Vegetoneurosis manifests itself in different ways.
For example, a patient complains of pain in the heart, but all studies show that the organ is in perfect order. Or the patient has problems with the digestive system (vomiting, nausea, stool problems, pain in the stomach), but the doctor does not detect any pathologies. It is likely that the true cause of the disease was a disruption of the autonomic nervous system, and it is not just anything else that needs to be treated, namely autonomic neurosis.
When we talk about vegetative neurosis, we mean cases in which the autonomic nervous system ceases to function correctly. This leads to a variety of pathologies, the true causes of which not every diagnostician can determine.
Function of the autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a complex mechanism. It is part of the general nervous system and is responsible for connecting various organs, glands and blood vessels. A person cannot control its activity. However, the full functioning of the autonomic nervous system is important for normal physical and mental state.
Among its main functions are the following:
- regulation of the body's functioning during sleep;
- restoration and replenishment of energy resources;
- ensuring normal speed of metabolic processes;
- regulation of tissue excitability;
- impact on mental functions;
- participation in behavioral reactions.
Any disruptions in the functioning of the ANS negatively affect the functioning of the entire body.
Autonomic disorders in neuroses can have 2 origins. Neurosomatic nature manifests itself in dysfunction of the genitourinary, digestive, cardiac or respiratory systems. In such cases, patients suffer from speech or motor function disorders, and they may experience migraines. Neurosis can also have a psychopathological nature. In this case, disturbances in the functioning of the psyche are observed. They can be expressed in the form of depressive disorders and the appearance of phobias.
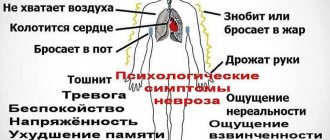
Main symptoms
Absolutely all disorders of the autonomic nervous system are usually classified in medicine as neurasthenia.
All diseases in this group have the same symptoms, which you should know in order to identify autonomic neurosis.
- The appearance of all kinds of erosions and ulcers on the body, muscle atrophy, as well as changes in the structure of hair and nails are all signs of vegetative-trophic syndrome. Usually, with this syndrome, all other organs remain completely healthy.
- Vasomotor syndrome is considered one of the most unpleasant. In this case, there is a severe headache, which can be either constant or come in the form of migraine attacks. Blood pressure also constantly increases and decreases. Due to such changes, Meniere's syndrome often develops, when a person suffers from dizziness and nausea.
- Against the background of simultaneous stress and a predisposition to allergic reactions, a vegetative-allergic syndrome develops. It is accompanied by itching and nasal congestion, sneezing, redness of the eyes, and general weakness of the body. In complex forms, Quincke's edema develops, which can be eliminated with the help of special medications.
- Vegetative skin syndrome develops in those people whose skin on the face and body is hypersensitive. When such a vascular neurosis begins to develop, the skin becomes pale and sometimes acquires a bluish tint. The face is flaky, there is a feeling of tightness and increased dryness.
- A very terrible symptom of neurosis is considered to be a complete disruption of metabolic processes in the human body. This is accompanied by stool disturbances, lack of air, and stomach pain. This syndrome is called vegetative-visceral.
All these described syndromes are symptoms of autonomic neurosis. If neurosis is provoked by injury, then first of all the organs that are located near the injured area begin to work poorly. With neurosis, which arose solely on nervous grounds, organ dysfunction appears somewhat later.
Definition of disorder
Autonomic neurosis is usually understood as a whole complex of symptoms that characterizes a disruption in the functioning of internal organs. It develops against the background of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. Most often, patients consult a doctor with complaints of pain in the heart, head and general weakness. However, diagnostic studies do not reveal structural changes. Patients may also experience a constant feeling of anxiety, insomnia and loss of energy. Most people associate them with weakened immunity, cardiac problems, or ordinary fatigue.
The pathological condition usually develops as a result of prolonged stress, excessive physical exertion or disruption of the work/rest regime. Bad habits or poor nutrition can affect its occurrence. Children also suffer from symptoms of autonomic neurosis. However, in them the occurrence of pathology is most often due to strong experiences associated with conflicts at school or with parents.
It is noteworthy that there is no mention of autonomic neurosis in any classification of diseases. This is not a disease, but a symptom complex that characterizes various disorders. Doctors are still arguing about the appropriateness of such a diagnosis. Therefore, there is no universal treatment. It all depends on the lesion and complaints directly from the patient himself.
Complications of the disease
The neurovegetative form of vasomotor rhinitis with severe symptoms contributes to the formation of complications. Polyps often form in the nasal concha and septum. They block the nasal passage and sinus openings. Surgical treatment consists of removing the polyp.
Purulent sinusitis and sinusitis occur against the background of a long course of vasomotor rhinitis. Swelling of the mucous membrane leads to the accumulation of viscous exudate, which prevents its natural removal. Bacterial flora joins and purulent contents form in the paranasal sinuses. Patients complain of headaches, elevated body temperature and purulent nasal discharge. Treatment requires the use of antibiotics and rinsing the sinuses with antiseptics after puncture of the paranasal sinus.
Causes of pathology
Currently, doctors have been able to identify almost all the factors influencing the occurrence of pathology. The main causes of autonomic neurosis are the following:
- history of traumatic brain injury;
- infectious processes of acute or chronic course;
- exhaustion due to a strict diet;
- prolonged exposure to stress;
- individual characteristics of the nervous system;
- systematic lack of sleep;
- bad habits;
- excessive physical activity.
The disorder has a genetic predisposition. 70% of people whose close relatives suffered from manifestations of autonomic neurosis have a similar diagnosis. This is due to inherited mechanisms regulating the functioning of the nervous system.
The main causes of the development of autonomic neurosis
Autonomic neurosis is a lesion of various tissues and organs associated with functional and dynamic disorders of the autonomic nervous system. This disease is accompanied by various manifestations. However, during a general examination, doctors do not detect structural changes in the organs the person is complaining about.
In a normal state, the autonomic system is a complex of cells that provide innervation to systems, organs, vessels and glands. A person cannot control the functions of this system. They are as follows:
- strengthening metabolic processes;
- increased tissue excitability;
- regulation of systems operation during sleep;
- restoration of energy reserves;
- effects on mental and physical functions;
- participation in behavioral reactions.
If there are problems in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, disturbances in these functions occur. That is why this disease can lead to any pathological conditions in humans.
According to its occurrence and development, vegetative neurosis is divided into several groups:
- The second group is vegetative neuroses that arose in connection with the pathology of the subcortical vegetative centers, which is functional and dynamic in nature. The consequence of this is disruption of the activity of certain body systems. If the vascular system is affected, vascular neurosis occurs, leading to an increase in pressure (hypertension) or a decrease (primary hypotension). When the respiratory system is damaged, bronchial asthma develops. Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract lead to peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum. Disturbances in the functioning of other body systems lead to the occurrence of corresponding diseases. In patients with neurosis of the second group, the synergistic activity of different parts of the autonomic nervous system is also impaired.
- In the first group, the development of vegetative neurosis occurs against the background of general neurosis, manifested in the form of neurasthenia, hysteria or psychasthenia. Autonomic disorders are manifested by such disorders as changes in heart rate, arrhythmia, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, and shortness of breath. Vegetative neuroses belonging to the first group develop as a result of impaired functioning of the cortical-hypothalamic structures of the brain (the hypothalamus is the highest vegetative center). In addition, the development of vegetative neurosis is facilitated by the patient’s personality traits, as well as infections and vitamin deficiency, which weaken the nervous system.
- The third group includes vegetative neuroses, which are a consequence of a pathological process that has arisen in the periphery. The cause of these processes is local traumatic injuries, damage to one or another organ.
Currently, almost all factors that can provoke this pathology have been identified. The development of autonomic disorder can be observed against the background of both various psychological and physical disorders. The following reasons for this pathological condition can be identified:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- acute and chronic infections;
- exhaustion of the body due to a strict diet;
- prolonged exposure to stress;
- individual characteristics of the nervous system;
- grief from the loss of loved ones or relatives;
- systematic lack of sleep;
- bad habits;
- excessive physical activity.
In some cases, the appearance of such autonomic disorders of the nervous system has no apparent reason. Autonomic dystonia can manifest itself even in childhood. This is often facilitated by a long-standing internal conflict against the backdrop of an unfavorable emotional climate in the family.
Because of this, autonomic neurosis can also develop in an adult. Often this problem is associated with genetic factors. It was noted that vegetative-vascular neurosis develops in approximately 70% of people who have close blood relatives suffering from this pathological condition. A possible reason is inherited mechanisms of regulation of the nervous system.
Physiological manifestations
Physiological symptoms of autonomic neurosis in men are primarily manifested by decreased libido (in 30% of cases). Impotence gradually develops and the desire for intimacy disappears. Women also experience similar manifestations. A sudden hormonal imbalance occurs. Menstruation is irregular or completely absent.
Other physiological signs of the disorder include the following:
- Impaired functioning of the respiratory system (shortness of breath, feeling of suffocation during sleep).
- Problems with the cardiovascular system (increased heart rate, joint pain).
- Dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system (muscle weakness, difficulty moving, cold extremities).
Another manifestation of autonomic neurosis is spasms of cerebral vessels. Patients complain of severe headaches, which sometimes end in fainting. There is a sharp increase or decrease in blood pressure, which leads to problems with sleep. Pain appears in the stomach and intestines. Food is difficult to digest and appetite disappears. This is reflected in a person's weight. Due to nervousness, he begins to rapidly lose weight.
Symptoms
The neurovegetative form of rhinitis has some similarities with the runny nose of another pathogenesis, but the disease is not characterized by an increase in body temperature. The clinical picture looks like this:
lack of nasal breathing, worsening when the patient lies horizontally;
- copious mucous discharge;
- headache and migraine;
- sleep disturbance and insomnia are observed;
- dry superficial cough;
- decreased performance and memory impairment;
- mild signs of cerebral hypoxia;
- dyspnea;
- nervousness and irritability;
- burning and itching in the lower part of the nose;
- feeling of nasal congestion in the bridge of the nose;
- tearfulness (may be absent);
- fatigue and absent-mindedness.
In the absence of timely treatment, the symptoms become more intense, and nasal congestion causes secondary infections through the oral cavity.
A notable feature of neurovegetative rhinitis is temporary relief of breathing or a feeling of complete recovery without the use of medications. This condition lasts no more than 20 minutes and often occurs in the evening.
Associated bacterial or viral agents cause a number of complications affecting the ENT organs (ears, paranasal appendages and nasopharynx).
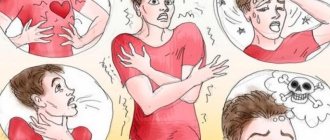
Psychological symptoms
This group of symptoms of autonomic neurosis resembles the clinical picture characteristic of depression or mental disorders. The patient becomes irritated. He burns out emotionally. For this reason, difficulties arise with study or work. He is constantly haunted by a feeling of fear and anxiety.
Men may experience excess energy. On the other hand, physical and emotional exhaustion and loss of strength are possible. The patient feels constantly tired, even if he has not done anything during the day. As a result, he has suicidal thoughts, his general well-being worsens, and the desire to do anything disappears.
Among the fair sex, autonomic neurosis is manifested by excessive concern for one’s health. They can measure temperature, pulse and blood pressure several times a day. Gradually, self-esteem falls, and a negative attitude towards appearance appears.
A previously emotional person becomes depressed. On the contrary, calm people get a charge of vivacity, however, it does not affect their professional success. There are also changes in relationships with people. Conflicts become constant companions during conversation. A person may cry when he realizes his loneliness.
About provoking factors
The reasons for the appearance of vegetative neurosis include the following factors:
Quite often, the development of autonomic neurosis has its roots in distant childhood. Often this disease can be associated with serious psychological trauma - for example, violence or improper behavior of adults.
In this case, the child experiences an internal conflict, which over time transforms into autonomic neurosis. It can appear even with a lack of love from parents.
In adult life, provoking factors can be any conflicts in the family and at work, which are the cause of internal protest. Sometimes the cause of the disease is hormonal fluctuations. In women, this often happens during pregnancy or menopause.
Unfavorable environmental conditions, intoxication, and changes in climatic zones often act as provoking factors.
Intelligent traits
Intellectual manifestations of autonomic neurosis are reflected in the ability to concentrate. A person is constantly distracted and may confuse individual phrases or words in a conversation.
Other symptoms of the disorder include the following:
- memory impairment;
- lack of desire for self-development, improvement of quality of life or financial situation;
- difficulties with time management.
Quite often, doctors have to deal with symptoms of the disorder from three groups simultaneously. This indicates the progression of neurosis, which requires longer and more complex therapy.
Diagnostic methods
VSD is not a diagnosis in the sense of a specific disease, but contains an uncharacteristic conditional picture in which the functions of the ANS are disrupted. The doctor will first ask about your medical history (anamnesis). Therefore, he will ask what conditions provoked the symptoms, when the disorders arose, in what situations they occur, and whether there are other incriminating symptoms. The patient's living situation, alcohol and drug use will provide important information to the doctor.
Tests are then carried out to check for the presence or absence of physical causes for the symptoms.
A physical examination will shed light on some symptoms. For example: in a patient with frequent gastrointestinal problems, the doctor scans the abdominal wall. If there are complaints about the heart, then he checks the sounds of the valves with a stethoscope.
Pulse and blood pressure measurements are needed to identify circulatory disorders. The doctor can check the patient with 24-hour blood pressure monitoring if necessary.
Holter
Blood tests can check for inflammation in the body, nutritional deficiencies, and excess or deficiency of hormones. And possible physical causes: thyroid dysfunction or iron deficiency can be excluded.
If a physical disorder cannot be ruled out and symptoms persist for a long period of time, special examinations are prescribed depending on the disease: electrocardiography (ECG), stool or urine examination, ultrasound and x-ray examination. However, the doctor tries to avoid unnecessary and stressful tests.
Advice! VSD cannot be diagnosed, but it is difficult to refute. The diagnosis is made by doctors if there are no physical symptoms.
Establishing diagnosis
Symptoms and treatment of autonomic neurosis can be dealt with simultaneously by several specialists (therapist, cardiologist, endocrinologist, etc.). It all depends on which system is affected.
However, diagnosing the disorder is quite difficult due to the lack of specific symptoms. It can occur in any of the body systems, and is accompanied by an extensive clinical picture. Each of the symptoms is typical for a separate disease. Therefore, the doctor has to prescribe a comprehensive examination of the patient to exclude the disease of which he complains. After excluding specialized pathologies and assessing health by specialists, the doctor can make a correct diagnosis.
Characteristics and description of the problem
Autonomic dysfunction is a set of functional disorders that are caused by a disorder of vascular tone and the development of neuroses that worsen a person’s quality of life.
With this condition, the normal response of blood vessels to internal or external impulses is lost, and they either expand or contract. The ANS monitors the activity of organs and systems in the body, which are influenced by various internal and external causes. It helps the body adapt to changing environmental conditions. This nervous system has two subsystems in its structure:
- Sympathetic NS promotes intestinal contractions, increased sweating, heart rate, vasoconstriction, and increased blood pressure as a result of increased heart activity.
- Parasympathetic nervous system promotes muscle contraction, stimulation of the activity of all glands in the body, dilation of blood vessels, and reduction of pressure as a result of slowing down the heart.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QDWF-HCpjkA
There is a balance between the activities of these subsystems; if this balance is disturbed, the functioning of internal organs and the whole organism occurs, and autonomic dysfunction syndrome develops. This disorder is a condition in which symptoms of somatic pathologies appear in the absence of organic lesions.
VNS dysfunction is very common in medicine today; it is observed in 15% of children and 80% of adults. The disease usually appears between the ages of twenty and forty years. Women are more susceptible to developing pathology. Autonomic dysfunction in adolescents always manifests itself.
Treatment recommendations
After confirming the diagnosis of “vegetative neurosis,” many patients begin treatment with herbs and other folk remedies. However, this approach gives only temporary results. With such a diagnosis, it is impossible to do without qualified medication and sometimes psychotherapeutic help.
In addition, doctors recommend completely reconsidering your lifestyle. It is necessary to take time to rest, try to eat right, and eliminate all bad habits. Don't overload yourself. It is better to abandon planned activities for the next few months while therapy continues. Rational use of your own strength helps strengthen the nervous system, which means it will help in the fight against pathology.
Types of ANS disorders
It is customary to distinguish several types of disorders of the autonomic nervous system:
- Somatoform autonomic dysfunction, the treatment of which is quite successful. This pathology occurs most often. It is characterized by the manifestation of neurosis in the form of signs of various chronic diseases, which in fact do not exist. In this case, panic attacks, psychogenic cough, dizziness and indigestion are often observed. This phenomenon is associated with chronic stress and depression.
- Damage to the cerebral cortex that develops as a result of road accidents, brain injuries, and central nervous system pathologies. In this case, a person feels severe dizziness, his blood pressure decreases, frequent urination and diarrhea develop. After such attacks, the patient complains of weakness and lethargy.
- Continuous irritation of the structures of the peripheral nervous system often occurs before menstruation, with urolithiasis, pain in the neck. Such dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system manifests symptoms clearly, which is associated with the development of serious pathologies in the body. If any signs of the disease appear, you should visit a doctor.
Drug therapy
Autonomic disorders in neuroses require drug treatment. Doctors use a wide range of medications to treat symptoms of the disorder.
Treatment usually begins with sedatives. They help to calm down, get rid of feelings of anxiety and increased nervousness. Such products are made on the basis of herbs and medicinal plants (hawthorn, valerian, lemon balm, mint). “Novopassit” and “Persen” have proven themselves well.
To treat serious nervous disorders, tranquilizers are used. They are prescribed in cases of prolonged depression, the emergence of fears and phobias that interfere with leading a full life. They also help cope with panic attacks and increased anxiety. Among the tranquilizers, Diazepam, Atarax or Tranxen are usually prescribed. They can only be purchased with a doctor's prescription.
Drug treatment of autonomic neurosis cannot be imagined without the use of nootropics and vascular agents. They help improve memory, normalize brain function and vascular function. For this purpose, Piracetam, Phenibut, and Cerebrolysin are prescribed.
Treatment
Treatment for false rhinitis depends on how intense the clinical manifestations of the disease and the patient’s condition are. In mild cases of neurovegetative rhinitis, it is enough to eliminate the cause or minimize contact with cold air or gas vapor. The patient is advised to avoid stressful situations and normalize their lifestyle. In more severe cases, specialized treatment is carried out aimed at restoring the body's defenses, eliminating the cause of VNR and alleviating the signs of the disease.
Drug treatment
Part of complex therapy. The following groups of drugs are used:
rinsing the nasopharynx using antiseptic solutions;
- sanitization of the nasal passages with salt components;
- vasoconstrictor local drugs prescribed by a doctor (used for no more than 5 days to eliminate swelling and mucus);
- sedative medications that normalize the activity of the cardiovascular system and eliminate neurotic syndromes;
- antihistamines, in particular based on corticosteroids (depending on the degree of the disease);
- anti-inflammatory drugs to strengthen the body's defenses and prevent re-infection;
- immunomodulators of general and local action.
Psychotherapy sessions
In the process of diagnosis and treatment, it is important to establish whether there is a connection between autonomic neurosis and psychological trauma and disorders. Otherwise, drug therapy will be ineffective.
Quite often, a person does not even suspect that the traumas experienced in childhood are the cause of increased anxiety in adulthood. Being in constant conflict with himself and the world around him, the patient experiences prolonged depression. This negatively affects the functioning of his autonomic system.
In this case, psychotherapy can be one of the effective treatment methods. These can be either individual meetings or group sessions. Through various techniques (hypnosis, self-analysis), the patient gets rid of old memories and traumas. To find peace and mental balance, you can use meditative techniques and auto-training. With their help, patients begin to perceive reality in a new way and become more confident.
Vegetoneurosis: symptoms and treatment of autonomic disorders in neuroses – Neurology
Experiencing colossal daily stress, experiencing family quarrels and professional conflicts, suffering from a lack of creative fulfillment, a person drives himself into a state of prolonged stress.
Depression negatively affects not only the emotional background, but also the overall well-being of the body. This is how autonomic neurosis manifests itself, from which a huge number of people suffer.
Everyone should know the main symptoms of this disease and effective treatment methods.
Determining the value
When diagnosing a patient with vegetative-vascular dystonia, doctors mean autonomic neurosis - an ailment manifested by various symptoms that are easily confused with the etiology of other diseases. This is a mental disorder that provokes the occurrence of somatic manifestations in a person.
According to statistics, 70% of the adult population live with this diagnosis. Children also suffer from autonomic neurosis.
Every year, 15% of young patients undergo appropriate treatment for VN. The most common symptoms with which people consult a doctor are heart pain (97%), headaches (90%) and general weakness (85%).
Patients experience a constant feeling of anxiety, low mood and insomnia.
Patients do not connect these alarming factors with each other, mistaking VN for cardiac problems, overwork and weakened immunity.
The pathological condition can develop as a result of prolonged nervous strain, enormous physical activity, disruption of the daily routine and irregular nutrition.
Bad habits (smoking, alcohol, drugs, computer addiction) can affect the occurrence of vegetative neurosis.
In childhood, VN appears due to strong experiences associated with constant conflicts with parents or at school.
Vegetoneurosis requires mandatory timely treatment.
Without medical care, both the mental and physiological condition of a person will only worsen. To diagnose and prescribe effective treatment methods, the patient will have to seek advice from several specialists at once:
- To a psychotherapist.
- Neurologist.
- Family doctor.
Causes of the disease
Many factors that cause an imbalance in a person’s psychological state can provoke vegetative neurosis.
Hereditary predisposition.
Doctors have established that vegetative neurosis is transmitted: children inherit the temperament of their parents, therefore, adults with an easily excitable nervous system, increased nervousness and vulnerability, and a heightened sense of justice give birth to children predisposed to the development of VN. A huge role in the process of forming a healthy psyche is played by the general situation in the family and the methods of education that are applied to the baby.
Dysfunction often manifests itself in adolescence, when the child comes into conflict with the surrounding reality.
- Stressful situations that a person is not able to cope with on his own: the death of a loved one, loss of a job and stable income, lack of self-realization. As a result of stress, the patient’s body begins to intensively produce norepinephrine and adrenaline, which leads to interruptions in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. This provokes dystonia and dysfunction of the entire body. Patients become irritable, hot-tempered, tense and emotionally unstable.
- A different climate can become a mechanism that triggers vegetative manifestations of neurosis. Over time, the body adapts and the functioning of the nervous system normalizes.
- Neurological pathologies. The disease becomes the result of a person’s constant internal experiences. Having experienced heart pain, a person independently diagnoses himself, after which he begins to worry that the problem will worsen and he will not be able to recover. His whole life begins to revolve around this thought, as a result of which not only the vegetative syndrome worsens, but also neurosis develops.
- Hormonal imbalance. In adolescence, when active puberty begins and the body’s functioning is restructured, the child’s autonomic system may not have time to adapt to the changes taking place. Rapid growth, as well as weight gain, provoke disruptions in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. The consequence of this is pressure drops, chest pain and fainting. A general deterioration in health can also be observed in women who are in menopause. Due to the reduced level of hormones, representatives of the fair sex experience severe dizziness and emotional outbursts.
- Impaired mental functioning. In many cases, vegetoneurosis becomes the result of a malfunction of the nervous system, which is caused by nervous disorders, neurasthenia, panic attacks, and hypochondria. Identifying the causes of VN will help the attending physician correctly diagnose the disease in a timely manner and prescribe effective treatment.
Symptoms of autonomic neurosis
Doctors distinguish 2 main types of vegetative neurosis: hypertensive and hypotonic. Each of the subspecies manifests itself with separate symptoms.
Hypertensive neurosis appears due to the increased influence of the sympathetic nervous system on the human body. In this case, the disease reminds itself of itself with irregular heartbeats, migraines, and dizziness.
This type of vegetative neurosis can provoke hypertensive and ischemic heart disease, angina pectoris.
Hypotonic vegetative neurosis is based on disturbances in the functioning of the parasympathetic nervous system. Patients usually complain of low blood pressure, severe fatigue, drowsiness, bradycardia, fainting, and impaired thermoregulation of the body.
This disease has many different manifestations. Symptoms of vegetative syndrome are determined by certain factors.
- Vasomotor syndrome. This medical term hides headaches, migraines, attacks of nausea, pressure changes, joint pain, and problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
- Vegetative-skin syndrome, accompanied by heightened sensitivity and discoloration of the skin, persistent itching and dry skin.
- Muscle atrophy, skin erosions, brittle nails and hair loss. Autonomic-visceral syndrome. A person feels a lack of air and a lump in the throat, experiences sudden attacks of angina pectoris and arrhythmia. VN can also provoke allergic manifestations in the body - hives, swelling, runny nose.
The disease can occur in different ways:
- Malfunctions in the body and the manifestation of somatic symptoms occur after a severe nervous disorder.
- Dysfunction in the functioning of the brain and nervous system provokes deterioration in human health.
- The causes of autonomic neurosis are injuries, bruises and concussions of the head, and tumors in the brain.
The symptoms that a person with suspected autonomic neurosis complains about are carefully studied during medical diagnosis.
Since the manifestations of VN are very diverse, patients do not know which doctor to see and treat several ailments at the same time, without achieving the desired result.
To confirm the diagnosis of autonomic nervousness, the patient is examined, laboratory tests, ECG, ultrasound, encephalogram, MRI are taken.
Treatment methods for autonomic neurosis
Many people, feeling unwell, self-medicate, which only aggravates the manifestations of vegetative neurosis. The disease is progressing. If you do not seek medical help and start treatment in time, a severe form of VN can develop into more serious psychosomatic manifestations, leading to loss of social skills.
Therapy for vegetative neurosis includes the following areas:
- Setting up a daily routine.
- Normalization of sleep.
- Rest from work.
- Refusal of active physical activity.
- Setting the power mode.
- Therapeutic massage.
- Physiotherapy.
- Treatment with medications.
- Psychotherapy.
- Traditional medicine.
Psychotherapy sessions
It is important to accurately establish whether the disease is provoked by psychological trauma and disorders, otherwise drug treatment will be powerless, and VN will constantly remind itself.
In many cases, a person may not even suspect that in deep childhood he experienced traumatic events that, even after many years, subconsciously bother him.
Being in constant conflict with the outside world and himself, a person experiences prolonged depression, which disrupts the normal functioning of the nervous system.
One of the effective methods of treatment in this case will be psychotherapy sessions.
These can be either individual meetings with a psychotherapist or group sessions, during which, using various techniques (hypnosis, self-analysis), old memories will be identified and eliminated.
To gain peace of mind and peace of mind, it is recommended to use various meditative techniques and auto-training, which help the patient perceive reality in a new way, become more confident and purposeful.
Psychological assistance is essential for young patients whose illness is caused by an unstable situation in the family. In this case, the psychotherapist works not only with the child, but also with his parents.
Drug therapy
Autonomic dysfunction requires drug treatment. Doctors use a wide range of medications that effectively cope with autonomic neurosis.
Sedative medications help a person with vegetoneurosis to calm down and not worry about trifles, relieve feelings of anxiety, unconscious fear and increased nervousness. Such preparations are prepared on the basis of various herbal extracts from hawthorn, valerian, St. John's wort, mint and lemon balm. Such medications include Novopassit, Persen, Stressplant.
Tranquilizers are used to treat serious nervous disorders when the patient suffers from prolonged depression, persecutory mania, various phobias and fears that interfere with leading a normal life. The drugs help the patient cope with panic attacks and anxiety. Medicines Afobazol, Diazepam, Tranxen and Atarax should be taken as prescribed by a doctor.
Tranquilizers can only be purchased with a special prescription.
Nootropic and vascular drugs are aimed at restoring brain function, normalizing the functioning of blood vessels and blood supply to the head, and improving memory.
For this purpose, the patient is prescribed the following drugs: Phenibut, Piracetam, Cerebrolysin and Omaron. Traditional medicine recipes also show good results in the treatment of autonomic neurosis.
Conclusion
Autonomic neurosis is a disease based on mental disorders that provoke somatic disorders in the human body. The disease manifests itself with many symptoms that are often confused with other serious diseases.
To make a correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment, all signs of VN should be taken into account. Vegetoneurosis cannot be treated independently.
Be sure to seek help from your doctor who will help you overcome the disease and return to a healthy life.
Source:
We diagnose and treat autonomic neurosis
Autonomic neurosis is a disease that develops when the autonomic nervous system is disrupted. With this disease, the functions of tissues and internal organs are disrupted. The patient complains of pain in various organs and that they are not working correctly. But when the doctor conducts examinations, he finds no changes.
Source: https://perinatal39.ru/infektsionnye-zabolevaniya/vegetonevroz-simptomy-i-lechenie-vegetativnyh-narushenij-pri-nevrozah.html
Consequences and complications
Neurosis of the autonomic nervous system is a pathology that seriously changes the patient’s usual life. With moderate severity, his performance is reduced by approximately 50%. In more serious cases, a person loses the ability to perform the simplest work.
In the absence of therapy, neurosis can transform into heart disease, hypertension or hypotension, pathologies of the genitourinary system or gastrointestinal tract. It all depends on which internal organ responds to the disease.
During the period of development of autonomic neurosis, the patient develops a critical attitude. The disorder arises and progresses exclusively under psychogenic influence. Most often this happens after a long stressful situation. If the body does not recover after eliminating the stimulus, it means that the cause of the neurosis remains.
Another picture of development is also possible. After eliminating the irritating factor, the symptoms of neurosis persist. This indicates that the pathology has transformed into other mental disorders.
Causes of the disease
Vegetoneurosis has its own causes:
- Disturbances in the nervous system caused by head trauma;
- Exhaustion of the body caused by an unhealthy lifestyle. This phenomenon is usually observed in people with addiction to bad habits, as well as with chronic lack of sleep;
- Past infectious diseases;
- Constant stress and mental stress;
- Due to the characteristics of the nervous system, for example, if it is weak or the person is mentally ill.
In many dysfunctional families, autonomic neurosis and its symptoms most often occur in young children. After all, the baby’s psyche has not yet fully strengthened and due to constant quarrels between parents, stress and malnutrition, nervous system disorders may occur. For an adult, the reasons may be virtually the same, but the main trauma may be caused by their children, friends, spouses, etc.
Prevention methods
Autonomic disorders in neurosis do not pose a threat to a person’s life, but they significantly complicate it. It is easier to prevent any illness than to treat it later.
Prevention of autonomic neurosis comes down to compliance with the following rules:
- daily walks in the fresh air;
- normalization of the work and rest regime (sleep should be at least 8-10 hours a day);
- a reasonable approach to physical and intellectual stress;
- practical application of available relaxation methods.
When the first signs of neurosis appear, you should consult a doctor. Timely treatment minimizes the risk of complications and undesirable consequences.
Diagnostic features
As for the treatment of this type of disease, it is carried out only after an accurate diagnosis.
As a rule, organic pathologies are examined first. And if they are completely excluded, then the doctor prescribes further research to determine the specific type of autonomic neurosis.
Typically, the greatest attention is paid to skin and other reflexes, and the degree of excitability of the nervous system is also fully studied. Symptoms are the main guidelines on which to rely when treatment is prescribed.
The treatment is double. On the one hand, it is necessary to completely restore the functioning of the nervous system. On the other hand, to relieve the symptoms of the disease if they manifest themselves in disruption of the activity of certain organs. In any case, only a specialist can prescribe the most effective treatment for neurosis.
As for the treatment of individual organs, the doctor must write a prescription according to which certain pharmaceutical drugs should be taken. Sometimes injections may be prescribed. The doctor must take into account that the prescribed medications should not cause increased excitability.
But more attention should still be paid to putting the patient’s autonomic nervous system in order. For treatment to be effective, you should follow a few simple rules and recommendations. Then the body will quickly return to normal.
First of all, you should sign up for special psychotherapy sessions.
This works well for excitable individuals. Usually, first, the psychotherapist together with the patient establishes the main external factors that provoke autonomic neurosis. And then he develops individual therapy sessions.
It is important to properly distribute your sleep and rest schedule.
Usually, when a person does not get enough sleep, he becomes very nervous. You should start sleeping at least 5 hours a day. It is important for yourself to find the duration of sleep at which the body will feel as good and cheerful as possible.
You should also alternate active and quiet rest.
Before going to bed, it is better to take walks in the fresh air, and sometimes take a relaxing warm bath with foam. On weekends, you need to actively relax, move more, and play some kind of sport.
Special therapeutic exercise has a good effect.
A set of exercises should be selected by a specialist strictly individually, depending on which organs suffer from neurosis. It’s good if, in addition to exercises, it is possible to exercise on special simulators.
And finally, the last and most effective advice from doctors is a trip to the sea, to the mountains, or at least some sanatorium in an ecologically clean area. Not only the body, but also the soul rests in nature. This means that the nervous system gradually begins to work as it should. This is especially important for a person who has been exposed to constant stress for a long time.
So, the main symptoms and treatment of autonomic neurosis have been fully reviewed. It’s easy to see once again that all people’s health problems are caused by nerves. Therefore, it is important to exclude all external factors that disable the psyche.
vegetative dystonia, vegetative neurosis, vegetopathy, vegetosis. sympathosis) are diseases of various organs and tissues that arise as a result of dynamic, functional disorders in the autonomic devices that innervate them. Unlike organic lesions of the autonomic nervous system, in autonomic neurosis there are no macroscopic or microscopic structural changes in its formations. It should, however, be assumed that with the improvement of research methods (electron microscopy, histochemistry), in some cases it may be possible to detect subtle changes. In innervated tissues and organs during autonomic neurosis, clear structural disturbances may occur, resulting from functional changes in the innervation devices. Functional disorders can be observed at all levels of the autonomic nervous system - from the cortex to the peripheral parts. The etiological factors causing autonomic neurosis can be acute and chronic infections, intoxication, vitamin deficiencies, disorders of internal secretion, physical and mental trauma.
Pathogenetically, autonomic neurosis is conventionally divided into several groups. In the first group, autonomic disorders develop against the background of general neurosis (hysteria, neurasthenia, psychasthenia). Along with the symptoms characteristic of these diseases, it is possible to detect certain autonomic disorders: tachycardia, bradycardia, cardiac arrhythmia, shortness of breath, hiccups, appetite disturbance, vomiting, belching, diarrhea, constipation, sweating disorders, changes in skin color, sexual disorders (impotence , menstrual irregularities). In each specific case one is observed. two or more of the indicated Symptoms. This group of autonomic neuroses is based on disturbances in the activity of the cortical-hypothalamic structures. In addition, other etiological factors (infection, vitamin deficiency), weakening the nervous system and increasing the impact of the main etiological factor, are also of certain importance. Primary damage to the cortical centers appears through underlying vegetative formations. The personality traits of the patient play a certain role in the occurrence of neurosis. The second group includes autonomic neuroses, which are based on a pathological process (of a functional-dynamic nature) in the subcortical autonomic centers, which also extends to the sympathetic ganglia and peripheral autonomic plexuses. in these weaves, disturbances appear in certain systems: vascular (hypertension, primary hypotension), respiratory (bronchial asthma), gastrointestinal (peptic ulcer of the stomach, duodenum), etc. The nature of the lesion is largely determined by the initial predominance of sympathetic or parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. The doctrine of the antagonism of these systems has now been replaced by the idea of their synergistic activity, ensuring the subtle adaptation of the body to the environment. The basis of a number of diseases can be noted as an increase in the functional state of the sympathetic nervous system (hypertension, paroxysmal tachycardia) or the parasympathetic department (bronchial asthma, peptic ulcer, hypotension). Dysfunction of the cortical autonomic centers also occupies a certain, but insignificant place in the pathogenesis of this group. The third group includes autonomic neuroses, which are a consequence of a pathological process that primarily occurs in the periphery. It is observed after local trauma, when a certain organ is damaged. In these cases, pathological changes develop primarily in the local peripheral autonomic apparatus within the corresponding segment, where the arcs of autonomic reflexes close. This group includes local angioneuroses (see igiotrophoneuroses and reflex traumatic tissue lesions (vegetative-trophic disorders in the area of injury) a necessary condition for the occurrence of all groups of autonomic neuroses is increased lability, excitability in some cases cortical, in others - hypothalamic and stem, in others - peripheral vegetative formations, which leads to inadequate (quantitatively and qualitatively) reactions to various stimuli.Only the exclusion of organic damage to the actual anatomical structures of the autonomic nervous system allows us to interpret the disease as an autonomic neurosis.
Treatment. Etiological therapy consists of eliminating factors that traumatize the psyche, using antimicrobial agents (antibiotics and sulfonamides) and detoxifying glucose. sodium hyposulfite, etc.) means of treating a primarily diseased organ or tissue, up to surgical removal of a traumatic scar, which is a source of autonomic disorders. Pathogenetic therapy consists of direct and indirect psychotherapy (mainly for neuroses of the first group). effects on the subcortical and brainstem centers that normalize the state of autonomic tone (medicines, physiotherapy - diathermy on the hypothalamic region, nasal ionogalvanization), the use of sedatives affecting the cortical-hypothalamic-sgeol formations (bromides, aminazine, meprotan, andaxin), as well as ganglion blockers (pachycarpine, hexomethosine pentamine), interrupting pathological impulses from the center to the periphery (vegetative neuroses of the second group) and from the periphery to the center (vegetative neuroses of the third group). For the same purposes, surgical interventions on the sympathetic nervous system can be used (specific preganglionic sympathectomy. Treatment of individual neuroses of angiotrophoneurosis is outlined in the relevant sections. The prognosis is least favorable for autonomic neuroses of the second group. Prevention consists of hardening the body, strengthening the nervous system (rational rest, exercise physical education).
Experiencing colossal daily stress, experiencing family quarrels and professional conflicts, suffering from a lack of creative fulfillment, a person drives himself into a state of prolonged stress. Depression negatively affects not only the emotional background, but also the overall well-being of the body. This is how autonomic neurosis manifests itself, from which a huge number of people suffer. Everyone should know the main symptoms of this disease and effective treatment methods.
Symptoms of vegetative neurosis
Vegetative neurosis is characterized by disorders of the cardiovascular, genitourinary and digestive systems. Patients also often experience vasomotor syndrome, characterized by:
- migraine;
- pulsation in the head;
- surges in blood pressure;
- muscle and joint pain.
Asthenic syndrome with vegetative dystonia manifests itself:
- constant weakness that does not go away even after rest;
- increased fatigue;
- irritability;
- attention disorders (difficulty concentrating on the work at hand);
- sudden mood swings;
- intolerance to bright light and loud sounds.
Other syndromes that are signs of vegetative neurosis include:
- Skin-vegetative. The skin becomes dry, pigment spots and cracks appear on it. Or, on the contrary, there is an increased secretion of sweat and sebaceous glands.
- Trophic. Different muscle groups atrophy. Erosive and ulcerative lesions form. The condition of nails and hair deteriorates significantly.
- Vegetative-allergic. Allergic rashes appear on the skin. The patient complains of a runny nose and conjunctivitis.
- Visceral. The syndrome is characterized by stool disturbances, temporary lack of oxygen, and slower flow of bile.
- Phobic. The patient has unreasonable fears. At the same time, he himself understands the groundlessness of his experiences, but cannot get rid of them.
- Hypochondriacal. The patient is very concerned about his health. He constantly suspects that he has a fatal disease.
Symptoms of vegetoneurosis of the heart:
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- cardalgia;
- pain in the chest area;
- feeling of a sinking heart;
- cardiopalmus;
- dyspnea;
- blueness of fingers and toes.
At the same time, you need to understand that in reality there is no pathological condition that disrupts the functioning of the cardiovascular system. The discomfort is false.
Vegetoneurosis of the stomach manifests itself:
- abdominal pain;
- belching;
- diarrhea/constipation;
- loss of appetite;
- vomiting, nausea.
If you notice similar symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.