11.5. Violation of the strength of volitional impulses
A decrease in the strength of volitional impulses has been identified in various mental illnesses and organic brain lesions. Such disorders of the will as abulia, hypobulia, hyperbulia and parabulia were identified. Abulia
(from the Greek
abulia
- indecision) - a state of lack of will, lack of motivation to activity.
The patient stops all activities and loses all desires. He lies or sits in bed for a long time, often in a stereotypical position. Eventually, the patient stops performing even those actions that are associated with satisfying the most primitive physiological needs (stops eating, becomes sloppy, unkempt). Often with abulia, mutism
- silence: the patient does not speak, does not answer questions.
Under hypobulia
understand a less pronounced weakening of volitional impulses.
Hyperbulia
is characterized by an apparent increase in the patient’s volitional activity, although it is difficult to imagine that the will can increase under the influence of the disease. It should be more about an overly elevated, manic mood that increases activity.
The most severe violation of actions in pathology of the will is expressed in various forms of stupor
, states of complete immobility.
With one of the forms of stupor - catalepsy
- automatic subordination is preserved when the patient freezes in the position assigned to him. The most pronounced form of catalepsy is a state of waxy flexibility. The patient retains any position given to his body.
Patients with neuroses are characterized by indecision and difficulty initiating action in accordance with the decision made.
Psychology bookap
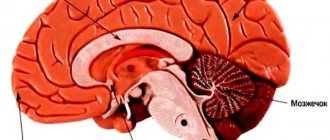
The studies of M. O. Gurevich [1948] showed that the frontal parts of the brain are responsible for volitional functions. Patients with damage to the left frontal lobe are passive and so demobilized that they are not capable of any voluntary effort (T. A. Bragina and N. N. Dobrokhotova [1981]).
In later studies (B. D. Karvasarsky et al. [1969]) it was found that the greatest impairments of volitional efforts were observed in the group of patients with schizophrenia with apato-abulic syndrome. As the task becomes more complex, such patients have no changes in physiological reactions (which indicates their weak mobilization) and the nature of the activity does not change, which is performed slowly, without the proper intensity and persistence. In order for these patients to continue working, constant stimulation from the experimenter was required. Violations of the will in patients with schizophrenia have received various names in the clinic: “reduction of energy potential”, “weakness of the intentional arc”, “weakness of will”, etc.
Violations of will
All topics in this section:
Definition of psychology as a science The word “psychology” comes from two Greek words: “psyche” - soul and “logos” - science.
Psychology is the science of the psyche, i.e. about this form of reflection of reality The main stages of the history of psychology In the history of psychology, the following stages can be distinguished: pre-scientific, pre-scientific, natural science, stage of scientific specialization. Donau lasted the longest
Objective nature of mental laws Since psychology is a science, it studies mental phenomena in their objective, i.e. independent of anything other than active causes. What does this mean? This
Psyche and brain The psyche is a function of nervous matter, nerve cells, the largest accumulation of which is the brain. The brain is incredibly complex. It consists of two
Nervous system and its structure The brain is the main organ of the nervous system in humans and animals. However, its activity is ensured by the entire nervous system of the body. Since the human nervous system is the most complex
Psyche and consciousness The psyche of a living being is a product of the nervous system and brain. In the process of evolution, the psyche arose from the primary forms of movements of plants and animals that occurred in response to external stimuli
Structure of consciousness Consciousness as the highest form of mental reflection has the following structure. Firstly, it is a body of knowledge about the world around us. Consequently, the structure of consciousness includes cognitive
Conscious and unconscious There are two levels in the human psyche: conscious and unconscious. The unconscious, the unconscious, is the totality of all mental processes and states
Modern psychology, its tasks and place in the system of sciences Modern psychology is a complex science. It represents an extensive system of scientific disciplines that study the psyche in all its diversity. Since the subject of psychology is the laws of
The structure of modern psychology Modern psychology is represented by many psychological disciplines. To understand the reasons and essence of this diversity, one should take into account 1) the peculiarities of the study of the psyche in
Interdisciplinary connections of modern psychology Since psychology is at the intersection of sciences, it widely develops connections with these sciences. First of all, these interdisciplinary connections are developed by borrowing research methods
General description of psychology methods The main methods of psychology are observation, conversation, experiment, testing. 1. Observation is a method of studying objects and phenomena, which I conclude
The problem of objectivity in psychological research and the organization of specific psychological research The psyche is not a natural phenomenon. It cannot be touched, weighed, or seen. The psyche belongs to a special reality - ideal. That is why the problem of obtaining objective, i.e. reliable,
When conducting psychological research, there are five stages. The first stage is indicative. It includes preliminary observations of the phenomenon being studied, the formulation of assumptions about the possible causes and properties of the phenomenon, and the formulation of
Correlation as an alternative to experiment Correlation (from the Latin correlation - ratio) is another method of both processing data and obtaining it. The fact is that sometimes it is impossible to apply an experiment in the study of the psyche
General characteristics of the physiological basis of sensations Sensation is considered the simplest of all mental processes. All living beings that have nerve cells have the ability to sense. Feeling is a reflection in the psyche
And the general properties of sensations Sensitivity is the property of the analyzer to respond to the corresponding stimulus. Special studies have shown that the stimulus causes in the analysis intended for it
And the physiological foundations of perception Perception is the mental process of reflecting objects and phenomena in the totality of their qualities and properties with their direct but non-contact impact on the senses.
Properties of human perception The primary property of human perception is objectivity. The objectivity of perception is expressed in the fact that everything that a person perceives when formulated into an image of perception, t
Perception of space The main role in the perception of space is played by binocular vision. Only one two-dimensional image is created on the retina of each eye. But since our eyes are located at some distance
Perception of motion Perception of motion is a reflection of changes in the position of objects in space. It is of vital importance. The main role in the perception of movement is played by the visual and muscle motors.
Perception of time Perception of time is a reflection of the duration, speed and sequence of phenomena. Orientation in time in humans is carried out with the help of the cortical parts of the brain, where a number of analyzers, volume
And its physiological foundations Memory is the total mental process of remembering, preserving and reproducing events and states related to previous life circumstances. Thanks to the memory of su
Psychological theories of memory Psychological research into memory has a long tradition. Currently, there are three main theories of memory in psychology. The first of these is called associative theory
Types of memory There are several bases for classifying the types of memory in humans. According to the duration of information storage, three types of memory are distinguished: long-term, short-term and o
Memory processes Remembering. According to its physiological mechanisms, memorization is the formation and consolidation of the required nerve connections in the cerebral cortex in the process
Memory impairments Memory impairment is called amnesia. With amnesia, a person forgets about certain events. The cause of amnesia is either a disease or another disorder (as a result of injury, blood
General characteristics of thinking Thinking is a mental process that provides the ability to compare, compare, i.e. analyze the received in direct sensation and perceive
Thinking and speech For human mental activity, its close relationship with language and speech is essential. It is this relationship that fundamentally distinguishes the human psyche from the psyche of animals. Animal thinking
The social nature of human thinking The organic connection of thinking with speech and language simultaneously forms and reveals the socio-historical, culturally conditioned, i.e. the social nature of thinking. The social nature of thinking
Psychological specificity of human thinking Many researchers identify two fundamentally different levels of thinking in humans. Concrete, based on more ancient brain structures, and abstract, produced
Logical aspects of thinking Logic is a science that studies how to think correctly. She explores the basic logical forms of thinking and the rules for deducing one thought from another. V l
Thinking in solving problems Thinking begins where a problem situation arises in front of a person, which is characterized by the fact that it does not provide all the necessary conditions for solving it. They must be found using thinking.
Types of thinking and quality of mind In psychology, the following types of thinking are distinguished: visual-effective, visual-figurative and verbal-logical. Visually effective thinking is genetically the earliest. WITH
Basic functions of speech Speech is the central mental process that distinguishes humans from animals. It is thanks to speech that human thinking itself exists, including and, above all, theoretical
Physiological bases of speech Like all mental processes, speech has a very definite and rather complex physiological basis. Its basis is a very complex and special system of temporary connections, which makes it possible to replace
Forms and types of speech In psychology, two forms of speech are distinguished: external and internal. External speech is divided into the following types: oral (monologues
Basic disorders of speech function and properties of speech Since speech is closely related to neuro-brain mechanisms, with any damage to the nerve centers (brain areas) responsible for speech processes, speech disorders occur, which are called
General characteristics of imagination Imagination, or fantasy, is a mental process, the essence of which is the creation of new images (objects, phenomena and situations) based on the combination and transformation of
Physiological bases of imagination Like all mental processes, imagination is determined by the activity of the brain, its cortex. It closes connections when perceiving and consolidating impressions from
Types and techniques of imagination There are the following main types of imagination: active and passive. Active imagination is imagination that
Imagination and creativity Imagination is a mental process that is a prerequisite and condition for such productive human activity in which a product is created, i.e. ideal (in image, in text) or real
General characteristics of will Will is a mental process, the essence of which is the regulation of human behavior and activities related to overcoming internal and external obstacles. IN
Physiological foundations of will Volitional behavior is based on special principles of the functioning of the human brain and central nervous system. The main one of these principles is the principle of dominance. Open ru
Psychological structure of volitional action Human will, manifested in volitional effort, is expressed in volitional actions. Volitional action is always associated with awareness of the purpose of the action, its significance, its meaning, i.e. values,
Volitional properties of a person Volitional properties (qualities) of a person are the skills fixed in his behavior and the corresponding readiness to perform volitional actions. To strong-willed qualities
General characteristics of attention Attention is a mental process that regulates the degree of concentration of a living being on certain aspects of reality or on its states. Vn
Physiological basis of attention The general physiological mechanism of attention is the orienting reflex, the essence and purpose of which is to ensure the safety of a living being. In addition, a person
Types of attention The following types of attention are distinguished: external and internal, voluntary (intentional) and involuntary (unintentional), as well as post-voluntary. External attention - uh
Properties of attention Like other mental processes, attention has a number of properties. The properties of attention are the features of its manifestation. The main ones: volume, distribution, concentration,
Development of attention The role of attention in the human psyche is determined by the fact that it ensures proper perception and understanding of the required information, as well as such a necessary condition for activity as control and self-control
Preliminary explanations The existence of any living creature in the world consists of continuous interaction with the environment. Human life in this regard is especially complex and diverse. First of all, because man
Emotional states. General characteristics An emotional state is a method of mental reflection that is expressed not in external objective actions that are provided by mental processes, but in active
Physiological bases of emotional states Special studies show that emotional states are caused primarily by excitation of subcortical centers and physiological processes in the autonomic nerve
Types of emotional reactions (emotions) and emotional states Among simple emotions, i.e. biologically determined mental states, the following can be distinguished: aggression (anger), pain, hunger, thirst, orgasm, fatigue, fear, disgust, pain
Higher emotions (feelings) of a person Higher emotions are the emotional states of a person caused by socially significant and culturally determined factors. They are called feelings or the highest feelings of a person. By content
General characteristics of the levels of activity of consciousness Since a person lives in a changing world, his psyche constantly reacts to the environment, either more or less actively. The physiological basis of mental response, like
Sleep, dreams and sleep disorders Sleep is a periodically occurring state of protective inhibition associated with the need to restore performance and the biological rhythms of life of the body, regulation
Trance states of consciousness Trance (from the Latin “trans” - through) states of consciousness are a more or less prolonged dream-like mental state in which self-control is reduced and the usual automatic
Hallucinatory and painful states of consciousness States of consciousness in which people are characterized by false perceptions are called hallucinatory. In other words, hallucinatory states are a state of perception in the absence of
Near-death states of consciousness The human psyche is formed during life, thanks to the presence of the brain and the existence of a person among people. The highest level of the human psyche is consciousness. Sometimes towards the end of life consciousness
General characteristics The term “temperament” comes from the Latin “temperamentum”, which means “mixture”. It was this word that was used in Ancient Greece and Rome, where, in fact, this term was born by the famous doctors Hippocrus
Physiological foundations of human temperament The physiological basis of human temperament consists of two main determining factors: physique (constitution) and the type of higher nervous activity. Developed by
And the psychological properties of temperament Choleric temperament is characterized by great intensity and vivid expression of emotional experiences and the speed of their occurrence. This feature is manifested in the characteristic
Taking into account the typology of temperament and its psychological properties in everyday life The fact that all people have a certain type of physique and a certain type of higher nervous activity determines the indisputable fact of their (our) belonging to a certain type of pace
General characteristics of character Character is a set of individual psychological and typological properties of a person that determine sustainable ways of a person’s response to life circumstances and a system of relationships with others.
Character structure Character structure is a stable and logical system of dependencies between its individual traits: core and surface, stable and situational, primary and secondary.
Character Properties In contrast to the structure of character as a holistic formation, individual character properties are also distinguished, i.e. basic character qualities that are the result of self-education.
Individual and typical in character In the character of each person, one can distinguish both individual and typical character traits characteristic of people of a given era, a given layer, a given ethical affiliation. If an individual
General characteristics of abilities Abilities are the mental properties of a person, the presence of which allows him to perform a particular activity in the most successful manner. Other things being equal, life and activity
Inclinations, inclinations and abilities The natural prerequisites for the manifestation and development of abilities are called inclinations. Inclinations are a set of morphological (anatomical and physiological
Structure, types and levels of development of abilities Abilities, as developed functional systems that determine the methods of action characteristic of a particular human activity, have a complex structure. Ability Structure
Development and formation of abilities The development and formation of abilities is determined by the specific socio-historical conditions of people’s lives and is associated with a person’s mastery of the material and spiritual culture accumulated over generations
General characteristics of activity Activity is a form of purposeful psychosocial activity of a person, the overall result of which is a constructive transformation of the surrounding world and the actor himself.
Psychological structure of activity and its meaning Activity as a psychosocial formation has a harmonious psychological structure, which can be understood by comparing the content elements of this structure (needs - motives
Types of activities The main types of human activities are: play, study and work. Each of these activities is leading at different stages.
General characteristics of the phenomenon Personality is a special psychosocial formation, the quality of a person, manifested in his spiritual maturity, social significance, meaningful and authorial involvement
Towards the study of personality Modern psychology has developed stable approaches to the study of personality, the most famous of which are: psychodynamic, behavioral, activity, cognitive, exi
Formation of personality The formation of personality represents the unity of the processes of its formation and development. Each type of concepts and theories discussed in the previous paragraph has a special premise associated with it.
Social types of personality Since personality is a phenomenon determined by the social and sociocultural characteristics of the life of a given society, psychologists from the first third of the twentieth century tried to establish the dependence of
General characteristics of the phenomenon Man, being a social being, does not live alone, by himself. He is one way or another included in a certain primary community in which his life takes place. This is relatively
Types of groups and levels of their development Modern psychology has developed a fairly detailed classification of groups. First of all, conditional and real groups are distinguished. Conditional (nominal
Interpersonal relationships in a group Relationships in a group are an extremely important and interesting aspect of life for both an individual and human society. They distinguish, depending on the type of group, the official relationship
Intimate interpersonal relationships In addition to obvious interpersonal relationships, people enter into secret relationships with each other. This is an intimate relationship, i.e. those that concern only two, occasionally three, and which love
General characteristics of the phenomenon In the process of joint activity, interpersonal and social relationships, people constantly come into contact, which involves one or another impact of their
And the features of social perception The process of communication begins primarily with the first impression that we form about another person. If this impression is favorable, a psychological
Effectiveness of Communication In the area of effectiveness of communication, the main question is how to achieve the necessary impact of the messages being conveyed. After all, it is the influence of some people on
Manipulation and psychological means of protection against it The principles and rules of effective manipulation, set out above, are applied in everyday life in all areas of professional information influence. However, there are also extreme
General characteristics of learning processes Man is a creature that differs from other types of living beings in the type of its life activity. It is as a result of the human way of living life on the globe, in contrast to
The psychological essence of learning Learning consists in the assimilation by a person of certain information and methods of action, as a result of which a person develops a functional organ
The psychological essence of learning Learning is an activity for the systematic acquisition of knowledge, skills and abilities. Learning takes place where a person’s actions are directed by a consciously set goal.
Education as the main condition for mental development The specificity of the human psyche, all its functions (processes, properties and states) is that they develop during the child’s mastery of the socio-historical heritage, i.e. To
Mental development of a child from birth to one year (infancy) A newborn is a child from the moment of birth to the end of the first month of life. Already at birth, the newborn has a number of reflexes, including breathing, sucking
From one to three years (early childhood) The age period from one to the end of the third year of life is called early childhood. Early childhood is a whole era in the mental maturation of a child. The main thing is
From three years to seven (first period of childhood) The age period from three years to seven is also called pre-preschool or the first period of childhood. This is the most interesting period when all the children
In primary school age (second period of childhood) The second period of childhood covers the age range from eight to twelve years. At this age, the place of play as the leading activity is taken by learning.
Adolescence Adolescence occupies a very special place in the development of modern man. Differing in age for boys (from 13 to 16 years) and girls (from 12 to 15 years), it is
Intellectual development of a teenager In a teenager, unlike children, the ability to reason using hypotheses and deductive conclusions matures. In other words, the teenager puts forward fairly well-reasoned proposals
In adolescence The main motivational determinants of adolescence are the desire for self-knowledge, self-expression and self-affirmation. Arosenew
Characterological problems of adolescents Due to the fact that adolescence is a period of rapid development of character, its typological features are manifested so clearly that they have even received the name “adolescents.”
Psychological specificity of behavior and relationships during early adolescence It is a well-known fact that in early adolescence young people are uncompromising. The ultimate strain of personal resources associated with consumption
At the age of early adolescence The age of early adolescence, in addition to the formation of personality traits, represents the most important stage in the development of mental processes and states. This development covers both quantitative
The core perspective of personal development The age of early adolescence, in which a person first faces the question of the meaning of life in all its depth and severity, involves decisions by young people, boys and girls
Life of an adult 24.1. Definition of the concept of “adulthood” Chronologically, adult age ranges from 25-35 (for men) and 21-35 years (for women) to 36-60 years (for men) and 36-55 years (
Specifics of mental processes during adulthood The adult period, as a rule, is the longest in a person’s life. It is this period - from 21-22 years to 55-60 years that is characterized by the highest level of intellectual, creative
Life tasks and crises of the adult period Currently, there are two main approaches to the study of adult development: 1) study of development throughout life; 2) study of the dynamics of life events
Advanced age. The overall potential of a person's life As they enter old age, people are closely faced with the process of aging of the body. Aging occurs in various structures of the body - as an individual, personality and su
Causes of volitional disorders
Mild volitional disorders are considered as features of the emotional-personal sphere, determined by the type of higher nervous activity, conditions of upbringing, and the nature of interpersonal relationships. For example, children who are often ill find themselves in a situation of overprotection from parents, teachers, and peers, and as a result, their strong-willed qualities are weakened. The reasons for pronounced changes in will are:
- Depressive disorders.
A decrease in willpower up to the complete absence of impulses is observed with endogenous depression. In neurotic and symptomatic forms, the intention is preserved, but the implementation of the action is inhibited. - Schizophrenia.
Weakening of volitional operations is a characteristic feature of the schizophrenic defect. Patients are suggestible, fall into a catatonic stupor, and are prone to stereotypies and echolalia. - Psychopathic disorders.
Disorders of the will can be the result of improper upbringing or sharpened character traits. Dependence on others, uncertainty and subordination are determined in persons with anxious, suspicious, hysterical traits, prone to alcoholism and drug addiction. - Manic states.
An increased desire for activity, a high speed of decision-making and their implementation are diagnosed in people with bipolar affective disorder in the manic phase. Also, pronounced symptoms develop during hysterical attacks. - Organic pathologies of the brain.
Damage to the central nervous system is accompanied by a decrease in all components of volitional activity. Hypobulia and abulia are found in encephalitis, consequences of head injury and intoxication.
Sleep disorder
Well, everyone knows what a dream is even without our definition. And if you forgot, ask in the comments. We remember, although we hardly practice, working around the clock on an encyclopedia of real definitions in psychiatry.
In preparation for a conversation about mental disorders, in this post we reviewed a list of what, in fact, can “get upset.” As you can see, there are many weak points. Next time we’ll talk about how disorders of consciousness manifest themselves. Next, step by step, we will run through the entire list. Follow the blog and stay healthy. Especially mentally.
Volitional disorders
Volitional disorders
Will is a mental function that ensures a person’s ability to consciously control his emotions, thoughts and actions. The basis of purposeful activity is motivation - a set of needs, motivations, desires. An act of will unfolds in stages: a motivation and a goal are formed, ways to achieve a result are realized, a struggle of motives unfolds, a decision is made, an action is carried out. If the volitional component is violated, the stages decrease, intensify or distort. The prevalence of volitional disorders is unknown due to the fact that mild deviations do not come to the attention of doctors, and more pronounced ones are found in a wide range of diseases - neurological, mental, general somatic.
Treatment of volitional disorders
Violations of volitional functions are treated in combination with the underlying disease that caused them. The selection and prescription of therapeutic measures is carried out by a psychiatrist and a neurologist. As a rule, treatment is carried out conservatively with the use of medications, and in some cases, psychotherapy. Rarely, for example, with a brain tumor, the patient needs surgery. The general treatment regimen includes the following procedures:
- Drug treatment.
With a decrease in willpower, a positive effect can be achieved by using antidepressants and psychostimulants. Hyperbulia and some types of parabulia are corrected with the help of antipsychotics, tranquilizers, and sedatives. Patients with organic pathology are prescribed vascular drugs and nootropics. - Psychotherapy.
Individual and group sessions are effective for pathologies of the volitional and affective sphere due to psychopathic and neurotic personality disorders. Patients with hypobulia are advised to undergo cognitive and cognitive-behavioral approaches, as well as psychoanalysis. Hyperbulic manifestations require mastering relaxation, self-regulation (auto-training), improving communication skills, and the ability to cooperate. - Physiotherapy.
Depending on the prevailing symptoms, procedures are used that stimulate or reduce the activity of the nervous system. Low-frequency current therapy and massages are used.