psychosis and neuroses.
An important property of aminazine is its blocking effect on central adrenergic and dopaminergic receptors. It reduces or even completely eliminates the increase in blood pressure and other effects caused by adrenaline and adrenomimetic substances. The hyperglycemic effect of adrenaline (an increase in blood sugar under the influence of adrenaline) is not relieved by aminazine. The central adrenolytic effect is strongly expressed. The blocking effect on cholinergic receptors is relatively weak.
The drug has a strong antiemetic effect and soothes hiccups.
Aminazine has a hypothermic (lowering body temperature) effect, especially during artificial cooling of the body. In some cases, in patients with parenteral (bypassing the gastrointestinal tract) administration of the drug, the body temperature rises, which is associated with the effect on thermoregulation centers and partly with local irritant effects.
The drug also has moderate anti-inflammatory properties, reduces vascular permeability, and reduces the activity of kinins and hyaluronidase. Has a weak antihistamine effect.
Aminazine enhances the effect of sleeping pills, narcotic analgesics (painkillers), and local anesthetics. It inhibits various interoceptive reflexes.
In psychiatric practice, aminazine is used in various states of psychomotor agitation in patients with schizophrenia (hallucinatory-delusional, hebephrenic, catatonic syndromes), in chronic paranoid and hallucinatory-paronoid states, manic agitation in patients with manic-depressive psychosis (psychosis with alternating excitement and depression of mood) , with psychotic disorders in patients with epilepsy, with agitated depression (motor excitation against a background of anxiety and fear) in patients with presenile (stressful), manic-depressive psychosis, as well as with other mental illnesses and neuroses accompanied by agitation, fear, insomnia, tension, in acute alcoholic psychosis.
Aminazine can be used either alone or in combination with other psychotropic drugs (antidepressants, butyrophenone derivatives, etc.).
A peculiarity of the action of aminazine in states of excitement in comparison with other antipsychotics (triftazine, haloperidol, etc.) is a pronounced sedative (calming) effect.
In neurological practice, aminazine is also prescribed for diseases accompanied by increased muscle tone (after a cerebral stroke, etc.). Sometimes used to relieve status epilepticus (if other treatment methods are ineffective). It is administered intravenously or intramuscularly for this purpose. It should be borne in mind that in patients with epilepsy, chlorpromazine can cause an increase in seizures, but usually when prescribed simultaneously with anticonvulsants, it enhances the effect of the latter.
The use of aminazine in combination with analgesics for persistent pain, including causalgia (intense burning pain due to damage to a peripheral nerve), and with sleeping pills and tranquilizers (sedatives) for persistent insomnia is effective.
Aminazine is sometimes used as an antiemetic agent for vomiting of pregnant women, Meniere's disease (a disease of the inner ear), in oncological practice - in the treatment of bis-(beta-chloroethyl)amine derivatives and other chemotherapeutic drugs, and during radiation therapy. In the clinic of skin diseases for itchy dermatoses (skin diseases) and other diseases.
Method of administration and dose. Aminazine is prescribed orally (in the form of pills), intramuscularly or intravenously (in the form of a 2.5% solution). With parenteral (bypassing the digestive tract) administration, the effect occurs faster and is more pronounced. It is recommended to take the drug internally after meals (to reduce the irritant effect on the gastric mucosa). When administered intramuscularly, 2-5 ml of 0.25%-0.5% novocaine solution or isotonic sodium chloride solution is added to the required amount of chlorpromazine solution. The solution is injected deep into the muscles (in the upper outer quadrant of the gluteal region or in the outer lateral surface of the thigh). Intramuscular injections are made no more than 3 times a day. For intravenous administration, the required amount of chlorpromazine solution is diluted in 10-20 ml of 5% (sometimes 20-40%) glucose solution or isotonic sodium chloride solution and administered slowly (over 5 minutes).
Doses of chlorpromazine depend on the route of administration, indications, age and condition of the patient. The most convenient and common way is to take chlorpromazine orally.
In the treatment of mental illnesses, the initial dose is usually 0.025-0.075 g per day (in 1-2-3 doses), then it is gradually increased to a daily dose of 0.3-0.6 g. In some cases, the daily dose when taken orally reaches 0 .7-1 g (especially in patients with a chronic course of the disease and psychomotor agitation). When treating with large doses, the daily dose is divided into 4 parts (taken in the morning, afternoon, evening and night). The duration of treatment with large doses should not exceed 1-1.5 months; if the effect is insufficient, it is advisable to switch to treatment with other drugs. Long-term treatment with aminazine alone is currently relatively rare. More often, aminazine is combined with triftazine, haloperidol and other drugs.
When administered intramuscularly, the daily dose of chlorpromazine should usually not exceed 0.6 g. Once the effect is achieved, the drug is taken orally.
By the end of the course of treatment with aminazine, which can last from 3-4 weeks. up to 3-4 months and longer, the dose is gradually reduced by 0.025-0.075 g per day. Patients with a chronic course of the disease are prescribed long-term maintenance therapy.
In states of severe psychomotor agitation, the initial dose for intramuscular administration is usually 0.1-0.15 g. For the purpose of emergency relief of acute agitation, chlorpromazine can be injected into a vein. To do this, 1 or 2 ml of a 2.5% solution (25-50 mg) of aminazine is diluted in 20 ml of a 5% or 40% glucose solution. If necessary, increase the dose of chlorpromazine to 4 ml of a 2.5% solution (in 40 ml of glucose solution). Enter slowly.
For acute alcoholic psychoses, 0.2-0.4 g of chlorpromazine per day is prescribed intramuscularly and orally. If the effect is insufficient, 0.05-0.075 g is administered intravenously (usually in combination with tizercin).
Higher doses for adults orally: single - 0.3 g, daily - 1.5 g; intramuscularly: single dose - 0.15 g, daily - 1 g; intravenously: single - 0.1 g, daily - 0.25 g.
For children, chlorpromazine is prescribed in smaller doses: depending on age, from 0.01-0.02 to 0.15-0.2 g per day. For weakened and elderly patients - up to 0.3 g per day.
For the treatment of diseases of internal organs, skin and other diseases, aminazine is prescribed in lower doses than in psychiatric practice (0.025 g 3-4 times a day for adults, older children - 0.01 g per dose).
Side effect. When treating with aminazine, side effects may be observed due to its local and resorptive (manifesting after the substance is absorbed into the blood) effect. Contact of aminazine solutions under the skin, on the skin and mucous membranes can cause tissue irritation; injection into a muscle is often accompanied by the appearance of painful infiltrates (seals); when administered into a vein, damage to the endothelium (inner layer of the vessel) is possible. To avoid these phenomena, chlorpromazine solutions are diluted with solutions of novocaine, glucose, and isotonic sodium chloride solution (glucose solutions should only be used for intravenous administration).
Parenteral administration of aminazine can cause a sharp decrease in blood pressure. Hypotension (a decrease in blood pressure below normal) can also develop with oral (by mouth) use of the drug, especially in patients with hypertension (high blood pressure); Aminazine should be prescribed to such patients in reduced doses.
After injection of chlorpromazine, patients should be in a lying position (11/2 hours). You should rise slowly, without sudden movements.
After taking aminazine, allergic manifestations on the skin and mucous membranes, swelling of the face and limbs, as well as skin photosensitivity (increased sensitivity of the skin to sunlight) may be observed.
When taken orally, dyspeptic symptoms (digestive disorders) are possible. Due to the inhibitory effect of aminazine on the motility of the gastrointestinal tract and the secretion of gastric juice, it is recommended that patients with atony (decreased tone) of the intestines and achylia (lack of secretion of hydrochloric acid and enzymes in the stomach) be given gastric juice or hydrochloric acid at the same time and monitor diet and function gastrointestinal tract.
There are known cases of jaundice, agranulocytosis (a sharp decrease in the number of granulocytes in the blood), and skin pigmentation.
When using aminazine, a neuroleptic syndrome develops relatively often, expressed in the phenomena of parkinsonism, akathisia (restlessness of the patient with a constant desire to move), indifference, delayed reaction to external stimuli and other mental changes. Sometimes there is a long-term subsequent depression (state of depression). To reduce depression, central nervous system stimulants (sydnocarb) are used. Neurological complications decrease with dose reduction; they can also be reduced or stopped by the simultaneous administration of cyclodol, tropacin or other anticholinergic drugs used to treat parkinsonism. With the development of dermatitis (skin inflammation), swelling of the face and limbs, antiallergic drugs are prescribed or treatment is canceled.
Contraindications. Aminazine is contraindicated in cases of liver damage (cirrhosis, hepatitis, hemolytic jaundice, etc.), kidney damage (nephritis); dysfunction of the hematopoietic organs, myxedema (sharp decrease in thyroid function, accompanied by edema), progressive systemic diseases of the brain and spinal cord, decompensated heart defects, thromboembolic disease (blockage of blood vessels with a blood clot). Relative contraindications are cholelithiasis, urolithiasis, acute pyelitis (inflammation of the renal pelvis), rheumatism, rheumatic carditis. For gastric and duodenal ulcers, aminazine should not be prescribed orally (administered intramuscularly). Aminazine is not prescribed to persons in a comatose (unconscious) state, including in cases associated with the use of barbiturates, alcohol, and drugs. The blood picture should be monitored, including determination of the prothrombin index, and liver and kidney functions should be examined. Aminazine should not be used to relieve agitation in acute brain injuries. Aminazine should not be prescribed to pregnant women.
Release form. Dragee 0.025, 0.05 and 0.1 g; 2.5% solution in ampoules of 1, 2, 5 and 10 ml. Aminazine tablets of 0.01 g, film-coated, are also available for children in jars of 50 pieces.
Storage conditions. List B. In a dry place, protected from light.
| print version | This information is not a guide to self-treatment. A doctor's consultation is required. |
Contraindications
In what cases is the antipsychotic drug Aminazine not prescribed? Reviews from doctors report that this remedy is not used for comatose states of any origin, as well as for severe depression of the nervous system, severe pathology of the heart and blood vessels, intolerance to the active substance, progressive diseases of the brain and spinal cord of a systemic nature, ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract and during breastfeeding. feeding.
Due to the high risk of developing hepatotoxic reactions, this drug is prescribed with extreme caution for alcoholism. The same applies to breast cancer, pathological changes in the blood, prostatic hyperplasia, closed-angle glaucoma, Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, myxedema, vomiting, cachexia, Reye's syndrome and old age.
The drug "Aminazine": instructions for use
The tablets, reviews of which are presented below, are used in psychiatric practice in an initial daily dosage of 25-100 mg. This amount is divided into 1-4 doses. Over time, the dose is increased every four days by 25 or 50 mg until the desired effect is achieved.
In case of anxiety, this drug is taken 2-3 hours before surgery.
View gallery
The maximum single dosage of this drug is 300 mg, and the daily dosage is 1.5 g.
As for the solution, it is administered intravenously or intramuscularly. The initial dosage of this medicine is 25-50 mg.
Before administering the drug, it is diluted with 2-5 ml of sodium chloride solution or procaine solution. Injections are given deep intramuscularly.
The maximum single dosage of this drug is 150 mg, and the daily dosage is 1 g. As for intravenous administration, these values correspond to 100 and 250 mg.
Composition of the drug
Aminazine is available in two forms:
- The solution for parenteral administration (transparent yellow-green liquid) contains 25 mg of chlorpromazine hydrochloride per 1 ml, packaged in ampoules of 2 ml, 10 pcs. in a pack. Auxiliary components: anhydrous sodium sulfite, ascorbic acid, sodium metabisulfite, water, sodium chloride.
- Dragee (coated with a yellow-orange film coating) contains 25, 50 or 100 mg of chlorpromazine hydrochloride per 1 piece, packaged in 10 pieces. in a pack. Auxiliary components: sunset yellow dye, calcium hydrogen phosphate, titanium dioxide, microcrystalline cellulose, hypromellose, potato starch, talc, colloidal silicon dioxide, polyethylene glycol, stearic acid, calcium stearate.
Undesirable effects
Does Aminazine (tablets) cause side effects? Reviews report that in the first stages of treatment, this medication can provoke dry mouth, accommodation paresis, frigidity, increased drowsiness, constipation, sleep disturbance, dizziness, appetite disturbance, tachycardia, a severe form of orthostatic hypotension, urinary retention, decreased potency, allergies and falls. blood pressure.
Long-term therapy with this drug causes muscle cramps in the neck and tongue, neuroleptic depression, akineto-rigid phenomena, extrapyramidal disorders, amenorrhea, akathisia, delayed reaction to various stimuli, hypercoagulation, vomiting, mental changes, heart rhythm disturbances, skin pigmentation, inhibition of bone marrow hematopoiesis , gynecomastia, cholestatic jaundice, galactorrhea, hyperplolactinemia, oliguria, diarrhea and neuroleptic malignant syndrome. With intravenous infusion, phlebitis is formed, and with intramuscular infusion, infiltrates are formed.
View gallery
Interaction
Aminazine may weaken the vasoconstrictor effect of the drug Ephedrine . Some manifestations of ototoxicity (severe dizziness, tinnitus) when taking ototoxic medications may be masked during treatment with chlorpromazine.
The drug reduces the severity of the antiparkinsonian effect of levodopa (as a result of blockade of dopamine receptors). A similar effect is observed when taking clonidine , amphetamine, and guanethidine.
The medication enhances the anticholinergic effect of other drugs, but at the same time there is a decrease in its own antipsychotic effect. The medication is compatible with antidepressants , antipsychotics, and anxiolytics. Long-term use of antipyretics and analgesics is not recommended due to the risk of hyperthermia .
The risk of developing neuroleptic malignant syndrome increases significantly when combined with tricyclic antidepressants, MAO inhibitors, and manprotiline.
Lithium preparations, antiparkinsonian drugs, antacid medications interfere with the absorption of chlorpromazine.
Reviews
According to experts, the medication in question has a powerful antipsychotic effect, eliminating all signs of psychomotor agitation. However, it should be noted that reviews about this product are of a different nature.
Some patients claim that this drug is effective for Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia, psychosis, epilepsy, and also relieves anxiety and tension well. Other consumers believe that the medicine in question provokes the development of epileptic seizures, hand tremors, various personality disorders and a state of increased drowsiness.
View gallery
In any case, this remedy should be used only as directed and under the supervision of the attending physician.